Abstract
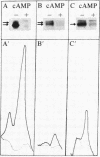
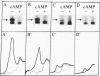
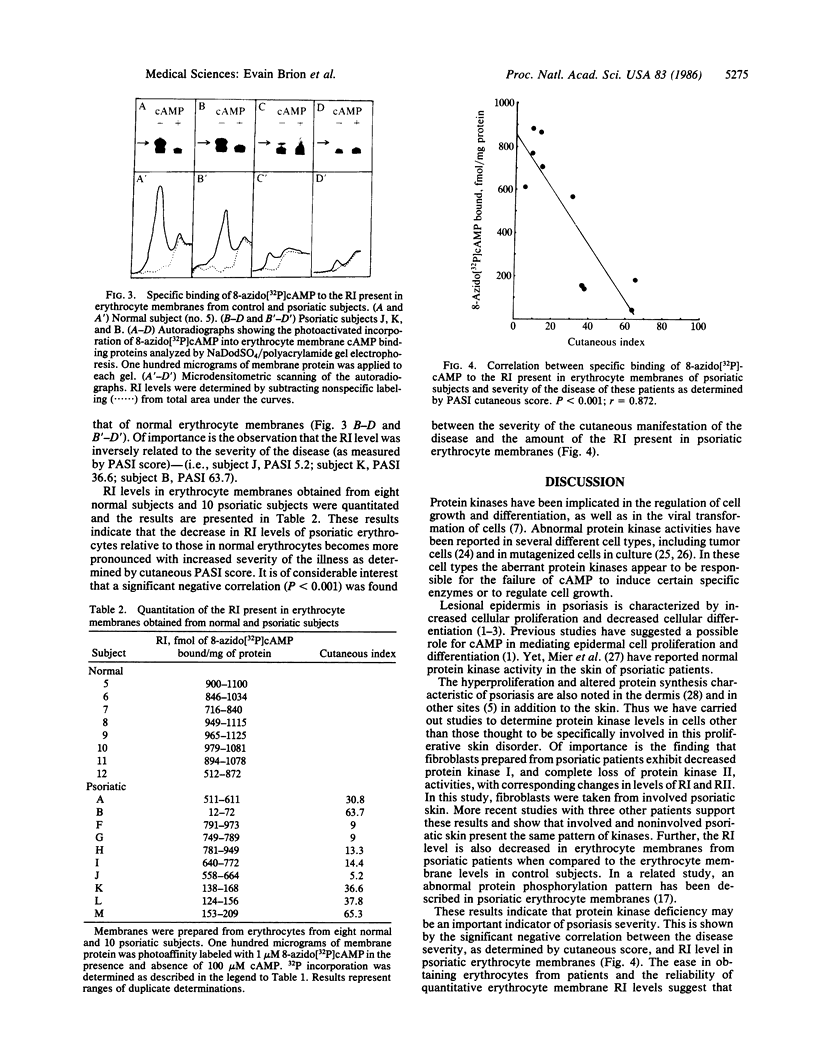
To determine possible differences in the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases of normal and psoriatic human fibroblasts, the levels of the regulatory subunits (RI and RII, respectively) of protein kinase I and protein kinase II were quantitated by photoaffinity labeling with 8-azido[32P]cAMP. The level of RII was significantly decreased, or was undetectable, in cytosol prepared from fibroblasts from five psoriatic subjects when compared to RII levels found with normal human fibroblasts. The level of cytosolic RI was decreased in fibroblasts from four psoriatic patients and was within the normal range for one diseased patient when compared to RI levels in normal human fibroblasts. The elution profile from a DEAE-cellulose column of protein kinase activity in the soluble fraction from two psoriatic patients also showed a decrease in type I kinase activity and the complete absence of type II kinase activity. Other results indicate that the level of RI in erythrocyte membranes from psoriatic subjects is significantly decreased when compared to that of erythrocyte membranes from eight normal subjects. A significant correlation (P less than 0.001) was observed between the severity of the cutaneous manifestation of the disease and the level of RI in psoriatic erythrocyte membranes. The changes noted in the levels of RI and RII in cell types other than those thought to be specifically involved in the proliferative epidermis disorder of the disease suggest a general protein kinase deficiency.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baden H. P., Kubilus J., Macdonald M. J. Normal and psoriatic keratinocytes and fibroblasts compared in culture. J Invest Dermatol. 1981 Jan;76(1):53–55. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12524875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bechtel P. J., Beavo J. A., Krebs E. G. Purification and characterization of catalytic subunit of skeletal muscle adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2691–2697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byus C. V., Klimpel G. R., Lucas D. O., Russell D. H. Type I and type II cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase as opposite effectors of lymphocyte mitogenesis. Nature. 1977 Jul 7;268(5615):63–64. doi: 10.1038/268063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chlapowski F. J., Kelly L. A., Butcher R. W. Cyclic nucleotides in cultured cells. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;6:245–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Keely S. L., Park C. R. The distribution and dissociation of cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases in adipose, cardiac, and other tissues. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):218–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M., Gerner E. W., Russell D. H. Cyclic AMP levels and types I and II cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase activity in synchronized cells and in quiescent cultures stimulated to proliferate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jan 3;538(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90246-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Schwartz K. J., Blout E. R. Compartmentalization of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases in human erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5926–5930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evain D., Gottesman M., Pastan I., Anderson W. B. A mutation affecting the catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in CHO cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):6931–6937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredriksson T., Pettersson U. Severe psoriasis--oral therapy with a new retinoid. Dermatologica. 1978;157(4):238–244. doi: 10.1159/000250839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochman J., Insel P. A., Bourne H. R., Coffino P., Tomkins G. M. A structural gene mutation affecting the regulatory subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in mouse lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5051–5055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger G. G., Bergstresser P. R., Lowe N. J., Voorhees J. J., Weinstein G. D. Psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1984 Nov;11(5 Pt 2):937–947. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(84)80018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar R., Weiss V. C., West D. P., Chiero L. A. Altered erythrocyte membrane phosphorylation in psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 1983 Sep;109(3):267–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1983.tb03541.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Greengard P. Cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. IV. Widespread occurrence of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in various tissues and phyla of the animal kingdom. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1349–1355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. C., Radloff D., Schweppe J. S., Jungmann R. A. Testicular protein kinases. Characterization of multiple forms and ontogeny. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 25;251(4):914–921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcelo C. L., Duell E. A., Stawiski M. A., Anderson T. F., Voorhees J. J. Cyclic nucleotide levels in psoriatic and normal keratomed epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1979 Jan;72(1):20–24. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12530112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcelo C. L., Voorhees J. J. Cyclic nucleotides, prostaglandins and polyamines in psoriasis. Pharmacol Ther. 1980;9(3):297–310. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(80)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mier P. D., van den Hurk J., Holla S. W., Hollman E. P., Porters J. E., Weemers M. B. Cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase of skin. II. Levels in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 1972 Dec;87(6):577–579. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1972.tb07448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell C. D., Mitchell W. B., Hanahan D. J. Enzyme and hemoglobin retention in human erythrocyte stroma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jul 8;104(2):348–358. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90340-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I. H., Johnson G. S., Anderson W. B. Role of cyclic nucleotides in growth control. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:491–522. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riou J. P., Evain D., Perrin F., Saez J. M. Adenosine 3'5'-cyclic monophosphate dependent protein kinase in human adrenocortical tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Feb;44(2):413–419. doi: 10.1210/jcem-44-2-413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. S. Characterization and comparison of membrane-associated and cytosolic cAMP-dependent protein kinases. Studies on human erythrocyte protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 25;254(24):12439–12449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan T. J. Microcirculation in psoriasis: blood vessels, lymphatics and tissue fluid. Pharmacol Ther. 1980;10(1):27–64. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(80)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voorhees J. J. "Psoriasis as a possible defect of the adenyl cyclase-cyclic AMP Cascade" by Voorhees and Duell, October 1971. Commentary: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate regulation of normal and psoriatic epidermis. Arch Dermatol. 1982 Oct;118(10):862–874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voorhees J. J., Duell E. A. Imbalanced cyclic AMP-cyclic GMP levels in psoriasis. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;5:735–758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Ashby C. D. Protein kinases: aspects of their regulation and diversity. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1973;29:329–359. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571129-6.50012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter U., Uno I., Liu A. Y., Greengard P. Identification, characterization, and quantitative measurement of cyclic AMP receptor proteins in cytosol of various tissues using a photoaffinity ligand. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6494–6500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]