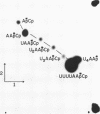
Abstract
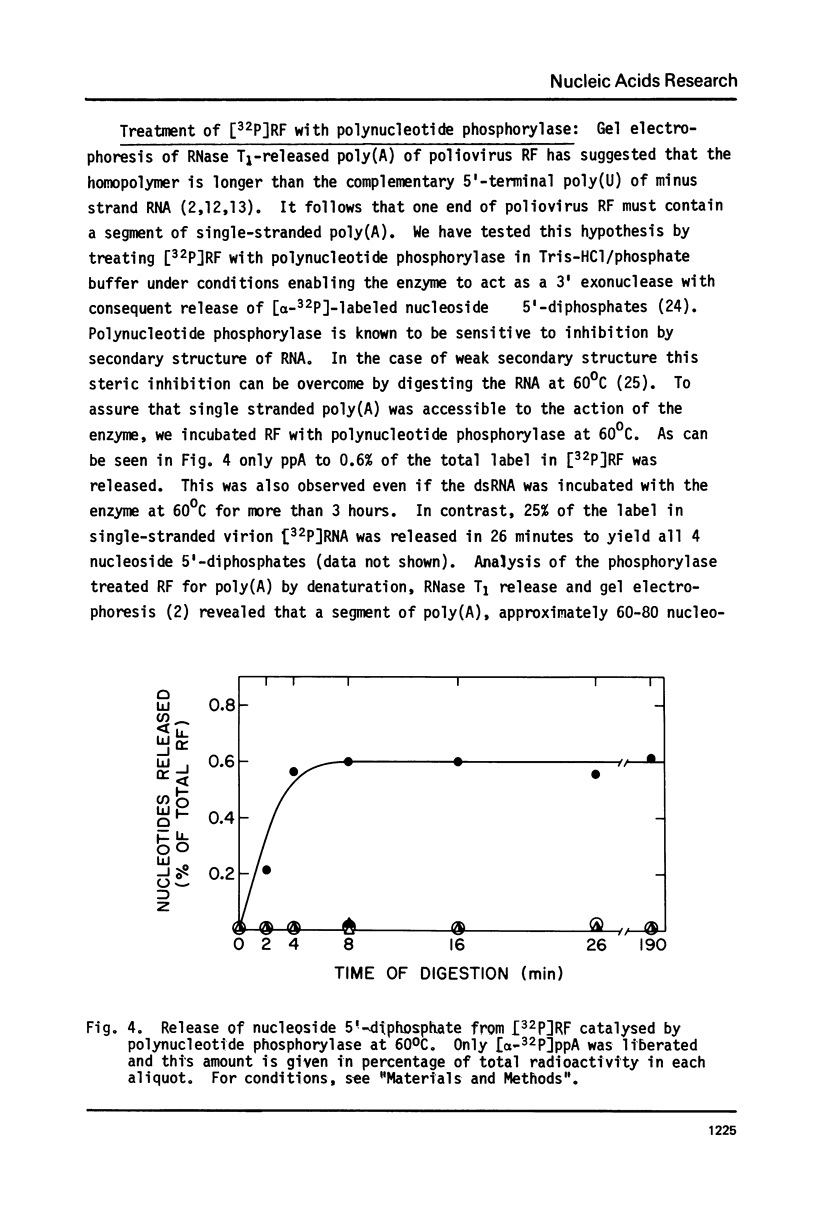
The structure of polio replicative form (RF) has been investigated by 3' end labeling and the use of polynucleotide phosphorylase to now allow a complete composite of the RF structure. The evidence presented indicates that the 3' terminal sequence of the minus strand is an exact complement to the 5' end of polio RNA. This suggests that the 5' terminal U of polio RNA is genetically coded. Other data is presented to show that in addition to the genetically coded poly(A) tract of the plus strand in RF, a single-stranded poly(A) tail protrudes beyond the double-stranded RNA.
Full text
PDF





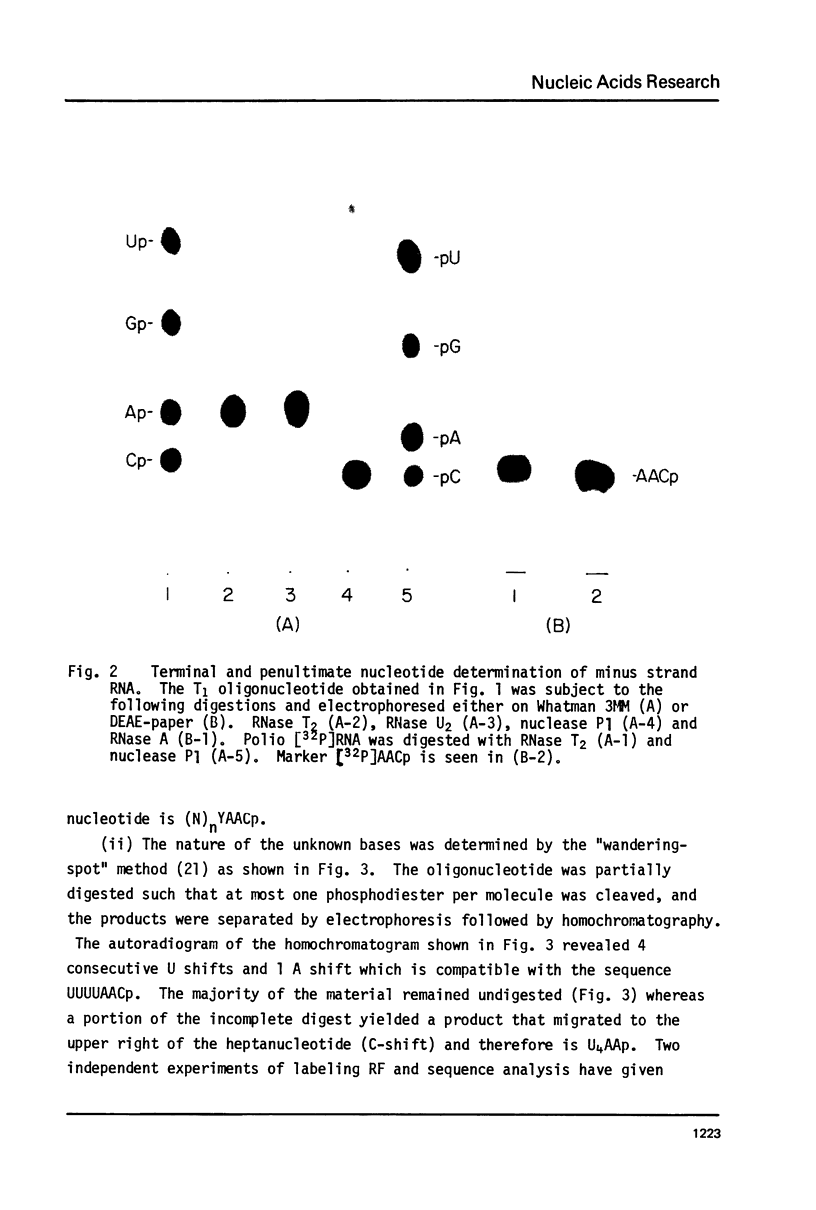





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlquist P., Kaesberg P. Determination of the length distribution of poly(A) at the 3' terminus of the virion RNAs of EMC virus, poliovirus, rhinovirus, RAV-61 and CPMV and of mouse globin mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1195–1204. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Purification and properties of poliovirus double-stranded ribonucleic acid. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jul;18(3):421–428. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80034-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detjen B. M., Lucas J., Wimmer E. Poliovirus single-stranded RNA and double-stranded RNA: differential infectivity in enucleate cells. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):582–586. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.582-586.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsch-Häsler K., Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Replication of picornaviruses. I. Evidence from in vitro RNA synthesis that poly(A) of the poliovirus genome is genetically coded. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1512–1517. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1512-1517.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld E., Hunt T. Double-stranded poliovirus RNA inhibits initiation of protein synthesis by reticulocyte lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):1075–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England T. E., Uhlenbeck O. C. 3'-terminal labelling of RNA with T4 RNA ligase. Nature. 1978 Oct 12;275(5680):560–561. doi: 10.1038/275560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England T. E., Uhlenbeck O. C. Enzymatic oligoribonucleotide synthesis with T4 RNA ligase. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2069–2076. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Petterson R. F., Ambros V., Hewlett N. J., Baltimore D. Covalent linkage of a protein to a defined nucleotide sequence at the 5'-terminus of virion and replicative intermediate RNAs of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):961–965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris T. J. The nucleotide sequence at the 5' end of foot and mouth disease virus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 11;7(7):1765–1785. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.7.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. A., Walseth T. F. The enzymatic preparation of [alpha-32P]ATP, [alpha-32P]GTP, [32P]cAMP, and [32P]cGMP, and their use in the assay of adenylate and guanylate cyclases and cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:135–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. F., Kitamura N., Nomoto A., Wimmer E. Sequence studies of poliovirus RNA. IV. Nucleotide sequence complexities of poliovirus type 1, type 2 and two type 1 defective interfering particles RNAs, and fingerprint of the poliovirus type 3 genome. J Gen Virol. 1979 Aug;44(2):311–322. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-2-311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. F., Nomoto A., Detjen B. M., Wimmer E. A protein covalently linked to poliovirus genome RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):59–63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Detjen B., Pozzatti R., Wimmer E. The location of the polio genome protein in viral RNAs and its implication for RNA synthesis. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):208–213. doi: 10.1038/268208a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Kitamura N., Golini F., Wimmer E. The 5'-terminal structures of poliovirion RNA and poliovirus mRNA differ only in the genome-linked protein VPg. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5345–5349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PONS M. INFECTIOUS DOUBLE-STRANDED POLIOVIRUS RNA. Virology. 1964 Nov;24:467–473. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90186-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson R. F., Ambros V., Baltimore D. Identification of a protein linked to nascent poliovirus RNA and to the polyuridylic acid of negative-strand RNA. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):357–365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.357-365.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirtle R. M., Pirtle I. L., Inouye M. Homologous nucleotide sequences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic mRNAs: the 5'-end sequence of the mRNA of the lipoprotein of the Escherichia coli outer membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2190–2194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A. G., Fellner P., Black D. N., Rowlands D. J., Harris T. J., Brown F. 3'-Terminal nucleotide sequences in the genome RNA of picornaviruses. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):298–301. doi: 10.1038/276298a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards O. C., Ehrenfeld E., Manning J. Strand-specific attachment of avidin-spheres to double-stranded poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):676–680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberklang M., Gillum A. M., RajBhandary U. L. The use of nuclease P1 in sequence analysis of end group labeled RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Dec;4(12):4091–4108. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.12.4091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Baltimore D. Polyadenylic acid on poliovirus RNA IV. Poly(U) in replicative intermediate and double-stranded RNA. Virology. 1975 Oct;67(2):498–505. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90450-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Baltimore D. Polyadenylic acid on poliovirus RNA. II. poly(A) on intracellular RNAs. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1418–1431. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1418-1431.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Baltimore D. Requirement of 3'-terminal poly(adenylic acid) for the infectivity of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):2983–2987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.2983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Davidson N., Wimmer E. An electron microscope study of the proteins attached to polio virus RNA and its replicative form (RF). Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Dec;5(12):4711–4723. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.12.4711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Teng M. H., Wimmer E. Poly(U) in poliovirus minus RNA is 5'-terminal. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 23;61(4):1101–1109. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80397-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Poly (A) and poly (U) in poliovirus double stranded RNA. Nat New Biol. 1973 Apr 11;242(119):171–174. doi: 10.1038/newbio242171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Polyadenylic acid at the 3'-terminus of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1877–1882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]