Abstract
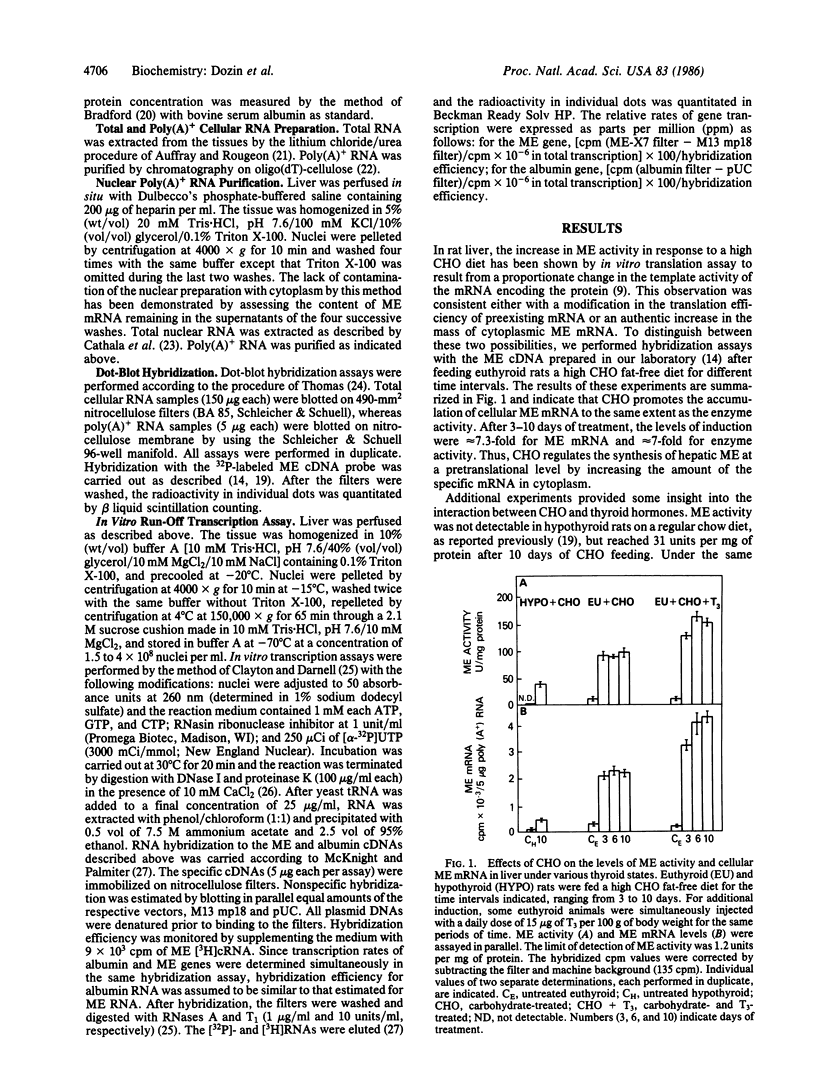
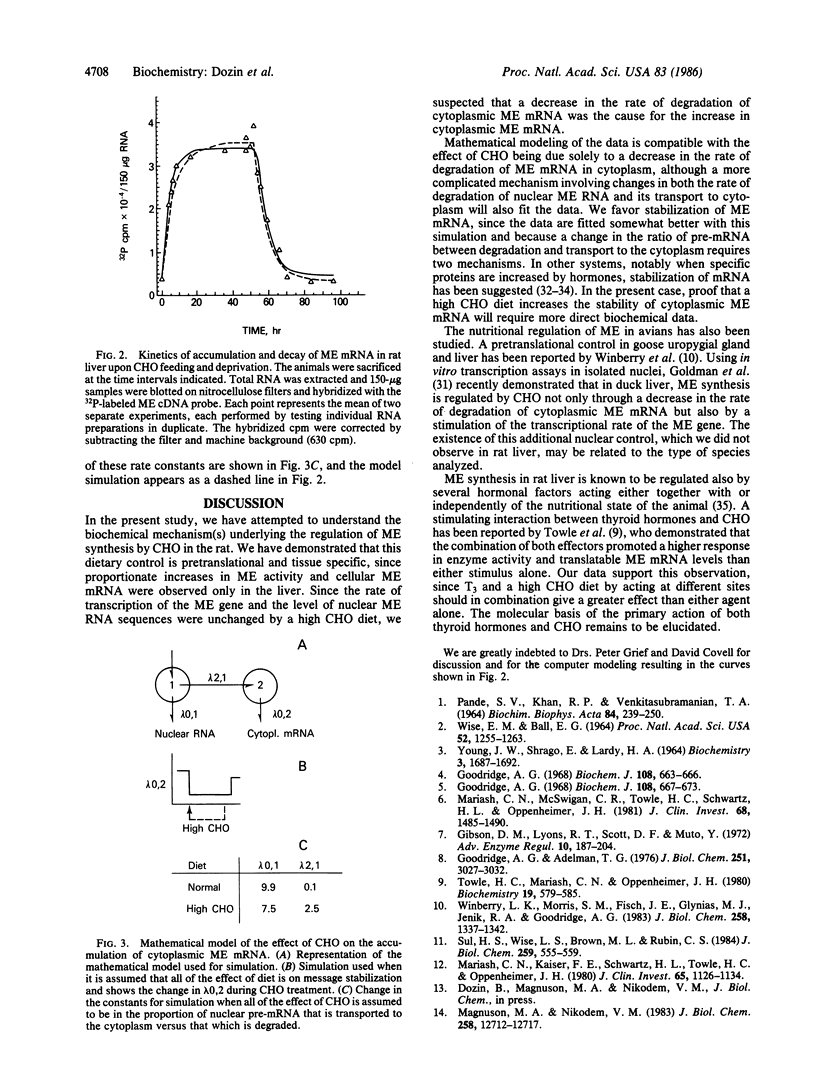
In euthyroid rats fed a high carbohydrate fat-free diet for 10 days, the mass of cellular malic enzyme mRNA in liver is increased 7- to 8-fold above the basal level. Malic enzyme activity is stimulated to the same extent. This effect does not result from an increase either in the transcriptional activity of the malic enzyme gene, as determined by nuclear run-off transcription assay, or in the content of intranuclear malic enzyme RNA sequences. Mathematical modeling shows that this increase in cytoplasmic mRNA is compatible with retarded degradation of cytoplasmic mRNA. Regulation of malic enzyme by carbohydrates is liver-specific, since no response is observed in the following nonhepatic tissues: brain, heart, spleen, kidney, testis, and lung. Furthermore, the amplitude of the response in liver depends on the thyroid state of the animals, being lower (by a factor of approximately 4) in hypothyroidism and higher (12- to 15-fold) when normal animals are injected simultaneously with a daily dose of 15 micrograms of triiodothyronine per 100 g of body weight for 10 days. Since thyroid hormones regulate liver malic enzyme synthesis predominantly at the nuclear level and carbohydrates at the cytoplasmic level, the additive effect of triiodothyronine and a high carbohydrate diet on the activity of malic enzyme is readily explicable.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin C. M., Schimke R. T. Influence of turnover rates on the responses of enzymes to cortisone. Mol Pharmacol. 1965 Sep;1(2):149–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Savouret J. F., Mendez B., West B. L., Karin M., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. A method for isolation of intact, translationally active ribonucleic acid. DNA. 1983;2(4):329–335. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton D. F., Darnell J. E., Jr Changes in liver-specific compared to common gene transcription during primary culture of mouse hepatocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;3(9):1552–1561. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.9.1552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dozin B., Magnuson M. A., Nikodem V. M. Tissue-specific regulation of two functional malic enzyme mRNAs by triiodothyronine. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5581–5586. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. M., Lyons R. T., Scott D. F., Muto Y. Synthesis and degradation of the lipogenic enzymes of rat liver. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1972;10:187–204. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(72)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman M. J., Back D. W., Goodridge A. G. Nutritional regulation of the synthesis and degradation of malic enzyme messenger RNA in duck liver. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4404–4408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodridge A. G., Adelman T. G. Regulation of malic enzyme synthesis by insulin triiodothyronine, and glucagon in liver cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 25;251(10):3027–3032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodridge A. G. Citrate-cleavage enzyme, 'malic' enzyme and certain dehydrogenases in embryonic and growing chicks. Biochem J. 1968 Jul;108(4):663–666. doi: 10.1042/bj1080663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodridge A. G. The effect of starvation and starvation followed by feeding on enzyme activity and the metabolism of [U-14C]glucose in liver from growing chicks. Biochem J. 1968 Jul;108(4):667–673. doi: 10.1042/bj1080667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu R. Y., Lardy H. A. Pigeon liver malic enzyme. II. Isolation, crystallization, and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 10;242(3):520–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. J., Ross C. R., Tepperman H. M., Tepperman J. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-malic enzyme of rat liver. Purification, properties, and immunochemical studies. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):141–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loose D. S., Cameron D. K., Short H. P., Hanson R. W. Thyroid hormone regulates transcription of the gene for cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) in rat liver. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 13;24(17):4509–4512. doi: 10.1021/bi00338a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loose D. S., Cameron D. K., Short H. P., Hanson R. W. Thyroid hormone regulates transcription of the gene for cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) in rat liver. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 13;24(17):4509–4512. doi: 10.1021/bi00338a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnuson M. A., Morioka H., Tecce M. F., Nikodem V. M. Coding nucleotide sequence of rat liver malic enzyme mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1183–1186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnuson M. A., Nikodem V. M. Molecular cloning of a cDNA sequence for rat malic enzyme. Direct evidence for induction in vivo of rat liver malic enzyme mRNA by thyroid hormone. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12712–12717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariash C. N., Kaiser F. E., Schwartz H. L., Towle H. C., Oppenheimer J. H. Synergism of thyroid hormone and high carbohydrate diet in the induction of lipogenic enzymes in the rat. Mechanisms and implications. J Clin Invest. 1980 May;65(5):1126–1134. doi: 10.1172/JCI109766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariash C. N., McSwigan C. R., Towle H. C., Schwartz H. L., Oppenheimer J. H. Glucose and triiodothyronine both induce malic enzyme in the rat hepatocyte culture: evidence that triiodothyronine multiplies a primary glucose-generated signal. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1485–1490. doi: 10.1172/JCI110401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S., Palmiter R. D. Transcriptional regulation of the ovalbumin and conalbumin genes by steroid hormones in chick oviduct. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9050–9058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S., Palmiter R. D. Transcriptional regulation of the ovalbumin and conalbumin genes by steroid hormones in chick oviduct. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9050–9058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueckler M. M., Moran S., Pitot H. C. Transcriptional control of ornithine aminotransferase synthesis in rat kidney by estrogen and thyroid hormone. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2302–2305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyborg J. K., Nguyen A. P., Spindler S. R. Relationship between thyroid and glucocorticoid hormone receptor occupancy, growth hormone gene transcription, and mRNA accumulation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12377–12381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H. Thyroid hormone action at the cellular level. Science. 1979 Mar 9;203(4384):971–979. doi: 10.1126/science.218285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PANDE S. V., KHAN R. P., VENKITASUBRAMANIAN T. A. NICOTINAMIDE ADENINE DINUCLEOTIDE PHOSPHATE-SPECIFIC DEHYDROGENASES IN RELATION TO LIPOGENESIS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jun 15;84:239–250. doi: 10.1016/0926-6542(64)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sul H. S., Wise L. S., Brown M. L., Rubin C. S. Cloning of cDNA sequences for murine malic enzyme and the identification of aberrantly large malic enzyme mRNA in MOD-1 null mice. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):555–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towle H. C., Mariash C. N., Oppenheimer J. H. Changes in the hepatic levels of messenger ribonucleic acid for malic enzyme during induction by thyroid hormone or diet. Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 5;19(3):579–585. doi: 10.1021/bi00544a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullis R. H., Rubin H. Calcium protects DNase I from proteinase K: a new method for the removal of contaminating RNase from DNase I. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):260–264. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90519-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISE E. M., Jr, BALL E. G. MALIC ENZYME AND LIPOGENESIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Nov;52:1255–1263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.5.1255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winberry L. K., Morris S. M., Jr, Fisch J. E., Glynias M. J., Jenik R. A., Goodridge A. G. Molecular cloning of cDNA sequences for avian malic enzyme. Nutritional and hormonal regulation of malic enzyme mRNA levels in avian liver cells in vivo and in culture. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1337–1342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUNG J. W., SHRAGO E., LARDY H. A. METABOLIC CONTROL OF ENZYMES INVOLVED IN LIPOGENESIS AND GLUCONEOGENESIS. Biochemistry. 1964 Nov;3:1687–1692. doi: 10.1021/bi00899a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


