Studies in the past four years in humans, mice, zebrafish and cultured cells have identified the cerebral cavernous malformation (CCM) multiprotein complex, which is localized in part to endothelial and epithelial cell–cell junctions, and is important in the stability of these junctions and in vascular development (Glading et al., 2007; Mably et al., 2006; Mably et al., 2003; Whitehead et al., 2004; Wustehube et al., 2010). In humans, mutations that affect at least two members of this complex are associated with a common (~0.5% prevalence) vascular malformation that leads to substantial morbidity and mortality. In animals, mutations in components of this complex lead to defects in cardiovascular development, increased vascular permeability (Boulday et al., 2009; Guclu et al., 2005; Laberge-le Couteulx et al., 1999) and are associated with exacerbation of Wnt/β-catenin-driven pathologies, such as intestinal adenomas (Glading and Ginsberg, 2010). Recent studies have identified a physical association of this complex with the transmembrane receptor heart of glass (HEG1) and have established the role of this complex in inhibiting Rho and Rho-associated protein kinase 1/2 (ROCK1/2), to stabilize endothelial and epithelial cell–cell junctions (Crose et al., 2009; Kleaveland et al., 2009; Stockton et al., 2010; Whitehead et al., 2009), in limiting permeability of the endothelial monolayer and in regulating Wnt/β-catenin-driven transcription (Glading and Ginsberg, 2010).
KRIT1 is a component of a multiprotein CCM complex
KRIT1 (also known as CCM1) contains a C-terminal FERM (for 4.1, ezrin, radixin, moesin) domain and several ankyrin repeats. The FERM domain is subdivided into three subdomains; F1 resembles a Ras association domain and F3 resembles a phosphorylated-tyrosine-binding (PTB) domain (Hamada et al., 2003; Serebriiskii et al., 1997; Wohlgemuth et al., 2005). The N-terminal region contains multiple NPxY/F (x=any residue) motifs, one of which (N192PAY) mediates binding to the integrin-binding protein ICAP1α (also known as ITGB1BP1) (Zawistowski et al., 2002). N192PAY has been reported to bind to the KRIT1 FERM domain (Beraud-Dufour et al., 2007); however, another study failed to confirm the role of N192PAY, although that study did confirm the KRIT1 N-terminal–FERM-domain intramolecular interaction (Francalanci et al., 2009). In addition to KRIT1, heterozygous loss-of-function mutations in two other genes, CCM2 and CCM3, are linked to the development of CCM (Bergametti et al., 2005; Denier et al., 2004). Two NPxF sequences (N231PLF and N250PYF) in KRIT1 mediate binding to the PTB domain of CCM2 (Zawistowski et al., 2005b). CCM2 acts as a scaffold for Rac1, actin, MEKK3 (also known as MAP3K3) and MKK3 (also known as MAP2K3) (Uhlik et al., 2003) in macrophages. CCM3 has been reported to bind to CCM2 (Voss et al., 2007); however, others have found that CCM3 associates with protein phosphatases and germinal center kinases to a much greater extent than it does with KRIT1 or CCM2 (Goudreault et al., 2009). Importantly, null mutations of the gene encoding CCM2 in both zebrafish (Mably et al., 2006) and mice (Whitehead et al., 2009) phenocopy the loss of KRIT1. Furthermore, depletion of KRIT1 or CCM2 from endothelial cells in vitro leads to similar effects on vascular permeability (Glading et al., 2007b; Stockton et al., 2010; Whitehead et al., 2009), and genetic and biochemical studies indicate that the major phenotypic effect of deficiency of KRIT1 or CCM2 is endothelial cell autonomous (Akers et al., 2008; Glading et al., 2007b; Pagenstecher et al., 2009; Stockton et al., 2010; Whitehead et al., 2009). Although studies have suggested that CCM3 might also act in an endothelial cell autonomous manner to cause CCMs (Akers et al., 2008; Pagenstecher et al., 2009), available evidence is less compelling than for the other two genes encoding CCM proteins (e.g. Louvi et al., 2011). Taken together, the combination of genetic, biochemical and cell biological studies show that a protein complex assembles around KRIT1 and CCM2, and that it acts in a cell autonomous fashion to regulate endothelial and epithelial cell–cell junctions and vascular development.
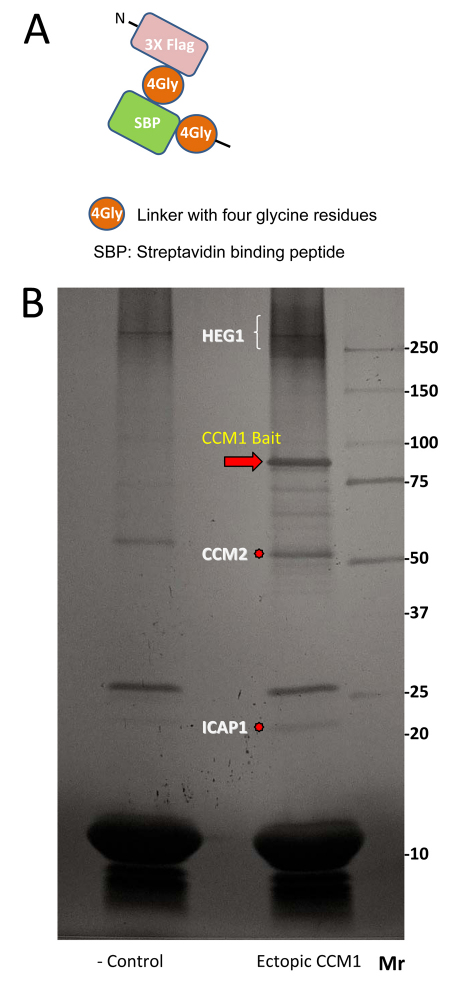
To obtain insights into the basis and regulation of interactions amongst components of this complex we have used a tandem affinity purification (TAP) tag on the core scaffold (KRIT1/CCM1) to purify it as a complex with associated proteins from U2OS cells, cells that form typical adherens junctions (Xue et al., 2005) (Fig. 1A,B). Our TAP protocol led to recovery of isolated bait protein (average yield=22%) and confirmed that ICAP1, CCM2 and HEG1 are KRIT1/CCM1-interacting proteins (Fig. 1B); however, no CCM3 was detected, confirming previous results (Goudreault et al., 2009). Here, we report on the phosphorylation sites in this CCM complex.
Fig. 1.
Tandem affinity purification of KRIT1. (A) Tandem affinity purification tag. (B) Silver stain gel of polypeptides isolated by tagged KRIT1 (right lane) and a control tag with no KRIT1 bait (left lane).
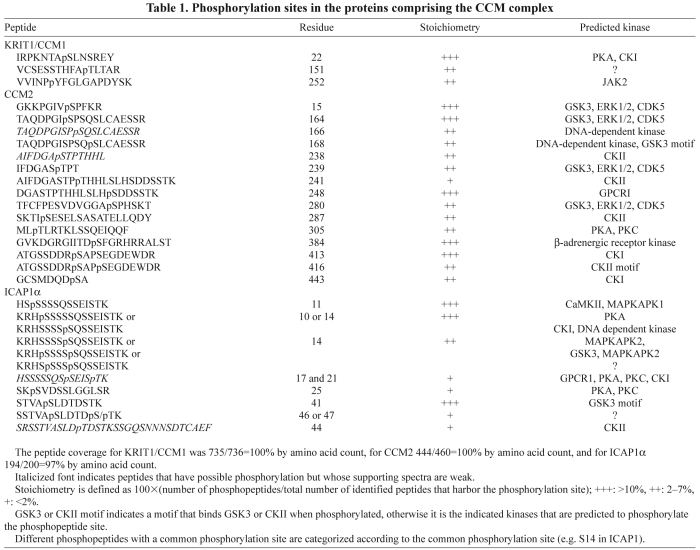
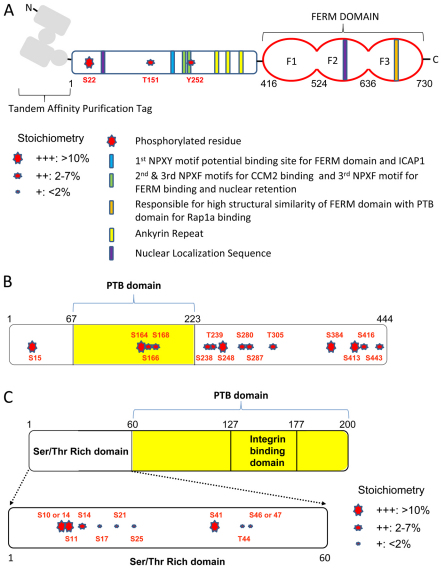
S22 was the only high-stoichiometry phosphorylation site in KRIT1/CCM1 (Table 1 and Fig. 2A). The Human Protein Reference Database PhosphoMotif finder (http://www.hprd.org/PhosphoMotif_finder) (Amanchy et al., 2007) indicates that this residue is a possible target site for protein kinase A or casein kinase I. NPxY/F motifs of KRIT1/CCM1 are known to be crucial for the interaction of KRIT1/CCM1 with ICAP1 (Zawistowski et al., 2002) and CCM2 (Zawistowski et al., 2005a), and they regulate nuclear localization (Francalanci et al., 2009). We found a low-stoichiometry tyrosine residue phosphorylation of N250PYF, a site that has been implicated in both the CCM2 binding and nuclear retention of CCM1 (Francalanci et al., 2009), and this is a possible JAK2 kinase target site.
Table 1.
Phosphorylation sites in the proteins comprising the CCM complex
Fig. 2.
Schematic of identified phosphorylation sites in the CCM complex. (A) Phosphorylation sites in KRIT1/CCM1. (B) Phosphorylation sites in CCM2. (C) Phosphorylation sites in ICAP1α. Note that the estimated stoichiometry is indicated by the size of the stars.
In CCM2, we found multiple serine/threonine phosphorylation sites scattered throughout the whole protein sequence (Table 1 and Fig. 2B). CCM2 might be the core functional unit of CCM complexes, the interaction of which with various proteins is regulated by multiple phosphorylation events. CCM2 is also a common binding partner of both KRIT1/CCM1 and CCM3. PhosphoMotif Analysis suggests that the two highest-stoichiometry sites, S15 and S164 in CCM2, are phosphorylated by GSK3 or ERK1/2. S164, S166 and S168 are phosphorylation sites within the PTB domain, suggesting that these residues might affect the interaction of CCM2 and KRIT1/CCM1. Tyrosine residue phosphorylation of CCM2 was not detected in our studies.
S11 and S41 were high-stoichiometry phosphorylation sites found in ICAP1 (Table 1 and Fig. 2C). S11 is a possible CaMKII or MAPK-activated protein kinase 1 (MAPKAPK1) target site. All of the phosphorylation sites identified on ICAP1 were located in the N-terminal serine/threonine-rich domain (amino acids 1–60). CaMKII is known to phosphorylate T38 in ICAP1, thereby increasing the binding of ICAP1 to the integrin β1 tail and thus blocking talin binding and suppressing integrin β1 integrin activation (Bouvard and Block, 1998; Harburger and Calderwood, 2009). Here, we found multiple serine/threonine phosphorylation sites in ICAP1. However, phosphorylation of T38 was not detected. Given that we specifically analyzed the fraction of ICAP1 that bound to KRIT1/CCM1 (Zawistowski et al., 2002; Zhang et al., 2001), it is possible that phosphorylation at this site leads to ICAP1 preferentially binding to integrin β1 rather than to CCM1.
Although we recovered HEG1 protein, we failed to identify any phosphorylation sites in this protein. The significance of this absence of phosphorylation is uncertain because this glycosylated membrane protein was present in multiple bands resulting in poor sequence coverage of the cytoplasmic domain.
Materials and Methods
A cDNA encoding a TAP tag of 3× FLAG peptide and a Strep-tag was subcloned 5′ of human KRIT1/CCM1 in pcDNA3.1c plasmid (TAP–CCM1). The human osteoblast U2OS cell line was transfected with TAP–CCM1 plasmid and a stable cell line was generated by geneticin selection. Cells were expanded on 10-cm culture plates and, to avoid possible keratin contamination, most procedures were performed in tissue culture hoods and all buffers were made with distilled and deionized water. In total, cells on 460 plates were scraped and lysed in the presence of Complete protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche), PhosphoStop (Roche), sodium orthovanadate (Sigma), sodium fluoride (Sigma) and calycurin (Cell Signaling). Lysates were precleared by centrifugation at 20,000 g for 15 minutes, and the supernatant was incubated with anti-FLAG M2 affinity gel (Sigma) overnight. Elution of anti-FLAG-antibody-bound bait proteins was performed with 3× FLAG peptide (Sigma) for 90 minutes, and the eluate was incubated with streptavidin ultralink resin (Pierce) for 6 hours before the resin was boiled in 2× sample buffer. Eluted proteins were separated in a Tris-glycine mini gel (4–12%; Invitrogen), and the gel was stained with the silver stain SNAPII kit (Pierce). The proteins were cut out as bands from the gel. Each band was divided into ~1-mm cubes and placed into a clean Eppendorf tube. The protein was reduced with DTT, alkylated with iodoacetamide and digested with enzymes (trypsin, chymotrypsin and elastase). Peptides extracted from each enzyme digest were eluted into a LTQ Orbitrap Velos mass spectrometer by microcapillary reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (rpHPLC) coupled to nano-electrospray ionization. The mass spectrometer was set to acquire a MS spectrum in high resolution (orbitrap) followed by up to 20 MS/MS spectra in low resolution (ion trap) using dynamic exclusion. The MS/MS spectra were searched against the specific protein sequence using the Sequest algorithm. Any peptides passing minimal scoring criteria and having putative phosphorylation sites were verified manually. All analyses were performed in the Mass Spectrometry & Proteomics Resource Core at Harvard University.
Acknowledgements
Further experimental details and raw data are posted at http://www.cellmigration.org.
Footnotes
Funding
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health: The Cell Migration Consortium [grant numbers U54 GM064346, HL106489-01 to M.H.G.]. Deposited in PMC for release after 12 months.
References
- Akers A. L., Johnson E., Steinberg G. K., Zabramski J. M., Marchuk D. A. (2008). Biallelic somatic and germline mutations in cerebral cavernous malformations (CCM): evidence for a two-hit mechanism of CCM pathogenesis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 18, 919-930 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amanchy R., Periaswamy B., Mathivanan S., Reddy R., Tattikota S. G., Pandey A. (2007). A curated compendium of phosphorylation motifs. Nat. Biotechnol. 25, 285-286 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beraud-Dufour S., Gautier R., Albiges-Rizo C., Chardin P., Faurobert E. (2007). Krit 1 interactions with microtubules and membranes are regulated by Rap1 and integrin cytoplasmic domain associated protein-1. FEBS J. 274, 5518-5532 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergametti F., Denier C., Labauge P., Arnoult M., Boetto S., Clanet M., Coubes P., Echenne B., Ibrahim R., Irthum B., et al. (2005). Mutations within the programmed cell death 10 gene cause cerebral cavernous malformations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 76, 42-51 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulday G., Blecon A., Petit N., Chareyre F., Garcia L. A., Niwa-Kawakita M., Giovannini M., Tournier-Lasserve E. (2009). Tissue-specific conditional CCM2 knockout mice establish the essential role of endothelial CCM2 in angiogenesis: implications for human cerebral cavernous malformations. Dis. Model. Mech. 2, 168-177 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvard D., Block M. R. (1998). Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II controls integrin alpha5beta1-mediated cell adhesion through the integrin cytoplasmic domain associated protein-1alpha. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 252, 46-50 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crose L. E., Hilder T. L., Sciaky N., Johnson G. L. (2009). Cerebral cavernous malformation 2 protein promotes Smad ubiquitin regulatory factor 1-mediated RhoA degradation in endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 13301-13305 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denier C., Goutagny S., Labauge P., Krivosic V., Arnoult M., Cousin A., Benabid A., Comoy J., Frerebeau P., Gilbert B., et al. (2004). Mutations within the MGC4607 gene cause cerebral cavernous malformations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 74, 326-337 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francalanci F., Avolio M., De Luca E., Longo D., Menchise V., Guazzi P., Sgro F., Marino M., Goitre L., Balzac F., et al. (2009). Structural and functional differences between KRIT1A and KRIT1B isoforms: a framework for understanding CCM pathogenesis. Exp. Cell Res. 315, 285-303 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glading A. J., Ginsberg M. H. (2010). Rap1 and Its Effector, KRIT1/CCM1, Regulate β-catenin signaling. Dis. Model. Mech. 3, 78-83 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glading A., Han J., Stockton R. A., Ginsberg M. H. (2007). KRIT-1/CCM1 is a Rap1 effector that regulates endothelial cell cell junctions. J. Cell Biol. 179, 247-254 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudreault M., D'Ambrosio L. M., Kean M. J., Mullin M. J., Larsen B. G., Sanchez A., Chaudhry S., Chen G. I., Sicheri F., Nesvizhskii A. I., et al. (2009). A PP2A phosphatase high density interaction network identifies a novel striatin-interacting phosphatase and kinase complex linked to the cerebral cavernous malformation 3 (CCM3) protein. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 8, 157-171 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guclu B., Ozturk A. K., Pricola K. L., Bilguvar K., Shin D., O'Roak B. J., Gunel M. (2005). Mutations in apoptosis-related gene, PDCD10, cause cerebral cavernous malformation 3. Neurosurgery 57, 1008-1013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada K., Shimizu T., Yonemura S., Tsukita S., Tsukita S., Hakoshima T. (2003). Structural basis of adhesion-molecule recognition by ERM proteins revealed by the crystal structure of the radixin-ICAM-2 complex. EMBO J. 22, 502-514 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harburger D. S., Calderwood D. A. (2009). Integrin signalling at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 122, 159-163 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleaveland B., Zheng X., Liu J. J., Blum Y., Tung J. J., Zou Z., Sweeney S. M., Chen M., Guo L., Lu M. M., et al. (2009). Regulation of cardiovascular development and integrity by the heart of glass-cerebral cavernous malformation protein pathway. Nat. Med. 15, 169-176 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laberge-le Couteulx S., Jung H. H., Labauge P., Houtteville J. P., Lescoat C., Cecillon M., Marechal E., Joutel A., Bach J. F., Tournier-Lasserve E. (1999). Truncating mutations in CCM1, encoding KRIT1, cause hereditary cavernous angiomas. Nat. Genet. 23, 189-193 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louvi A., Chen L., Two A. M., Zhang H., Min W., Gunel M. (2011). Loss of cerebral cavernous malformation 3 (Ccm3) in neuroglia leads to CCM and vascular pathology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108, 3737-3742 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mably J. D., Mohideen M. A., Burns C. G., Chen J. N., Fishman M. C. (2003). Heart of glass regulates the concentric growth of the heart in zebrafish. Curr. Biol. 13, 2138-2147 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mably J. D., Chuang L. P., Serluca F. C., Mohideen M. A., Chen J. N., Fishman M. C. (2006). Santa and valentine pattern concentric growth of cardiac myocardium in the zebrafish. Development 133, 3139-3146 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagenstecher A., Stahl S., Sure U., Felbor U. (2009). A two-hit mechanism causes cerebral cavernous malformations: complete inactivation of CCM1, CCM2 or CCM3 in affected endothelial cells. Hum. Mol. Genet. 18, 911-918 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serebriiskii I., Estojak J., Sonoda G., Testa J. R., Golemis E. A. (1997). Association of Krev-1/rap1a with Krit1, a novel ankyrin repeat-containing protein encoded by a gene mapping to 7q21-22. Oncogene 15, 1043-1049 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockton R. A., Shenkar R., Awad I. A., Ginsberg M. H. (2010). Cerebral cavernous malformations proteins inhibit rho kinase to stabilize vascular integrity. J. Exp. Med. I207, 881-896 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlik M. T., Abell A. N., Johnson N. L., Sun W., Cuevas B. D., Lobel-Rice K. E., Horne E. A., Dell'Acqua M. L., Johnson G. L. (2003). Rac-MEKK3-MKK3 scaffolding for p38 MAPK activation during hyperosmotic shock. Nat. Cell Biol. 5, 1104-1110 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voss K., Stahl S., Schleider E., Ullrich S., Nickel J., Mueller T. D., Felbor U. (2007). CCM3 interacts with CCM2 indicating common pathogenesis for cerebral cavernous malformations. Neurogenetics 8, 249-256 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead K. J., Plummer N. W., Adams J. A., Marchuk D. A., Li D. Y. (2004). Ccm1 is required for arterial morphogenesis: implications for the etiology of human cavernous malformations. Development 131, 1437-1448 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead K. J., Chan A. C., Navankasattusas S., Koh W., London N. R., Ling J., Mayo A. H., Drakos S. G., Jones C. A., Zhu W., et al. (2009). The cerebral cavernous malformation signaling pathway promotes vascular integrity via Rho GTPases. Nat. Med. 15, 177-184 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohlgemuth S., Kiel C., Kramer A., Serrano L., Wittinghofer F., Herrmann C. (2005). Recognizing and defining true Ras binding domains I: biochemical analysis. J. Mol. Biol. 348, 741-758 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wustehube J., Bartol A., Liebler S. S., Brutsch R., Zhu Y., Felbor U., Sure U., Augustin H. G., Fischer A. (2010). Cerebral cavernous malformation protein CCM1 inhibits sprouting angiogenesis by activating DELTA-NOTCH signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 12640-12645 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xue B., Wen C., Shi Y., Zhao D., Li C. (2005). Human NRAGE disrupts E-cadherin/beta-catenin regulated homotypic cell-cell adhesion. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 336, 247-251 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawistowski J. S., Serebriiskii I. G., Lee M. F., Golemis E. A., Marchuk D. A. (2002). KRIT1 association with the integrin-binding protein ICAP-1: a new direction in the elucidation of cerebral cavernous malformations (CCM1) pathogenesis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 11, 389-396 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawistowski J. S., Stalheim L., Uhlik M. T., Abell A. N., Ancrile B. B., Johnson G. L., Marchuk D. A. (2005a). CCM1 and CCM2 protein interactions in cell signaling: implications for cerebral cavernous malformations pathogenesis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 14, 2521-2531 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawistowski J. S., Stalheim L., Uhlik M. T., Abell A. N., Ancrile B. B., Johnson G. L., Marchuk D. A. (2005b). CCM1 and CCM2 protein interactions in cell signaling: implications for cerebral cavernous malformations pathogenesis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 14, 2521 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Clatterbuck R. E., Rigamonti D., Chang D. D., Dietz H. C. (2001). Interaction between krit1 and icap1alpha infers perturbation of integrin beta1-mediated angiogenesis in the pathogenesis of cerebral cavernous malformation. Hum. Mol. Genet. 10, 2953-2960 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]