Abstract
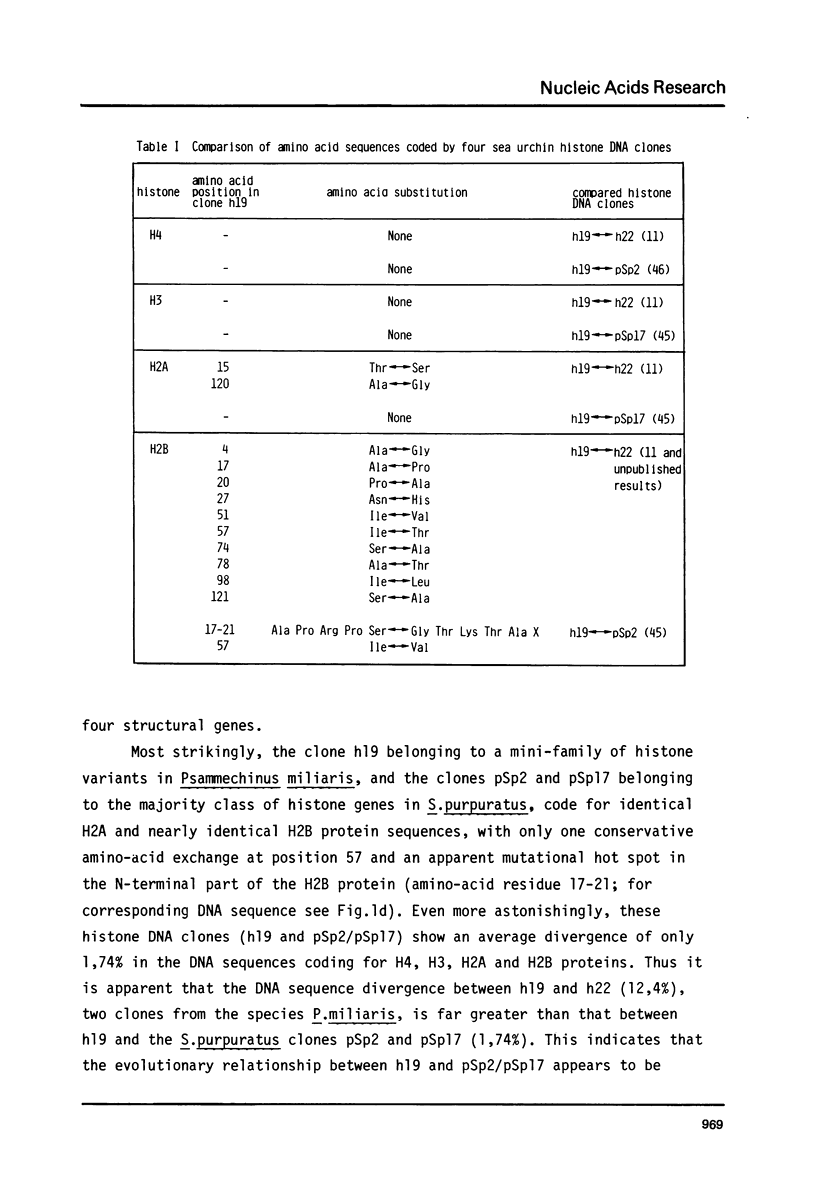
The DNA sequences of the entire structural H4, H3, H2A and H2B genes and of their 5' flanking regions have been determined in the histone DNA clone h19 of the sea urchin Psammechinus miliaris. In clone h19 the polarity of transcription and the relative arrangement of the histone genes is identical to that in clone h22 of the same species. The histone proteins encoded by h19 DNA differ in their primary structure from those encoded by clone h22 and have been compared to histone protein sequences of other sea urchin species as well as other eukaryotes. A comparative analysis of the 5' flanking DNA sequences of the structural histone genes in both clones revealed four ubiquitous sequence motifs; a pentameric element GATCC, followed at short distance by the Hogness box GTATAAATAG, a conserved sequence PyCATTCPu, in or near which the 5' ends of the mRNAs map in h22 DNA and lastly a sequence A, containing the initiation codon. These sequences are also found, sometimes in modified version, in front of other eukaryotic genes transcribed by polymerase II. When prelude sequences of isocoding histone genes in clone h19 and h22 are compared areas of homology are seen to extend beyond the ubiquitous sequence motifs towards the divergent AT-rich spacer and terminate between approximately 140 and 240 nucleotides away from the structural gene. These prelude regions contain quite large conservative sequence blocks which are specific for each type of histone genes.
Full text
PDF


















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnstiel M. L., Schaffner W., Smith H. O. DNA sequences coding for the H2B histone of Psammechinus miliaris. Nature. 1977 Apr 14;266(5603):603–607. doi: 10.1038/266603a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blankstein L. A., Stollar B. D., Franklin S. G., Zweidler A., Levy S. B. Biochemical and immunological characterization of two distinct variants of histone H2A in Friend leukemia. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4557–4562. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boseley P., Moss T., Mächler M., Portmann R., Birnstiel M. Sequence organization of the spacer DNA in a ribosomal gene unit of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):19–31. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90291-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt W. F., Strickland W. N., Strickland M., Carlisle L., Woods D., von Holt C. A histone programme during the life cycle of the sea urchin. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Feb 15;94(1):1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12864.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt W. F., von Holt C. The determination of the primary structure of histone F3 from chicken erythrocytes by automatic Edman degradation. 2. Sequence analysis of histone F3. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 15;46(2):419–429. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busslinger M., Portmann R., Birnsteil M. L. A regulatory sequence near the 3' end of sea urchin histone genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 11;6(9):2997–3008. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.9.2997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs G., Maxson R., Kedes L. H. Histone gene expression during sea urchin embryogenesis: isolation and characterization of early and late messenger RNAs of Strongylocentrotus purpuratus by gene-specific hybridization and template activity. Dev Biol. 1979 Nov;73(1):153–173. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90144-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson S. G., Smith H. O., Schaffner W., Gross K. W., Birnstiel M. L. Integration of eukaryotic genes for 5S RNA and histone proteins into a phage lambda receptor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Oct;3(10):2617–2632. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.10.2617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet M., Gannon F., Hen R., Maroteaux L., Perrin F., Chambon P. Organization and sequence studies of the 17-piece chicken conalbumin gene. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):567–574. doi: 10.1038/282567a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen L. H., Newrock K. M., Zweidler A. Stage-specific switches in histone synthesis during embryogenesis of the sea urchin. Science. 1975 Dec 5;190(4218):994–997. doi: 10.1126/science.1237932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLange R. J., Fambrough D. M., Smith E. L., Bonner J. Calf and pea histone IV. II. The complete amino acid sequence of calf thymus histone IV; presence of epsilon-N-acetyllysine. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 25;244(2):319–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLange R. J., Hooper J. A., Smith E. L. Histone 3. 3. Sequence studies on the cyanogen bromide peptides; complete amino acid sequence of calf thymus histone 3. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 10;248(9):3261–3274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson R. C., Abelson J., Barnes W. M., Reznikoff W. S. Genetic regulation: the Lac control region. Science. 1975 Jan 10;187(4171):27–35. doi: 10.1126/science.1088926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust M., Millward S., Duchastel A., Fromson D. Methylated constituents of poly(A)- and poly(A)+ polyribosomal RNA of sea urchin embryos. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 1):597–604. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90042-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon F., O'Hare K., Perrin F., LePennec J. P., Benoist C., Cochet M., Breathnach R., Royal A., Garapin A., Cami B. Organisation and sequences at the 5' end of a cloned complete ovalbumin gene. Nature. 1979 Mar 29;278(5703):428–434. doi: 10.1038/278428a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin G. H., Nicolas R. H., Johns E. W. A quantitative analysis of histone H1 in rabbit thymus nuclei. Biochem J. 1977 Nov 1;167(2):485–488. doi: 10.1042/bj1670485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross K., Schaffner W., Telford J., Birnstiel M. Molecular analysis of the histone gene cluster of Psammechinus miliaris: III. Polarity and asymmetry of the histone-coding sequences. Cell. 1976 Aug;8(4):479–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90215-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Grunstein J. E. The histone H4 gene of Strongylocentrotus purpuratus: DNA and mRNA sequences at the 5' end. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):1083–1092. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper J. A., Smith E. L., Sommer K. R., Chalkley R. Histone 3. IV. Amino acid sequence of histone 3 of the testes of the carp, Letiobus bubalus. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 10;248(9):3275–3279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg I. Histones. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:159–191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwai K., Hayashi H., Ishikawa K. Calf thymus lysine- and serine-rich histone. 3. Complete amino acid sequence and its implication for interactions of histones with DNA. J Biochem. 1972 Aug;72(2):357–367. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H., Cohn R. H., Lowry J. C., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. The organization of sea urchin histone genes. Cell. 1975 Nov;6(3):359–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90185-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konkel D. A., Maizel J. V., Jr, Leder P. The evolution and sequence comparison of two recently diverged mouse chromosomal beta--globin genes. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):865–873. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90138-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kootstra A., Bailey G. S. Primary structure of histone H2B from trout (Salmo trutta) testes. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 27;17(13):2504–2510. doi: 10.1021/bi00606a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D. Chromatin structure: a repeating unit of histones and DNA. Science. 1974 May 24;184(4139):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4139.868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel N. S., Weinberg E. S. Histone gene transcripts in the cleavage and mesenchyme blastula embryo of the sea urchin, S. purpuratus. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):313–326. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laine B., Kmiecik D., Sautiere P., Biserte G. Primary structure of chicken erythrocyte histone H2A. Biochimie. 1978;60(2):147–150. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(78)80747-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laine B., Sautière P., Biserte G. Primary structure and microheterogeneities of rat chloroleukemia histone H2A (histone ALK, IIbl or F2a2). Biochemistry. 1976 Apr 20;15(8):1640–1645. doi: 10.1021/bi00653a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. The determination of the molecular weight of ribonucleic acid by polyacrylamide-gel electrophresis. The effects of changes in conformation. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(1):131–138. doi: 10.1042/bj1130131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newrock K. M., Cohen L. H., Hendricks M. B., Donnelly R. J., Weinberg E. S. Stage-specific mRNAs coding for subtypes of H2A and H2B histones in the sea urchin embryo. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka Y., Leder P. The complete sequence of a chromosomal mouse alpha--globin gene reveals elements conserved throughout vertebrate evolution. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):875–882. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90139-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata R. T., Gilbert W. An amino-terminal fragment of lac repressor binds specifically to lac operator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5851–5854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa Y., Quagliarotti G., Jordan J., Taylor C. W., Starbuck W. C., Busch H. Structural analysis of the glycine-rich, arginine-rich histone. 3. Sequence of the amino-terminal half of the molecule containing the modified lysine residues and the total sequence. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4387–4392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohe Y., Hayashi H., Iwai K. Human spleen histone H2B. Isolation and amino acid sequence. J Biochem. 1979 Feb;85(2):615–624. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overton G. C., Weinberg E. S. Length and sequence heterogeneity of the histone gene repeat unit of the sea urchin, S. purpuratus. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):247–257. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portmann R., Schaffner W., Birnstiel M. Partial denaturation mapping of cloned histone DNA from the sea urchin Psammechinus miliaris. Nature. 1976 Nov 4;264(5581):31–34. doi: 10.1038/264031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pribnow D. Nucleotide sequence of an RNA polymerase binding site at an early T7 promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):784–788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Gross K., Telford J., Birnstiel M. Molecular analysis of the histone gene cluster of psammechinus miliaris: II. The arrangement of the five histone-coding and spacer sequences. Cell. 1976 Aug;8(4):471–478. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90214-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Kunz G., Daetwyler H., Telford J., Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. Genes and spacers of cloned sea urchin histone DNA analyzed by sequencing. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):655–671. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90249-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller H., Gray C., Herrmann K. Nucleotide sequence of an RNA polymerase binding site from the DNA of bacteriophage fd. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):737–741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U. RNA polymerase unwinds an 11-base pair segment of a phage T7 promoter. Nature. 1979 Jun 14;279(5714):651–652. doi: 10.1038/279651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M., Leung D. W., Gillam S., Astell C. R., Montgomery D. L., Hall B. D. Sequence of the gene for iso-1-cytochrome c in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):753–761. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland M., Strickland W. N., Brandt W. F., Von Holt C., Wittmann-Liebold B. The complete amino-acid sequence of histone H2B(3) from sperm of the sea urchin Parechinus angulosus. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Sep 1;89(2):443–452. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12547.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sures I., Lowry J., Kedes L. H. The DNA sequence of sea urchin (S. purpuratus) H2A, H2B and H3 histone coding and spacer regions. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1033–1044. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surrey S., Nemer M. Methylated blocked 5' terminal sequences of sea urchin embryo messenger RNA classes containing and lacking poly(A). Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 1):589–595. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90041-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S., Maxam A. M., Tizard R., Bernard O., Gilbert W. Sequence of a mouse germ-line gene for a variable region of an immunoglobulin light chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1485–1489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y., Suzuki Y. The DNA sequence of Bombyx mori fibroin gene including the 5' flanking, mRNA coding, entire intervening and fibroin protein coding regions. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):591–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wienand U., Schwarz Z., Feix G. Electrophoretic elution of nucleic acids from gels adapted for subsequent biological tests. Application for analysis of mRNAs from maize endosperm. FEBS Lett. 1979 Feb 15;98(2):319–323. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80208-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wouters-Tyrou D., Sautière P., Bisterte G. Covalent structure of the sea urchin histone H4. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jun 1;65(2):225–228. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80485-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeoman L. C., Olson M. O., Sugano N., Jordan J. J., Taylor D. W., Starbuck W. C., Busch H. Amino acid sequence of the center of the arginine-lysine-rich histone from calf thymus. The total sequence. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 10;247(19):6018–6023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziff E. B., Evans R. M. Coincidence of the promoter and capped 5' terminus of RNA from the adenovirus 2 major late transcription unit. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1463–1475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Helden P. D., Strickland W. N., Brandt W. F., von Holt C. The complete amino-acid sequence of histone H2B from the mollusc Patella granatina. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jan 2;93(1):71–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12796.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ooyen A., van den Berg J., Mantei N., Weissmann C. Comparison of total sequence of a cloned rabbit beta-globin gene and its flanking regions with a homologous mouse sequence. Science. 1979 Oct 19;206(4416):337–344. doi: 10.1126/science.482942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]