Abstract
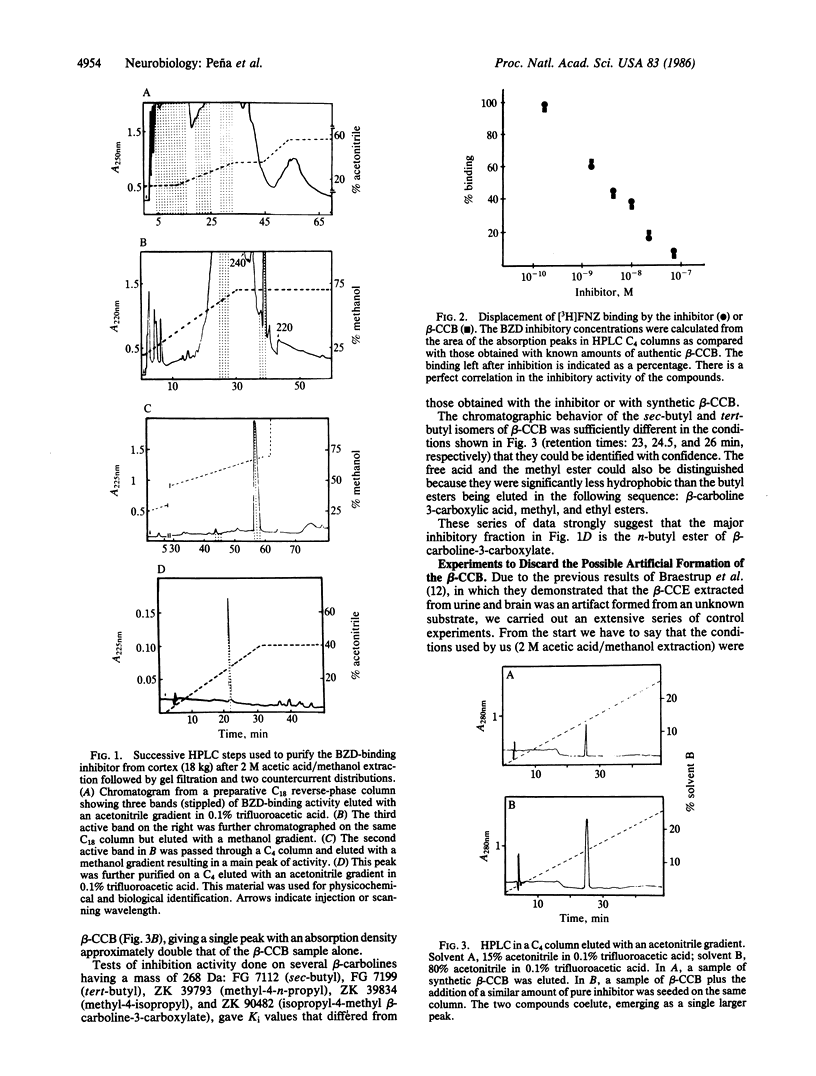
A substance having benzodiazepine-binding inhibitory activity has been extracted from 18 kg of gray matter of bovine cerebral cortex and purified to homogeneity. This substance inhibits competitively [3H]flunitrazepam and ethyl beta-[3H]carboline-3-carboxylate binding with high affinity (Ki, 3 nM), but it is inactive upon 3H-labeled Ro 5-4864, [3H]quinuclidinyl benzylate, [3H]prazosin, [3H]clonidine, [3H]dihydroalprenolol, and upon high-affinity [3H]muscimol binding. This inhibitor has been identified as n-butyl beta-carboline-3-carboxylate (beta-CCB) by fast atom bombardment mass spectroscopy (Mr, 268) and electron bombardment fragmentography, ultraviolet and fluorescence spectra, coelution in HPLC with standard beta-CCB, and by the exact correspondence in Ki with beta-CCB on the displacement of [3H]flunitrazepam binding. The possible artificial formation of beta-CCB has been discarded by a series of control experiments including addition of tryptophan to the starting homogenate, extraction from liver, isolation and purification by an alternative procedure avoiding organic solvents, and by the impossibility of making beta-CCB from beta-carboline-3-carboxylic acid or its methyl ester in the conditions of our extraction and purification procedures.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asano T., Spector S. Identification of inosine and hypoxanthine as endogenous ligands for the brain benzodiazepine-binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):977–981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Nielsen M., Olsen C. E. Urinary and brain beta-carboline-3-carboxylates as potent inhibitors of brain benzodiazepine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2288–2292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Squires R. F. Specific benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain characterized by high-affinity (3H)diazepam binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3805–3809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawley J. N., Ninan P. T., Pickar D., Chrousos G. P., Linnoila M., Skolnick P., Paul S. M. Neuropharmacological antagonism of the beta-carboline-induced "anxiety" response in rhesus monkeys. J Neurosci. 1985 Feb;5(2):477–485. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-02-00477.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. G., Cohen R. K. Identification of an endogenous peptide-ligand for the benzodiazepine receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 15;92(1):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91531-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrero P., Guidotti A., Conti-Tronconi B., Costa E. A brain octadecaneuropeptide generated by tryptic digestion of DBI (diazepam binding inhibitor) functions as a proconflict ligand of benzodiazepine recognition sites. Neuropharmacology. 1984 Nov;23(11):1359–1362. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(84)90061-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti A., Forchetti C. M., Corda M. G., Konkel D., Bennett C. D., Costa E. Isolation, characterization, and purification to homogeneity of an endogenous polypeptide with agonistic action on benzodiazepine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3531–3535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karobath M., Sperk G., Schönbeck G. Evidence for an endogenous factor interfering with 3H-diazepam binding to rat brain membranes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Jun 1;49(3):323–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90111-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korneyev AYa, Factor M. I. Change in Bmax and Kd for [3H]flunitrazepam observed in the course washing rat brain tissue with distilled water. Mol Pharmacol. 1983 Mar;23(2):310–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marangos P. J., Paul S. M., Goodwin F. K., Skolnick P. Putative endogenous ligands for the benzodiazepine receptor. Life Sci. 1979 Sep 24;25(13):1093–1102. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medina J. H., Novas M. L., De Robertis E. Heterogeneity of benzodiazepine receptors: experimental differences between [3H]flunitrazepam and [3H]ethyl-beta-carboline-3-carboxylate binding sites in rat brain membranes. J Neurochem. 1983 Sep;41(3):703–709. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb04797.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H., Okada T. Benzodiazepine receptor: demonstration in the central nervous system. Science. 1977 Nov 25;198(4319):849–851. doi: 10.1126/science.918669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novas M. L., Medina J. H., De Robertis E. Benzodiazepine receptors in the rat hippocampal formation: action of catecholaminergic, serotoninergic and commissural denervation. Neuroscience. 1983 Mar;8(3):459–465. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90192-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sangameswaran L., de Blas A. L. Demonstration of benzodiazepine-like molecules in the mammalian brain with a monoclonal antibody to benzodiazepines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5560–5564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnick P., Marangos P. J., Goodwin F. K., Edwards M., Paul S. Identification of inosine and hypoxanthine as endogenous inhibitors of [3H] diazepam binding in the central nervous system. Life Sci. 1978 Oct 9;23(14):1473–1480. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90128-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



