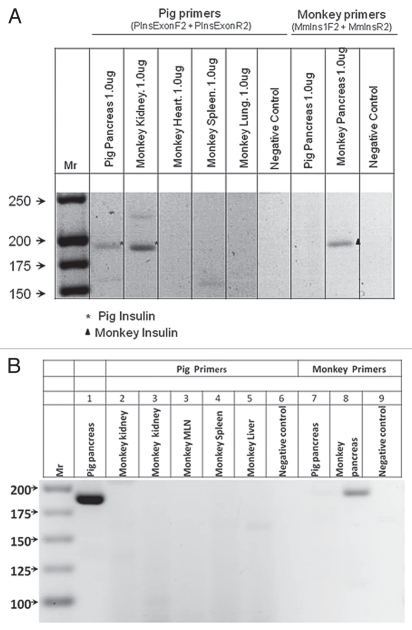
Figure 7.
RT-PCR: (A) Shown left to right are DNA molecular weights (Mr); amplification of bands using primers specific for porcine proinsulin from 1 µg RNA extracted from pig pancreas; or from a rhesus macaque (monkey) transplanted with E28 pig pancreatic primordia in mesentery, followed by implantation of porcine islets in the renal subcapsular space (Diab-E28-Islets), kidney, heart, spleen, lung, a negative control for porcine-specific primers (no RNA); and amplification of bands using primers specific for monkey proinsulin from 1 µg of pig pancreas RNA, monkey pancreas and a second negative control for macaque-specific primers. (B) Shown left to right are DNA molecular weights (Mr); amplification of bands using primers specific for porcine proinsulin from 2 µg RNA extracted from pig pancreas; or from a rhesus macaque (monkey) implanted with porcine islets in the renal subcapsular space with no previous transplantation of E28 pig pancreatic primordia (Diab-Islets), kidneys, mesenteric lymph node (MLN) spleen, liver, a negative control for porcine-specific primers (no RNA); and amplification of bands using primers specific for monkey proinsulin from 2 µg of pig pancreas RNA, monkey pancreas and a second negative control for macaque-specific primers. Pig primers amplify a 193 bps band. Monkey primers amplify a 199 bps band.