Abstract
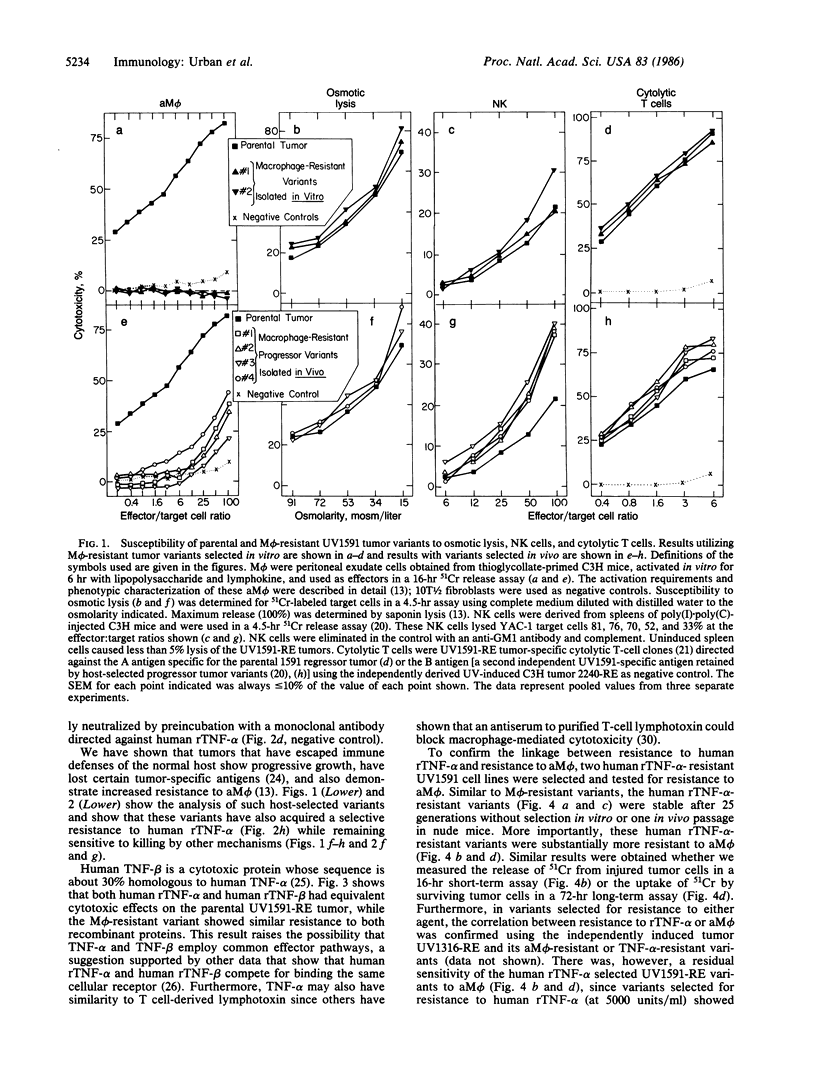
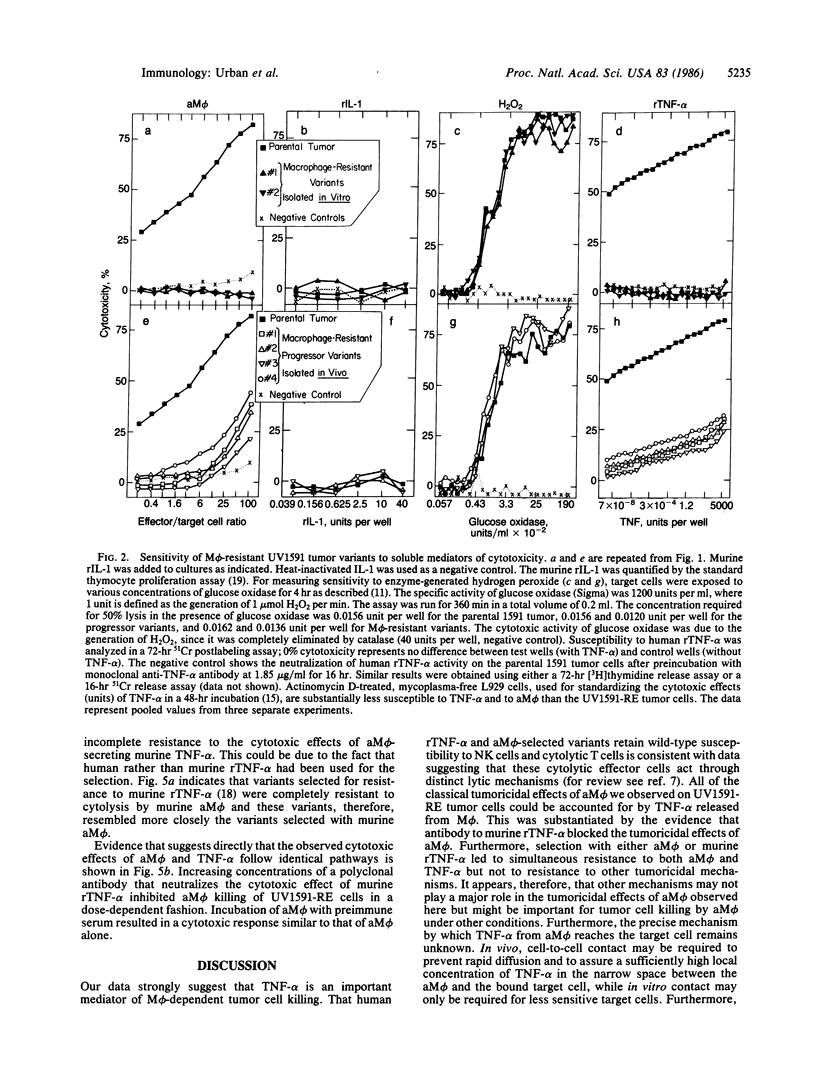
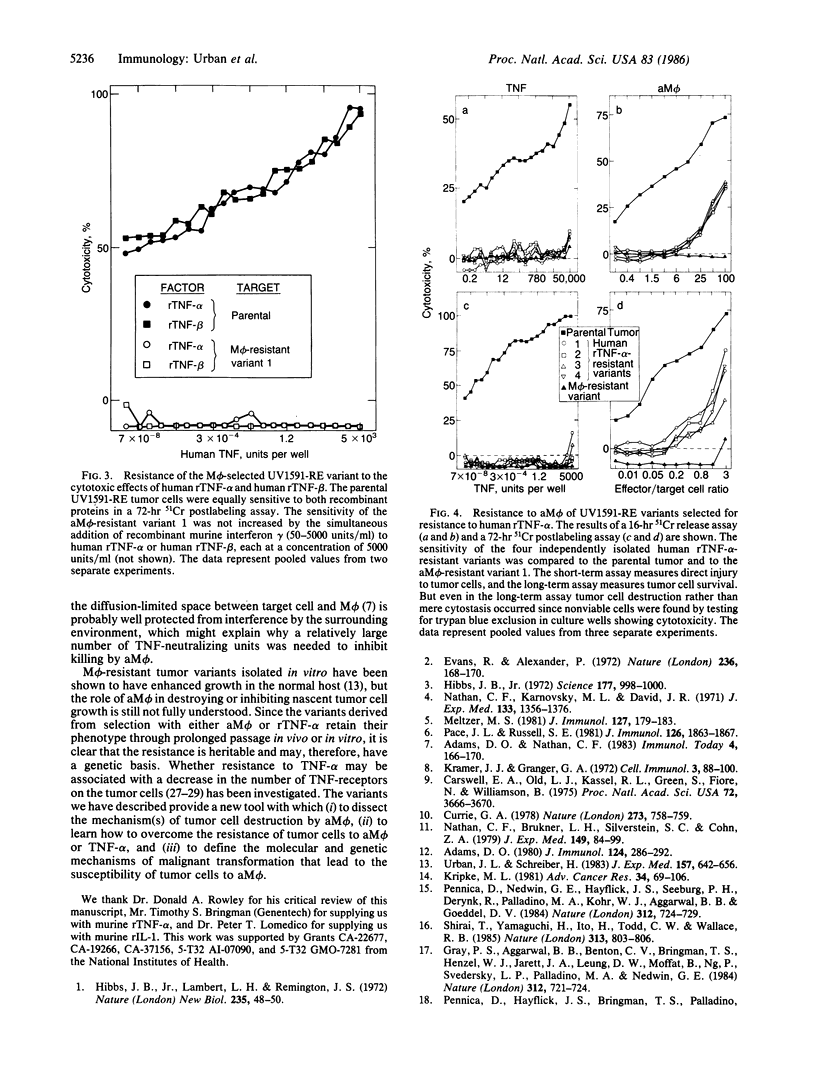
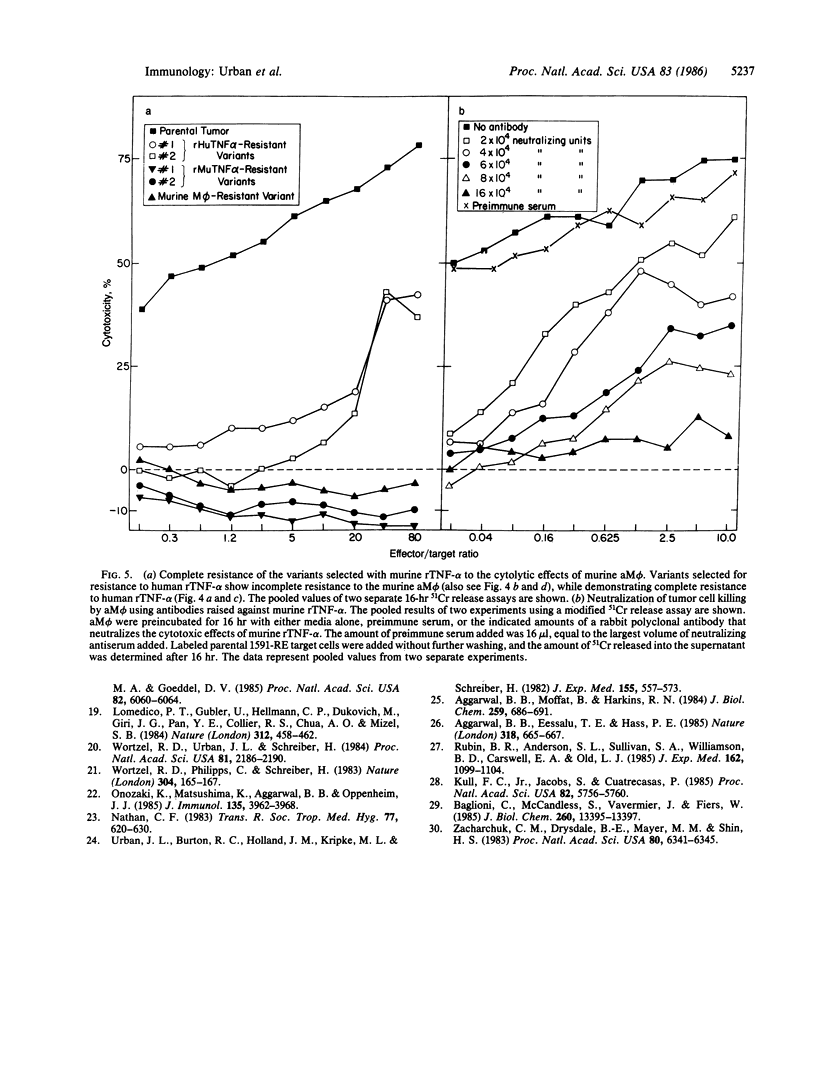
Activated macrophages (aM phi) destroy more effectively cancer cells than normal cells. The mechanism by which macrophages destroy cancer cells is not known. We report here that tumor cells susceptible to aM phi were killed by recombinant (r) tumor necrosis factor type alpha (TNF-alpha), whereas variant tumor cells resistant to aM phi after selection in vitro or in vivo were resistant to killing by rTNF-alpha. The converse selection for rTNF-alpha-resistant variants resulted in cells that were also resistant to killing by aM phi. The sensitivity of macrophage-resistant variants was not changed to other tumoricidal cells or soluble mediators, except that the macrophage-resistant variants were also resistant to the effects of another cytotoxic protein, B-cell lymphotoxin, which is structurally related to rTNF-alpha. Similar results were obtained regardless of whether short-term or long-term cytotoxic effects of aM phi were measured. Finally, it was shown that killing of tumor cells by murine aM phi was completely inhibited with a polyclonal antibody that neutralizes the effects of murine TNF-alpha. These results suggest a major role for TNF-alpha in tumor cell destruction by aM phi in vitro and in vivo.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. O. Effector mechanisms of cytolytically activated macrophages. I. Secretion of neutral proteases and effect of protease inhibitors. J Immunol. 1980 Jan;124(1):286–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal B. B., Eessalu T. E., Hass P. E. Characterization of receptors for human tumour necrosis factor and their regulation by gamma-interferon. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):665–667. doi: 10.1038/318665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal B. B., Moffat B., Harkins R. N. Human lymphotoxin. Production by a lymphoblastoid cell line, purification, and initial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):686–691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baglioni C., McCandless S., Tavernier J., Fiers W. Binding of human tumor necrosis factor to high affinity receptors on HeLa and lymphoblastoid cells sensitive to growth inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13395–13397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell E. A., Old L. J., Kassel R. L., Green S., Fiore N., Williamson B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currie G. A. Activated macrophages kill tumour cells by releasing arginase. Nature. 1978 Jun 29;273(5665):758–759. doi: 10.1038/273758a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R., Alexander P. Mechanism of immunologically specific killing of tumour cells by macrophages. Nature. 1972 Mar 24;236(5343):168–170. doi: 10.1038/236168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Aggarwal B. B., Benton C. V., Bringman T. S., Henzel W. J., Jarrett J. A., Leung D. W., Moffat B., Ng P., Svedersky L. P. Cloning and expression of cDNA for human lymphotoxin, a lymphokine with tumour necrosis activity. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):721–724. doi: 10.1038/312721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Lambert L. H., Jr, Remington J. S. Control of carcinogenesis: a possible role for the activated macrophage. Science. 1972 Sep 15;177(4053):998–1000. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4053.998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Lambert L. H., Jr, Remington J. S. Possible role of macrophage mediated nonspecific cytotoxicity in tumour resistance. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 12;235(54):48–50. doi: 10.1038/newbio235048a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer J. J., Granger G. A. The in vitro induction and release of a cell toxin by immune C57B1-6 mouse peritoneal macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1972 Jan;3(1):88–100. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90229-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kripke M. L. Immunologic mechanisms in UV radiation carcinogenesis. Adv Cancer Res. 1981;34:69–106. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60239-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kull F. C., Jr, Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P. Cellular receptor for 125I-labeled tumor necrosis factor: specific binding, affinity labeling, and relationship to sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5756–5760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomedico P. T., Gubler U., Hellmann C. P., Dukovich M., Giri J. G., Pan Y. C., Collier K., Semionow R., Chua A. O., Mizel S. B. Cloning and expression of murine interleukin-1 cDNA in Escherichia coli. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):458–462. doi: 10.1038/312458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer M. S. Macrophage activation for tumor cytotoxicity: characterization of priming and trigger signals during lymphokine activation. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):179–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Brukner L. H., Silverstein S. C., Cohn Z. A. Extracellular cytolysis by activated macrophages and granulocytes. I. Pharmacologic triggering of effector cells and the release of hydrogen peroxide. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):84–99. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Karnovsky M. L., David J. R. Alterations of macrophage functions by mediators from lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1971 Jun 1;133(6):1356–1376. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.6.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F. Mechanisms of macrophage antimicrobial activity. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1983;77(5):620–630. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(83)90190-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onozaki K., Matsushima K., Aggarwal B. B., Oppenheim J. J. Human interleukin 1 is a cytocidal factor for several tumor cell lines. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3962–3968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace J. L., Russell S. W. Activation of mouse macrophages for tumor cell killing. I. Quantitative analysis of interactions between lymphokine and lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1863–1867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Hayflick J. S., Bringman T. S., Palladino M. A., Goeddel D. V. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the cDNA for murine tumor necrosis factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6060–6064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Nedwin G. E., Hayflick J. S., Seeburg P. H., Derynck R., Palladino M. A., Kohr W. J., Aggarwal B. B., Goeddel D. V. Human tumour necrosis factor: precursor structure, expression and homology to lymphotoxin. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):724–729. doi: 10.1038/312724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin B. Y., Anderson S. L., Sullivan S. A., Williamson B. D., Carswell E. A., Old L. J. High affinity binding of 125I-labeled human tumor necrosis factor (LuKII) to specific cell surface receptors. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):1099–1104. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai T., Yamaguchi H., Ito H., Todd C. W., Wallace R. B. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the gene for human tumour necrosis factor. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):803–806. doi: 10.1038/313803a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban J. L., Burton R. C., Holland J. M., Kripke M. L., Schreiber H. Mechanisms of syngeneic tumor rejection. Susceptibility of host-selected progressor variants to various immunological effector cells. J Exp Med. 1982 Feb 1;155(2):557–573. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.2.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban J. L., Schreiber H. Selection of macrophage-resistant progressor tumor variants by the normal host. Requirement for concomitant T cell-mediated immunity. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):642–656. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wortzel R. D., Philipps C., Schreiber H. Multiple tumour-specific antigens expressed on a single tumour cell. Nature. 1983 Jul 14;304(5922):165–167. doi: 10.1038/304165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wortzel R. D., Urban J. L., Schreiber H. Malignant growth in the normal host after variant selection in vitro with cytolytic T-cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2186–2190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharchuk C. M., Drysdale B. E., Mayer M. M., Shin H. S. Macrophage-mediated cytotoxicity: role of a soluble macrophage cytotoxic factor similar to lymphotoxin and tumor necrosis factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6341–6345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



