Abstract
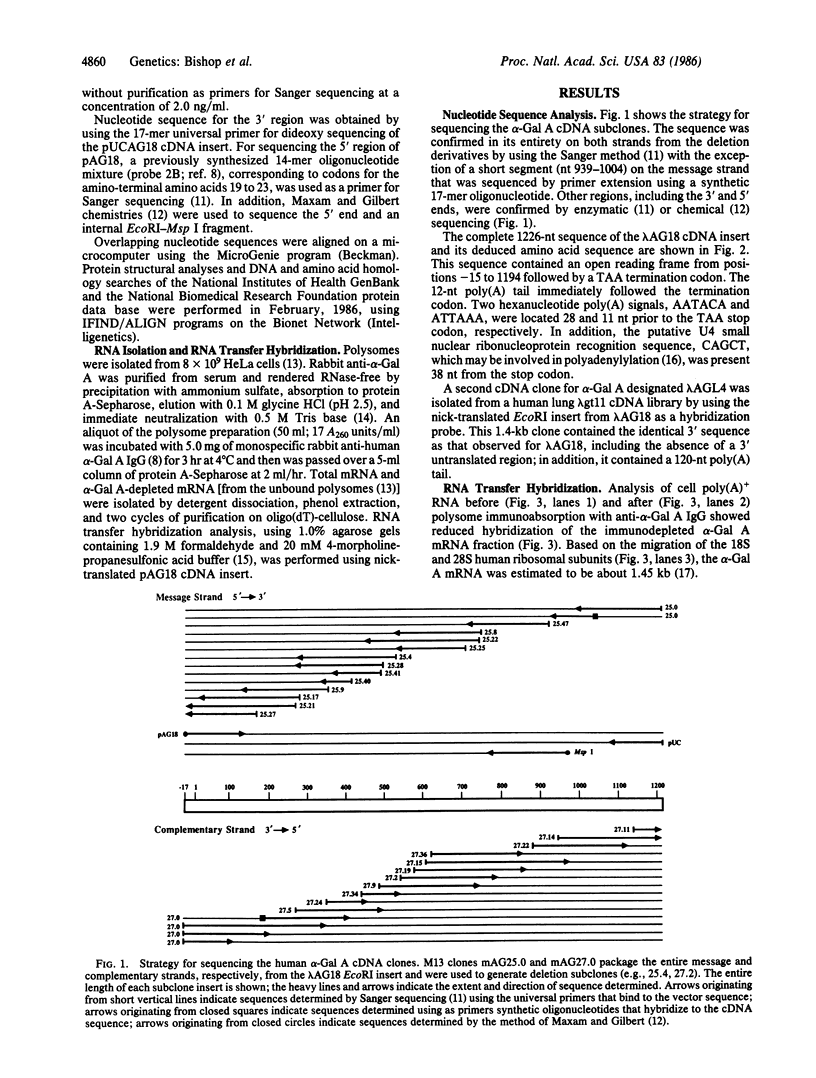
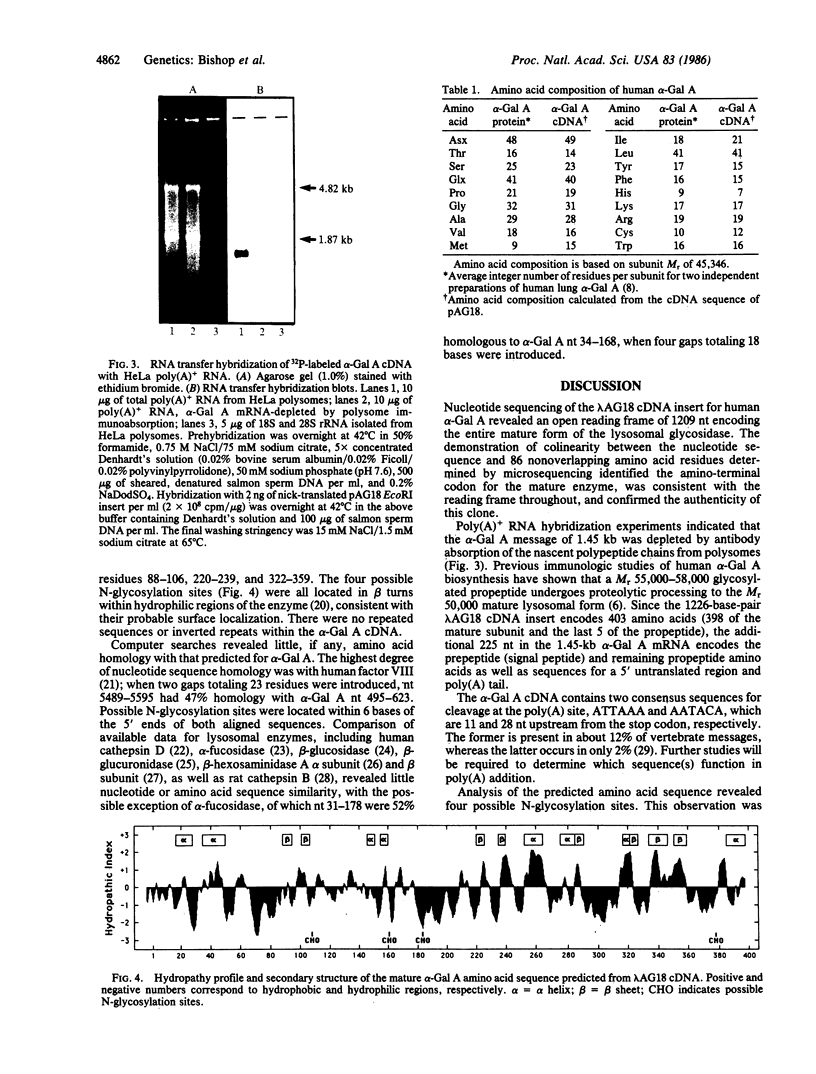
The complete nucleotide sequence has been determined for a lambda gt11 cDNA clone (lambda AG18) containing the full-length coding region for the mature lysosomal form of human alpha-galactosidase A (alpha-Gal A; EC 3.2.1.22). The lambda AG18 insert contained a 1226-base-pair sequence with an open reading frame encoding 398 amino acids of the mature polypeptide (predicted Mr = 45,356) and the last 5 amino acids of the propeptide sequence. The poly(A) signals AATACA and ATTAAA occurred 28 and 11 nucleotides prior to the TAA stop codon, respectively. There was no 3' untranslated region as the poly(A) sequence immediately followed the TAA termination codon; a second independently cloned cDNA confirmed this finding. The predicted amino acid sequence was colinear with 86 nonoverlapping residues (22% of the mature subunit) determined by microsequencing amino-terminal, tryptic, and cyanogen bromide peptides of the purified mature enzyme. Four potential N-glycosylation sites were identified, all of which occurred at predicted beta turns in hydrophilic regions of secondary structure. RNA transfer hybridization analysis of HeLa poly(A)+ RNA demonstrated a single 1.45-kilobase band whose signal was decreased by prior immunoabsorption of polysomes with monospecific alpha-Gal A antibodies. Searches of nucleic acid and protein data bases did not reveal significant homology even with the limited sequences available for mammalian lysosomal enzymes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S., Bankier A. T., Barrell B. G., de Bruijn M. H., Coulson A. R., Drouin J., Eperon I. C., Nierlich D. P., Roe B. A., Sanger F. Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):457–465. doi: 10.1038/290457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubert J. P., Biserte G., Loucheux-Lefebvre M. H. Carbohydrate-peptide linkage in glycoproteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Aug;175(2):410–418. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90528-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berget S. M. Are U4 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins involved in polyadenylation? Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):179–182. doi: 10.1038/309179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. F., Desnick R. J. Affinity purification of alpha-galactosidase A from human spleen, placenta, and plasma with elimination of pyrogen contamination. Properties of the purified splenic enzyme compared to other forms. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 10;256(3):1307–1316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady R. O., Gal A. E., Bradley R. M., Mårtensson E. The metabolism of ceramide trihexosides. I. Purification and properties of an enzyme that cleaves the terminal galactose molecule of galactosylgalactosylglucosylceramide. J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 10;242(5):1021–1026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calhoun D. H., Bishop D. F., Bernstein H. S., Quinn M., Hantzopoulos P., Desnick R. J. Fabry disease: isolation of a cDNA clone encoding human alpha-galactosidase A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7364–7368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen-Kiang S., Wolgemuth D. J., Hsu M. T., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcription and accurate polyadenylation in vitro of RNA from the major late adenovirus 2 transcription unit. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):575–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90212-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. M., McClure B. A., Houchins J. P. A rapid single-stranded cloning strategy for producing a sequential series of overlapping clones for use in DNA sequencing: application to sequencing the corn mitochondrial 18 S rDNA. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean K. J., Sweeley C. C. Studies on human liver alpha-galactosidases. I. Purification of alpha-galactosidase A and its enzymatic properties with glycolipid and oligosaccharide substrates. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):9994–10000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust P. L., Kornfeld S., Chirgwin J. M. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for human cathepsin D. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4910–4914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox M. F., DuToit D. L., Warnich L., Retief A. E. Regional localization of alpha-galactosidase (GLA) to Xpter----q22, hexosaminidase B (HEXB) to 5q13----qter, and arylsulfatase B (ARSB) to 5pter----q13. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1984;38(1):45–49. doi: 10.1159/000132028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima H., de Wet J. R., O'Brien J. S. Molecular cloning of a cDNA for human alpha-L-fucosidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1262–1265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guise K. S., Korneluk R. G., Waye J., Lamhonwah A. M., Quan F., Palmer R., Ganschow R. E., Sly W. S., Gravel R. A. Isolation and expression in Escherichia coli of a cDNA clone encoding human beta-glucuronidase. Gene. 1985;34(1):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90300-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korman A. J., Knudsen P. J., Kaufman J. F., Strominger J. L. cDNA clones for the heavy chain of HLA-DR antigens obtained after immunopurification of polysomes by monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1844–1848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeDonne N. C., Jr, Fairley J. L., Sweeley C. C. Biosynthesis of alpha-galactosidase A in cultured Chang liver cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jul 1;224(1):186–195. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90203-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas T., Sparkes R. S., Bishop D. F., Desnick R. J., Shapiro L. J. Frequency of reactivation and variability in expression of X-linked enzyme loci. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Jul;36(4):916–925. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R., Piekarz R., Neufeld E. F., Shows T. B., Suzuki K. Human beta-hexosaminidase alpha chain: coding sequence and homology with the beta chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7830–7834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dowd B. F., Quan F., Willard H. F., Lamhonwah A. M., Korneluk R. G., Lowden J. A., Gravel R. A., Mahuran D. J. Isolation of cDNA clones coding for the beta subunit of human beta-hexosaminidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- San Segundo B., Chan S. J., Steiner D. F. Identification of cDNA clones encoding a precursor of rat liver cathepsin B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2320–2324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. Z., Young J. R. An immunochemical method for mRNA purification. Application to messenger RNA encoding trypanosome variable surface antigen. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1495–1498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sly W. S., Fischer H. D. The phosphomannosyl recognition system for intracellular and intercellular transport of lysosomal enzymes. J Cell Biochem. 1982;18(1):67–85. doi: 10.1002/jcb.1982.240180107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorge J., West C., Westwood B., Beutler E. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of human glucocerebrosidase cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7289–7293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M., Stephenson P. Role of the conserved AAUAAA sequence: four AAUAAA point mutants prevent messenger RNA 3' end formation. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1045–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.6208611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf S. F., Migeon B. R. Clusters of CpG dinucleotides implicated by nuclease hypersensitivity as control elements of housekeeping genes. Nature. 1985 Apr 4;314(6010):467–469. doi: 10.1038/314467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Capon D. J., Simonsen C. C., Eaton D. L., Gitschier J., Keyt B., Seeburg P. H., Smith D. H., Hollingshead P., Wion K. L. Expression of active human factor VIII from recombinant DNA clones. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):330–337. doi: 10.1038/312330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wool I. G. The structure and function of eukaryotic ribosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:719–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.003443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]