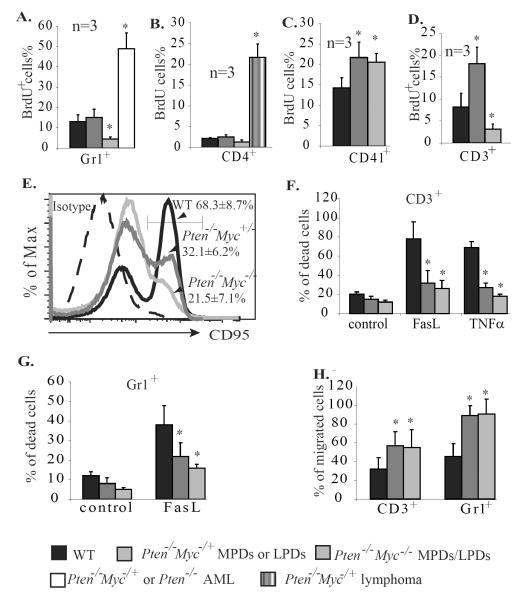
Figure 7.
Myc is required for the proliferation but not the survival nor migration of granulocytes and lymphocytes. A–C. All mice were injected with BrdU 4 hr. before being sacrificed. Three mice were injected in each group (for the AML group, 1 mouse with Pten−/−/Myc+/− genotype and 2 with Pten−/− genotype were used). Percentages of cells incorporating BrdU (BrdU+%) in Gr1+ granulocytes from BM (A), CD4+ lymphocytes from lymph nodes (B), and CD41+ Mks from spleens (C) of the mice were analyzed to determine the proliferation of these cells. D–F. CD3+ lymphocytes were isolated from spleens of WT, Pten−/−/Myc+/−, and Pten−/−/Myc−/− mice 25 days after polyI:C injection and were treated with anti-CD3ε and IL-2 to induce activation. Activation-induced proliferation (D) and Fas expression (E) were examined by BrdU pulse-labeling and CD95 antibody staining, respectively. Activation-related cell deaths of CD3+ T cells were analyzed by PI staining 12 hr. after TNFα or FasL stimulation (F.) G. Gr1+ granulocytes were isolated from BM of WT, Pten−/−/Myc+/− and Pten−/−/Myc−/− mice 25 days after polyI:C injection and treated with 20ng/ml FasL for 12 hr. Cell death was analyzed by PI staining and flow cytometry. H. Migration of the CD3+ and Gr1+ cells was analyzed 3 hr. after SDF1 induction. * indicates significant difference compared to WT controls.