Abstract
In the title molecule, C10H7ClO3, the butyrolactone core, a furan-2(5H)-one, forms a dihedral angle of 59.21 (5)° with the benzene ring. In the crystal, two types of hydrogen bonds (O—H⋯O and C—H⋯Cl) link molecules into infinite chains along the b axis. π–π contacts [centroid–centroid distances = 3.6359 (10) and 3.8776 (11) Å] link the chains into a three-dimensional network.
Related literature
For the antibacterial activity of furanones, see: Xiao et al. (2011 ▶). For related structures, see: Peng et al. (2011 ▶); Xiao et al. (2010 ▶).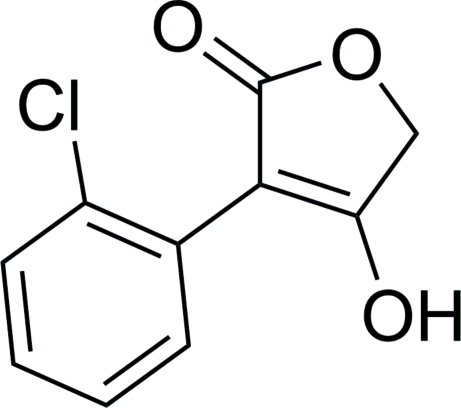
Experimental
Crystal data
C10H7ClO3
M r = 210.61
Monoclinic,
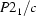
a = 9.9699 (15) Å
b = 11.8308 (18) Å
c = 8.1562 (12) Å
β = 104.898 (2)°
V = 929.7 (2) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.39 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.30 × 0.20 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.893, T max = 0.927
7259 measured reflections
2240 independent reflections
2037 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.018
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.034
wR(F 2) = 0.108
S = 1.12
2240 reflections
132 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.32 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.33 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811048641/pv2483sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811048641/pv2483Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811048641/pv2483Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O3—H3⋯O1i | 0.82 (3) | 1.80 (3) | 2.6182 (16) | 170 (3) |
| C9—H9B⋯Cl1i | 0.97 | 2.77 | 3.7126 (16) | 165 |
Symmetry code: (i) 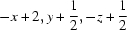 .
.
Acknowledgments
The work was financed by the Planned Science and Technology Project of Hunan Province, China (grant No. 2011 F J3056), the Key Laboratory of Plant Resources Conservation and Utilization (Jishou University), College of Hunan Province (grant No. JSK201106) and Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No. 11 J J3113).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Recently, we have reported the antibacterial activities of a few γ-butyrolactones (furanones) (Xiao et al., 2011). As a part of our ongoing studies of γ-butyrolactones (Xiao et al., 2010), we herein report the crystal structure of the title compound.
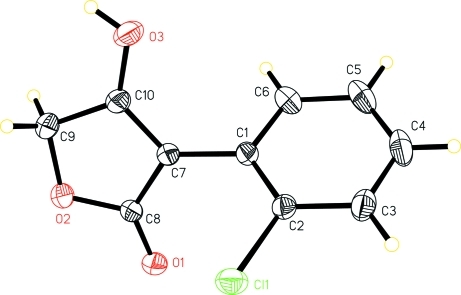
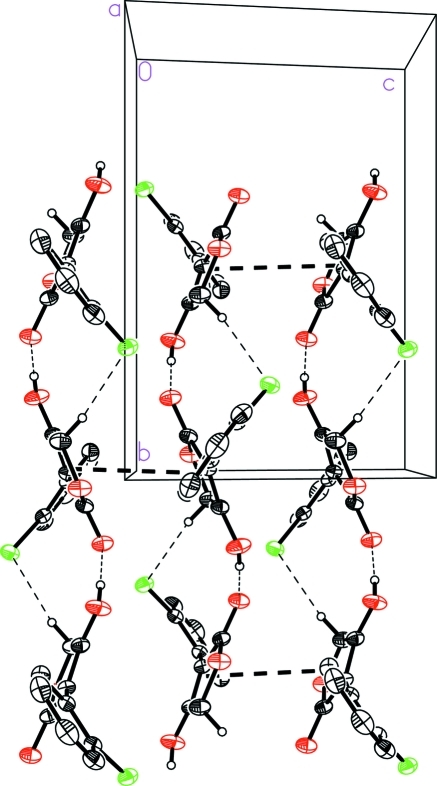
In the title compound (Fig. 1), the butyrolactone moiety makes a dihedral angle of 59.21 (5) ° with the benzene ring. Relatively strong intermolecular hydrogen bonds (O—H···O) link molecules into an infinite chain running along the b axis, which is further consolidated by weak intermolecular C—H···Cl interactions. There are π–π contacts between benzene rings and butyrolactone rings with centroid–centroid distances 3.6359 (10) and 3.8776 (11) Å, respectively (Fig. 2). The molecular dimensions in the title molecule agree very well with the corresponding molecular dimensions reported in a few similar structures (Peng et al., 2011; Xiao et al., 2010).
Experimental
A dropwise solution of 2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl 2-(2-chlorophenyl)acetate (1.03 g, 4 mmol) in dry THF was added to a suspension of NaH in dry THF in an ice cold bath. The stirring was maintained at room temperature for 6 h. Water was added and the solution was extracted twice with ethyl ether. The aqueous phase was cooled to 273 K and then acidified with concentrated hydrochloric acid to give a solid precipitate. The title compound thus obtained was crystallized from ethanol-water (2:1) to give the colorless blocks suitable for single-crystal structure determination.
Refinement
The H-atoms bonded to C-atoms were placed in geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms with C—H = 0.93 and 0.97 Å for aryl and methylene type H atoms, respectively, with Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(C). The hydroxyl H atom was located from a difference Fourier map and was allowed to refine freely.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of the title compound, showing the atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.
A unit cell packing diagram of the title compound showing a three-dimensional network built through intermolecular hydrogen bonds and π–π contacts.
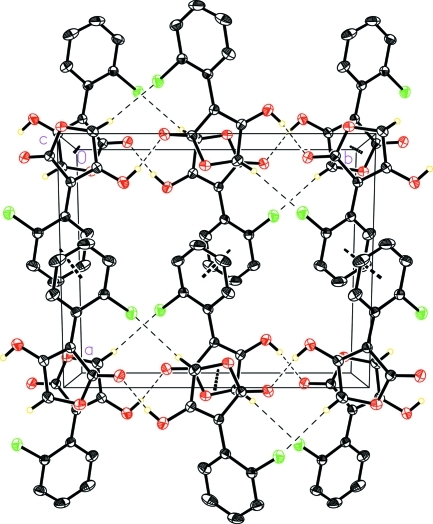
Fig. 3.
A unit cell packing diagram of the title compound
Crystal data
| C10H7ClO3 | F(000) = 432 |
| Mr = 210.61 | Dx = 1.505 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 2125 reflections |
| a = 9.9699 (15) Å | θ = 2.7–27.8° |
| b = 11.8308 (18) Å | µ = 0.39 mm−1 |
| c = 8.1562 (12) Å | T = 296 K |
| β = 104.898 (2)° | Block, colorless |
| V = 929.7 (2) Å3 | 0.30 × 0.20 × 0.20 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer | 2240 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2037 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.018 |
| φ and ω scan | θmax = 28.0°, θmin = 2.1° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −13→10 |
| Tmin = 0.893, Tmax = 0.927 | k = −15→15 |
| 7259 measured reflections | l = −10→10 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.034 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.108 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0607P)2 + 0.1971P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.12 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 2240 reflections | Δρmax = 0.32 e Å−3 |
| 132 parameters | Δρmin = −0.33 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.021 (4) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.70093 (13) | 0.46964 (11) | 0.22948 (16) | 0.0334 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.62894 (13) | 0.38058 (11) | 0.13494 (17) | 0.0350 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.48970 (15) | 0.36149 (14) | 0.1245 (2) | 0.0475 (4) | |
| H3A | 0.4435 | 0.3010 | 0.0617 | 0.057* | |
| C4 | 0.42063 (16) | 0.43319 (17) | 0.2082 (2) | 0.0567 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.3274 | 0.4206 | 0.2022 | 0.068* | |
| C5 | 0.48850 (17) | 0.52330 (17) | 0.3006 (2) | 0.0556 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.4408 | 0.5719 | 0.3553 | 0.067* | |
| C6 | 0.62747 (16) | 0.54126 (14) | 0.3117 (2) | 0.0455 (3) | |
| H6 | 0.6729 | 0.6019 | 0.3748 | 0.055* | |
| C7 | 0.84833 (13) | 0.49225 (10) | 0.23989 (17) | 0.0337 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.96157 (13) | 0.41569 (11) | 0.31055 (18) | 0.0365 (3) | |
| C9 | 1.05960 (15) | 0.57272 (12) | 0.2315 (2) | 0.0459 (3) | |
| H9A | 1.0901 | 0.5790 | 0.1281 | 0.055* | |
| H9B | 1.1076 | 0.6290 | 0.3119 | 0.055* | |
| C10 | 0.90647 (14) | 0.58691 (11) | 0.19598 (18) | 0.0380 (3) | |
| Cl1 | 0.71082 (4) | 0.29321 (3) | 0.01933 (5) | 0.04628 (15) | |
| H3 | 0.897 (3) | 0.730 (2) | 0.125 (3) | 0.080 (7)* | |
| O1 | 0.95949 (11) | 0.32284 (8) | 0.37570 (15) | 0.0465 (3) | |
| O2 | 1.08432 (10) | 0.46088 (9) | 0.30186 (16) | 0.0482 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.84132 (12) | 0.67963 (10) | 0.12899 (18) | 0.0564 (3) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0298 (6) | 0.0325 (6) | 0.0387 (6) | 0.0021 (4) | 0.0102 (5) | 0.0046 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0319 (6) | 0.0325 (6) | 0.0400 (6) | 0.0003 (5) | 0.0082 (5) | 0.0070 (5) |
| C3 | 0.0328 (7) | 0.0490 (8) | 0.0568 (9) | −0.0059 (6) | 0.0046 (6) | 0.0136 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0296 (7) | 0.0776 (12) | 0.0647 (10) | 0.0058 (7) | 0.0156 (7) | 0.0213 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0430 (8) | 0.0773 (12) | 0.0514 (9) | 0.0217 (8) | 0.0208 (7) | 0.0107 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0417 (7) | 0.0505 (8) | 0.0454 (7) | 0.0105 (6) | 0.0128 (6) | −0.0012 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0306 (6) | 0.0290 (6) | 0.0419 (6) | −0.0011 (4) | 0.0101 (5) | −0.0033 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0318 (6) | 0.0314 (6) | 0.0470 (7) | 0.0004 (5) | 0.0117 (5) | −0.0048 (5) |
| C9 | 0.0356 (7) | 0.0384 (7) | 0.0648 (9) | −0.0071 (5) | 0.0149 (6) | −0.0014 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0345 (6) | 0.0311 (6) | 0.0469 (7) | −0.0040 (5) | 0.0080 (5) | −0.0031 (5) |
| Cl1 | 0.0483 (2) | 0.0362 (2) | 0.0521 (2) | 0.00220 (13) | 0.00863 (16) | −0.00722 (13) |
| O1 | 0.0408 (5) | 0.0334 (5) | 0.0656 (7) | 0.0049 (4) | 0.0140 (5) | 0.0054 (4) |
| O2 | 0.0304 (5) | 0.0397 (5) | 0.0752 (7) | 0.0007 (4) | 0.0146 (5) | 0.0014 (5) |
| O3 | 0.0410 (6) | 0.0344 (5) | 0.0876 (9) | −0.0053 (4) | 0.0056 (6) | 0.0141 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—C2 | 1.3912 (18) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C6 | 1.3987 (19) | C7—C10 | 1.3510 (18) |
| C1—C7 | 1.4745 (17) | C7—C8 | 1.4465 (17) |
| C2—C3 | 1.3873 (19) | C8—O1 | 1.2228 (17) |
| C2—Cl1 | 1.7377 (14) | C8—O2 | 1.3539 (16) |
| C3—C4 | 1.379 (3) | C9—O2 | 1.4382 (18) |
| C3—H3A | 0.9300 | C9—C10 | 1.488 (2) |
| C4—C5 | 1.378 (3) | C9—H9A | 0.9700 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C9—H9B | 0.9700 |
| C5—C6 | 1.381 (2) | C10—O3 | 1.3195 (17) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | O3—H3 | 0.82 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 117.73 (12) | C10—C7—C8 | 106.29 (11) |
| C2—C1—C7 | 122.26 (11) | C10—C7—C1 | 128.63 (12) |
| C6—C1—C7 | 119.97 (12) | C8—C7—C1 | 125.00 (11) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 121.53 (13) | O1—C8—O2 | 119.61 (12) |
| C3—C2—Cl1 | 118.17 (11) | O1—C8—C7 | 129.56 (12) |
| C1—C2—Cl1 | 120.26 (10) | O2—C8—C7 | 110.81 (11) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.25 (15) | O2—C9—C10 | 104.08 (11) |
| C4—C3—H3A | 120.4 | O2—C9—H9A | 110.9 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 120.4 | C10—C9—H9A | 110.9 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.60 (14) | O2—C9—H9B | 110.9 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.7 | C10—C9—H9B | 110.9 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.7 | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.0 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.86 (15) | O3—C10—C7 | 126.86 (13) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.1 | O3—C10—C9 | 123.04 (12) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.1 | C7—C10—C9 | 110.09 (12) |
| C5—C6—C1 | 121.02 (16) | C8—O2—C9 | 108.65 (10) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.5 | C10—O3—H3 | 111.0 (18) |
| C1—C6—H6 | 119.5 | ||
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −1.21 (19) | C6—C1—C7—C8 | 119.84 (15) |
| C7—C1—C2—C3 | −179.04 (12) | C10—C7—C8—O1 | 175.41 (15) |
| C6—C1—C2—Cl1 | 176.21 (10) | C1—C7—C8—O1 | −1.6 (2) |
| C7—C1—C2—Cl1 | −1.61 (17) | C10—C7—C8—O2 | −2.92 (16) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.7 (2) | C1—C7—C8—O2 | −179.92 (12) |
| Cl1—C2—C3—C4 | −176.74 (12) | C8—C7—C10—O3 | −178.86 (15) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.4 (2) | C1—C7—C10—O3 | −2.0 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.9 (3) | C8—C7—C10—C9 | 2.03 (16) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.4 (2) | C1—C7—C10—C9 | 178.90 (13) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.6 (2) | O2—C9—C10—O3 | −179.72 (14) |
| C7—C1—C6—C5 | 178.52 (14) | O2—C9—C10—C7 | −0.57 (17) |
| C2—C1—C7—C10 | 121.29 (16) | O1—C8—O2—C9 | −175.94 (13) |
| C6—C1—C7—C10 | −56.5 (2) | C7—C8—O2—C9 | 2.58 (16) |
| C2—C1—C7—C8 | −62.39 (19) | C10—C9—O2—C8 | −1.25 (16) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O3—H3···O1i | 0.82 (3) | 1.80 (3) | 2.6182 (16) | 170 (3) |
| C9—H9B···Cl1i | 0.97 | 2.77 | 3.7126 (16) | 165. |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, y+1/2, −z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: PV2483).
References
- Bruker (2007). SMART and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Peng, W., Wang, L., Wu, F. & Xu, Q. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o2329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.-P., Ma, T.-W., Liao, M.-L., Feng, Y.-T., Peng, X.-C., Li, J.-L., Li, Z.-P., Wu, Y., Luo, Q., Deng, Y. & Zhu, H.-L. (2011). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 46, 4904–4914. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.-P., Zhu, J., Jiang, W., Li, G.-X. & Wang, X.-D. (2010). Z. Kristallogr. New Cryst. Struct. 225, 797–798.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811048641/pv2483sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811048641/pv2483Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811048641/pv2483Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report