Abstract
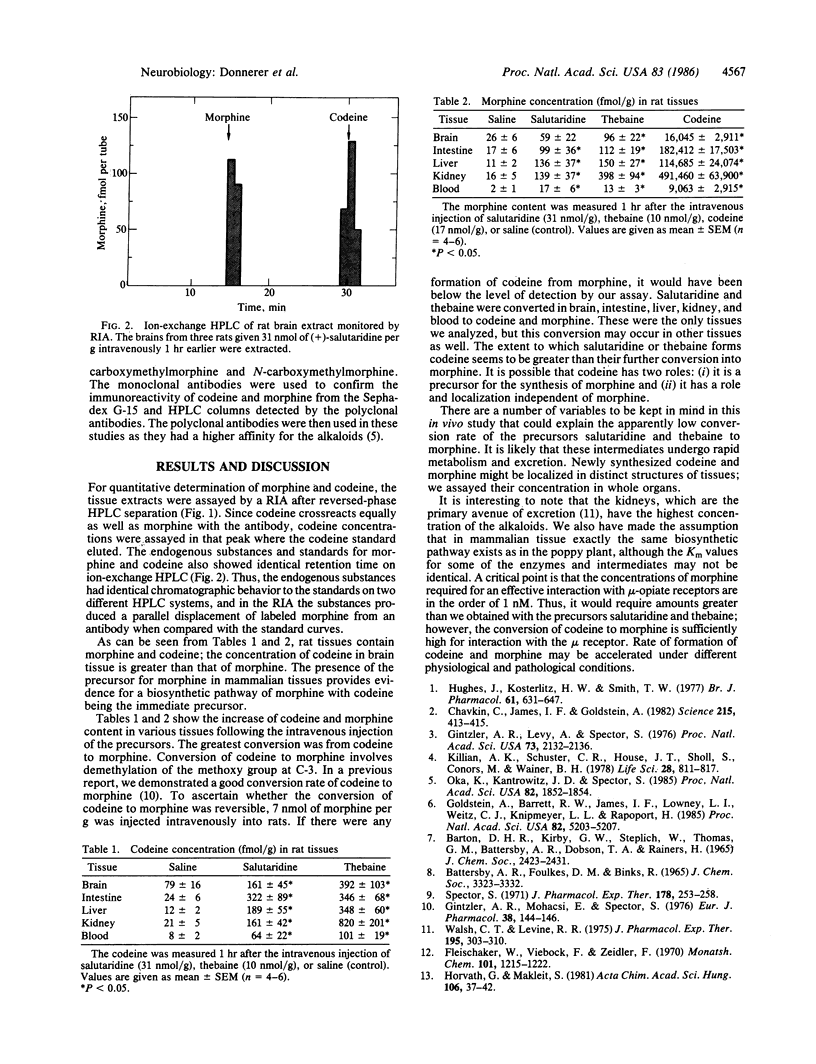
Endogenous codeine and morphine were identified in rat brain by immunological determination following HPLC. To demonstrate occurrence of a biosynthetic pathway to morphine in mammals similar to that used by the poppy plant, (+)-salutaridine, (-)-thebaine, and (-)-codeine were administered to rats intravenously. These compounds, which are intermediates in the synthesis of morphine in Papaver somniferum, caused a marked increase in the codeine and morphine levels in rat tissues. This provides evidence for a biosynthetic pathway to morphine in mammalians.
Full text
PDF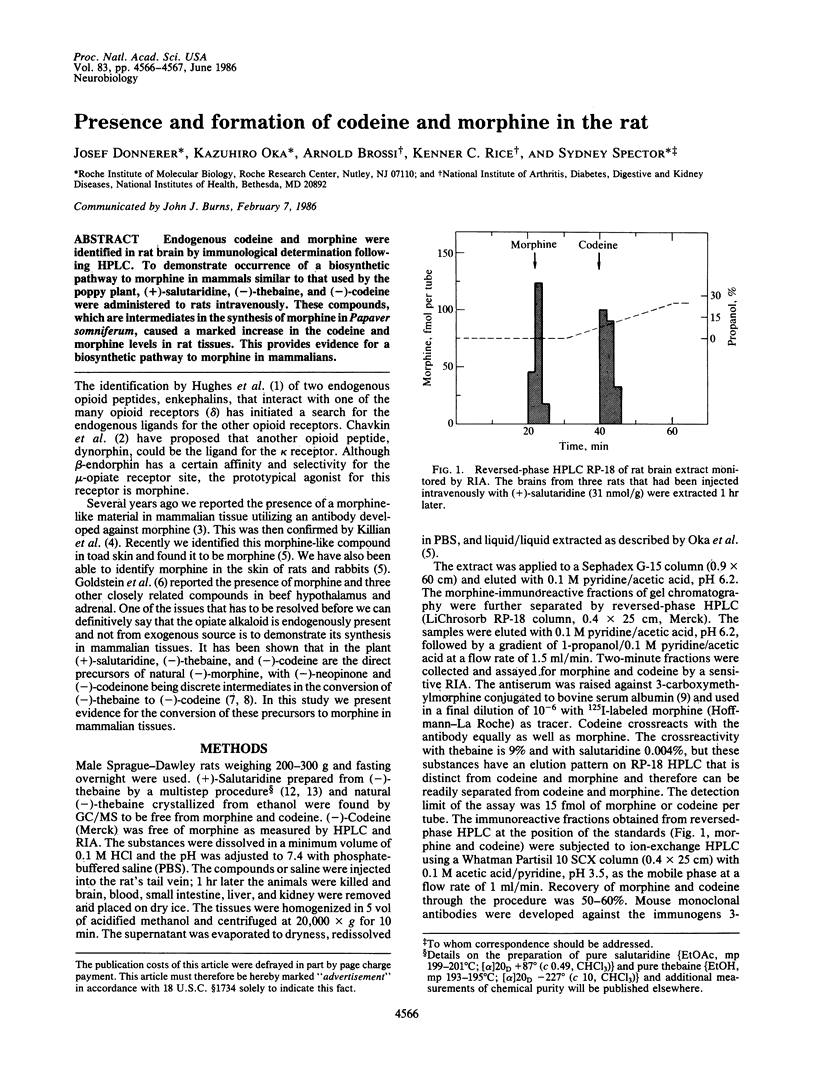
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTON D. H., KIRBY G. W., STEGLICH W., THOMAS G. M., BATTERSBY A. R., DOBSON T. A., RAMUZ H. INVESTIGATIONS ON THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF MORPHINE ALKALOIDS. J Chem Soc. 1965 Apr;65:2423–2438. doi: 10.1039/jr9650002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BATTERSBY A. R., FOULKES D. M., BINKS R. ALKALOID BIOSYNTHESIS. 8. USE OF OPTICALLY ACTIVE PRECURSORS FOR INVESTIGATIONS ON THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF MORPHINE ALKALOIDS. J Chem Soc. 1965 May;33:3323–3332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavkin C., James I. F., Goldstein A. Dynorphin is a specific endogenous ligand of the kappa opioid receptor. Science. 1982 Jan 22;215(4531):413–415. doi: 10.1126/science.6120570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gintzler A. R., Levy A., Spector S. Antibodies as a means of isolating and characterizing biologically active substances: presence of a non-peptide, morphine-like compound in the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2132–2136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Barrett R. W., James I. F., Lowney L. I., Weitz C. J., Knipmeyer L. L., Rapoport H. Morphine and other opiates from beef brain and adrenal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5203–5207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W., Smith T. W. The distribution of methionine-enkephalin and leucine-enkephalin in the brain and peripheral tissues. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Dec;61(4):639–647. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07557.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killian A. K., Schuster C. R., House J. T., Sholl S., Connors M., Wainer B. H. A non-peptide morphine-like compound from brain. Life Sci. 1981 Feb 16;28(7):811–817. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka K., Kantrowitz J. D., Spector S. Isolation of morphine from toad skin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1852–1854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector S. Quantitative determination of morphine in serum by radioimmunoassay. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Aug;178(2):253–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh C. T., Levine R. R. Studies of the enterohepatic circulation of morphine in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Nov;195(2):303–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


