Abstract
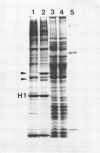
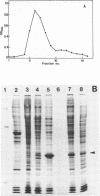
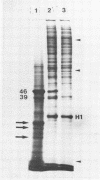
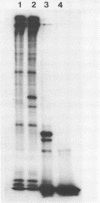
After 5 minutes heat shock at 37 degrees C Drosophila melanogaster Kc-cell nuclear proteins were extracted wit 0.4M NaCl and compared by SDS gel electrophoresis with extracts from cells grown at 25 degrees C. Two proteins (39 000 and 46 000) were only found in heat shock nuclei. Reconstitution with total Drosophila DNA or a DNA fragment from the heat inducible locus 87A/C covalently coupled to sepharose was performed. In the presence of calf thymus competitor DNA these proteins and also others of lower molecular weight showed preferential binding to the homologous DNA.
Full text
PDF





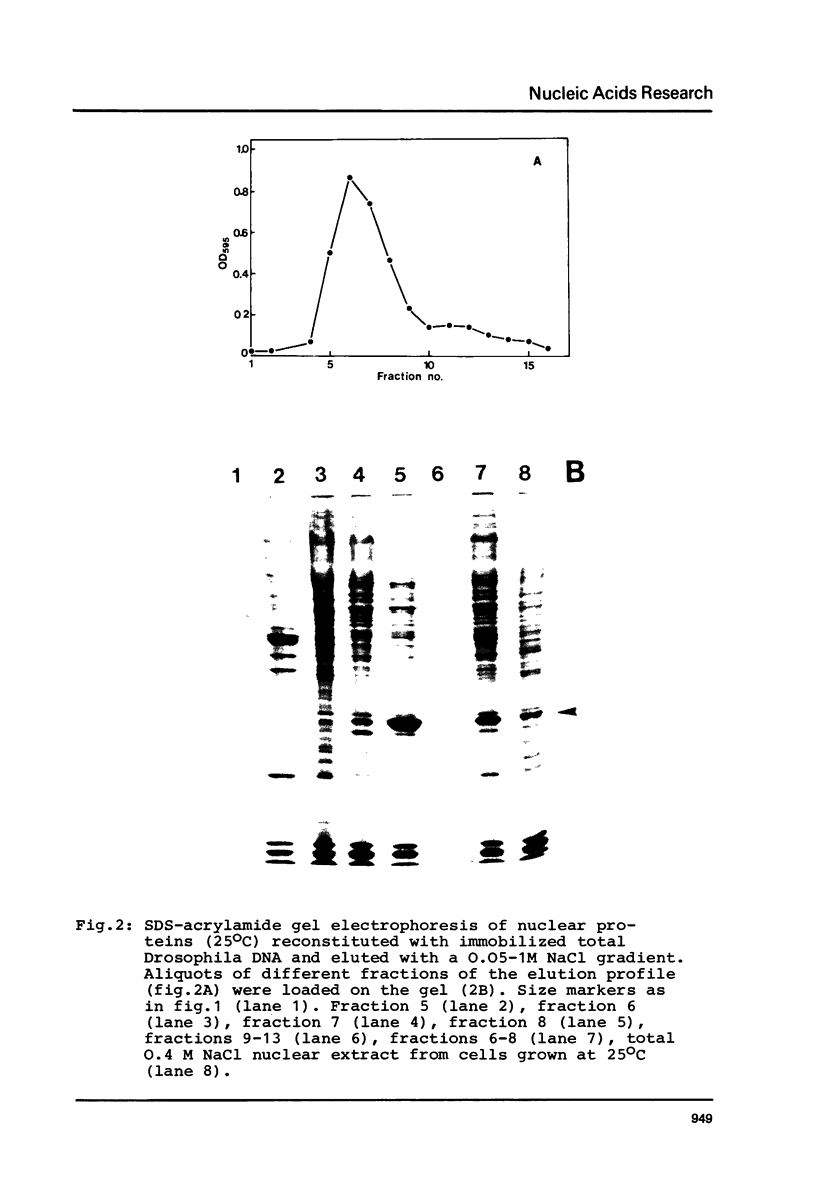






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashburner M., Bonner J. J. The induction of gene activity in drosophilia by heat shock. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berendes H. D. Factors involved in the expression of gene activity in polytene chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1968;24(4):418–437. doi: 10.1007/BF00285017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner J. J., Pardue M. L. The effect of heat shock on RNA synthesis in Drosophila tissues. Cell. 1976 May;8(1):43–50. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90183-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter D. B., Chae C. B. Chromatin-bound protease: degradation of chromosomal proteins under chromatin dissociation conditions. Biochemistry. 1976 Jan 13;15(1):180–185. doi: 10.1021/bi00646a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton J. L., Bonner J. J. An in vitro assay for the specific induction and regression of puffs in isolated polytene nuclei of Drosophila melanogaster. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):835–838. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton J. L., McCarthy B. J. Induction of the Drosophila heat shock response in isolated polytene nuclei. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):191–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90313-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., McCarthy B. J., Wadsworth S. C. Sequence organization of two recombinant plasmids containing genes for the major heat shock-induced protein of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):575–588. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dastugue B., Crepin M. Interaction of non-histone proteins with DNA and chromatin from Drosophila and mouse cells. Specificity, isolation and analysis of complexes. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Sep;99(3):491–498. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13280.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echalier G., Ohanessian A. In vitro culture of Drosophila melanogaster embryonic cells. In Vitro. 1970 Nov-Dec;6(3):162–172. doi: 10.1007/BF02617759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellgaard E. G., Clever U. RNA metabolism during puff induction in Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma. 1971;36(1):60–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00326422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenleaf A. L., Plagens U., Jamrich M., Bautz E. K. RNA polymerase B (or II) in heat induced puffs of Drosophila polytene chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1978 Jan 16;65(2):127–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00329465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross-Bellard M., Oudet P., Chambon P. Isolation of high-molecular-weight DNA from mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):32–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmsing P. J., Berendes H. D. Induced accumulation of nonhistone proteins in polytene nuclei of Drosophila hydei. J Cell Biol. 1971 Sep;50(3):893–896. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.3.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt T. K. Local protein accumulation during gene activation. II. Interferometric measurements of the amount of solid material in temperature induced puffs of Drosophila hydei. Chromosoma. 1971 Mar 16;32(4):428–435. doi: 10.1007/BF00285253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh T., Brutlag D. L. A protein that preferentially binds Drosophila satellite DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):726–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacq B., Jourdan R., Jordan B. R. Structure and processing of precursor 5 S RNA in Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1977 Dec 15;117(3):785–795. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagodzinski L. L., Castro C. E., Sherrod P., Lee D., Sevall J. S. Reassociation kinetics of non-histone-bound DNA sites. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):3038–3044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagodzinski L. L., Chilton J. C., Sevall J. S. DNA-binding nonhistone proteins: DNA site reassociation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 May;5(5):1487–1499. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.5.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinsmith L. J., Heidema J., Carroll A. Specific binding of rat liver nuclear proteins to DNA. Nature. 1970 Jun 13;226(5250):1025–1026. doi: 10.1038/2261025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinsmith L. J. Specific binding of phosphorylated non-histone chromatin proteins to deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 25;248(16):5648–5653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koninkx J. F. Protein synthesis in salivary glands of Drosophila hydei after experimental gene induction. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 15;158(3):623–628. doi: 10.1042/bj1580623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M., Helmsing P. J., Ashburner M. Parallel changes in puffing activity and patterns of protein synthesis in salivary glands of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3604–3608. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March S. C., Parikh I., Cuatrecasas P. A simplified method for cyanogen bromide activation of agarose for affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayfield J. E., Serunian L. A., Silver L. M., Elgin S. C. A protein released by DNAase I digestion of drosophila nuclei is preferentially associated with puffs. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):539–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90240-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie S. L., Henikoff S., Meselson M. Localization of RNA from heat-induced polysomes at puff sites in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1117–1121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell H. K., Lipps L. S. Rapidly labeled proteins on the salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem Genet. 1975 Oct;13(9-10):585–602. doi: 10.1007/BF00484917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RITOSSA F. M. BEHAVIOUR OF RNA AND DNA SYNTHESIS AT THE PUFF LEVEL IN SALIVARY GLAND CHROMOSOMES OF DROSOPHILA. Exp Cell Res. 1964 Dec;36:515–523. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(64)90308-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Hogness D. S. Effect of heat shock on the synthesis of low molecular weight RNAs in drosophilia: accumulation of a novel form of 5S RNA. Cell. 1975 Oct;6(2):207–213. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sevall J. S., Cockburn A., Savage M., Bonner J. DNA-protein interactions of the rat liver non-histone chromosomal protein. Biochemistry. 1975 Feb 25;14(4):782–789. doi: 10.1021/bi00675a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver L. M., Elgin S. C. Distribution patterns of three subfractions of drosophila nonhistone chromosomal proteins: possible correlations with gene activity. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):971–983. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90308-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storti R. V., Horovitch S. J., Scott M. P., Rich A., Pardue M. L. Myogenesis in primary cell cultures from Drosophila melanogaster: protein synthesis and actin heterogeneity during development. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):589–598. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tissières A., Mitchell H. K., Tracy U. M. Protein synthesis in salivary glands of Drosophila melanogaster: relation to chromosome puffs. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 15;84(3):389–398. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90447-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent M., Tanguay R. M. Heat-shock induced proteins present in the cell nucleus of Chironomus tentans salivary gland. Nature. 1979 Oct 11;281(5731):501–503. doi: 10.1038/281501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S., Chiu J. F., Klyszejko-Stefanowicz L., Fujitani H., Hnilica L. S. Tissue-specific chromosomal non-histone protein interactions with DNA. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1471–1475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weideli H., Schedl P., Artavanis-Tsakonas S., Steward R., Yuan R., Gehring W. J. Purification of a protein from unfertilized eggs of Drosophila with specific affinity for a defined DNA sequence and the cloning of this DNA sequence in bacterial plasmids. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):693–700. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]