Abstract
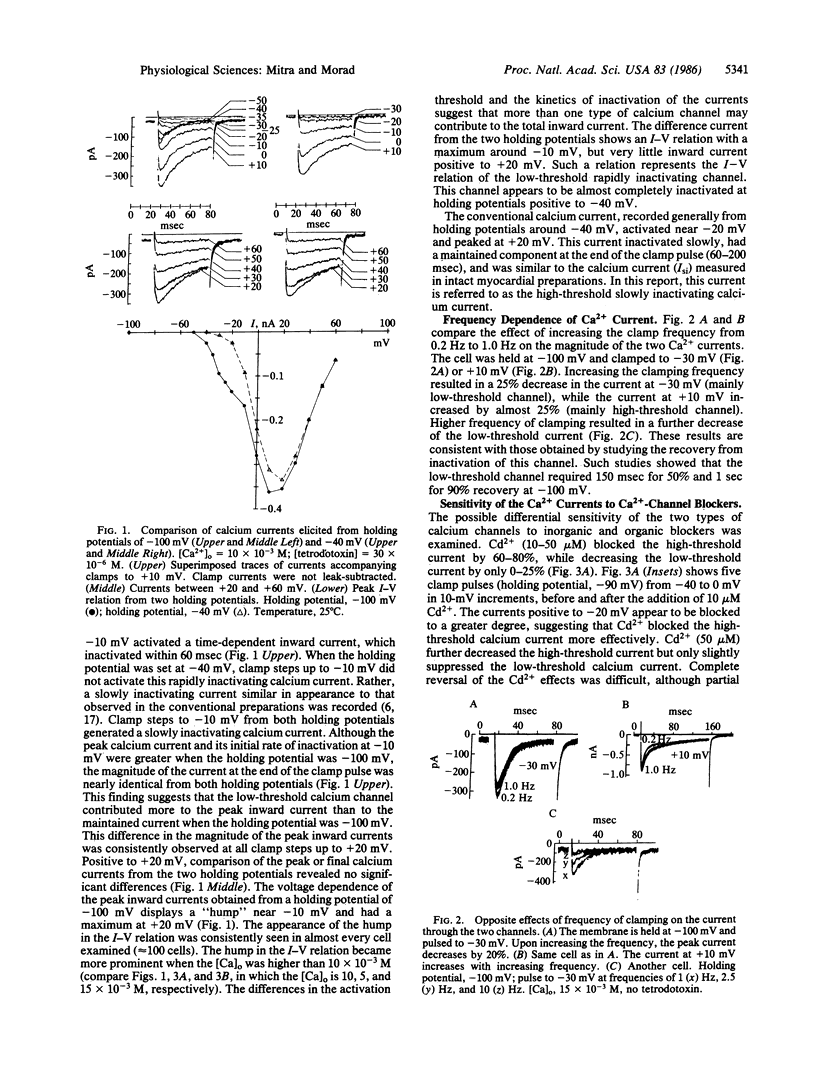
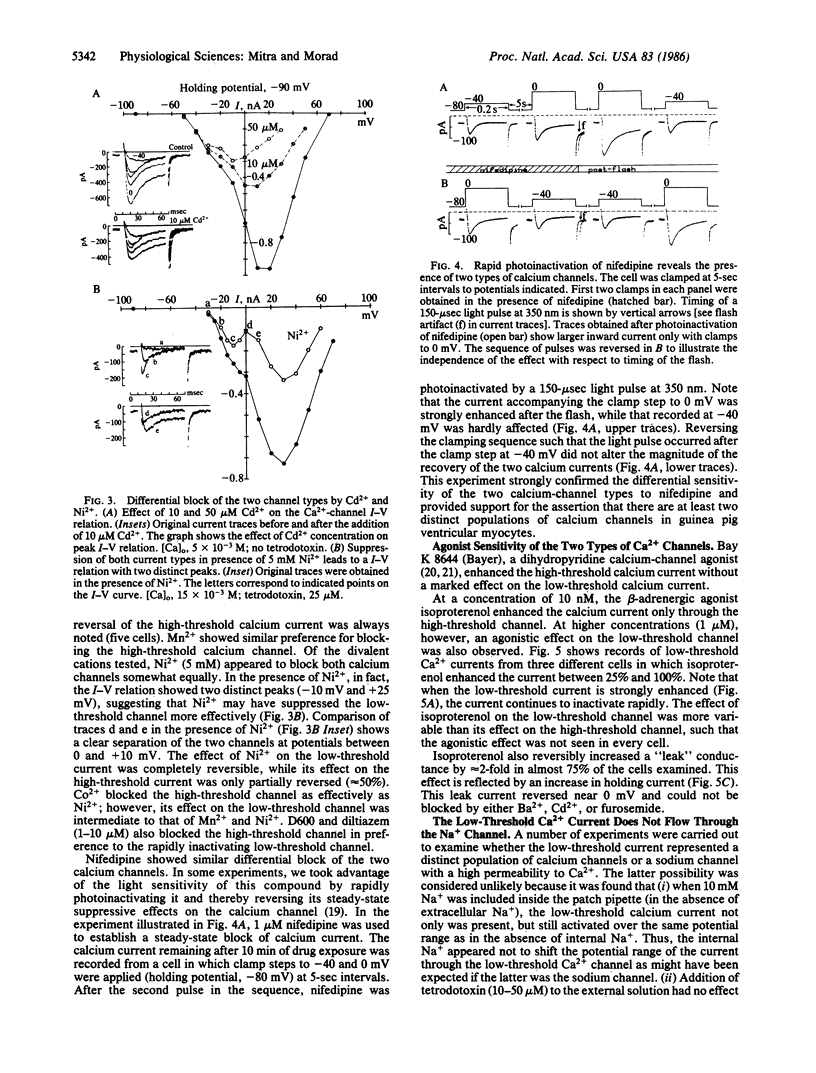
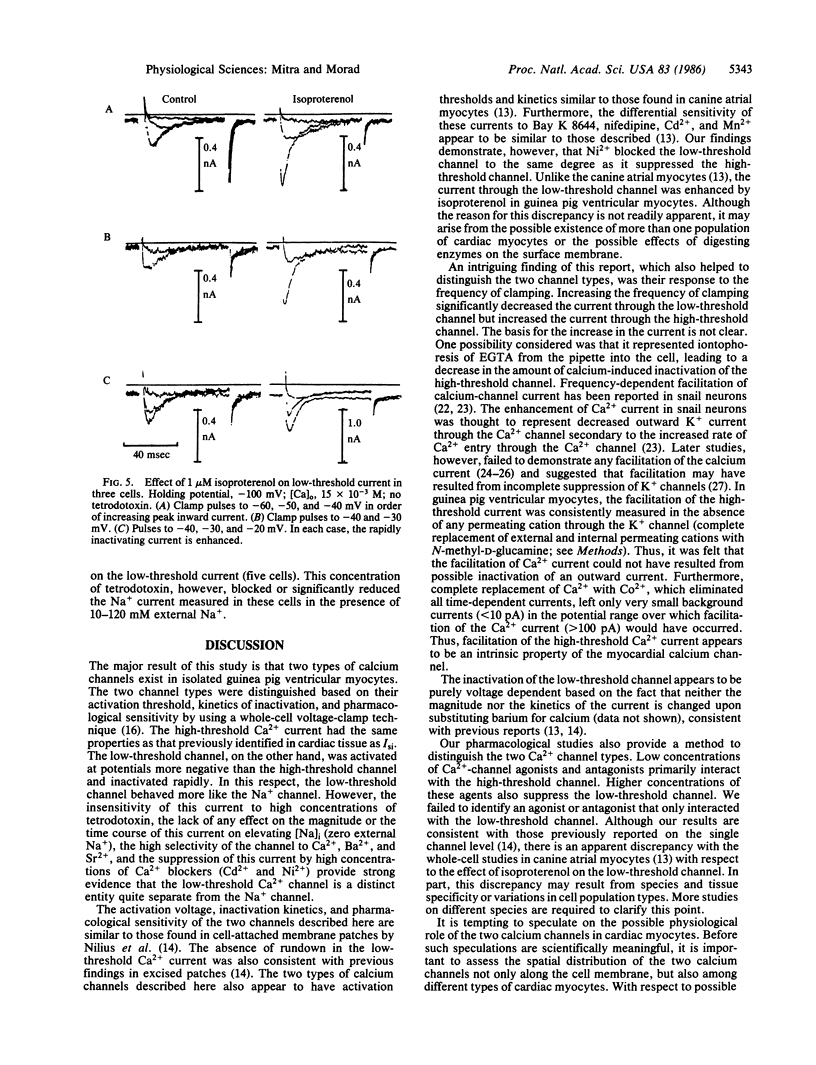
In cardiac muscle, Ca2+ plays a key role in regulation of numerous processes, including generation of the action potential and development of tension. The entry of Ca2+ into the cell is regulated primarily by voltage-gated channels in the membrane. Until recently, it was felt that only one type of Ca2+ channel existed in cardiac ventricular muscle. Experiments reported here suggest that in isolated guinea pig ventricular myocytes, there are two distinct types of Ca2+ channels with markedly different activation thresholds, inactivation kinetics, and sensitivities to inorganic and organic Ca2+ channel blockers. The channels were also distinguished based on their response to increased frequency of clamping such that the current through the low-threshold channel decreased while that through the high-threshold channel increased. In a few cells, the current through both channels was enhanced by isoproterenol, a beta-adrenergic agonist, but only the high-threshold channel was enhanced by the Ca2+-channel agonist Bay K 8644. Thus, isolated guinea pig ventricular myocytes appear to have two types of Ca2+ channels distinguished by various criteria.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. J., Gage P. W. Characteristics of sodium and calcium conductance changes produced by membrane depolarization in an Aplysia neurone. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:143–161. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akaike N., Lee K. S., Brown A. M. The calcium current of Helix neuron. J Gen Physiol. 1978 May;71(5):509–531. doi: 10.1085/jgp.71.5.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Matteson D. R. Two distinct populations of calcium channels in a clonal line of pituitary cells. Science. 1985 Jan 4;227(4682):65–67. doi: 10.1126/science.2578071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. Two kinds of calcium channels in canine atrial cells. Differences in kinetics, selectivity, and pharmacology. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Jul;86(1):1–30. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeler G. W., Jr, Reuter H. Membrane calcium current in ventricular myocardial fibres. J Physiol. 1970 Mar;207(1):191–209. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone E., Lux H. D. A low voltage-activated, fully inactivating Ca channel in vertebrate sensory neurones. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):501–502. doi: 10.1038/310501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitmer J. W. Evidence for two voltage-dependent calcium currents in the membrane of the ciliate Stylonychia. J Physiol. 1984 Oct;355:137–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedulova S. A., Kostyuk P. G., Veselovsky N. S. Two types of calcium channels in the somatic membrane of new-born rat dorsal root ganglion neurones. J Physiol. 1985 Feb;359:431–446. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A. P., Krasne S. Two calcium currents in Neanthes arenaceodentatus egg cell membranes. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:491–505. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Ozawa S., Sand O. Voltage clamp analysis of two inward current mechanisms in the egg cell membrane of a starfish. J Gen Physiol. 1975 May;65(5):617–644. doi: 10.1085/jgp.65.5.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyer C. B., Lux H. D. Properties of a facilitating calcium current in pace-maker neurones of the snail, Helix pomatia. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(2):319–348. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irisawa H., Kokubun S. Modulation by intracellular ATP and cyclic AMP of the slow inward current in isolated single ventricular cells of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1983 May;338:321–337. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg G., Klöckner U. Calcium currents of isolated bovine ventricular myocytes are fast and of large amplitude. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Oct;395(1):30–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00584965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Tsien R. W. Reversal of current through calcium channels in dialysed single heart cells. Nature. 1982 Jun 10;297(5866):498–501. doi: 10.1038/297498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux H. D., Eckert R. Inferred slow inward current in snail neurones. Nature. 1974 Aug 16;250(467):574–576. doi: 10.1038/250574a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascher D., Peper K. Two components of inward current in myocardial muscle fibers. Pflugers Arch. 1969;307(3):190–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00592084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda H., Noma A. Isolation of calcium current and its sensitivity to monovalent cations in dialysed ventricular cells of guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:553–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra R., Morad M. A uniform enzymatic method for dissociation of myocytes from hearts and stomachs of vertebrates. Am J Physiol. 1985 Nov;249(5 Pt 2):H1056–H1060. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1985.249.5.H1056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morad M., Goldman Y. E., Trentham D. R. Rapid photochemical inactivation of Ca2+-antagonists shows that Ca2+ entry directly activates contraction in frog heart. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):635–638. doi: 10.1038/304635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morad M., Trautwein W. The effect of the duration of the action potential on contraction in the mammalian heart muscle. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1968;299(1):66–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00362542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilius B., Hess P., Lansman J. B., Tsien R. W. A novel type of cardiac calcium channel in ventricular cells. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):443–446. doi: 10.1038/316443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noma A., Morad M., Irisawa H. Does the "pacemaker current" generate the diastolic depolarization in the rabbit SA node cells? Pflugers Arch. 1983 May;397(3):190–194. doi: 10.1007/BF00584356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. The dependence of slow inward current in Purkinje fibres on the extracellular calcium-concentration. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(2):479–492. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougier O., Vassort G., Garnier D., Gargouil Y. M., Coraboeuf E. Existence and role of a slow inward current during the frog atrial action potential. Pflugers Arch. 1969;308(2):91–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00587018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramm M., Thomas G., Towart R., Franckowiak G. Novel dihydropyridines with positive inotropic action through activation of Ca2+ channels. Nature. 1983 Jun 9;303(5917):535–537. doi: 10.1038/303535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. J., Zucker R. S. Aequorin response facilitation and intracellular calcium accumulation in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1980 Mar;300:167–196. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson D., Horn R. Inactivation without facilitation of calcium conductance in caesium-loaded neurones of Aplysia. Nature. 1978 May 25;273(5660):312–314. doi: 10.1038/273312a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zipes D. P., Fischer J. C. Effects of agents which inhibit the slow channel on sinus node automaticity and atrioventricular conduction in the dog. Circ Res. 1974 Feb;34(2):184–192. doi: 10.1161/01.res.34.2.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



