Abstract
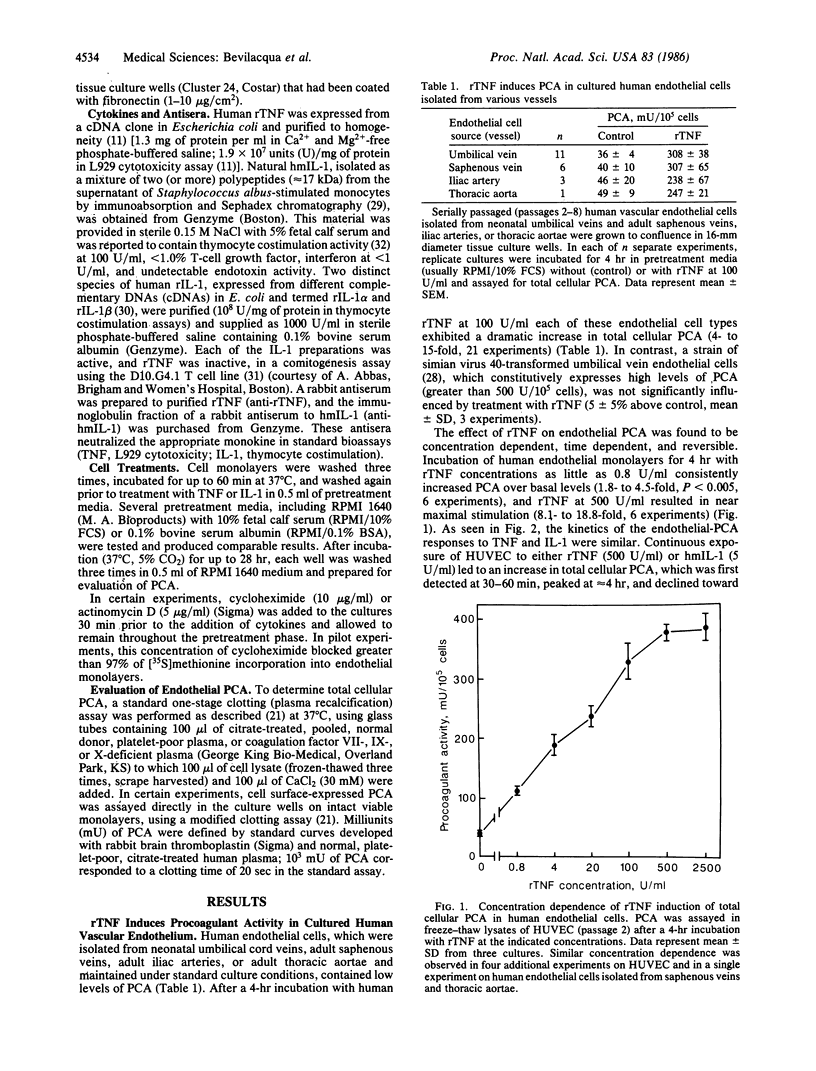
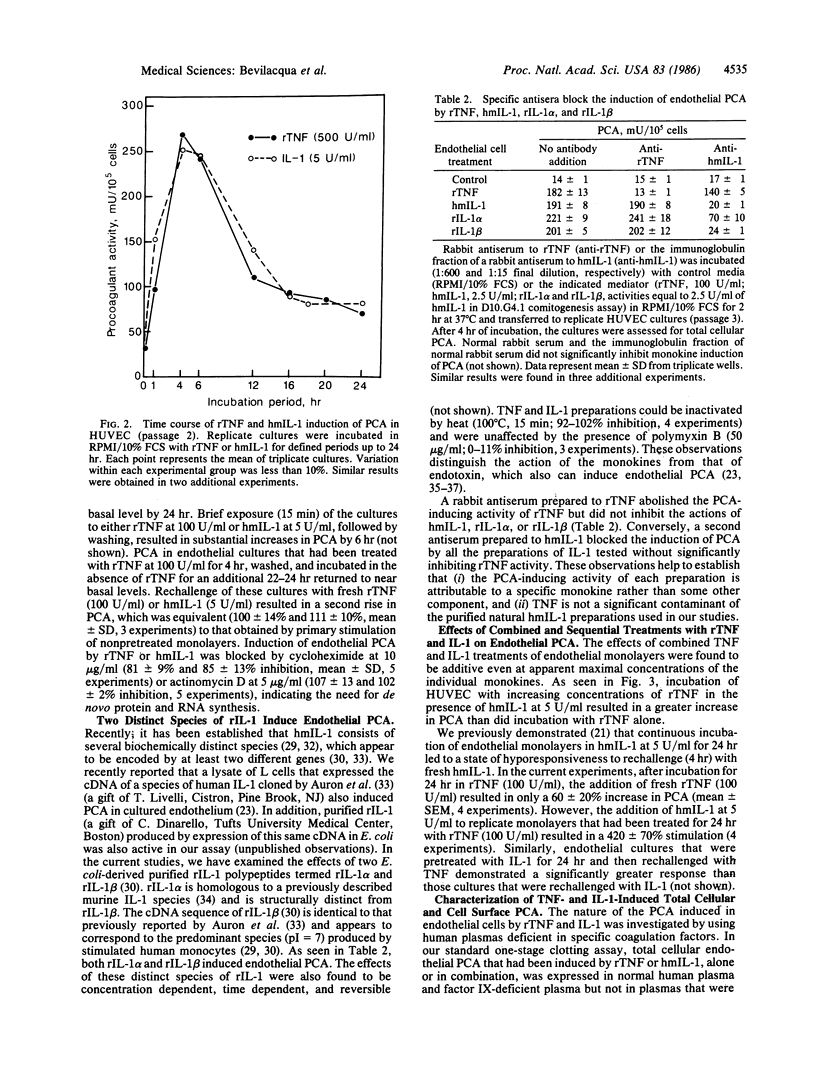
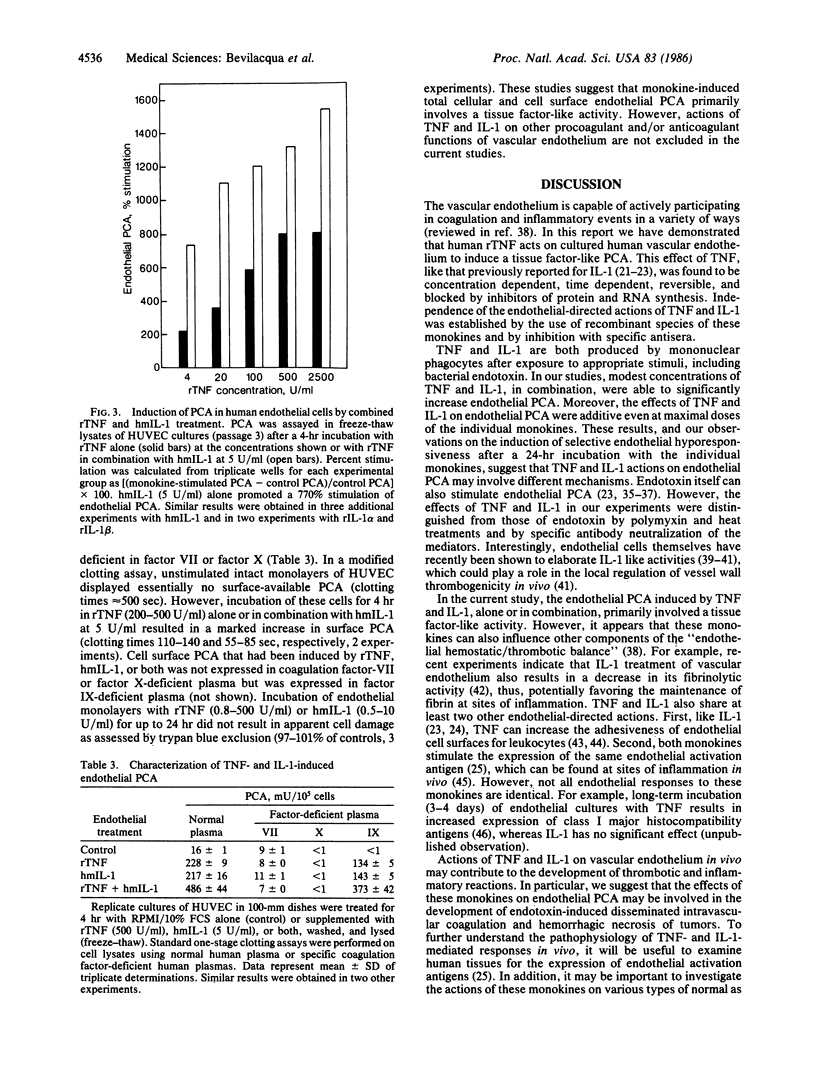
Human recombinant tumor necrosis factor (rTNF) was found to act directly on cultured human vascular endothelium to induce a tissue factor-like procoagulant activity (PCA). After a 4-hr incubation in rTNF (100 units/ml), serially passaged endothelial cells isolated from umbilical veins, saphenous veins, iliac arteries, and thoracic aortae demonstrated a dramatic increase (4- to 15-fold, 21 experiments) in total cellular PCA as measured with a one-stage clotting assay. rTNF-induced PCA was also expressed at the surface of intact viable endothelial monolayers. Induction of PCA by rTNF was concentration dependent (maximum, 500 units/ml), time dependent, reversible, and blocked by cycloheximide and actinomycin D, and it occurred without detectable endothelial cell damage. Actions of rTNF were compared with those of natural human interleukin 1 (IL-1) derived from stimulated monocytes and two distinct species of recombinant IL-1, each of which also induced endothelial PCA. The use of recombinant polypeptides and specific neutralizing antisera established the distinct natures of the mediators. The kinetics of the endothelial PCA responses to TNF and IL-1 were similar, demonstrating a rapid rise to peak activity at approximately equal to 4 hr, and a decline toward basal levels by 24 hr. This characteristic decline in PCA after prolonged incubation with TNF or IL-1 was accompanied by selective endothelial hyporesponsiveness to the initially stimulating monokine. Interestingly, the effects of TNF and IL-1 were found to be additive even at apparent maximal doses of the individual monokines. Endothelial-directed actions of TNF, alone or in combination with other monokines, may be important in the initiation of coagulation and inflammatory responses in vivo.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggarwal B. B., Kohr W. J., Hass P. E., Moffat B., Spencer S. A., Henzel W. J., Bringman T. S., Nedwin G. E., Goeddel D. V., Harkins R. N. Human tumor necrosis factor. Production, purification, and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2345–2354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auron P. E., Webb A. C., Rosenwasser L. J., Mucci S. F., Rich A., Wolff S. M., Dinarello C. A. Nucleotide sequence of human monocyte interleukin 1 precursor cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7907–7911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Greenwald D., Hulmes J. D., Chang M., Pan Y. C., Mathison J., Ulevitch R., Cerami A. Identity of tumour necrosis factor and the macrophage-secreted factor cachectin. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):552–554. doi: 10.1038/316552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Mahoney J., Le Trang N., Pekala P., Cerami A. Purification of cachectin, a lipoprotein lipase-suppressing hormone secreted by endotoxin-induced RAW 264.7 cells. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):984–995. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Pober J. S., Majeau G. R., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Interleukin 1 (IL-1) induces biosynthesis and cell surface expression of procoagulant activity in human vascular endothelial cells. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):618–623. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Pober J. S., Wheeler M. E., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Interleukin 1 acts on cultured human vascular endothelium to increase the adhesion of polymorphonuclear leukocytes, monocytes, and related leukocyte cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):2003–2011. doi: 10.1172/JCI112200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Pober J. S., Wheeler M. E., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Interleukin-1 activation of vascular endothelium. Effects on procoagulant activity and leukocyte adhesion. Am J Pathol. 1985 Dec;121(3):394–403. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell E. A., Old L. J., Kassel R. L., Green S., Fiore N., Williamson B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T., Lapierre L. A., Fiers W., Strominger J. L., Pober J. S. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor increases mRNA levels and surface expression of HLA-A,B antigens in vascular endothelial cells and dermal fibroblasts in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):446–450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colucci M., Balconi G., Lorenzet R., Pietra A., Locati D., Donati M. B., Semeraro N. Cultured human endothelial cells generate tissue factor in response to endotoxin. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1893–1896. doi: 10.1172/JCI110945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransen L., Müller R., Marmenout A., Tavernier J., Van der Heyden J., Kawashima E., Chollet A., Tizard R., Van Heuverswyn H., Van Vliet A. Molecular cloning of mouse tumour necrosis factor cDNA and its eukaryotic expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4417–4429. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble J. R., Harlan J. M., Klebanoff S. J., Vadas M. A. Stimulation of the adherence of neutrophils to umbilical vein endothelium by human recombinant tumor necrosis factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8667–8671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr Culture of vascular endothelium. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1976;3:1–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Fareed G. C. Transformation of cultured human vascular endothelium by SV40 DNA. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):685–693. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90132-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J., Gillis S., Mizel S. B., Shevach E. M., Malek T. R., Dinarello C. A., Lachman L. B., Janeway C. A., Jr Growth of a cloned helper T cell line induced by a monoclonal antibody specific for the antigen receptor: interleukin 1 is required for the expression of receptors for interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1339–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kull F. C., Jr, Cuatrecasas P. Preliminary characterization of the tumor cell cytotoxin in tumor necrosis serum. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1279–1283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kull F. C., Jr, Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P. Cellular receptor for 125I-labeled tumor necrosis factor: specific binding, affinity labeling, and relationship to sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5756–5760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomedico P. T., Gubler U., Hellmann C. P., Dukovich M., Giri J. G., Pan Y. C., Collier K., Semionow R., Chua A. O., Mizel S. B. Cloning and expression of murine interleukin-1 cDNA in Escherichia coli. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):458–462. doi: 10.1038/312458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyberg T., Galdal K. S., Evensen S. A., Prydz H. Cellular cooperation in endothelial cell thromboplastin synthesis. Br J Haematol. 1983 Jan;53(1):85–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb01989.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March C. J., Mosley B., Larsen A., Cerretti D. P., Braedt G., Price V., Gillis S., Henney C. S., Kronheim S. R., Grabstein K. Cloning, sequence and expression of two distinct human interleukin-1 complementary DNAs. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):641–647. doi: 10.1038/315641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews N., Ryley H. C., Neale M. L. Tumour-necrosis factor from the rabbit. IV. Purification and chemical characterization. Br J Cancer. 1980 Sep;42(3):416–422. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1980.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Männel D. N., Meltzer M. S., Mergenhagen S. E. Generation and characterization of a lipopolysaccharide-induced and serum-derived cytotoxic factor for tumor cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):204–211. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.204-211.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Stern D. M., Kisiel W., Bach R. Cellular requirements for tissue factor generation by bovine aortic endothelial cells in culture. Thromb Res. 1985 Dec 1;40(5):677–691. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(85)90305-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Stern D. M. Modulation of endothelial cell hemostatic properties by tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):740–745. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):630–632. doi: 10.1126/science.2413547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Nedwin G. E., Hayflick J. S., Seeburg P. H., Derynck R., Palladino M. A., Kohr W. J., Aggarwal B. B., Goeddel D. V. Human tumour necrosis factor: precursor structure, expression and homology to lymphotoxin. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):724–729. doi: 10.1038/312724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Bevilacqua M. P., Mendrick D. L., Lapierre L. A., Fiers W., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Two distinct monokines, interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor, each independently induce biosynthesis and transient expression of the same antigen on the surface of cultured human vascular endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1680–1687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouzer C. A., Cerami A. Hypertriglyceridemia associated with Trypanosoma brucei brucei infection in rabbits: role of defective triglyceride removal. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1980 Oct;2(1):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(80)90046-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin B. Y., Anderson S. L., Sullivan S. A., Williamson B. D., Carswell E. A., Old L. J. High affinity binding of 125I-labeled human tumor necrosis factor (LuKII) to specific cell surface receptors. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):1099–1104. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai T., Yamaguchi H., Ito H., Todd C. W., Wallace R. B. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the gene for human tumour necrosis factor. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):803–806. doi: 10.1038/313803a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. M., Bank I., Nawroth P. P., Cassimeris J., Kisiel W., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Dinarello C., Chess L., Jaffe E. A. Self-regulation of procoagulant events on the endothelial cell surface. J Exp Med. 1985 Oct 1;162(4):1223–1235. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.4.1223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugarman B. J., Aggarwal B. B., Hass P. E., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, Shepard H. M. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha: effects on proliferation of normal and transformed cells in vitro. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):943–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3933111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton S. C., Mueller S. N., Levine E. M. Human endothelial cells: use of heparin in cloning and long-term serial cultivation. Science. 1983 Nov 11;222(4624):623–625. doi: 10.1126/science.6635659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torti F. M., Dieckmann B., Beutler B., Cerami A., Ringold G. M. A macrophage factor inhibits adipocyte gene expression: an in vitro model of cachexia. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):867–869. doi: 10.1126/science.3839597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner C. R., Vetto R. M., Burger D. R. The mechanism of antigen presentation by endothelial cells. Immunobiology. 1984 Dec;168(3-5):453–469. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(84)80130-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. M., Creasey A. A., Ladner M. B., Lin L. S., Strickler J., Van Arsdell J. N., Yamamoto R., Mark D. F. Molecular cloning of the complementary DNA for human tumor necrosis factor. Science. 1985 Apr 12;228(4696):149–154. doi: 10.1126/science.3856324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. D., Bayne E. K., Goldring M. B., Gowen M., Hamerman D., Humes J. L., Ihrie E. J., Lipsky P. E., Staruch M. J. The four biochemically distinct species of human interleukin 1 all exhibit similar biologic activities. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):895–903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



