Abstract
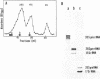
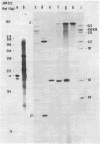
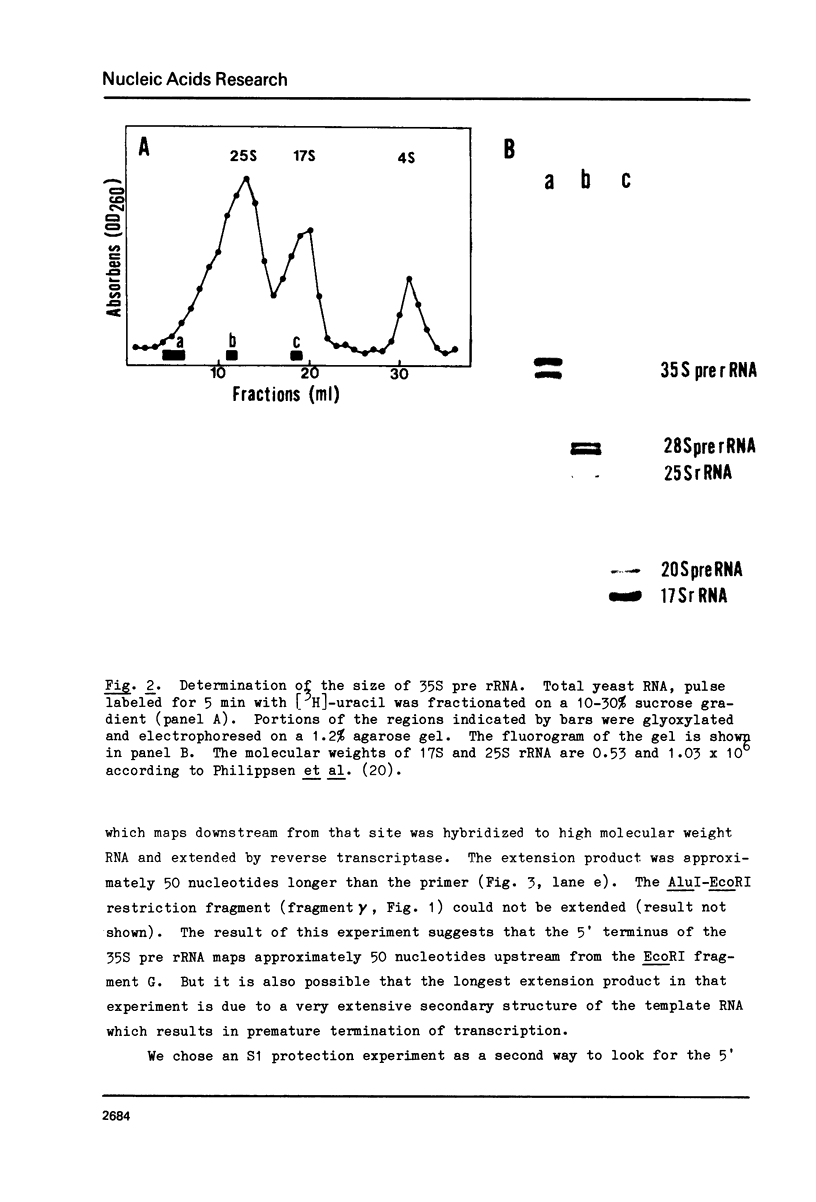
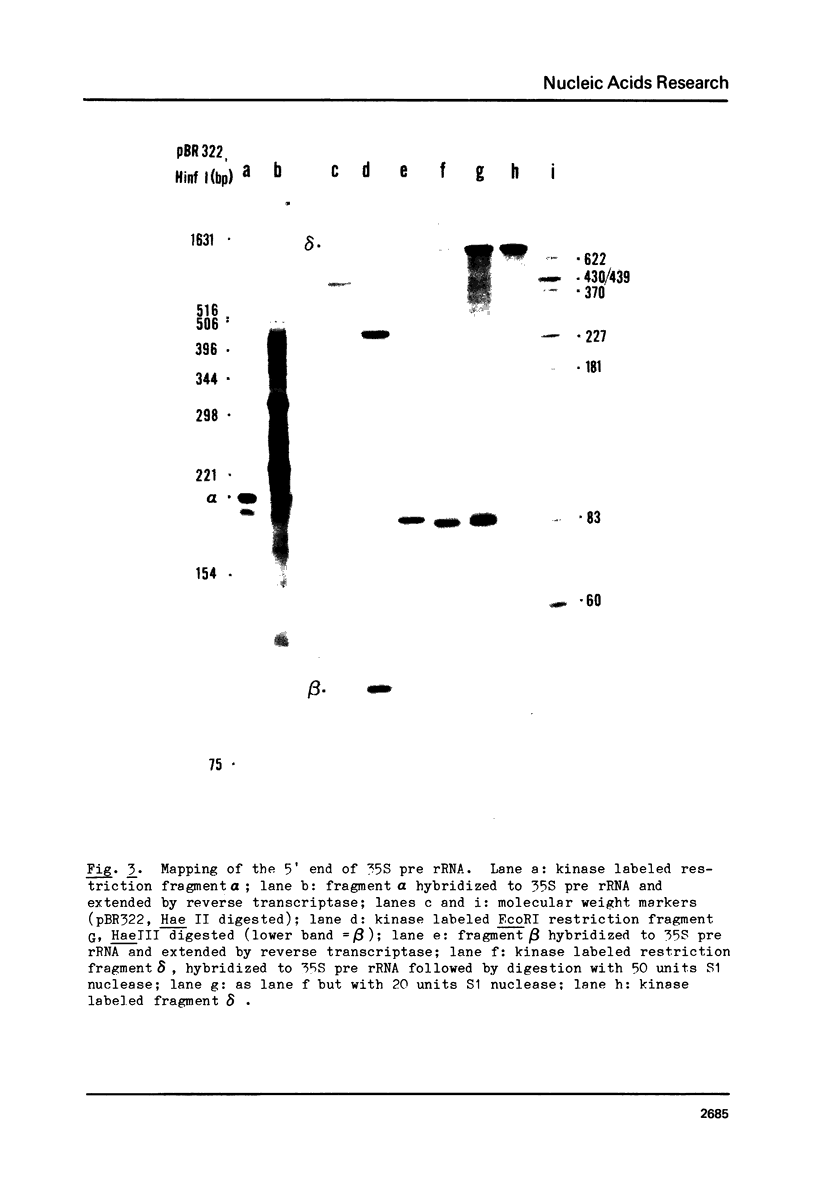
The 5' terminus of Saccharomyces cereviasiae 35S pre rRNA was mapped on the rDNA using two methods: 1) Suitable restriction endonuclease fragments were hybridized to total high molecular weight RNA and extended with reverse transcriptase to the 5' end of the RNA template. 2) Other restriction fragments spanning the 5' terminus of 35S pre rRNA and radioactively labeled at their ends were hybridized to high molecular weight RNA and the non hybridized nucleic acids were digested with S1 nuclease. On the basis of these experiments, the 5' terminus of 35S pre rRNA was placed approximately 670 nucleotides upstream from the 17S rRNA coding region. The exact position was determined by reverse transcription as above, but in the presence of dideoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, which served as a way of sequencing the 5' terminal region. 35S pre rRNA synthesis is initiated at a site in EcoRI restriction fragment B which is 48 nucleotides upstream from the EcoRI cleavage site in the coding strand.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Sakonju S., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: II. The 3' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J., Davidson N. Rates of formation and thermal stabilities of RNA:DNA and DNA:DNA duplexes at high concentrations of formamide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1539–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Properties of a supercoiled deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex and strand specificity of the relaxation event. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 27;9(22):4428–4440. doi: 10.1021/bi00824a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudov K. P., Dabeva M. D., Hadjiolov A. A. Simple agar--urea-gel electrophoretic fractionation of high molecular weight ribonucleic acids. Anal Biochem. 1976 Nov;76(50):250–258. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90283-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson J., Davis R. W. A new electron microscopic technique for establishing the positions of genes: an analysis of the yeast ribosomal RNA coding region. J Mol Biol. 1978 Aug 15;123(3):417–430. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90088-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert S. F., de Boer H. A., Nomura M. Identification of initiation sites for the in vitro transcription of rRNA operons rrnE and rrnA in E. coli. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):211–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser G., Cashel M. In vitro transcripts from the rrn B ribosomal RNA cistron originate from two tandem promoters. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):111–121. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90192-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Periodic density fluctuation during the yeast cell cycle and the selection of synchronous cultures. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1280–1285. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1280-1285.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRBY K. S. A new method for the isolation of ribonucleic acids from mammalian tissues. Biochem J. 1956 Nov;64(3):405–408. doi: 10.1042/bj0640405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klootwijk J., de Jonge P., Planta R. J. The primary transcript of the ribosomal repeating unit in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):27–39. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. A., Cameron J. R., Davis R. W. Isolation of bacteriophage lambda containing yeast ribosomal RNA genes: screening by in situ RNA hybridization to plaques. Cell. 1976 Jun;8(2):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. A., Philippsen P., Davis R. W. Divergent transcription in the yeast ribosomal RNA coding region as shown by hybridization to separated strands and sequence analysis of cloned DNA. J Mol Biol. 1978 Aug 15;123(3):405–416. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikolaev N., Georgiev O. I., Venkov P. V., Hadjiolov A. A. The 37 S precursor to ribosomal RNA is the primary transcript of ribosomal RNA genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jan 25;127(3):297–308. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90331-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petes T. D., Hereford L. M., Skryabin K. G. Characterization of two types of yeast ribosomal DNA genes. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):295–305. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.295-305.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippsen P., Kramer R. A., Davis R. W. Cloning of the yeast ribosomal DNA repeat unit in SstI and HindIII lambda vectors using genetic and physical size selections. J Mol Biol. 1978 Aug 15;123(3):371–386. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90085-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippsen P., Thomas M., Kramer R. A., Davis R. W. Unique arrangement of coding sequences for 5 S, 5.8 S, 18 S and 25 S ribosomal RNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae as determined by R-loop and hybridization analysis. J Mol Biol. 1978 Aug 15;123(3):387–404. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90086-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. The use of thin acrylamide gels for DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer E., Loring D., Hurwitz J., Monroy G. Enzymatic conversion of 5'-phosphate-terminated RNA to 5'-di- and triphosphate-terminated RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4793–4797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udem S. A., Warner J. R. Ribosomal RNA synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol. 1972 Mar 28;65(2):227–242. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90279-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela P., Bell G. I., Venegas A., Sewell E. T., Masiarz F. R., DeGennaro L. J., Weinberg F., Rutter W. J. Ribosomal RNA genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. II. Physical map and nucleotide sequence of the 5 S ribosomal RNA gene and adjacent intergenic regions. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):8126–8135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney P. A., Cooper T. G. Urea carboxylase and allophanate hydrolase. Two components of adenosine triphosphate:urea amido-lyase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 10;247(5):1349–1353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Steitz J. A. Tandem promoters direct E. coli ribosomal RNA synthesis. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer H. A., Gilbert S. F., Nomura M. DNA sequences of promoter regions for rRNA operons rrnE and rrnA in E. coli. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):201–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90308-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]