Abstract
Polynucleotides adsorb on natural and model phospholipid membranes in the presence of Mg2+-cations. Adsorption of nucleic acids on membranes results in a considerable change of their secondary structure. The presence of model phosphatidylcholine membranes greatly stimulates the rate of the synthesis of RNA by E. coli RNA-polymerase on DNA template.
Full text
PDF






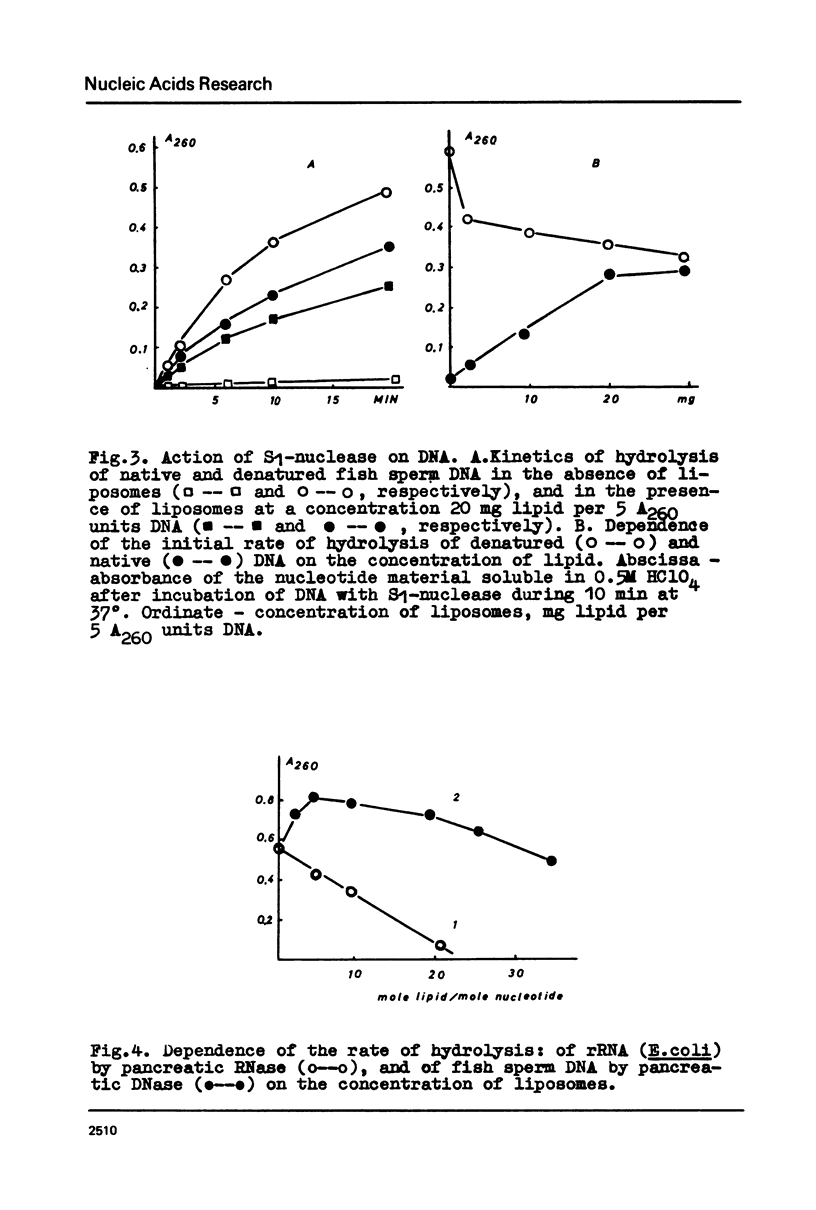
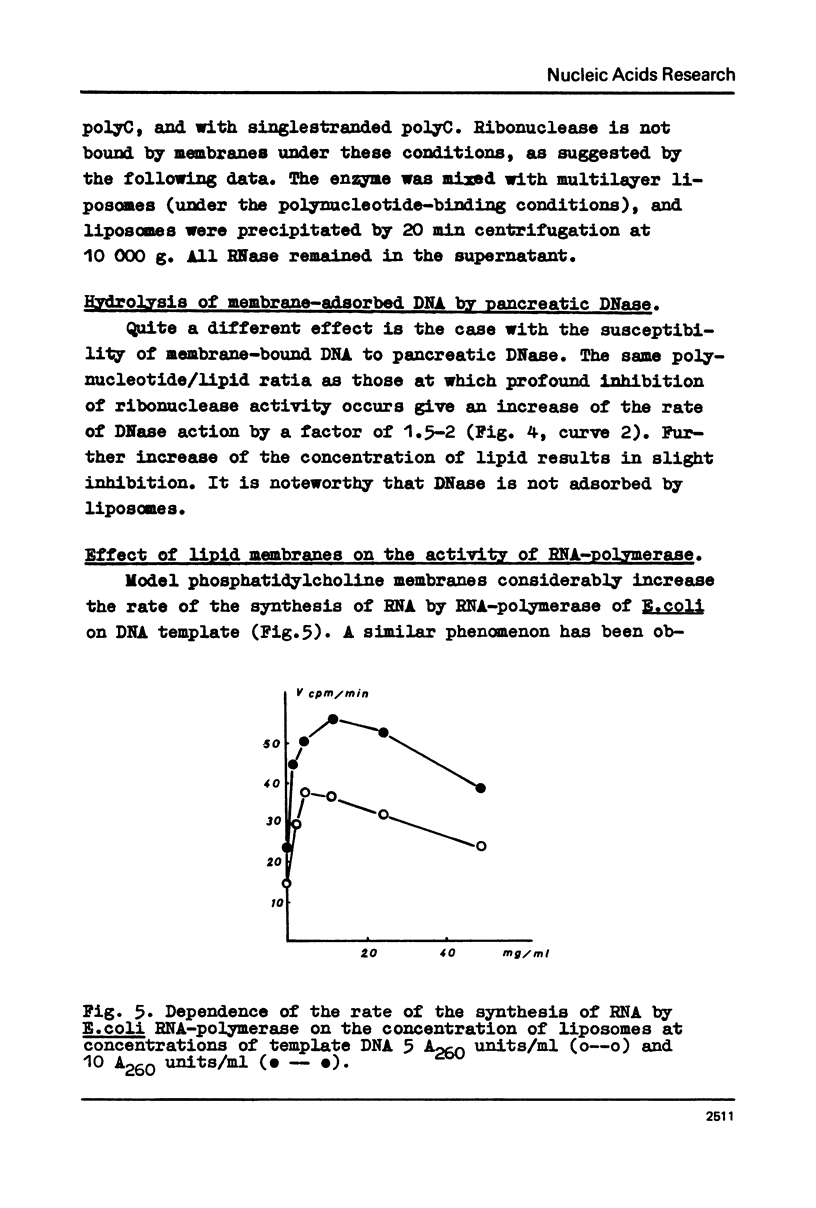
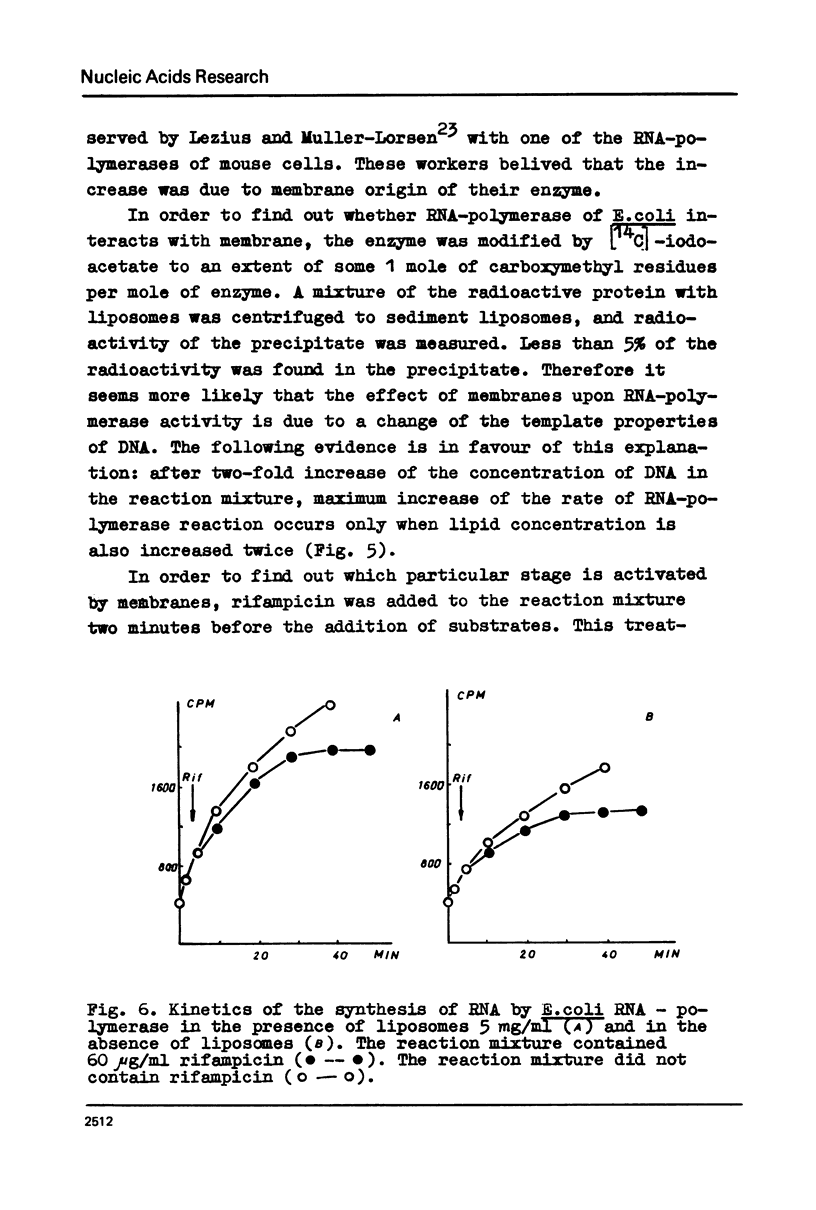



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Budker V. G., Kazachkov Iu A., Naumova L. P. Vzaimodeístvie polinukleotidov s mitokhondriiami iz pecheni krys. Biokhimiia. 1978 Nov;43(11):2105–2108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabradilla C. D., Toliver A. P. S-phase dependent forms of DNA - nuclear membrane complexes in HeLa cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 21;402(2):188–198. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90038-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capitani S., Maraldi N. M., Santi P., Martoni E., Manzoli-Guidotti L. Analisi dell'interazione DNA-(F1+F2b+F3)-sfingomielina. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper. 1976 Jul 15;52(13):966–972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damadian R. Biological ion exchanger resins. I. Quantitative electrostatic correspondence of fixed charge and mobile counter ion. Biophys J. 1971 Sep;11(9):739–760. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(71)86251-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dod B. J., Gray G. M. The lipid composition of rat-liver plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 29;150(3):397–404. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90138-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon J. M., Taber H. W. Some properties of a membrane-deoxyribonucleic acid complex isolated from Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):789–795. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.789-795.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Infante A. A., Firshein W., Hobart P., Murray L. A nuclear membrane-associated DNA complex in cultured mammalian cells capable of synthesizing DNA in vitro. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 2;15(22):4810–4817. doi: 10.1021/bi00667a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. C., Nishida T. Nature of interaction of dextran sulfate with lecithin dispersions and lysolecithin micelles. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1243–1249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lezius A., Müller-Lornsen B. Effects of phospholipids and dimethylsulfoxide on the activity of RNA polymerase A from mouse myeloma cells. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1972 Dec;353(12):1872–1876. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1972.353.2.1872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzoli F. A., Muchmore J. H., Bonora B., Sabioni A., Stefoni S. Interaction between sphingomyelin and DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 25;277(2):251–255. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90405-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirzabekov A. D., Melnikova A. F. Localization of chromatin proteins within DNA grooves by methylation of chromatin with dimethyl sulphate. Mol Biol Rep. 1974 Sep;1(7):379–384. doi: 10.1007/BF00385669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randerath K., Randerath E. Analysis of nucleic acid derivatives at the subnanomole level. 3. A tritium labeling procedure for quantitative analysis of ribose derivatives. Anal Biochem. 1969 Apr 4;28(1):110–118. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton W. D. A crude nuclease preparation suitable for use in DNA reassociation experiments. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jul 29;240(4):522–531. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90709-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasilenko S. K., Serbo N. A., Ven'iaminova A. G., Boldyreva L. G., Budker V. G. Preparativnoe poluchenie 5'-oligoribonukleotidov s pomoshch'iu ribonukleazy iz iada kobry. Biokhimiia. 1976 Feb;41(2):260–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



