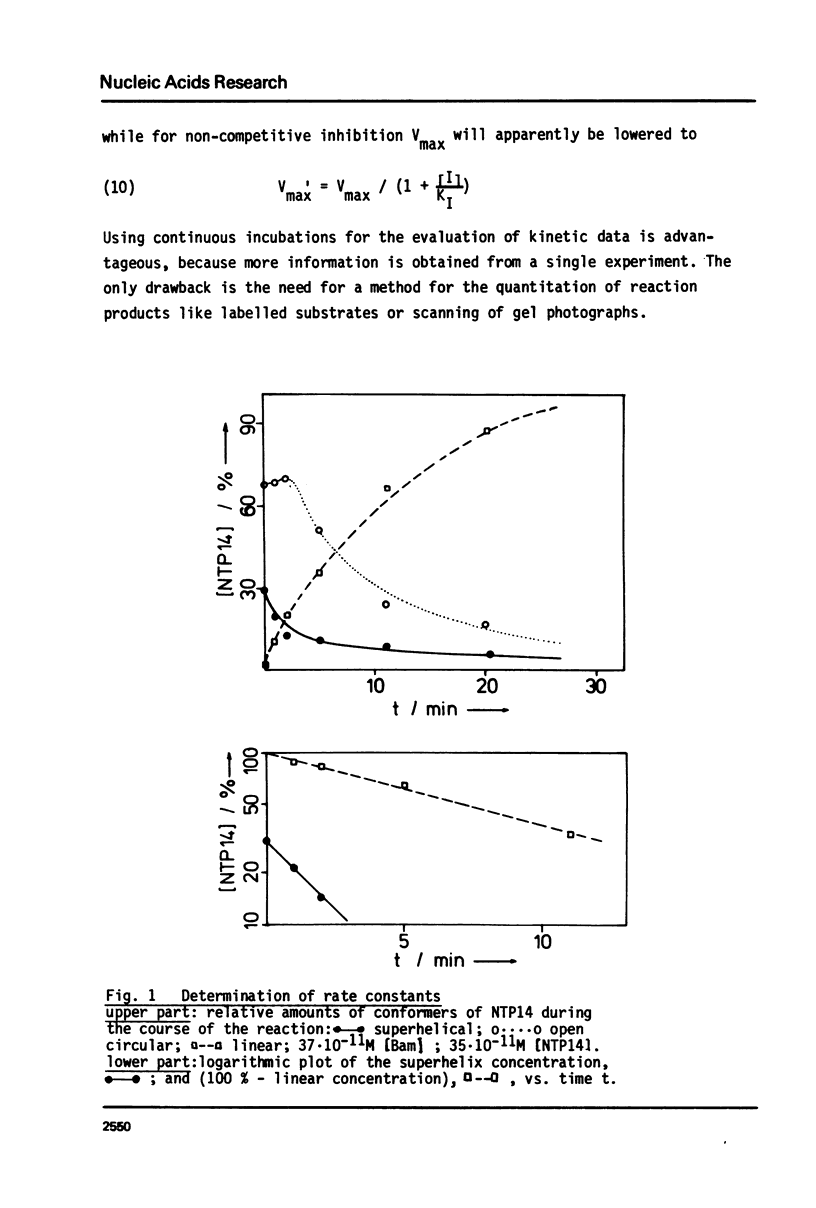
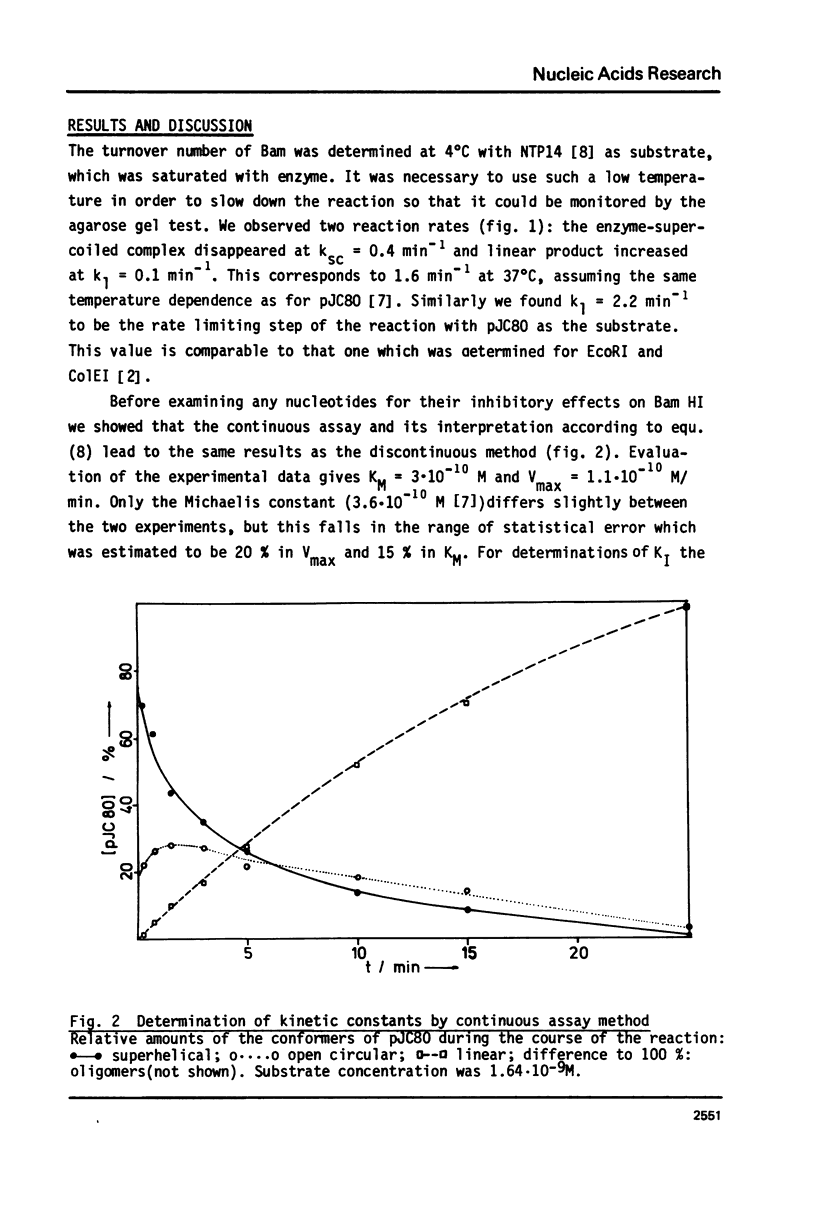
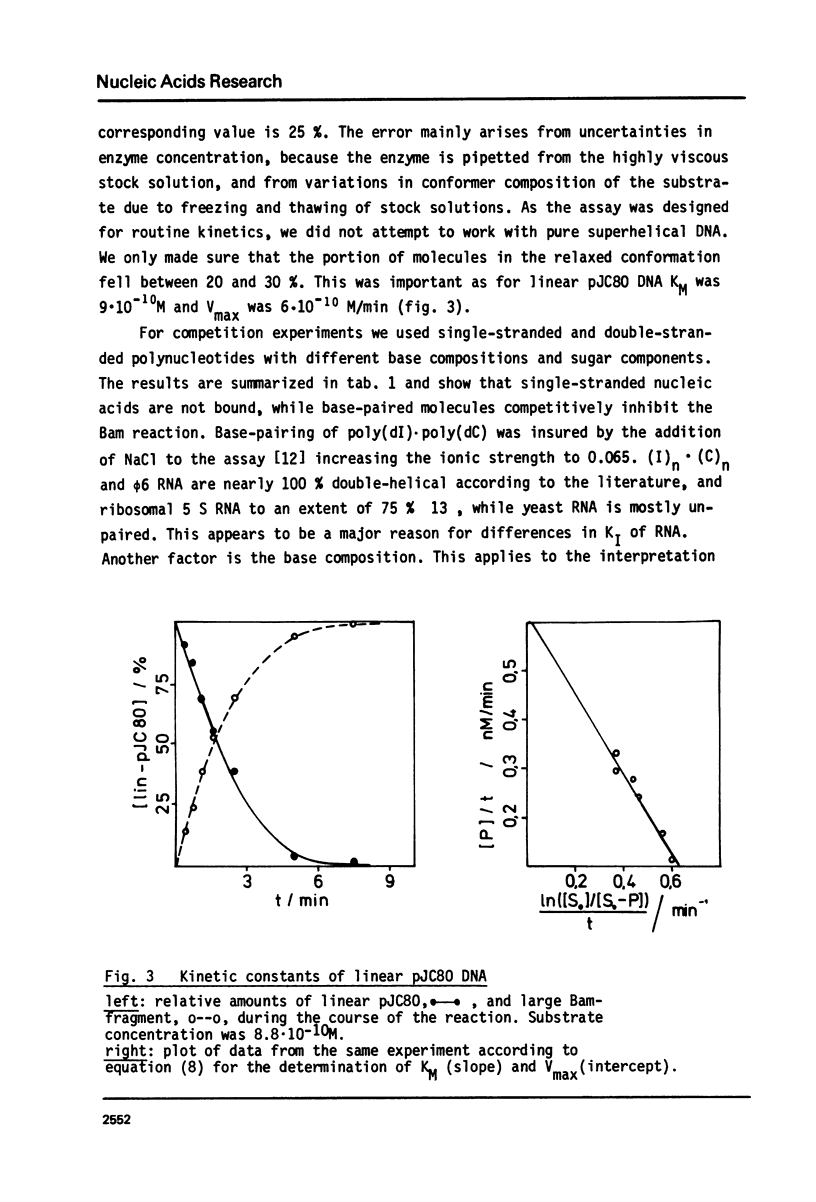
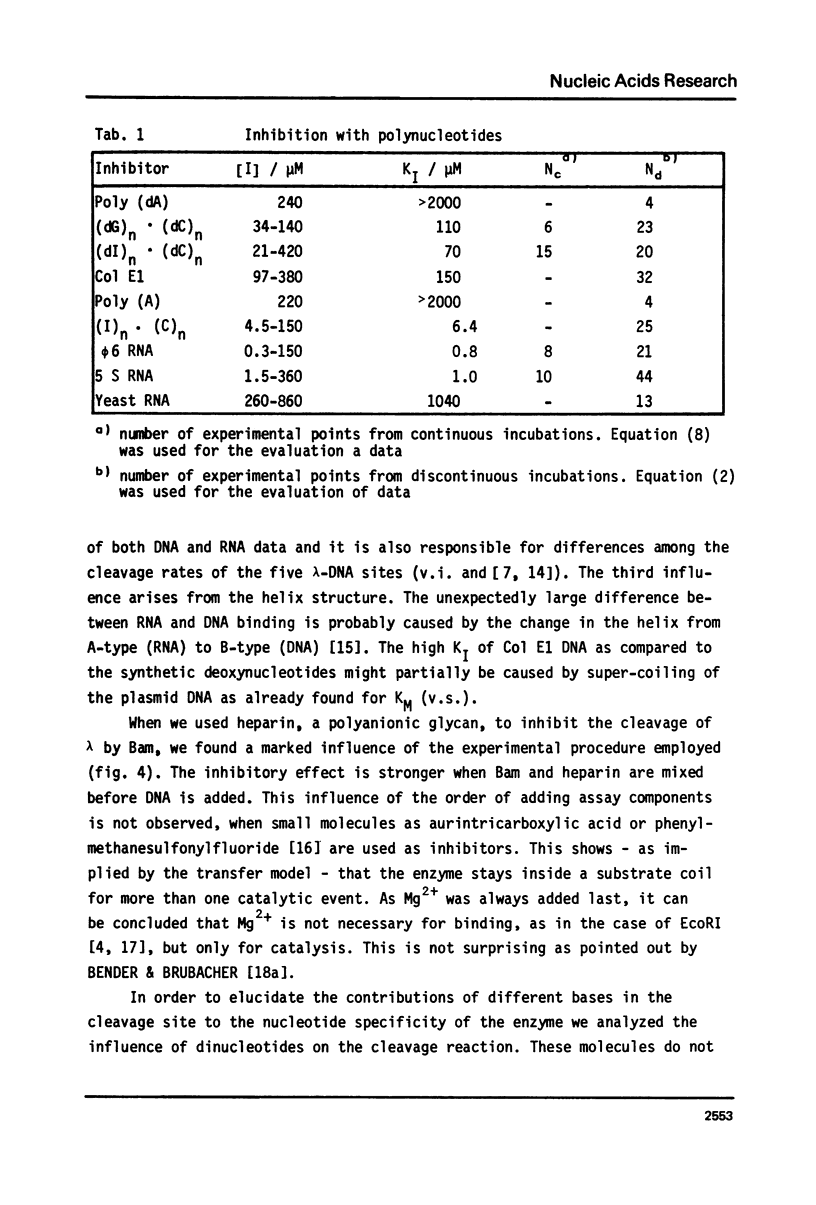
Abstract
The kinetic constants of the site-specific endonuclease Bam HI for various substrates were determined and binding of non-substrate nucleotides to the enzyme was studied. Agarose gel assays in combination with an integrated Michaelis-Menten equation were used for the evaluation of data. The turnover number was 2.2 min-1 at 37 degrees C with pJC80 DNA as the substrate. It depends on the conformation and base composition of the substrate. Michaelis constants also depend on substrate conformation. Non-substrate polynucleotides were found to inhibit Bam competitively with KI ranging from 10(-6) to > 10(-3) M depending on base composition, base pairing, and helix conformation. Dinucleotides showed sequence-specific, competitive inhibition with KIs ranging from 10(-5) to > 10(-3) M. Mononucleotides and -nucleosides acted noncompetitively. Binding was influenced by the extent of phosphorylation, but not by the nature of the base. KIs varied between 10(-3) and 10(-2) M. The results are discussed with respect to the recognition requirements of Bam HI.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berkner K. L., Folk W. R. The effects of substituted pyrimidines in DNAs on cleavage by sequence-specific endonucleases. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2551–2560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. W., Wong K. P. The hydrodynamic shape, conformation, and molecular model of Escherichia coli ribosomal 5 S RNA. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10139–10144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebel W., Bonewald R. Class of small multicopy plasmids originating from the mutant antibiotic resistance factor R1 drd-19B2. J Bacteriol. 1975 Aug;123(2):658–665. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.2.658-665.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goppelt M., Pingoud A., Maass G., Mayer H., Köster H., Frank R. The interaction of the EcoRI restriction endonuclease with its substrate. A physico-chemical study employing natural and synthetic oligonucleotides and polynucleotides. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Feb;104(1):101–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04405.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattman S., Keister T., Gottehrer A. Sequence specificity of DNA methylases from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and Bacillus brevis. J Mol Biol. 1978 Oct 5;124(4):701–711. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90178-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinsch B., Kula M. R. Physical and kinetic properties of the site specific endonuclease Bam HI from Bacillus amylolique-faciens. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Feb 11;8(3):623–633. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.3.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INMAN R. B., BALDWIN R. L. HELIX--RANDOM COIL TRANSITIONS IN DNA HOMOPOLYMER PAIRS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Apr;8:452–469. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jovin T. M. Recognition mechanisms of DNA-specific enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:889–920. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.004325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann M. B., Smith H. O. Specificity of Hpa II and Hae III DNA methylases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Dec;4(12):4211–4221. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.12.4211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modrich P., Zabel D. EcoRI endonuclease. Physical and catalytic properties of the homogenous enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 10;251(19):5866–5874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai C., Glinsmann W. Interactions between polyamines and nucleotides. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 13;16(25):5636–5641. doi: 10.1021/bi00644a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirrotta V. Two restriction endonucleases from Bacillus globiggi. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Jul;3(7):1747–1760. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.7.1747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prunell A., Strauss F., Leblanc B. Photographic quantitation of DNA in gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1977 Mar;78(1):57–65. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter P. H., Eigen M. Diffusion controlled reaction rates in spheroidal geometry. Application to repressor--operator association and membrane bound enzymes. Biophys Chem. 1974 Oct;2(3):255–263. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(74)80050-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. J., Wilson G. A., Young F. E. Recognition sequence of specific endonuclease BamH.I from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens H. Nature. 1977 Jan 6;265(5589):82–84. doi: 10.1038/265082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman N. C., Rosenberg J. M., Rich A. Sequence-specific recognition of double helical nucleic acids by proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):804–808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. R., Humphreys G. O., Willshaw G. A., Anderson E. S. Characterisation of plasmids coding for the restriction endonuclease EcoRI. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Feb 2;143(3):319–325. doi: 10.1007/BF00269410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M., Davis R. W. Studies on the cleavage of bacteriophage lambda DNA with EcoRI Restriction endonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 25;91(3):315–328. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90383-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhead J. L., Malcolm A. D. Non-specific binding of restriction endonuclease EcoR1 to DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 25;8(2):389–402. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.2.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



