Abstract
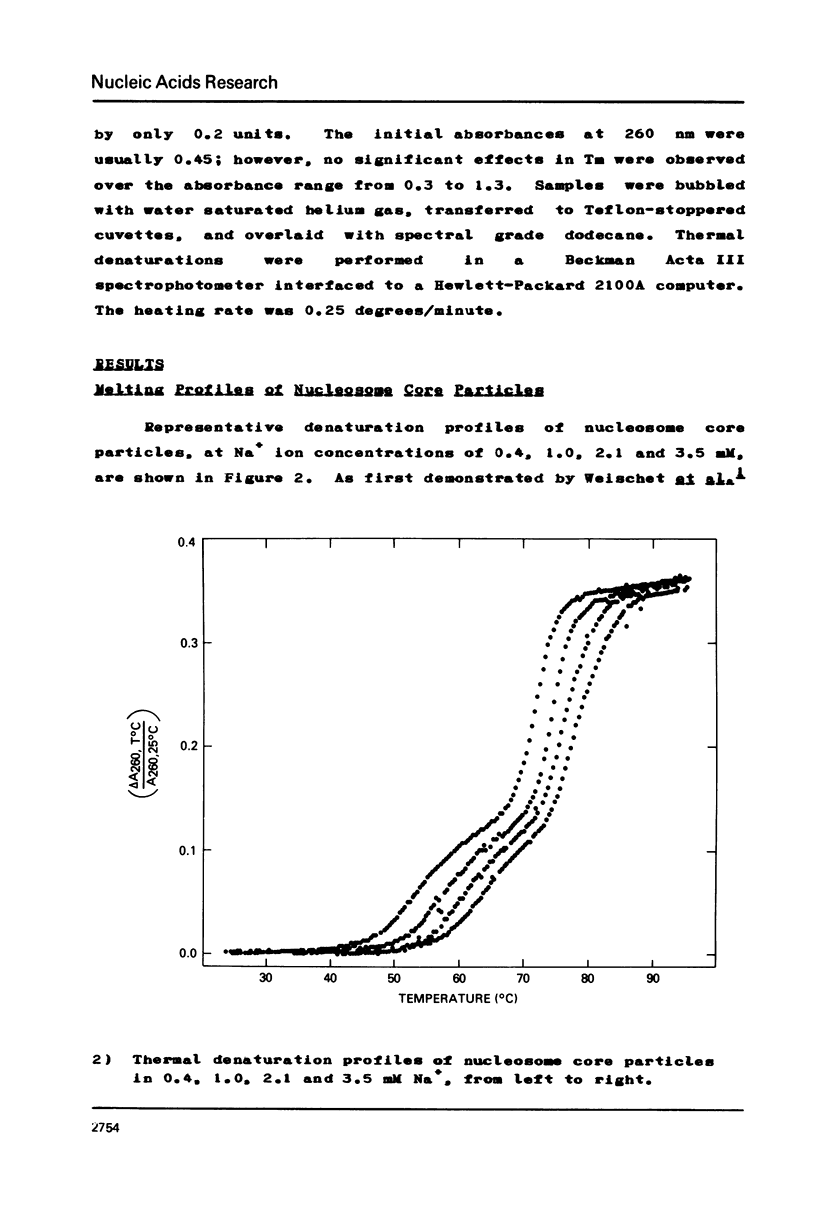
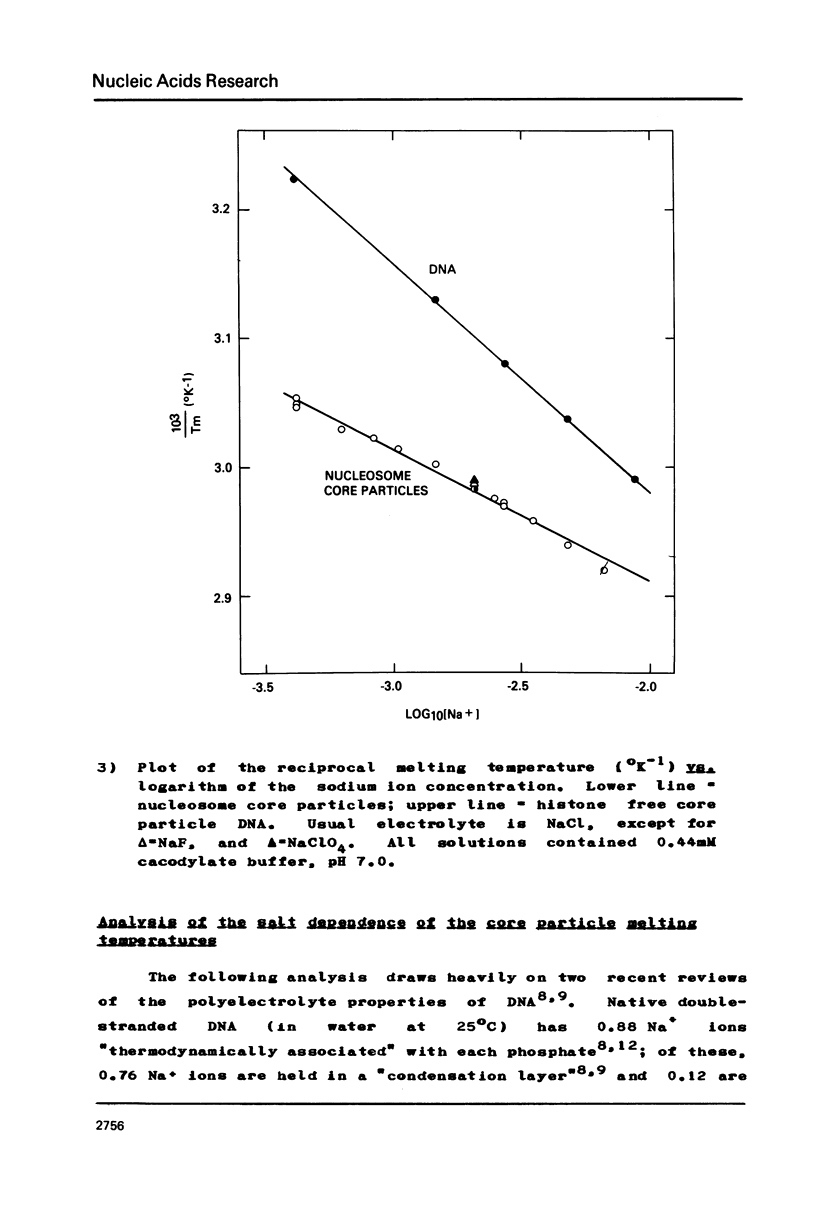
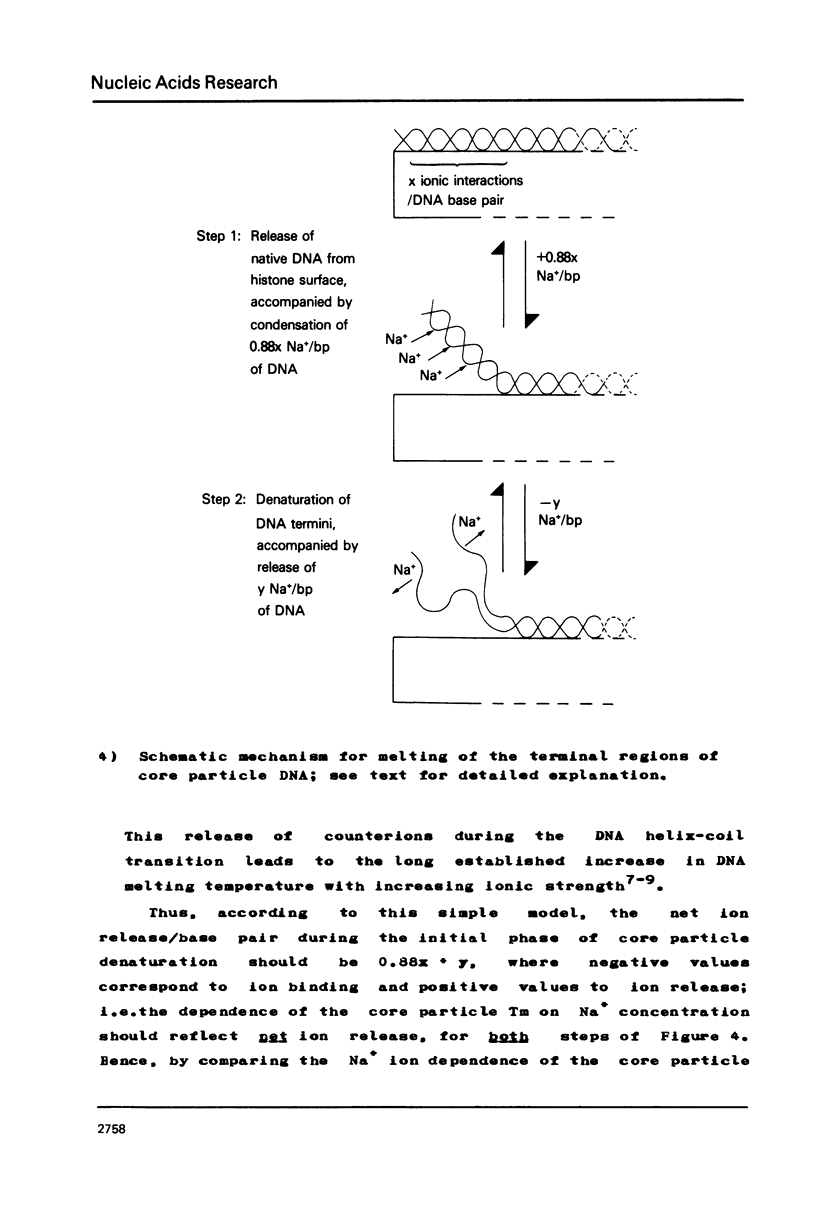
It has been shown by others that the melting of DNA in the nucleosome core particle is biphasic (ref. 1) and that the initial denaturation phase is due to melting of the DNA termini (refs. 1 & 2). We analyze the salt dependence of the melting temperature of this first transition and estimate that only 15% of the phosphates of the DNA termini are involved in intimate charge-charge interactions with histones. (The simplest model yields approximately 9%, whereas a calculated overestimate yields approximately 21% neutralization.) This is a surprisingly small number of interactions but we suggest that it may nonetheless be representative of all the core particle DNA.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Camerini-Otero R. D., Felsenfeld G. Supercoiling energy and nucleosome formation: the role of the arginine-rich histone kernel. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1159–1181. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1159-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cary P. D., Moss T., Bradbury E. M. High-resolution proton-magnetic-resonance studies of chromatin core particles. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Sep 1;89(2):475–482. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12551.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M. Statistical thermodynamics of nucleic acid melting transitions with coupled binding equilibria. Biopolymers. 1971 Nov;10(11):2147–2160. doi: 10.1002/bip.360101110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieterich A. E., Axel R., Cantor C. R. Salt-induced structural changes of nucleosome core particles. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 25;129(4):587–602. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch J. T., Lutter L. C., Rhodes D., Brown R. S., Rushton B., Levitt M., Klug A. Structure of nucleosome core particles of chromatin. Nature. 1977 Sep 1;269(5623):29–36. doi: 10.1038/269029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon V. C., Knobler C. M., Olins D. E., Schumaker V. N. Conformational changes of the chromatin subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):660–663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon V. C., Schumaker V. N., Olins D. E., Knobler C. M., Horwitz J. The temperature and pH dependence of conformational transitions of the chromatin subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 24;6(12):3845–3858. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.12.3845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt M. How many base-pairs per turn does DNA have in solution and in chromatin? Some theoretical calculations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):640–644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Felsenfeld G. Reaction of nucleosome DNA with dimethyl sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2133–2137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., von Hippel P. H. Theoretical aspects of DNA-protein interactions: co-operative and non-co-operative binding of large ligands to a one-dimensional homogeneous lattice. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):469–489. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Record M. T., Jr, Anderson C. F., Lohman T. M. Thermodynamic analysis of ion effects on the binding and conformational equilibria of proteins and nucleic acids: the roles of ion association or release, screening, and ion effects on water activity. Q Rev Biophys. 1978 May;11(2):103–178. doi: 10.1017/s003358350000202x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Record M. T., Jr, Lohman M. L., De Haseth P. Ion effects on ligand-nucleic acid interactions. J Mol Biol. 1976 Oct 25;107(2):145–158. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross P. D., Shapiro J. T. Heat of interaction of DNA with polylysine, spermine, and Mg++. Biopolymers. 1974;13(2):415–416. doi: 10.1002/bip.1974.360130218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligy V. L., Poon N. H. Alteration in nucleosome structure induced by thermal denaturation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jul;5(7):2233–2252. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.7.2233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shindo H., McGhee J. D., Cohen J. S. 31P-NMR studies of DNA in nucleosome core particles. Biopolymers. 1980 Mar;19(3):523–537. doi: 10.1002/bip.1980.360190307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T. Mechanism of a reversible, thermally induced conformational change in chromatin core particles. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10123–10127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T., Shindo H. Conformation of DNA in chromatin core particles containing poly(dAdT)-poly(dAdT) studied by 31 P NMR spectroscopy. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 25;7(2):481–492. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.2.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Felsenfeld G. Pancreatic DNAase cleavage sites in nuclei. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):537–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Van Lente F. Dissection of chromosome structure with trypsin and nucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4249–4253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weischet W. O., Tatchell K., Van Holde K. E., Klump H. Thermal denaturation of nucleosomal core particles. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jan;5(1):139–160. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock J. P., Jr, Stein A. Folding of DNA by histones which lack their NH2-terminal regions. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3857–3861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Dattagupta N., Hogan M., Crothers D. M. Structural changes of nucleosomes in low-salt concentrations. Biochemistry. 1979 Sep 4;18(18):3960–3965. doi: 10.1021/bi00585a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]