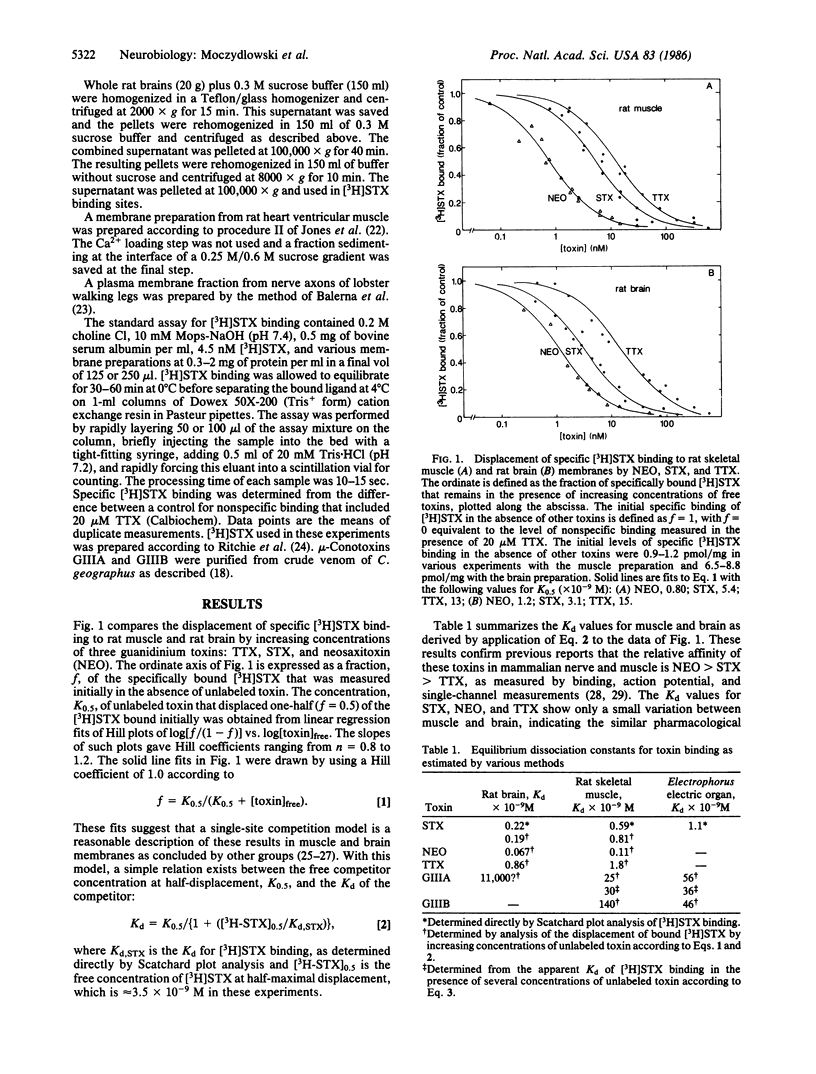
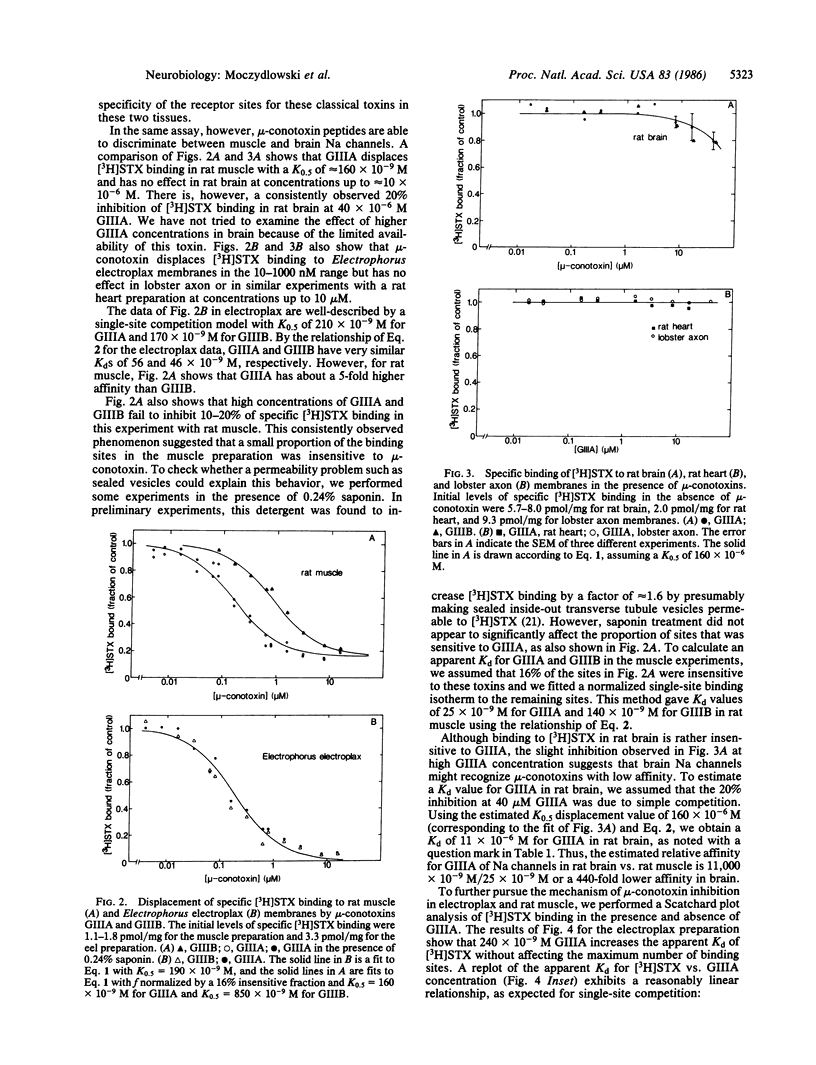
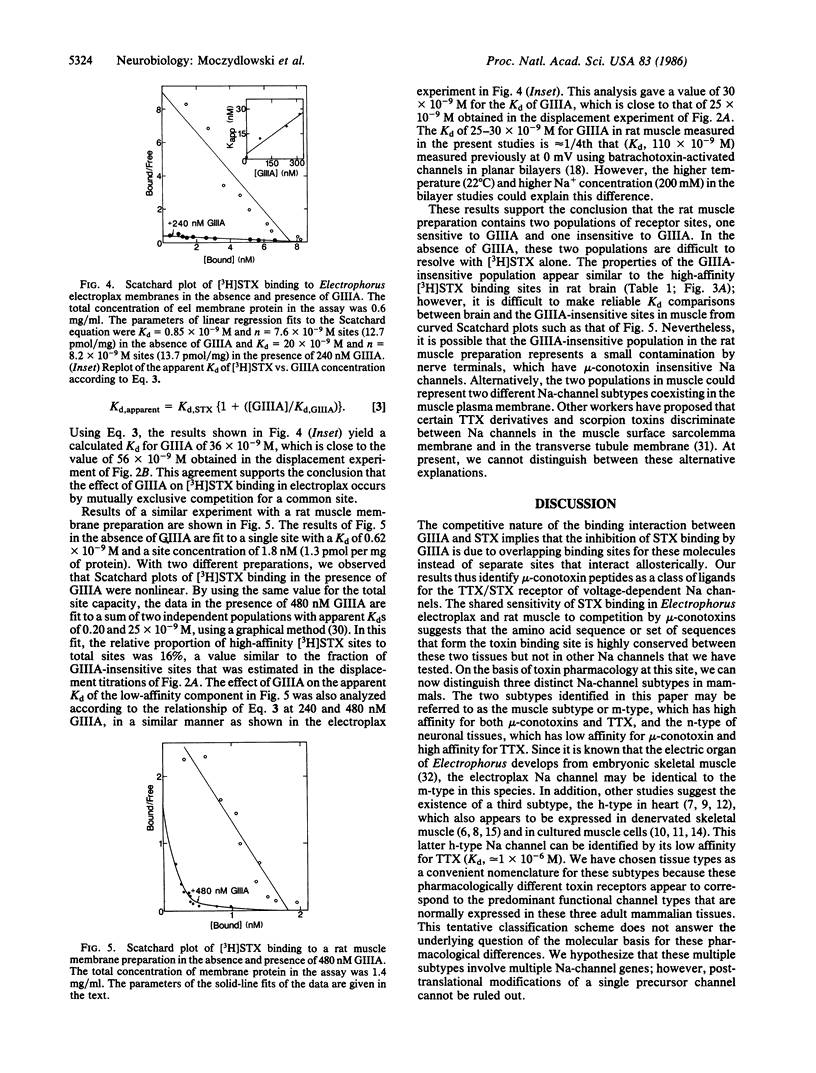
Abstract
The effect of two mu-conotoxin peptides on the specific binding of [3H]saxitoxin was examined in isolated plasma membranes of various excitable tissues. mu-Conotoxins GIIIA and GIIIB inhibit [3H]saxitoxin binding in Electrophorus electric organ membranes with similar KdS of approximately equal to 50 X 10(-9) M in a manner consistent with direct competition for a common binding site. GIIIA and GIIIB similarly compete with the majority (80-95%) of [3H]saxitoxin binding sites in rat skeletal muscle with KdS of approximately 25 and approximately 140 X 10(-9) M, respectively. However, the high-affinity saxitoxin sites in lobster axons, rat brain, and rat heart are virtually insensitive to GIIIA concentrations up to 10 microM. These results and previously published data suggest that three Na-channel subtypes can be distinguished on the basis of toxin pharmacology: Na channels of skeletal muscle and Electrophorus electroplax have high affinity for mu-conotoxins and tetrodotoxin, neuronal Na channels have low affinity for mu-conotoxins and high affinity for tetrodotoxin, while heart Na channels and a similar subtype also found in denervated muscle have low affinity for both mu-conotoxin and tetrodotoxin.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer M., Best P. M., Reuter H. Voltage-dependent action of tetrodotoxin in mammalian cardiac muscle. Nature. 1976 Sep 23;263(5575):344–345. doi: 10.1038/263344a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balerna M., Fosset M., Chicheportiche R., Romey G., Lazdunski M. Constitution and properties of axonal membranes of crustacean nerves. Biochemistry. 1975 Dec 16;14(25):5500–5511. doi: 10.1021/bi00696a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barchi R. L. Protein components of the purified sodium channel from rat skeletal muscle sarcolemma. J Neurochem. 1983 May;40(5):1377–1385. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb13580.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barchi R. L., Weigele J. B. Characteristics of saxitoxin binding to the sodium channel of sarcolemma isolated from rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1979 Oct;295:383–396. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bay C. M., Strichartz G. R. Saxitoxin binding to sodium channels of rat skeletal muscles. J Physiol. 1980 Mar;300:89–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. T., Hille B. Kinetic and pharmacological properties of the sodium channel of frog skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Mar;67(3):309–323. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.3.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A., Coppersmith J. High-affinity saxitoxin receptor sites in vertebrate heart. Evidence for sites associated with autonomic nerve endings. Mol Pharmacol. 1981 Nov;20(3):526–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A., Coppersmith J. Pharmacological properties of sodium channels in cultured rat heart cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1981 Nov;20(3):533–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz L. J., Gray W. R., Olivera B. M., Zeikus R. D., Kerr L., Yoshikami D., Moczydlowski E. Conus geographus toxins that discriminate between neuronal and muscle sodium channels. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9280–9288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endean R., Parish G., Gyr P. Pharmacology of the venom of Conus geographus. Toxicon. 1974 Mar;12(2):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(74)90236-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frelin C., Vigne P., Lazdunski M. Na+ channels with high and low affinity tetrodotoxin binding sites in the mammalian skeletal muscle cell. Difference in functional properties and sequential appearance during rat skeletal myogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7256–7259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonoi T., Sherman S. J., Catterall W. A. Voltage clamp analysis of tetrodotoxin-sensitive and -insensitive sodium channels in rat muscle cells developing in vitro. J Neurosci. 1985 Sep;5(9):2559–2564. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-09-02559.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne R. P., Catterall W. A. The sodium channel from rat brain. Purification and subunit composition. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1667–1675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaimovich E., Chicheportiche R., Lombet A., Lazdunski M., Ildefonse M., Rougier O. Differences in the properties of Na+ channels in muscle surface and T-tubular membranes revealed by tetrodotoxin derivatives. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Apr;397(1):1–5. doi: 10.1007/BF00585159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. R., Besch H. R., Jr, Fleming J. W., McConnaughey M. M., Watanabe A. M. Separation of vesicles of cardiac sarcolemma from vesicles of cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Comparative biochemical analysis of component activities. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):530–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. C., Catterall W. A. Tetrodotoxin-insensitive sodium channels. Ion flux studies of neurotoxin action in a clonal rat muscle cell line. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 25;256(12):6213–6222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombet A., Lazdunski M. Characterization, solubilization, affinity labeling and purification of the cardiac Na+ channel using Tityus toxin gamma. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jun 15;141(3):651–660. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08241.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. A., Agnew W. S., Levinson S. R. Principal glycopeptide of the tetrodotoxin/saxitoxin binding protein from Electrophorus electricus: isolation and partial chemical and physical characterization. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 18;22(2):462–470. doi: 10.1021/bi00271a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moczydlowski E. G., Latorre R. Saxitoxin and ouabain binding activity of isolated skeletal muscle membrane as indicators of surface origin and purity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 27;732(2):412–420. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moczydlowski E., Hall S., Garber S. S., Strichartz G. S., Miller C. Voltage-dependent blockade of muscle Na+ channels by guanidinium toxins. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Nov;84(5):687–704. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.5.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohizumi Y., Nakamura H., Kobayashi J., Catterall W. A. Specific inhibition of [3H] saxitoxin binding to skeletal muscle sodium channels by geographutoxin II, a polypeptide channel blocker. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6149–6152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappone P. A. Voltage-clamp experiments in normal and denervated mammalian skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1980 Sep;306:377–410. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfern P., Thesleff S. Action potential generation in denervated rat skeletal muscle. II. The action of tetrodotoxin. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 May;82(1):70–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb04943.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renaud J. F., Kazazoglou T., Lombet A., Chicheportiche R., Jaimovich E., Romey G., Lazdunski M. The Na+ channel in mammalian cardiac cells. Two kinds of tetrodotoxin receptors in rat heart membranes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8799–8805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie J. M., Rogart R. B., Strichartz G. R. A new method for labelling saxitoxin and its binding to non-myelinated fibres of the rabbit vagus, lobster walking leg, and garfish olfactory nerves. J Physiol. 1976 Oct;261(2):477–494. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogart R. B., Regan L. J., Dziekan L. C., Galper J. B. Identification of two sodium channel subtypes in chick heart and brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1106–1110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogart R. B., Regan L. J. Two subtypes of sodium channel with tetrodotoxin sensitivity and insensitivity detected in denervated mammalian skeletal muscle. Brain Res. 1985 Mar 11;329(1-2):314–318. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90541-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. L., Tomiko S. A., Agnew W. S. Single-channel properties of the reconstituted voltage-regulated Na channel isolated from the electroplax of Electrophorus electricus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5594–5598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal H. E. A graphic method for the determination and presentation of binding parameters in a complex system. Anal Biochem. 1967 Sep;20(3):525–532. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90297-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato S., Nakamura H., Ohizumi Y., Kobayashi J., Hirata Y. The amino acid sequences of homologous hydroxyproline-containing myotoxins from the marine snail Conus geographus venom. FEBS Lett. 1983 May 8;155(2):277–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80620-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strichartz G. Structural determinants of the affinity of saxitoxin for neuronal sodium channels. Electrophysiological studies on frog peripheral nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Aug;84(2):281–305. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.2.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigele J. B., Barchi R. L. Analysis of saxitoxin binding in isolated rat synaptosomes using a rapid filtration assay. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jul 15;91(2):310–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81199-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagawa Y., Abe T., Satake M. Blockade of [3H]lysine-tetrodotoxin binding to sodium channel proteins by conotoxin GIII. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Feb 14;64(1):7–12. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90654-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



