Abstract
The title compound, C22H20N2O2, was synthesized via a multicomponent reaction using naphthalen-2-ol, morpholine and 4-formylbenzonitrile. The dihedral angle between the naphthalene ring system and the benzene ring is 81.25 (10)°. The morpholine ring adopts a chair conformation. The molecular conformation is stabilized by intramolecular O—H⋯N and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. In the crystal, intermolecular C—H⋯N hydrogen bonds link molecules into helical chains running parallel to the c axis.
Related literature
For background to multi-component reactions, see: Devi & Bhuyan (2004 ▶); Domling & Ugi (2000 ▶). Hulme & Gore (2003 ▶); Ugi (1962 ▶). For ring puckering parameters, see: Cremer & Pople (1975 ▶).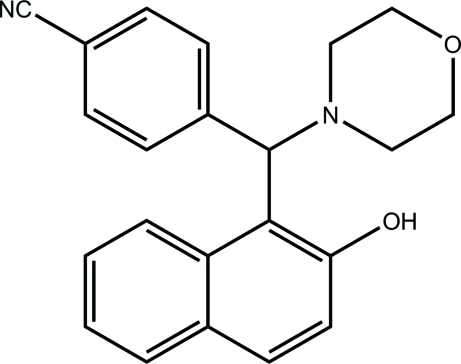
Experimental
Crystal data
C22H20N2O2
M r = 344.40
Trigonal,
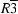
a = 18.294 (3) Å
c = 28.738 (6) Å
V = 8329 (4) Å3
Z = 18
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.08 mm−1
T = 298 K
0.20 × 0.15 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Rigaku Mercury2 diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.910, T max = 1.000
24077 measured reflections
3326 independent reflections
1786 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.138
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.081
wR(F 2) = 0.210
S = 1.03
3326 reflections
235 parameters
7 restraints
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.22 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.27 e Å−3
Data collection: CrystalClear (Rigaku, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: CrystalClear; data reduction: CrystalClear; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681104997X/rz2668sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681104997X/rz2668Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681104997X/rz2668Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1⋯N1 | 0.85 | 1.82 | 2.601 (4) | 151 |
| C21—H21A⋯O1 | 0.93 | 2.54 | 3.300 (4) | 139 |
| C7—H7A⋯N2i | 0.93 | 2.44 | 3.327 (9) | 160 |
Symmetry code: (i) 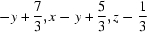 .
.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a start-up grant from Anyang Institute of Technology, China.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Multi-component reactions (MCRs) (Hulme & Gore, 2003; Ugi, 1962) involving at least three starting materials in a one-pot reaction have attracted considerable attention in terms of saving both energy and raw materials (Devi & Bhuyan, 2004). Compared to conventional multi-step organic syntheses, MCRs have advantages that include the simplicity of a one-pot procedure and the buildup of complex molecules (Domling & Ugi, 2000). We report here the synthesis and crystal structure of the title compound, 4-4-[(2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)(morpholino)methyl]benzonitrile.
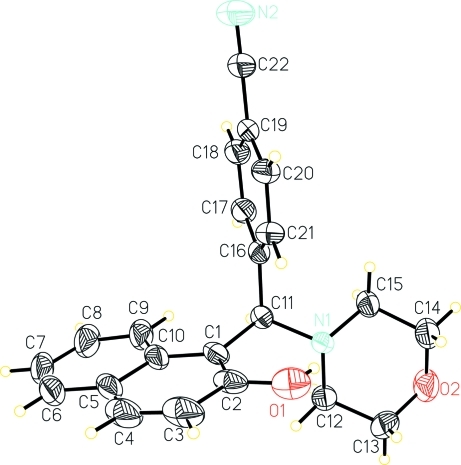
In the title compound (Fig. 1) bond lengths and angles have normal values. The dihedral angle between the naphthalene ring system and the benzene ring is 81.25 (10)°. The morpholine ring (N1/C12/C13/O2/C14/C15) assumes a boat conformation, with puckering parameters <i<Q, θ and φ (Cremer & Pople, 1975) of 0.559 (4) Å, 179.3 (4)° and -159 (4)°, respectively. The molecular conformation is stabilized by intramolecular O—H···N and C—H···O hydrogen bonds (Table 1). In the crystal structure, molecules are linked into helical chains parallel to the c axis by intermolecular C—H···N hydrogen bonds.
Experimental
A dry 100 ml flask was charged with 4-formylbenzonitrile (15 mmol), naphthalen-2-ol (15 mmol) and morpholine (15 mmol). The mixture was stirred at 373 K for 12 h, then ethanol (15 ml) was added. After heating under reflux for 1 h, the precipitate was filtrated out and washed with ethanol (10 ml × 3) to give the title compound. Colourless crystals were obtained by slow evaporation of a dichloromethane solution.
Refinement
All the H atoms attached to C atoms were situated into the idealized positions and treated as riding, with C–H = 0.93 Å (aromatic), 0.97 Å (methylene) and 0.98 Å (methine), and with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C). The hydroxyl H atom was located in a difference Fourier map and refined as riding, with O—H = 0.82 Å and with Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(O). Restraints (SIMU and DELU) were used for stabilizing the refinement of atoms C5 and C6. The quality of the crystal available was not optimal and it was weakly diffracting, with no significant data obtained beyond θ = 20°. Although recrystallization was attempted repeatedly, no better crystals could be obtained. This could account for the rather high Rint value (0.138) and for the poor precision of the analysis.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound showing displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 30% probability level.
Crystal data
| C22H20N2O2 | Dx = 1.236 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 344.40 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Trigonal, R3 | Cell parameters from 3326 reflections |
| Hall symbol: -R 3 | θ = 3.1–25.2° |
| a = 18.294 (3) Å | µ = 0.08 mm−1 |
| c = 28.738 (6) Å | T = 298 K |
| V = 8329 (4) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 18 | 0.20 × 0.15 × 0.10 mm |
| F(000) = 3276 |
Data collection
| Rigaku Mercury2 diffractometer | 3326 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1786 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.138 |
| Detector resolution: 13.6612 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 25.2°, θmin = 3.1° |
| CCD profile fitting scans | h = −21→21 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku, 2005) | k = −21→21 |
| Tmin = 0.910, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −34→34 |
| 24077 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.081 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.210 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.03 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0825P)2 + 7.1283P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3326 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 235 parameters | Δρmax = 0.22 e Å−3 |
| 7 restraints | Δρmin = −0.27 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.6590 (2) | 0.9543 (2) | −0.01901 (11) | 0.0550 (9) | |
| N1 | 0.58212 (15) | 0.86806 (15) | 0.04966 (8) | 0.0455 (7) | |
| O1 | 0.51037 (19) | 0.90933 (18) | −0.01526 (10) | 0.0841 (9) | |
| H1 | 0.5181 | 0.8920 | 0.0108 | 0.126* | |
| C2 | 0.5846 (3) | 0.9432 (2) | −0.03881 (13) | 0.0713 (12) | |
| N2 | 0.7870 (3) | 1.3181 (3) | 0.14213 (18) | 0.146 (2) | |
| O2 | 0.48604 (18) | 0.71036 (17) | 0.09733 (11) | 0.0913 (10) | |
| C3 | 0.5833 (5) | 0.9667 (3) | −0.08470 (18) | 0.110 (2) | |
| H3A | 0.5334 | 0.9598 | −0.0972 | 0.132* | |
| C4 | 0.6527 (7) | 0.9991 (4) | −0.11117 (19) | 0.140 (3) | |
| H4A | 0.6504 | 1.0157 | −0.1414 | 0.168* | |
| C5 | 0.7294 (5) | 1.0085 (3) | −0.09428 (18) | 0.119 (2) | |
| C6 | 0.8038 (6) | 1.0382 (4) | −0.1215 (2) | 0.145 (3) | |
| H6A | 0.8020 | 1.0527 | −0.1524 | 0.174* | |
| C7 | 0.8752 (5) | 1.0465 (4) | −0.1058 (3) | 0.160 (4) | |
| H7A | 0.9223 | 1.0672 | −0.1250 | 0.192* | |
| C8 | 0.8794 (4) | 1.0236 (3) | −0.0596 (2) | 0.131 (2) | |
| H8A | 0.9289 | 1.0275 | −0.0484 | 0.158* | |
| C9 | 0.8103 (3) | 0.9956 (2) | −0.03107 (17) | 0.0894 (15) | |
| H9A | 0.8146 | 0.9826 | −0.0003 | 0.107* | |
| C10 | 0.7325 (3) | 0.9858 (2) | −0.04718 (13) | 0.0728 (12) | |
| C11 | 0.66336 (19) | 0.93938 (19) | 0.03258 (10) | 0.0459 (8) | |
| H11A | 0.7076 | 0.9249 | 0.0374 | 0.055* | |
| C12 | 0.5716 (2) | 0.7879 (2) | 0.03122 (13) | 0.0606 (10) | |
| H12A | 0.6184 | 0.7811 | 0.0413 | 0.073* | |
| H12B | 0.5719 | 0.7894 | −0.0025 | 0.073* | |
| C13 | 0.4897 (3) | 0.7141 (2) | 0.04806 (16) | 0.0834 (13) | |
| H13A | 0.4428 | 0.7192 | 0.0363 | 0.100* | |
| H13B | 0.4842 | 0.6621 | 0.0360 | 0.100* | |
| C14 | 0.4948 (3) | 0.7858 (2) | 0.11521 (14) | 0.0771 (12) | |
| H14A | 0.4925 | 0.7828 | 0.1489 | 0.092* | |
| H14B | 0.4480 | 0.7922 | 0.1045 | 0.092* | |
| C15 | 0.5765 (2) | 0.8617 (2) | 0.10044 (12) | 0.0584 (9) | |
| H15A | 0.5798 | 0.9124 | 0.1132 | 0.070* | |
| H15B | 0.6235 | 0.8572 | 0.1126 | 0.070* | |
| C16 | 0.6885 (2) | 1.0214 (2) | 0.05850 (10) | 0.0478 (8) | |
| C17 | 0.7626 (2) | 1.0606 (2) | 0.08376 (12) | 0.0621 (10) | |
| H17A | 0.7954 | 1.0350 | 0.0863 | 0.075* | |
| C18 | 0.7886 (2) | 1.1370 (3) | 0.10521 (13) | 0.0733 (12) | |
| H18A | 0.8395 | 1.1633 | 0.1214 | 0.088* | |
| C19 | 0.7396 (3) | 1.1747 (2) | 0.10287 (12) | 0.0651 (11) | |
| C20 | 0.6641 (2) | 1.1355 (2) | 0.07818 (12) | 0.0626 (10) | |
| H20A | 0.6302 | 1.1600 | 0.0767 | 0.075* | |
| C21 | 0.6400 (2) | 1.0603 (2) | 0.05593 (11) | 0.0554 (9) | |
| H21A | 0.5902 | 1.0349 | 0.0388 | 0.067* | |
| C22 | 0.7657 (3) | 1.2544 (3) | 0.12509 (16) | 0.0976 (16) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.086 (3) | 0.047 (2) | 0.036 (2) | 0.036 (2) | 0.0023 (19) | −0.0008 (15) |
| N1 | 0.0493 (16) | 0.0456 (16) | 0.0418 (16) | 0.0238 (13) | 0.0012 (12) | −0.0033 (12) |
| O1 | 0.090 (2) | 0.090 (2) | 0.084 (2) | 0.0538 (18) | −0.0321 (17) | −0.0075 (16) |
| C2 | 0.118 (4) | 0.054 (2) | 0.045 (2) | 0.045 (3) | −0.022 (2) | −0.0062 (18) |
| N2 | 0.126 (4) | 0.096 (3) | 0.153 (4) | 0.008 (3) | 0.030 (3) | −0.067 (3) |
| O2 | 0.106 (2) | 0.0635 (19) | 0.092 (2) | 0.0338 (17) | 0.0362 (18) | 0.0195 (16) |
| C3 | 0.189 (6) | 0.092 (4) | 0.060 (3) | 0.077 (4) | −0.045 (4) | −0.004 (3) |
| C4 | 0.280 (10) | 0.078 (4) | 0.047 (4) | 0.078 (5) | −0.024 (5) | 0.001 (3) |
| C5 | 0.231 (6) | 0.043 (2) | 0.049 (3) | 0.043 (3) | 0.054 (3) | 0.005 (2) |
| C6 | 0.250 (6) | 0.058 (3) | 0.066 (3) | 0.031 (4) | 0.070 (4) | −0.002 (2) |
| C7 | 0.193 (7) | 0.068 (4) | 0.144 (7) | 0.008 (5) | 0.123 (6) | −0.008 (4) |
| C8 | 0.129 (5) | 0.080 (3) | 0.154 (6) | 0.028 (3) | 0.087 (4) | −0.007 (3) |
| C9 | 0.099 (4) | 0.064 (3) | 0.095 (3) | 0.034 (3) | 0.051 (3) | 0.004 (2) |
| C10 | 0.112 (4) | 0.041 (2) | 0.055 (3) | 0.031 (2) | 0.028 (2) | −0.0009 (18) |
| C11 | 0.0470 (19) | 0.049 (2) | 0.044 (2) | 0.0261 (17) | 0.0012 (15) | 0.0000 (15) |
| C12 | 0.068 (2) | 0.052 (2) | 0.063 (2) | 0.0313 (19) | 0.0085 (19) | 0.0001 (17) |
| C13 | 0.086 (3) | 0.048 (2) | 0.098 (4) | 0.021 (2) | 0.013 (3) | −0.004 (2) |
| C14 | 0.083 (3) | 0.068 (3) | 0.077 (3) | 0.036 (2) | 0.026 (2) | 0.010 (2) |
| C15 | 0.063 (2) | 0.063 (2) | 0.049 (2) | 0.032 (2) | 0.0085 (17) | 0.0072 (17) |
| C16 | 0.048 (2) | 0.053 (2) | 0.0362 (19) | 0.0210 (17) | 0.0011 (15) | 0.0025 (15) |
| C17 | 0.051 (2) | 0.073 (3) | 0.055 (2) | 0.025 (2) | −0.0007 (17) | −0.0086 (19) |
| C18 | 0.051 (2) | 0.083 (3) | 0.059 (3) | 0.014 (2) | 0.0010 (18) | −0.020 (2) |
| C19 | 0.068 (3) | 0.053 (2) | 0.045 (2) | 0.009 (2) | 0.0174 (19) | −0.0085 (17) |
| C20 | 0.074 (3) | 0.054 (2) | 0.059 (2) | 0.032 (2) | 0.002 (2) | −0.0073 (18) |
| C21 | 0.065 (2) | 0.049 (2) | 0.052 (2) | 0.0287 (19) | −0.0093 (17) | −0.0094 (17) |
| C22 | 0.081 (3) | 0.073 (3) | 0.088 (3) | 0.000 (2) | 0.024 (2) | −0.033 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—C2 | 1.392 (5) | C9—H9A | 0.9300 |
| C1—C10 | 1.422 (5) | C11—C16 | 1.526 (4) |
| C1—C11 | 1.517 (4) | C11—H11A | 0.9800 |
| N1—C15 | 1.464 (4) | C12—C13 | 1.511 (5) |
| N1—C12 | 1.478 (4) | C12—H12A | 0.9700 |
| N1—C11 | 1.488 (4) | C12—H12B | 0.9700 |
| O1—C2 | 1.359 (5) | C13—H13A | 0.9700 |
| O1—H1 | 0.8517 | C13—H13B | 0.9700 |
| C2—C3 | 1.391 (6) | C14—C15 | 1.505 (5) |
| N2—C22 | 1.137 (5) | C14—H14A | 0.9700 |
| O2—C14 | 1.405 (4) | C14—H14B | 0.9700 |
| O2—C13 | 1.418 (5) | C15—H15A | 0.9700 |
| C3—C4 | 1.337 (9) | C15—H15B | 0.9700 |
| C3—H3A | 0.9300 | C16—C17 | 1.381 (4) |
| C4—C5 | 1.410 (9) | C16—C21 | 1.389 (4) |
| C4—H4A | 0.9300 | C17—C18 | 1.377 (5) |
| C5—C6 | 1.423 (10) | C17—H17A | 0.9300 |
| C5—C10 | 1.425 (7) | C18—C19 | 1.379 (5) |
| C6—C7 | 1.317 (10) | C18—H18A | 0.9300 |
| C6—H6A | 0.9300 | C19—C20 | 1.391 (5) |
| C7—C8 | 1.403 (10) | C19—C22 | 1.437 (6) |
| C7—H7A | 0.9300 | C20—C21 | 1.374 (4) |
| C8—C9 | 1.373 (6) | C20—H20A | 0.9300 |
| C8—H8A | 0.9300 | C21—H21A | 0.9300 |
| C9—C10 | 1.420 (6) | ||
| C2—C1—C10 | 118.9 (4) | N1—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—C11 | 120.6 (3) | C13—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| C10—C1—C11 | 120.3 (3) | N1—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C15—N1—C12 | 108.1 (3) | C13—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C15—N1—C11 | 113.5 (2) | H12A—C12—H12B | 108.1 |
| C12—N1—C11 | 109.2 (2) | O2—C13—C12 | 111.4 (3) |
| C2—O1—H1 | 107.0 | O2—C13—H13A | 109.4 |
| O1—C2—C3 | 116.4 (5) | C12—C13—H13A | 109.4 |
| O1—C2—C1 | 123.0 (3) | O2—C13—H13B | 109.4 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.6 (5) | C12—C13—H13B | 109.4 |
| C14—O2—C13 | 109.8 (3) | H13A—C13—H13B | 108.0 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 121.1 (6) | O2—C14—C15 | 112.1 (3) |
| C4—C3—H3A | 119.4 | O2—C14—H14A | 109.2 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 119.4 | C15—C14—H14A | 109.2 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 121.6 (5) | O2—C14—H14B | 109.2 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 119.2 | C15—C14—H14B | 109.2 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 119.2 | H14A—C14—H14B | 107.9 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 124.1 (7) | N1—C15—C14 | 110.6 (3) |
| C4—C5—C10 | 118.2 (6) | N1—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C10 | 117.6 (8) | C14—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 124.0 (8) | N1—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—H6A | 118.0 | C14—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6A | 118.0 | H15A—C15—H15B | 108.1 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 119.3 (6) | C17—C16—C21 | 118.4 (3) |
| C6—C7—H7A | 120.3 | C17—C16—C11 | 120.1 (3) |
| C8—C7—H7A | 120.3 | C21—C16—C11 | 121.5 (3) |
| C9—C8—C7 | 119.9 (7) | C18—C17—C16 | 120.9 (4) |
| C9—C8—H8A | 120.0 | C18—C17—H17A | 119.6 |
| C7—C8—H8A | 120.0 | C16—C17—H17A | 119.6 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 121.9 (5) | C17—C18—C19 | 120.3 (3) |
| C8—C9—H9A | 119.0 | C17—C18—H18A | 119.8 |
| C10—C9—H9A | 119.0 | C19—C18—H18A | 119.8 |
| C9—C10—C1 | 123.4 (4) | C18—C19—C20 | 119.5 (3) |
| C9—C10—C5 | 117.2 (5) | C18—C19—C22 | 121.1 (4) |
| C1—C10—C5 | 119.4 (5) | C20—C19—C22 | 119.4 (4) |
| N1—C11—C1 | 111.2 (3) | C21—C20—C19 | 119.5 (4) |
| N1—C11—C16 | 112.3 (2) | C21—C20—H20A | 120.2 |
| C1—C11—C16 | 108.5 (2) | C19—C20—H20A | 120.2 |
| N1—C11—H11A | 108.3 | C20—C21—C16 | 121.4 (3) |
| C1—C11—H11A | 108.3 | C20—C21—H21A | 119.3 |
| C16—C11—H11A | 108.3 | C16—C21—H21A | 119.3 |
| N1—C12—C13 | 110.6 (3) | N2—C22—C19 | 179.0 (5) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1···N1 | 0.85 | 1.82 | 2.601 (4) | 151. |
| C21—H21A···O1 | 0.93 | 2.54 | 3.300 (4) | 139 |
| C7—H7A···N2i | 0.93 | 2.44 | 3.327 (9) | 160 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −y+7/3, x−y+5/3, z−1/3.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: RZ2668).
References
- Cremer, D. & Pople, J. A. (1975). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97, 1354–1358.
- Devi, I. & Bhuyan, P. J. (2004). Tetrahedron Lett. 45, 8625–8627.
- Domling, A. & Ugi, I. (2000). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 39, 3168–3210. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Hulme, C. & Gore, V. (2003). Curr. Med. Chem. 10, 51–80. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rigaku (2005). CrystalClear Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ugi, I. (1962). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1, 8–21.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681104997X/rz2668sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681104997X/rz2668Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681104997X/rz2668Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report