Abstract
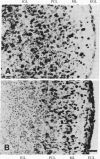
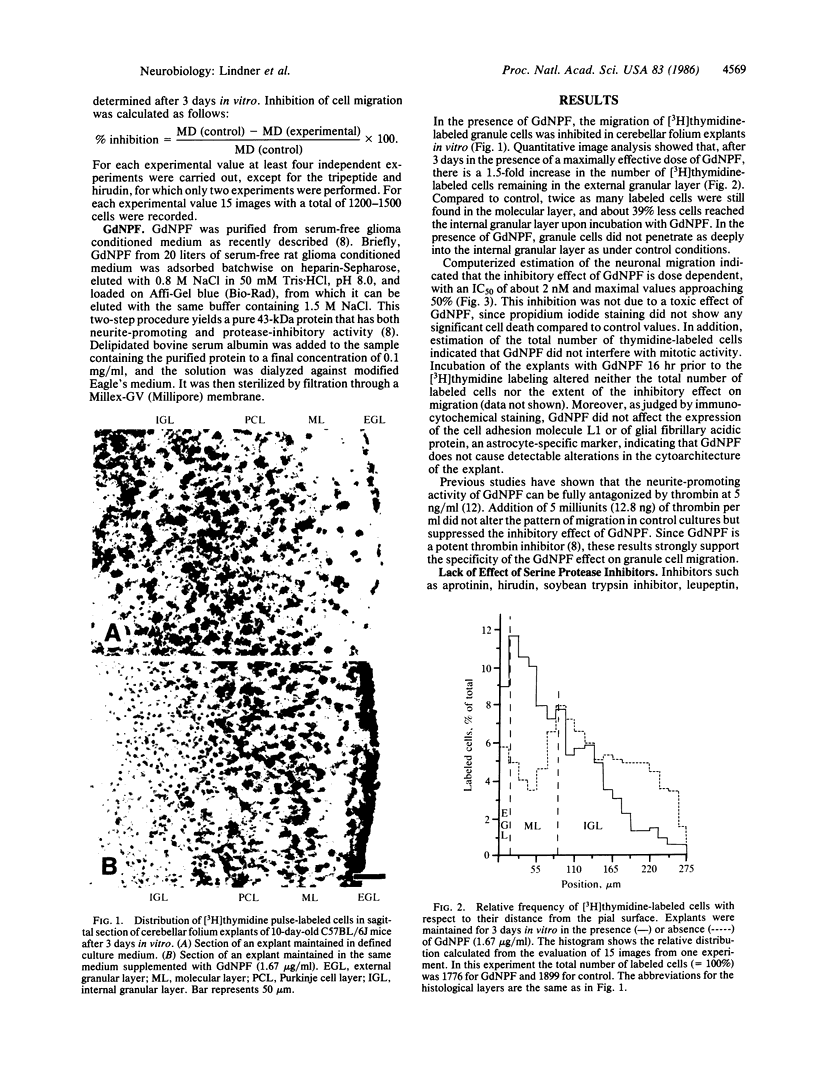
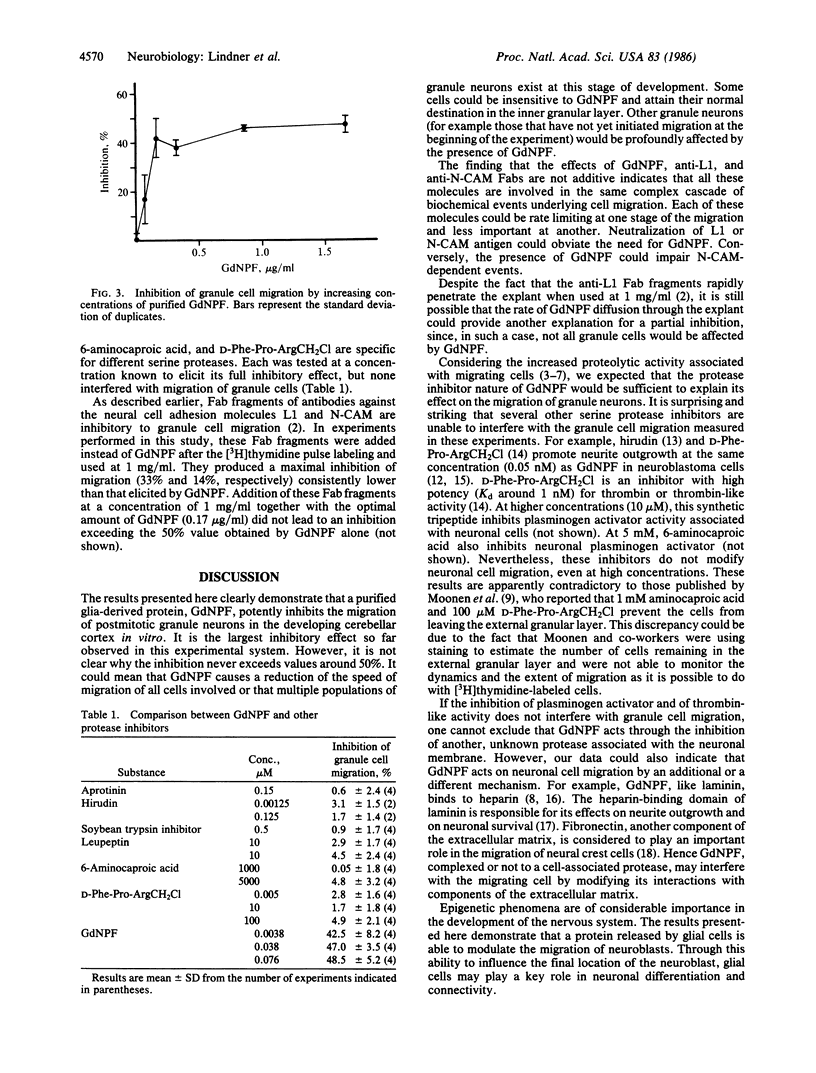
Cultured explants from early postnatal mouse cerebellum were used to examine the influence of a 43-kDa glia-derived neurite-promoting factor (GdNPF) on the migration of [3H]thymidine-labeled granule cell neurons. GdNPF, which is a potent serine protease inhibitor, significantly reduced the extent of granule cell migration in a dose-dependent manner. This effect could be neutralized by addition of thrombin, which binds GdNPF. Other protease inhibitors such as aprotinin, hirudin, soybean trypsin inhibitor, leupeptin, 6-aminocaproic acid, and D-Phe-Pro-ArgCH2Cl do not show this inhibitory effect. These results demonstrate that a glia-derived protein can regulate the migration of postmitotic neurons, an important cellular event in the development of the nervous system.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Edgar D., Timpl R., Thoenen H. The heparin-binding domain of laminin is responsible for its effects on neurite outgrowth and neuronal survival. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1463–1468. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01997.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guenther J., Nick H., Monard D. A glia-derived neurite-promoting factor with protease inhibitory activity. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):1963–1966. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03878.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettner C., Shaw E. D-Phe-Pro-ArgCH2C1-A selective affinity label for thrombin. Thromb Res. 1979;14(6):969–973. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komitowski D., Zinser G., Stute C. Digital picture analysis as an integral part of the information system for experimental oncopathology of the German Cancer Research Center. Methods Inf Med. 1983 Apr;22(2):69–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystosek A., Seeds N. W. Plasminogen activator secretion by granule neurons in cultures of developing cerebellum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7810–7814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindner J., Rathjen F. G., Schachner M. L1 mono- and polyclonal antibodies modify cell migration in early postnatal mouse cerebellum. 1983 Sep 29-Oct 5Nature. 305(5933):427–430. doi: 10.1038/305427a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monard D. Neuronal cell behaviour: modulation by protease inhibitors derived from non-neuronal cells. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1985 Apr;9(4):297–305. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(85)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monard D., Niday E., Limat A., Solomon F. Inhibition of protease activity can lead to neurite extension in neuroblastoma cells. Prog Brain Res. 1983;58:359–364. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)60037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moonen G., Grau-Wagemans M. P., Selak I. Plasminogen activator-plasmin system and neuronal migration. Nature. 1982 Aug 19;298(5876):753–755. doi: 10.1038/298753a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L., Quigley J. P., Reich E. Fibrinolysis associated with oncogenic transformation. Morphological correlates. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4312–4320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman M. I., Strickland S., Reich E. Differentiation of early mouse embryonic and teratocarcinoma cells in vitro: plasminogen activator production. Cancer Res. 1976 Nov;36(11 Pt 2):4208–4216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiery J. P., Duband J. L., Delouvée A. Pathways and mechanisms of avian trunk neural crest cell migration and localization. Dev Biol. 1982 Oct;93(2):324–343. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90121-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topp W., Hall J. D., Marsden M., Teresky A. K., Rifkin D., Levine A. J., Pollack R. In vitro differentiation of teratomas and the distribution of creatine phosphokinase and plasminogen activator in teratocarcinoma-derived cells. Cancer Res. 1976 Nov;36(11 Pt 2):4217–4223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Tobia A., Ossowski L., Quigley J. P., Rifkin D. B., Reich E. An enzymatic function associated with transformation of fibroblasts by oncogenic viruses. I. Chick embryo fibroblast cultures transformed by avian RNA tumor viruses. J Exp Med. 1973 Jan 1;137(1):85–111. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]