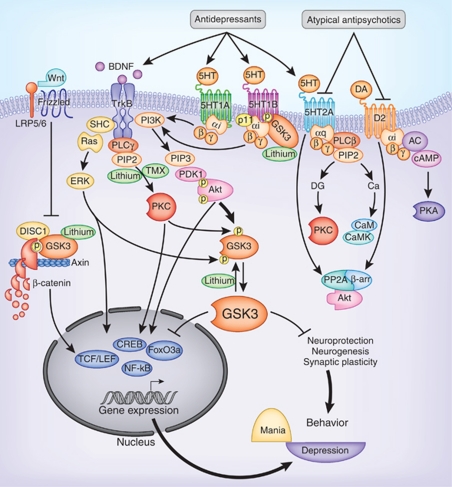
Figure 1.
Signal transduction pathways mediating the actions of lithium and monoamine-regulating drugs. Lithium directly inhibits GSK3 and facilitates the phosphorylation of GSK3 at the N-terminal serine. Lithium also inhibits inositol phosphatases to block phosphatidylinositol signaling. Antidepressants facilitate serotonin action on serotonin receptors as well as facilitate neurotrophic receptor activity. Atypical antipsychotics block both serotonin 2A and dopamine D2 receptors. Activation of these monoamine receptors causes the activation or inhibition of Akt, PKC, or Erk through different signaling pathways. Akt and PKC phosphorylate GSK3 at the N-terminal serine and Erk phosphorylates GSK3 at the C-terminal serine, which cause GSK3 inactivation. Tamoxifen inhibits PKC. These signaling cascades directly or indirectly regulate gene expression and neuroplasticity that have an impact in mood regulation. AC, adenylyl cyclase; Ca, calcium; CaM, calmodulin; CaMK, calmodulin-dependent protein kinase; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; CREB, cAMP-responsive element-binding protein; DG, diacylglycerol; DISC1, disrupted in schizophrenia-1; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; FoxO, forkhead ‘O' transcription factor; GSK3, glycogen synthase kinase-3; IP3, inositol trisphosphate; LRP5/6, low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-5/6; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κ-B; PDK1, phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PtdIns(4,5)P2); PIP3, phosphatidylinositol-(3,4,5)-trisphosphate (PtdIns(3,4,5)P3); PKA, protein kinase-A; PKC, protein kinase-C; PLC, phospholipase-C; PP1, protein phosphatase-1; PP2, protein phosphatase-2, TMX, tamoxifen; TrkB, tyrosine kinase-B; β-arr, β-arrestin.