Abstract
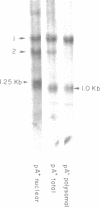
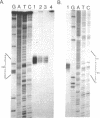
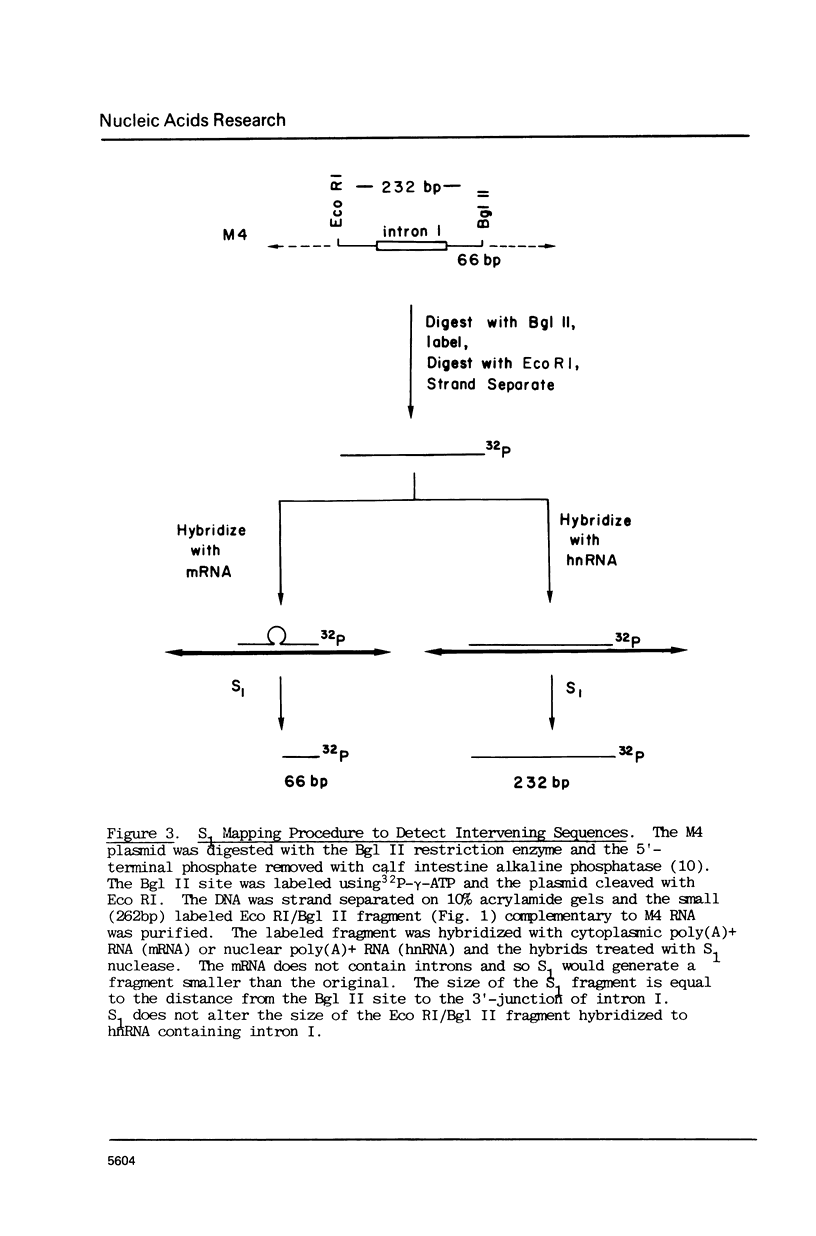
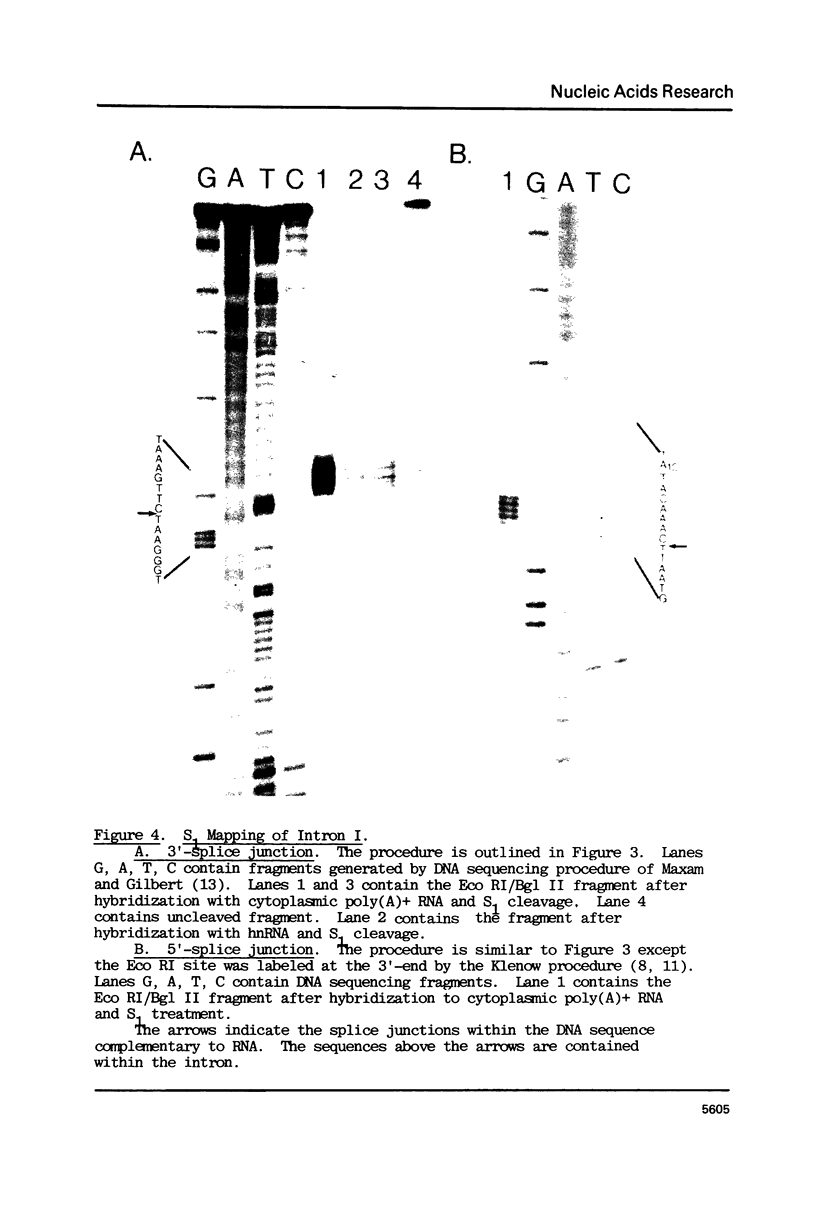
Using S1 nuclease protection experiments and DNA sequencing, we have identified two intervening sequences (introns) within a Dictyostelium gene that codes for a low abundance class mRNA. The two introns are located within the protein coding region of this gene. Both are small (approximately 100 bp) and extremely (approximately 95%) A + T rich. The splice junction sequences are similar to the splice sites in other eukaryotes. Finally, we have shown that these introns are transcribed as part of a higher molecular weight nuclear precursor.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aleström P., Akusjärvi G., Perricaudet M., Mathews M. B., Klessig D. F., Pettersson U. The gene for polypeptide IX of adenovirus type 2 and its unspliced messenger RNA. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):671–681. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80044-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berget S. M., Moore C., Sharp P. A. Spliced segments at the 5' terminus of adenovirus 2 late mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3171–3175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Benoist C., O'Hare K., Gannon F., Chambon P. Ovalbumin gene: evidence for a leader sequence in mRNA and DNA sequences at the exon-intron boundaries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4853–4857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crick F. Split genes and RNA splicing. Science. 1979 Apr 20;204(4390):264–271. doi: 10.1126/science.373120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawid I. B., Wahli W. Application of recombinant DNA technology to questions of developmental biology: a review. Dev Biol. 1979 Mar;69(1):305–328. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90294-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firtel R. A., Cockburn A., Frankel G., Hershfield V. Structural organization of the genome of Dictyostelium discoideum: analysis by EcoR1 restriction endonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1976 Apr 25;102(4):831–852. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90294-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firtel R. A., Kindle K., Huxley M. P. Structural organization and processing of the genetic transcript in the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. Fed Proc. 1976 Jan;35(1):13–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firtel R. A., Lodish H. F. A small nuclear precursor of messenger RNA in the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):295–314. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firtel R. A., Timm R., Kimmel A. R., McKeown M. Unusual nucleotide sequences at the 5' end of actin genes in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6206–6210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrberg E. A., Kindle K. L., Davidson N., Kindle K. L. The actin genes of Drosophila: a dispersed multigene family. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):365–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90511-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Sures I. Structure of a split yeast gene: complete nucleotide sequence of the actin gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2546–2550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P., Lai C. J., Dhar R., Khoury G. Splicing as a requirement for biogenesis of functional 16S mRNA of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4317–4321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer D. H., Leder P. Splicing and the formation of stable RNA. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1299–1302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90240-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel A. R., Firtel R. A. A family of short, interspersed repeat sequences at the 5' end of a set of Dictyostelium single-copy mRNAs. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):787–796. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90094-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindle K. L., Firtel R. A. Evidence that populations of Dictyostelium single-copy mRNA transcripts carry common repeat sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jun 11;6(7):2403–2422. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.7.2403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F. Two adenovirus mRNAs have a common 5' terminal leader sequence encoded at least 10 kb upstream from their main coding regions. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):9–21. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90181-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Mount S. M., Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. Are snRNPs involved in splicing? Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):220–224. doi: 10.1038/283220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F., Firtel R. A., Jacobson A. Transcription and structure of the genome of the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:899–914. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery D. L., Leung D. W., Smith M., Shalit P., Faye G., Hall B. D. Isolation and sequence of the gene for iso-2-cytochrome c in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):541–545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Steps in the processing of Ad2 mRNA: poly(A)+ nuclear sequences are conserved and poly(A) addition precedes splicing. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1477–1493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng R., Abelson J. Isolation and sequence of the gene for actin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3912–3916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunberg J. H., Kaufman R. J., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N., Schimke R. T. Structure and genomic organization of the mouse dihydrofolate reductase gene. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):355–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90510-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowekamp W., Poole S., Firtel R. A. Analysis of the multigene family coding the developmentally regulated carbohydrate-binding protein discoidin-I in D. discoideum. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):495–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90636-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T., Kaufman R. J., Alt F. W., Kellems R. F. Gene amplification and drug resistance in cultured murine cells. Science. 1978 Dec 8;202(4372):1051–1055. doi: 10.1126/science.715457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seif I., Khoury G., Dhar R. BKV splice sequences based on analysis of preferred donor and acceptor sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 25;6(10):3387–3398. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.10.3387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M., Leung D. W., Gillam S., Astell C. R., Montgomery D. L., Hall B. D. Sequence of the gene for iso-1-cytochrome c in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):753–761. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda M., Ohshima Y., Suzuki Y. Assumed initiation site of fibroin gene transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4872–4876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Padgett R. A., Stark G. R. Gene amplification causes overproduction of the first three enzymes of UMP synthesis in N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate-resistant hamster cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8679–8689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]