Abstract
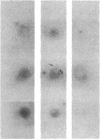
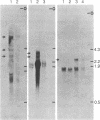
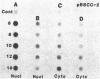
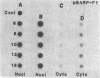
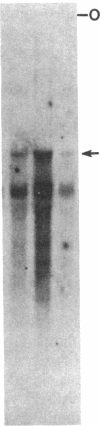
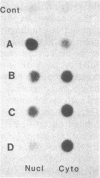
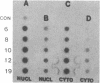
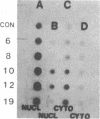
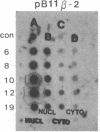
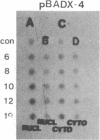
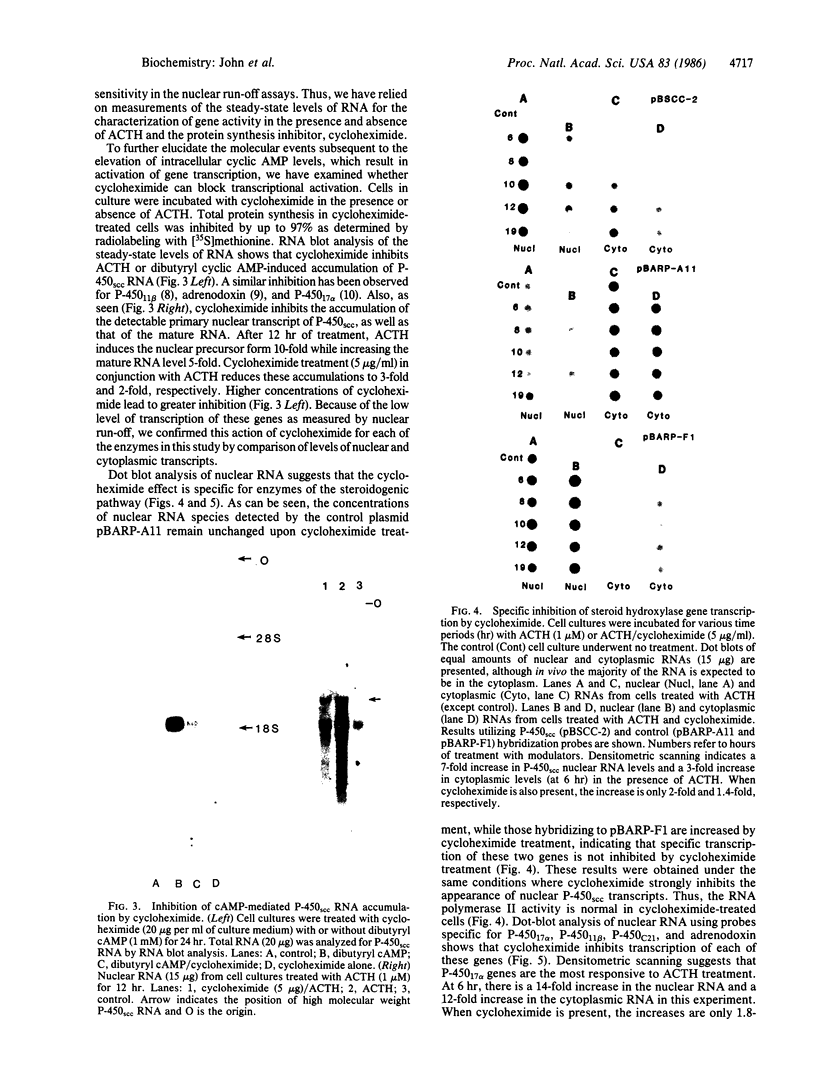
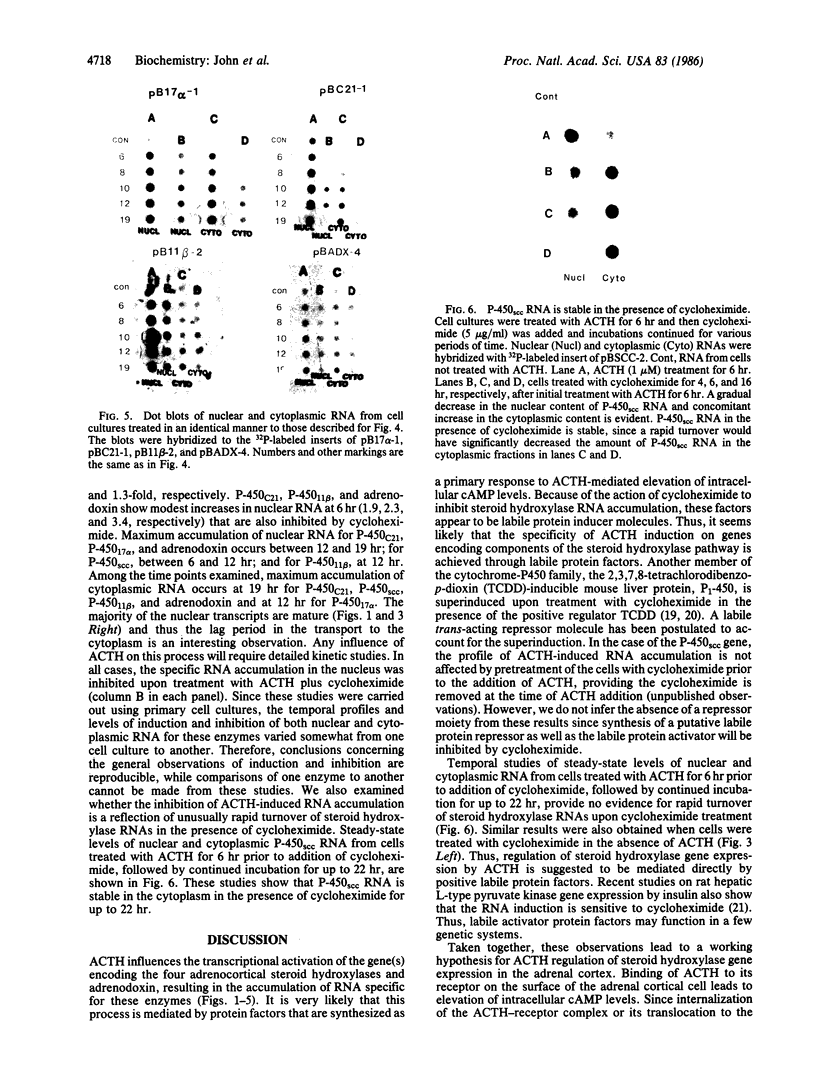
Maintenance of optimal steroidogenic capacity in the adrenal cortex is the result of a cAMP-dependent response to the peptide hormone corticotropin (ACTH). The molecular mechanism of this action of ACTH has been examined by using five recombinant DNA clones specific for enzymes of the steroidogenic pathway (P-450scc, P-45011 beta, P-450C21, P-45017 alpha, and adrenodoxin). The presence of nuclear precursors in steady-state RNA samples derived from cultured bovine adrenocortical cells and moderate increases in the number of RNA chain initiations, as determined by in vitro nuclear run-off assays, indicate that ACTH controls the expression of the gene(s) for each of these proteins at the transcriptional level. The ACTH-mediated increase in accumulation of transcripts specific for steroid hydroxylases in nuclear RNA can be specifically blocked by inhibiting protein synthesis in bovine adrenocortical cell cultures. The steady-state concentrations of nuclear RNA for control genes show no decrease upon cycloheximide treatment. These studies suggest that a primary action of ACTH in the adrenal cortex is to activate (via cAMP) the synthesis of rapidly turning over protein factors that in turn mediate increased initiation of transcription of steroid hydroxylase genes. We propose that these protein factors impart specificity of induction to genes encoding components of this pathway in steroidogenic tissues.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boggaram V., Zuber M. X., Waterman M. R. Turnover of newly synthesized cytochromes P-450scc and P-45011 beta and adrenodoxin in bovine adrenocortical cells in monolayer culture: effect of adrenocorticotropin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Jun;231(2):518–523. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90416-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Manly S. P., McMahon M., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of interferon-induced gene expression in human cells. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):745–755. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90270-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funkenstein B., McCarthy J. L., Dus K. M., Simpson E. R., Waterman M. R. Effect of adrenocorticotropin on steroid 21-hydroxylase synthesis and activity in cultured bovine adrenocortical cells. Increased synthesis in the absence of increased activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9398–9405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman M. J., Back D. W., Goodridge A. G. Nutritional regulation of the synthesis and degradation of malic enzyme messenger RNA in duck liver. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4404–4408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Nebert D. W. Autoregulation plus upstream positive and negative control regions associated with transcriptional activation of the mouse P1(450) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7269–7288. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granner D., Andreone T., Sasaki K., Beale E. Inhibition of transcription of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene by insulin. Nature. 1983 Oct 6;305(5934):549–551. doi: 10.1038/305549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel D. I., Whitlock J. P., Jr Regulation of cytochrome P1-450 gene transcription by 2,3,7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in wild type and variant mouse hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5400–5402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John M. E., John M. C., Ashley P., MacDonald R. J., Simpson E. R., Waterman M. R. Identification and characterization of cDNA clones specific for cholesterol side-chain cleavage cytochrome P-450. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5628–5632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John M. E., John M. C., Simpson E. R., Waterman M. R. Regulation of cytochrome P-45011 beta gene expression by adrenocorticotropin. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5760–5767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. B., Galeazzi D. R., Fisher J. M., Whitlock J. P., Jr Control of cytochrome P1-450 gene expression by dioxin. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1499–1502. doi: 10.1126/science.3856321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. E., Rainey W. E., Funkenstein B., Dee A., Simpson E. R., Waterman M. R. Induction of synthesis of mitochondrial steroidogenic enzymes of bovine adrenocortical cells by analogs of cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):707–713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangiarotti G., Ceccarelli A., Lodish H. F. Cyclic AMP stabilizes a class of developmentally regulated Dictyostelium discoideum mRNAs. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):616–618. doi: 10.1038/301616a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer R. A. Transcriptional regulation of the prolactin gene by ergocryptine and cyclic AMP. Nature. 1981 Nov 5;294(5836):94–97. doi: 10.1038/294094a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo K. E., Palmiter R. D. Glucocorticoid regulation of metallothionein-I mRNA synthesis in cultured mouse cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2621–2624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murdoch G. H., Rosenfeld M. G. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulation and chromatin-associated protein phosphorylation by cyclic AMP. Science. 1982 Dec 24;218(4579):1315–1317. doi: 10.1126/science.6293056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagamine Y., Sudol M., Reich E. Hormonal regulation of plasminogen activator mRNA production in porcine kidney cells. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1181–1190. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90301-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi T., Inoue H., Tanaka T. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of L-type pyruvate kinase in diabetic rat liver by insulin and dietary fructose. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14393–14397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura T., John M. E., Zuber M. X., Simpson E. R., Waterman M. R. Molecular cloning and amino acid sequence of the precursor form of bovine adrenodoxin: evidence for a previously unidentified COOH-terminal peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5705–5709. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter E., Nicolaisen A. K., Ong E. S., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone exerts rapid nuclear effects to increase production of the primary prolactin mRNA transcript. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6662–6666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purvis J. L., Canick J. A., Mason J. I., Estabrook R. W., McCarthy J. L. Lifetime of adrenal cytochrome P-450 as influenced by ACTH. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973;212:319–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb47605.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. A., Coffino P. Two-dimensional gel analysis of cyclic AMP effects in cultured S49 mouse lymphoma cells: protein modifications, inductions and repressions. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):719–733. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90126-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Tsang A. S., Mahbubani H. A change in the rate of transcription of a eukaryotic gene in response to cyclic AMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7171–7175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber M. X., John M. E., Okamura T., Simpson E. R., Waterman M. R. Bovine adrenocortical cytochrome P-450(17 alpha). Regulation of gene expression by ACTH and elucidation of primary sequence. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2475–2482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber M. X., Simpson E. R., Hall P. F., Waterman M. R. Effects of adrenocorticotropin on 17 alpha-hydroxylase activity and cytochrome P-450(17 alpha) synthesis in bovine adrenocortical cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1842–1848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]