Abstract
The title compound, C11H22NO2 +·I−, is a chiral molecule with five stereogenic centres. The absolute configuration was assigned from the synthesis and confirmed by the structure determination. The central six-membered ring of the indolizine system adopts a chair conformation, with two atoms displaced by −0.690 (2) and 0.550 (2) Å from the plane of the other four atoms. The conformation of the pyrrolidine ring is close to that of an envelope, with the flap atom displaced by 0.563 (2) Å from the plane of the remaining four atoms. In the crystal, there are two O—H⋯I hydrogen bonds.
Related literature
For the biological activity of indolizine derivatives, see: Gubin et al. (1992 ▶); Gupta et al. (2003 ▶); Malonne et al. (1998 ▶); Medda et al. (2003 ▶); Nardelli (1983 ▶); Pearson & Guo (2001 ▶); Ruprecht et al. (1989 ▶). For puckering analysis, see: Cremer & Pople (1975 ▶). For the preparation, see: Šafář et al. (2010 ▶). For related structures, see: Clark & Reid (1995 ▶); Pedersen (1967 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C11H22NO2 +·I−
M r = 327.20
Monoclinic,
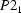
a = 8.18603 (14) Å
b = 10.82977 (14) Å
c = 8.19874 (13) Å
β = 110.3688 (19)°
V = 681.39 (2) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 2.34 mm−1
T = 298 K
0.30 × 0.25 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Oxford Diffraction Gemini R CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2009 ▶) T min = 0.520, T max = 0.638
18648 measured reflections
3330 independent reflections
3176 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.020
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.019
wR(F 2) = 0.049
S = 0.91
3330 reflections
141 parameters
1 restraint
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.64 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.69 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 1359 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: −0.026 (17)
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Oxford Diffraction, 2009 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: DIAMOND (Brandenburg, 2001 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97, PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶) and WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811051099/bq2323sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811051099/bq2323Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811051099/bq2323Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1⋯I1i | 0.82 | 2.80 | 3.6187 (18) | 173 |
| O2—H2⋯I1ii | 0.82 | 2.67 | 3.4798 (16) | 172 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 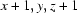 ; (ii)
; (ii) 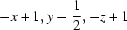 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Grant Agency of Slovak Republic (grant Nos. 1/0429/11, 1/0679/11) and the Slovak Research and Development Agency (under contract No. APVV-0204–10) for financial support of this research program.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
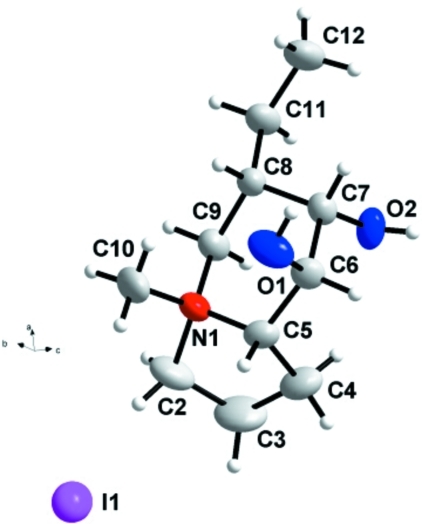
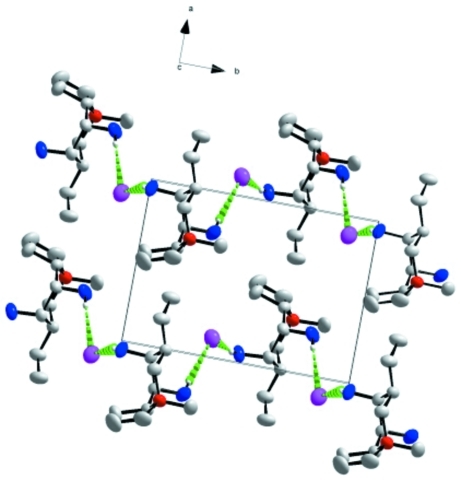
Indolizine derivatives have been found to possess a variety of biological activities such as antiinflammatory (Malonne et al., 1998), antiviral (Medda et al., 2003), and antitumor (Pearson & Guo, 2001) activities. They have also shown to be calcium entry blockers (Gupta et al., 2003). As such, indolizines are important synthetic targets in view of developing new pharmaceuticals for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases (Gubin et al., 1992) and HIV infections (Ruprecht et al., 1989). Based on these facts and in continuation of our interest in developing simple and efficient route for the synthesis of novel indolizine derivatives, we report here the synthesis, molecular and crystal structure of the title compound. The molecular structure of the compound and the atom labeling scheme are shown in Fig. 1. The absolute configuration was established by synthesis and confirmed by the structure determination. The expected stereochemistry of atoms N1, C5, C6, C7 and C8 was confirmed as R,S,S,S and S, respectively (Fig.1). The central six-membered N-heterocyclic ring is not planar and adopts a chair conformation (Cremer & Pople, 1975). A calculation of least-squares planes shows that this ring is puckered in such a manner that the four atoms C6, C7, N1 and C9 are coplanar within 0.022 (2) Å, while atoms C8 and C5 are displaced from this plane on opposite sides, with out-of-plane displacements of -0.690 (2) and 0.550 (2) Å, respectively. The pyrrolidine ring attached to the indolizine ring system has envelope conformation, with atom N1 on the flap. The maximum deviation from planarity for N1 is -0.563 (2) Å. The two aromatic rings are almost perpendicular to each other. The dihedral angle between the plane of the four atoms C2, C3, C4 and C5 of pyrrolidine ring and the plane of the four atoms C6, C7, N1 and C9 forming the base of the chair conformation is 89.6 (1)°. Intermolecular O1–H1···I1 and O2–H2···I1 hydrogen bonds link the molecules into extended chains running along the b axis (Table 1. and Figure 2.).
Experimental
The title compound was prepared according to a standard protocol described in literature (Šafář et al., 2010).
Refinement
All H atoms were positioned with idealized geometry using a riding model with C—H distances in the range 0.93 - 0.98 Å and O—H distance 0.82 Å. The Uiso(H) values were set at 1.5Ueq(C-methyl,O) and 1.2Ueq(other C atoms)
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of the title compound showing the atom labeling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level (Brandenburg, 2001).
Fig. 2.
Packing view of the title compound. Molecular chains along b are generated by O–H···I hydrogen bonds which are shown as dashed lines. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding have been omitted.
Crystal data
| C11H22NO2+·I− | F(000) = 328 |
| Mr = 327.20 | Dx = 1.595 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2yb | Cell parameters from 3330 reflections |
| a = 8.18603 (14) Å | θ = 3.6–29.4° |
| b = 10.82977 (14) Å | µ = 2.34 mm−1 |
| c = 8.19874 (13) Å | T = 298 K |
| β = 110.3688 (19)° | Prism, colourless |
| V = 681.39 (2) Å3 | 0.30 × 0.25 × 0.20 mm |
| Z = 2 |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Gemini R CCD diffractometer | 3330 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3176 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.020 |
| Detector resolution: 10.434 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 29.4°, θmin = 3.6° |
| ω and φ scans | h = −11→11 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2009) | k = −14→14 |
| Tmin = 0.520, Tmax = 0.638 | l = −11→10 |
| 18648 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.019 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0335P)2 + 0.2787P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.049 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 0.91 | Δρmax = 0.64 e Å−3 |
| 3330 reflections | Δρmin = −0.69 e Å−3 |
| 141 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| 1 restraint | Extinction coefficient: 0.044 (2) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 1359 Friedel pairs |
| Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map | Flack parameter: −0.026 (17) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C2 | 0.5506 (4) | 0.1519 (3) | 0.1098 (4) | 0.0581 (7) | |
| H2A | 0.4507 | 0.2056 | 0.0599 | 0.070* | |
| H2B | 0.6055 | 0.1385 | 0.0237 | 0.070* | |
| C3 | 0.4953 (5) | 0.0317 (3) | 0.1635 (5) | 0.0735 (9) | |
| H3A | 0.5487 | −0.0365 | 0.1238 | 0.088* | |
| H3B | 0.3697 | 0.0229 | 0.1134 | 0.088* | |
| C4 | 0.5545 (4) | 0.0321 (3) | 0.3627 (4) | 0.0538 (6) | |
| H4A | 0.4590 | 0.0099 | 0.4012 | 0.065* | |
| H4B | 0.6495 | −0.0256 | 0.4122 | 0.065* | |
| C5 | 0.6143 (3) | 0.1645 (2) | 0.4157 (3) | 0.0376 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.5115 | 0.2133 | 0.4092 | 0.045* | |
| C6 | 0.7478 (3) | 0.1787 (2) | 0.5989 (3) | 0.0358 (4) | |
| H6 | 0.7088 | 0.1294 | 0.6787 | 0.043* | |
| C7 | 0.9331 (3) | 0.13766 (19) | 0.6181 (3) | 0.0336 (4) | |
| H7 | 1.0133 | 0.1641 | 0.7321 | 0.040* | |
| C8 | 0.9902 (3) | 0.19544 (19) | 0.4777 (3) | 0.0340 (4) | |
| H8 | 0.9914 | 0.2854 | 0.4913 | 0.041* | |
| C9 | 0.8601 (3) | 0.1627 (2) | 0.2992 (3) | 0.0395 (5) | |
| H9A | 0.8994 | 0.1978 | 0.2103 | 0.047* | |
| H9B | 0.8562 | 0.0737 | 0.2853 | 0.047* | |
| C10 | 0.6736 (4) | 0.3470 (2) | 0.2554 (4) | 0.0565 (7) | |
| H10A | 0.7083 | 0.3703 | 0.1592 | 0.085* | |
| H10B | 0.7517 | 0.3834 | 0.3603 | 0.085* | |
| H10C | 0.5572 | 0.3757 | 0.2352 | 0.085* | |
| C11 | 1.1720 (3) | 0.1536 (3) | 0.4865 (3) | 0.0477 (6) | |
| H11A | 1.1688 | 0.0662 | 0.4598 | 0.057* | |
| H11B | 1.2044 | 0.1977 | 0.3994 | 0.057* | |
| C12 | 1.3095 (3) | 0.1765 (3) | 0.6658 (4) | 0.0586 (7) | |
| H12A | 1.4233 | 0.1615 | 0.6611 | 0.088* | |
| H12B | 1.2894 | 0.1220 | 0.7492 | 0.088* | |
| H12C | 1.3020 | 0.2606 | 0.6998 | 0.088* | |
| N1 | 0.6791 (2) | 0.20968 (18) | 0.2730 (2) | 0.0373 (4) | |
| O1 | 0.7466 (2) | 0.30534 (17) | 0.6448 (3) | 0.0537 (5) | |
| H1 | 0.8265 | 0.3185 | 0.7367 | 0.080* | |
| O2 | 0.9442 (2) | 0.00727 (14) | 0.6053 (2) | 0.0444 (4) | |
| H2 | 0.9405 | −0.0249 | 0.6945 | 0.067* | |
| I1 | 0.11548 (2) | 0.38255 (2) | 0.028309 (17) | 0.05615 (7) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C2 | 0.0441 (13) | 0.079 (2) | 0.0373 (12) | −0.0013 (13) | −0.0032 (10) | −0.0131 (12) |
| C3 | 0.0651 (18) | 0.070 (2) | 0.072 (2) | −0.0226 (16) | 0.0065 (16) | −0.0302 (17) |
| C4 | 0.0494 (13) | 0.0441 (13) | 0.0663 (17) | −0.0150 (11) | 0.0180 (12) | −0.0109 (12) |
| C5 | 0.0291 (9) | 0.0385 (10) | 0.0444 (12) | −0.0017 (8) | 0.0118 (8) | −0.0050 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0329 (9) | 0.0395 (11) | 0.0371 (10) | 0.0043 (8) | 0.0150 (8) | −0.0039 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0351 (10) | 0.0352 (10) | 0.0304 (10) | 0.0048 (8) | 0.0112 (8) | 0.0018 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0288 (9) | 0.0361 (10) | 0.0351 (10) | 0.0007 (8) | 0.0088 (8) | 0.0050 (8) |
| C9 | 0.0354 (10) | 0.0501 (12) | 0.0321 (10) | 0.0021 (9) | 0.0107 (8) | 0.0033 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0488 (13) | 0.0441 (14) | 0.0606 (15) | 0.0033 (9) | −0.0011 (11) | 0.0162 (10) |
| C11 | 0.0309 (10) | 0.0685 (17) | 0.0435 (13) | 0.0013 (10) | 0.0127 (10) | 0.0097 (11) |
| C12 | 0.0313 (11) | 0.082 (2) | 0.0570 (16) | −0.0028 (12) | 0.0086 (11) | 0.0059 (15) |
| N1 | 0.0317 (8) | 0.0411 (9) | 0.0318 (9) | −0.0007 (7) | 0.0017 (7) | 0.0010 (7) |
| O1 | 0.0487 (10) | 0.0491 (10) | 0.0534 (10) | 0.0136 (8) | 0.0054 (8) | −0.0195 (8) |
| O2 | 0.0575 (10) | 0.0344 (8) | 0.0492 (10) | 0.0114 (7) | 0.0286 (8) | 0.0114 (7) |
| I1 | 0.06754 (11) | 0.06164 (10) | 0.04070 (9) | −0.00802 (11) | 0.02063 (6) | −0.01043 (10) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C2—C3 | 1.494 (5) | C8—C9 | 1.522 (3) |
| C2—N1 | 1.520 (3) | C8—C11 | 1.533 (3) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9700 | C8—H8 | 0.9800 |
| C2—H2B | 0.9700 | C9—N1 | 1.510 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.533 (5) | C9—H9A | 0.9700 |
| C3—H3A | 0.9700 | C9—H9B | 0.9700 |
| C3—H3B | 0.9700 | C10—N1 | 1.493 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.528 (3) | C10—H10A | 0.9600 |
| C4—H4A | 0.9700 | C10—H10B | 0.9600 |
| C4—H4B | 0.9700 | C10—H10C | 0.9600 |
| C5—N1 | 1.523 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.529 (4) |
| C5—C6 | 1.527 (3) | C11—H11A | 0.9700 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9800 | C11—H11B | 0.9700 |
| C6—O1 | 1.423 (3) | C12—H12A | 0.9600 |
| C6—C7 | 1.535 (3) | C12—H12B | 0.9600 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9800 | C12—H12C | 0.9600 |
| C7—O2 | 1.421 (3) | O1—H1 | 0.8200 |
| C7—C8 | 1.519 (3) | O2—H2 | 0.8200 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9800 | ||
| C3—C2—N1 | 106.7 (2) | C7—C8—C11 | 113.04 (18) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 110.4 | C9—C8—C11 | 108.61 (19) |
| N1—C2—H2A | 110.4 | C7—C8—H8 | 108.5 |
| C3—C2—H2B | 110.4 | C9—C8—H8 | 108.5 |
| N1—C2—H2B | 110.4 | C11—C8—H8 | 108.5 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 108.6 | N1—C9—C8 | 112.42 (18) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 107.2 (2) | N1—C9—H9A | 109.1 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 110.3 | C8—C9—H9A | 109.1 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 110.3 | N1—C9—H9B | 109.1 |
| C2—C3—H3B | 110.3 | C8—C9—H9B | 109.1 |
| C4—C3—H3B | 110.3 | H9A—C9—H9B | 107.9 |
| H3A—C3—H3B | 108.5 | N1—C10—H10A | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 104.9 (2) | N1—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 110.8 | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 110.8 | N1—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—H4B | 110.8 | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4B | 110.8 | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| H4A—C4—H4B | 108.8 | C12—C11—C8 | 112.0 (2) |
| N1—C5—C6 | 113.69 (17) | C12—C11—H11A | 109.2 |
| N1—C5—C4 | 104.21 (19) | C8—C11—H11A | 109.2 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 115.0 (2) | C12—C11—H11B | 109.2 |
| N1—C5—H5 | 107.9 | C8—C11—H11B | 109.2 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 107.9 | H11A—C11—H11B | 107.9 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 107.9 | C11—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| O1—C6—C5 | 106.78 (18) | C11—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| O1—C6—C7 | 110.46 (18) | H12A—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 114.51 (17) | C11—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| O1—C6—H6 | 108.3 | H12A—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 108.3 | H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—H6 | 108.3 | C10—N1—C9 | 110.1 (2) |
| O2—C7—C8 | 108.01 (17) | C10—N1—C2 | 109.6 (2) |
| O2—C7—C6 | 111.47 (18) | C9—N1—C2 | 109.31 (19) |
| C8—C7—C6 | 110.88 (17) | C10—N1—C5 | 112.8 (2) |
| O2—C7—H7 | 108.8 | C9—N1—C5 | 111.69 (16) |
| C8—C7—H7 | 108.8 | C2—N1—C5 | 103.01 (19) |
| C6—C7—H7 | 108.8 | C6—O1—H1 | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 109.65 (17) | C7—O2—H2 | 109.5 |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | 13.6 (3) | C7—C8—C9—N1 | 60.6 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 10.0 (3) | C11—C8—C9—N1 | −175.43 (19) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | −29.6 (3) | C7—C8—C11—C12 | −54.9 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −154.8 (2) | C9—C8—C11—C12 | −176.8 (2) |
| N1—C5—C6—O1 | 77.7 (2) | C8—C9—N1—C10 | 71.0 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—O1 | −162.2 (2) | C8—C9—N1—C2 | −168.5 (2) |
| N1—C5—C6—C7 | −44.9 (3) | C8—C9—N1—C5 | −55.1 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 75.2 (3) | C3—C2—N1—C10 | −152.2 (3) |
| O1—C6—C7—O2 | 168.90 (18) | C3—C2—N1—C9 | 87.0 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—O2 | −70.5 (2) | C3—C2—N1—C5 | −31.8 (3) |
| O1—C6—C7—C8 | −70.7 (2) | C6—C5—N1—C10 | −78.1 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 49.9 (2) | C4—C5—N1—C10 | 155.86 (19) |
| O2—C7—C8—C9 | 66.0 (2) | C6—C5—N1—C9 | 46.5 (2) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | −56.5 (2) | C4—C5—N1—C9 | −79.5 (2) |
| O2—C7—C8—C11 | −55.4 (2) | C6—C5—N1—C2 | 163.7 (2) |
| C6—C7—C8—C11 | −177.79 (19) | C4—C5—N1—C2 | 37.7 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1···I1i | 0.82 | 2.80 | 3.6187 (18) | 173. |
| O2—H2···I1ii | 0.82 | 2.67 | 3.4798 (16) | 172. |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1, y, z+1; (ii) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BQ2323).
References
- Brandenburg, K. (2001). DIAMOND Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Clark, R. C. & Reid, J. S. (1995). Acta Cryst. A51, 887–897.
- Cremer, D. & Pople, J. A. (1975). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97, 1354–1362.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 837–838.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Gubin, J., Lucchetti, J., Mahaux, J., Nisato, D., Rosseels, G., Clinet, M., Polster, P. & Chatelain, P. (1992). J. Med. Chem. 35, 981–988. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S. P., Mathur, A. N., Nagappa, A. N., Kumar, D. & Kumaran, S. (2003). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 38, 867–873. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Malonne, H., Hanuise, J. & Fontaine, J. (1998). Pharm. Pharmacol. Commun. 4, 241–243.
- Medda, S., Jaisankar, P., Manna, R. K., Pal, B., Giri, V. S. & Basu, M. K. (2003). J. Drug Target. 11, 123–128. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Nardelli, M. (1983). Acta Cryst. C39, 1141–1142.
- Oxford Diffraction (2009). CrysAlis PRO Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Yarnton, England.
- Pearson, W. H. & Guo, L. (2001). Tetrahedron Lett. 42, 8267–8271.
- Pedersen, B. F. (1967). Acta Chem. Scand. 21, 1415–1424.
- Ruprecht, R. M., Mullaney, S., Andersen, J. & Bronson, R. (1989). J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2, 149–157. [PubMed]
- Šafář, P., Žužiová, J., Tóthová, E., Marchalín, Š., Prónayová, N., Švorc, Ľ., Vrábel, V., Comesse, S. & Daich, A. (2010). Tetrahedron Asymmetry, 21, 623–630.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811051099/bq2323sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811051099/bq2323Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811051099/bq2323Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report