Background
Long-term treatment with antipsychotic medications in early-episode schizophrenia spectrum disorders is common, but their short- and long-term effects on the illness are unclear. There have been numerous suggestions that people with early episodes of schizophrenia appear to respond differently than those with multiple prior episodes. The number of episodes may moderate response to drug treatment.
Objectives
To assess the effects of antipsychotic medication treatment on people with early-episode schizophrenia spectrum disorders.
Search Strategy
We searched the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group register (July 2006) as well as references of included studies. We contacted authors of studies for further data.
Selection Criteria
We included randomized clinical trials (RCTs) with a majority of first- and second-episode acute schizophrenia spectrum disorders comparing initial antipsychotic medication treatment with placebo, milieu, or psychosocial treatment.
Data Collection and Analysis
Working independently, we critically appraised records from 681 studies, of which 6 met inclusion criteria. When possible, we calculated risk ratios (RRs) and their 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for dichotomous data and weighted mean differences for continuous data. We calculated numbers needed to treat/harm (NNT/NNH) where appropriate.
Main Results
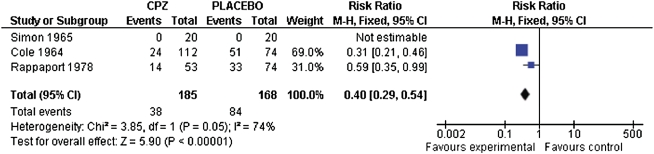
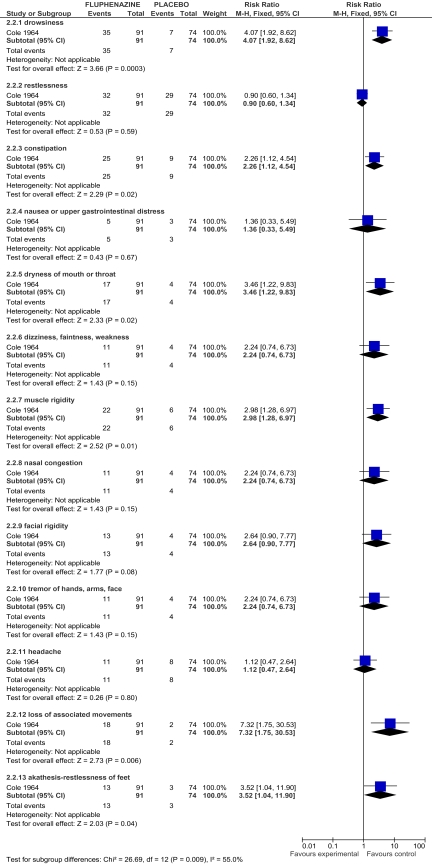
Six studies (total N = 1118) met inclusion criteria. The findings from 4 studies (N = 724) suggested that people treated with a typical antipsychotic medication are less likely to leave the study early than those treated with placebo (chlorpromazine: 3 RCTs, N = 353, RR 0.4, 95% CI 0.3–0.5, NNT = 3.2; fluphenaxine: 1 RCT, N = 240, RR 0.5, 95% CI 0.3–0.8, NNT = 5; thioridazine: 1 RCT, N = 236, RR 0.44, 95% CI 0.3–0.7, NNT = 4.3; and trifulperazine: 1 RCT, N = 94, RR 0.96, 95% CI 0.3–3.6, NNT = n/a). Two studies reported a general pattern of more frequent adverse effects for people treated with typical antipsychotic medications compared with placebo. One study reported a higher rehospitalization rate for those receiving chlorpromazine compared with placebo (N = 80, RR 2.29, 95% CI 1.3–4.0, NNH = 2.9); however, higher attrition in the placebo group is likely to have introduced a survivor bias, and this difference becomes non-significant in a sensitivity analysis on intent-to-treat participants (N = 127, RR 1.69, 95% CI 0.9–3.0). One study contributed data to a comparison of trifluoperazine with psychotherapy on long-term health and favored the trifluoperazine group (n = 92, MD Meninger Health Sickness Scale 5.8, 95% CI 1.6–0.0). However, this study is also likely to contain biases due to selection and attrition. One study found no between-group differences comparing typical antipsychotic medication with psychosocial treatment on 6-week outcome measures of global psychopathology (N = 89, MD Global Psychopathology Scale 0.01, 95% CI −0.6 to 0.6) and global improvement (N = 89, MD Global Improvement Scale −0.03, 95% CI −0.5 to 0.4), indicating no between-group differences. On the whole, there were very little useable data in the few studies meeting inclusion criteria.
Author’s Conclusions
There are only a few randomized trials of acute treatment for early-episode schizophrenia comparing initial antipsychotic medication to either placebo or psychosocial treatment. Preliminary evidence suggests that initial antipsychotic treatment may reduce attrition (see figure 1) while also increasing the risk for medication-induced adverse effects (see figure 2). Data are too limited to assess outcomes from initial antipsychotic medication treatment for individuals with an early-episode of schizophrenia.1 This finding contrasts with international agreement in published schizophrenia practice guidelines recommending treatment of early episodes of schizophrenia-type psychoses with antipsychotic medications for 6–24 months. Large-scale independent trials are urgently needed to address the discrepancy between available evidence and current clinical practice.
Fig. 1.
Leaving the study early: chlorpromazine vs placebo.
Fig. 2.
Adverse effects: fluphenazine vs placebo.
References
- 1.Bola JR, Kao D, Soydan H. Antipsychotic medication for early schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006374.pub2. (Issue 6. Art. No.: CD006374. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006374.pub2) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]