Abstract
The title compound, [Pd(C2H3OS2)2(C18H15P)], features a palladium complex with a triphenylphosphane ligand and two xanthate ligands, one of them coordinates in a bidentate and the other in a monodentate fashion, giving rise to a slightly distorted square-planar coordination of the PdII ion. As a result of this difference in the coordination modes, the C—S bond lengths are different, viz. 1.687 (2) and 1.692 (2) Å in the bidentate ligand and 1.723 (2) Å in the monodentate ligand, whereas the non-coordinating S atom has a C—S distance of 1.649 (2) Å. The crystal packing is stabilized by C—H⋯O interactions.
Related literature
For background information on xanthates, see: Karlin (2005 ▶); Friebolin et al. (2005 ▶). For crystal engineering, see: Tiekink (2003 ▶). For bond-length data, see: Allen (2002 ▶).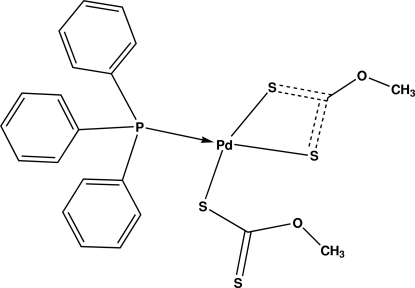
Experimental
Crystal data
[Pd(C2H3OS2)2(C18H15P)]
M r = 583.00
Triclinic,

a = 9.5595 (10) Å
b = 9.5883 (10) Å
c = 14.4661 (16) Å
α = 73.619 (1)°
β = 87.492 (2)°
γ = 69.617 (1)°
V = 1190.3 (2) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 1.22 mm−1
T = 298 K
0.30 × 0.22 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: analytical (SADABS, Bruker, 1999 ▶) T min = 0.712, T max = 0.817
9954 measured reflections
4371 independent reflections
4021 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.025
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.025
wR(F 2) = 0.064
S = 1.10
4371 reflections
274 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.32 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.42 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 1999 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 1999 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: XP in SHELXTL; software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811040487/bt5655sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811040487/bt5655Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C18—H18⋯O20i | 0.93 | 2.64 | 3.211 | 120 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Acknowledgments
RRM would like to thank CONACYT for a postdoctoral scholarship (Agreement 290586-UNAM). Support of this research by CONACYT (154732) and PAPIIT (IN201711) is gratefully acknowledged.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Xanthates ligands are a kind of compounds that can be coordinated to metal centers in different fashions, being found in coordination as monodentate, bidentate or even as a bridge, such richness in coordination modes very often leads to diverse structural motifs in the solid state (Karlin, 2005). It is precisely due to these structural features that these ligands are commonly involved in different supramolecular interactions such as D—H···S, D—H···O and S···Metal (D=C, N, O), all of these interactions being of important relevance to crystal engineering (Tiekink, 2003). Moreover, complexes including xanthate ligands in its structure have shown diverse applications at the industrial level, as chelating and flotation agents, while in bioinorganic chemistry they have found important applications as antitumoral agents (Friebolin et al. 2005).
The molecular structure of the title compound (I) shown in Figure 1, consists of two xanthate and one triphenylphosphane ligands coordinated to the Pd(II) center, in an almost square planar arrangement about the Pd(II) atom [0.0272 (3) Å]. The two xanthates ligands exhibiting different bond fashions, having one of them coordinated in a bidentate manner while the second one is attached to the palladium only by one sulfur atom in a monodentate way. The bond distances of Pd—S observed on the bidetate ligand 2.3386 (6)Å for Pd—S2 and 2.3581 (6)Å for Pd—S1 are larger than that observed Pd—S3 for the mondentate ligand. The difference between the above mentioned bond distances being due in part to the fact that the C22—S4 distance has a double bond character (1.649 (2) Å) and thus is shorter than C22—S4 (1.723 (2)Å which shows a commonly single bond character (Table 1). A revision of the Cambridge Structural Database (Allen, 2002), for Pd—S distances in bidentate and monodentate ligands, affords distance values of 2.31–2.33Å which are shorter than the data observed for the title compound (I). In absence of hydrogen bond donors, the molecules arrange as a centrosymmetric dimers generated by C—H···O and a weak intermolecular Pd–S interaction of 3.521 (2)Å.
Experimental
The title compound was synthesized by mixing Et3N (0.2 mL) and excess CS2 (2 mL) in methanol (10 mL). After stirring the resulting solution for 4 h at room temperature, trans-[(Ph3P)2PdCl2] (100 mg, 0.14 mmol) was added, affording a yellow precipitate that was filtered and washed with methanol. Crystals suitable for X-ray analysis were obtained upon recrystallization from a mixture of dichloromethane and isopropyl alcohol.
Refinement
The positional parameters of H atoms were calculated geometrically (C—H = 0.93Å for C—H arom. and 0.96 for C—H of methyl groups). The H atoms were fixed with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq and Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq of the attached non-H atom.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Crystal structure of the title compound with the numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are shown at the 40% probability level. H atoms have been omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| [Pd(C2H3OS2)2(C18H15P)] | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 583.00 | F(000) = 588 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.627 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 9.5595 (10) Å | Cell parameters from 8044 reflections |
| b = 9.5883 (10) Å | θ = 2.3–25.4° |
| c = 14.4661 (16) Å | µ = 1.22 mm−1 |
| α = 73.619 (1)° | T = 298 K |
| β = 87.492 (2)° | Prism, orange |
| γ = 69.617 (1)° | 0.30 × 0.22 × 0.20 mm |
| V = 1190.3 (2) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer | 4371 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 4021 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.025 |
| Detector resolution: 0.83 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 25.4°, θmin = 2.4° |
| ω scans | h = −11→11 |
| Absorption correction: analytical (SADABS, Bruker, 1999) | k = −11→11 |
| Tmin = 0.712, Tmax = 0.817 | l = −17→17 |
| 9954 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.025 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.064 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0336P)2 + 0.178P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.10 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 4371 reflections | Δρmax = 0.32 e Å−3 |
| 274 parameters | Δρmin = −0.42 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.0063 (7) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Pd | 0.557109 (17) | 0.946630 (17) | 0.158062 (11) | 0.03533 (8) | |
| S1 | 0.62793 (7) | 1.11131 (6) | 0.02530 (4) | 0.04484 (15) | |
| S2 | 0.77698 (7) | 0.78738 (7) | 0.10997 (4) | 0.04619 (15) | |
| S3 | 0.34534 (7) | 1.12011 (7) | 0.20223 (4) | 0.04483 (15) | |
| S4 | 0.16108 (9) | 1.44896 (8) | 0.16359 (6) | 0.0674 (2) | |
| P | 0.53719 (6) | 0.75832 (6) | 0.29129 (4) | 0.03699 (14) | |
| C1 | 0.6235 (2) | 0.5585 (2) | 0.28557 (16) | 0.0402 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.5382 (3) | 0.4710 (3) | 0.2782 (2) | 0.0540 (6) | |
| H2 | 0.4346 | 0.5130 | 0.2779 | 0.065* | |
| C3 | 0.6064 (3) | 0.3212 (3) | 0.2714 (2) | 0.0673 (8) | |
| H3 | 0.5482 | 0.2633 | 0.2661 | 0.081* | |
| C4 | 0.7577 (4) | 0.2585 (3) | 0.2723 (2) | 0.0650 (8) | |
| H4 | 0.8027 | 0.1579 | 0.2676 | 0.078* | |
| C5 | 0.8448 (3) | 0.3428 (3) | 0.2801 (2) | 0.0614 (7) | |
| H5 | 0.9484 | 0.2992 | 0.2811 | 0.074* | |
| C6 | 0.7775 (3) | 0.4931 (3) | 0.28646 (18) | 0.0511 (6) | |
| H6 | 0.8364 | 0.5503 | 0.2914 | 0.061* | |
| C7 | 0.6282 (3) | 0.7628 (3) | 0.39762 (16) | 0.0431 (5) | |
| C8 | 0.6358 (3) | 0.9006 (3) | 0.40261 (19) | 0.0527 (6) | |
| H8 | 0.5990 | 0.9893 | 0.3507 | 0.063* | |
| C9 | 0.6979 (3) | 0.9080 (4) | 0.4844 (2) | 0.0683 (8) | |
| H9 | 0.7010 | 1.0024 | 0.4876 | 0.082* | |
| C10 | 0.7548 (3) | 0.7795 (4) | 0.5605 (2) | 0.0745 (9) | |
| H10 | 0.7967 | 0.7856 | 0.6154 | 0.089* | |
| C11 | 0.7498 (4) | 0.6417 (4) | 0.5555 (2) | 0.0845 (10) | |
| H11 | 0.7905 | 0.5528 | 0.6067 | 0.101* | |
| C12 | 0.6853 (4) | 0.6327 (3) | 0.4754 (2) | 0.0739 (9) | |
| H12 | 0.6801 | 0.5384 | 0.4735 | 0.089* | |
| C13 | 0.3460 (2) | 0.7770 (2) | 0.32140 (16) | 0.0409 (5) | |
| C14 | 0.2973 (3) | 0.7726 (3) | 0.41336 (19) | 0.0536 (6) | |
| H14 | 0.3635 | 0.7585 | 0.4632 | 0.064* | |
| C15 | 0.1497 (3) | 0.7892 (4) | 0.4307 (2) | 0.0727 (9) | |
| H15 | 0.1165 | 0.7875 | 0.4923 | 0.087* | |
| C16 | 0.0524 (3) | 0.8082 (4) | 0.3579 (3) | 0.0754 (9) | |
| H16 | −0.0466 | 0.8190 | 0.3701 | 0.090* | |
| C17 | 0.1000 (3) | 0.8112 (3) | 0.2669 (2) | 0.0656 (8) | |
| H17 | 0.0340 | 0.8219 | 0.2179 | 0.079* | |
| C18 | 0.2455 (3) | 0.7983 (3) | 0.24803 (18) | 0.0521 (6) | |
| H18 | 0.2766 | 0.8039 | 0.1857 | 0.063* | |
| C19 | 0.7744 (2) | 0.9505 (3) | 0.02430 (16) | 0.0398 (5) | |
| O20 | 0.87376 (17) | 0.95924 (18) | −0.03937 (12) | 0.0483 (4) | |
| C21 | 0.9931 (3) | 0.8175 (3) | −0.0439 (2) | 0.0579 (7) | |
| H21A | 1.0437 | 0.7637 | 0.0187 | 0.087* | |
| H21B | 1.0629 | 0.8431 | −0.0894 | 0.087* | |
| H21C | 0.9516 | 0.7522 | −0.0641 | 0.087* | |
| C22 | 0.2955 (2) | 1.3103 (3) | 0.13247 (16) | 0.0414 (5) | |
| O23 | 0.3687 (2) | 1.33360 (19) | 0.05373 (13) | 0.0590 (5) | |
| C24 | 0.3206 (4) | 1.4853 (3) | −0.0161 (2) | 0.0767 (9) | |
| H24A | 0.2189 | 1.5127 | −0.0385 | 0.115* | |
| H24B | 0.3835 | 1.4834 | −0.0697 | 0.115* | |
| H24C | 0.3276 | 1.5606 | 0.0137 | 0.115* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Pd | 0.03777 (12) | 0.02838 (11) | 0.03679 (11) | −0.01107 (8) | 0.00156 (7) | −0.00519 (7) |
| S1 | 0.0442 (3) | 0.0308 (3) | 0.0494 (3) | −0.0087 (2) | 0.0092 (3) | −0.0027 (2) |
| S2 | 0.0444 (3) | 0.0313 (3) | 0.0524 (3) | −0.0074 (2) | 0.0049 (3) | −0.0038 (3) |
| S3 | 0.0462 (3) | 0.0334 (3) | 0.0465 (3) | −0.0086 (2) | 0.0072 (3) | −0.0061 (2) |
| S4 | 0.0682 (5) | 0.0440 (4) | 0.0658 (4) | 0.0038 (3) | 0.0171 (4) | −0.0105 (3) |
| P | 0.0415 (3) | 0.0315 (3) | 0.0367 (3) | −0.0151 (2) | −0.0002 (2) | −0.0046 (2) |
| C1 | 0.0460 (12) | 0.0321 (11) | 0.0396 (12) | −0.0144 (10) | 0.0015 (9) | −0.0044 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0512 (14) | 0.0393 (13) | 0.0719 (17) | −0.0182 (11) | 0.0005 (12) | −0.0130 (12) |
| C3 | 0.0733 (19) | 0.0424 (15) | 0.092 (2) | −0.0259 (14) | −0.0023 (16) | −0.0193 (15) |
| C4 | 0.079 (2) | 0.0354 (14) | 0.0713 (18) | −0.0102 (14) | 0.0053 (15) | −0.0130 (13) |
| C5 | 0.0541 (15) | 0.0444 (15) | 0.0676 (17) | −0.0055 (12) | 0.0035 (13) | −0.0033 (13) |
| C6 | 0.0478 (14) | 0.0423 (14) | 0.0576 (15) | −0.0166 (11) | −0.0018 (11) | −0.0038 (11) |
| C7 | 0.0448 (12) | 0.0462 (13) | 0.0390 (12) | −0.0183 (11) | 0.0016 (9) | −0.0100 (10) |
| C8 | 0.0506 (14) | 0.0484 (14) | 0.0602 (15) | −0.0137 (12) | −0.0036 (12) | −0.0208 (12) |
| C9 | 0.0618 (17) | 0.075 (2) | 0.076 (2) | −0.0173 (15) | −0.0012 (15) | −0.0412 (17) |
| C10 | 0.0581 (17) | 0.118 (3) | 0.0530 (17) | −0.0248 (18) | 0.0002 (13) | −0.0404 (19) |
| C11 | 0.113 (3) | 0.084 (2) | 0.0465 (16) | −0.032 (2) | −0.0208 (17) | −0.0012 (16) |
| C12 | 0.109 (2) | 0.0577 (17) | 0.0515 (16) | −0.0359 (18) | −0.0187 (16) | 0.0022 (13) |
| C13 | 0.0447 (12) | 0.0312 (11) | 0.0446 (12) | −0.0152 (10) | 0.0043 (10) | −0.0051 (9) |
| C14 | 0.0610 (16) | 0.0489 (14) | 0.0514 (14) | −0.0208 (13) | 0.0104 (12) | −0.0142 (12) |
| C15 | 0.0672 (19) | 0.075 (2) | 0.0714 (19) | −0.0249 (16) | 0.0293 (16) | −0.0181 (16) |
| C16 | 0.0468 (16) | 0.069 (2) | 0.099 (3) | −0.0192 (15) | 0.0192 (17) | −0.0101 (18) |
| C17 | 0.0473 (15) | 0.0649 (18) | 0.075 (2) | −0.0190 (14) | −0.0063 (14) | −0.0050 (15) |
| C18 | 0.0465 (13) | 0.0534 (15) | 0.0492 (14) | −0.0169 (12) | 0.0005 (11) | −0.0042 (12) |
| C19 | 0.0379 (11) | 0.0373 (12) | 0.0426 (12) | −0.0126 (10) | −0.0004 (9) | −0.0092 (10) |
| O20 | 0.0407 (9) | 0.0436 (9) | 0.0509 (9) | −0.0084 (7) | 0.0091 (7) | −0.0080 (8) |
| C21 | 0.0419 (13) | 0.0569 (16) | 0.0669 (17) | −0.0056 (12) | 0.0112 (12) | −0.0216 (14) |
| C22 | 0.0411 (12) | 0.0374 (12) | 0.0437 (12) | −0.0111 (10) | −0.0005 (10) | −0.0111 (10) |
| O23 | 0.0658 (11) | 0.0359 (9) | 0.0562 (10) | −0.0039 (8) | 0.0164 (9) | −0.0036 (8) |
| C24 | 0.093 (2) | 0.0384 (15) | 0.0670 (19) | −0.0032 (15) | 0.0225 (16) | 0.0050 (13) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Pd—P | 2.2924 (6) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| Pd—S3 | 2.3267 (6) | C10—C11 | 1.361 (5) |
| Pd—S2 | 2.3386 (6) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| Pd—S1 | 2.3581 (6) | C11—C12 | 1.373 (4) |
| S1—C19 | 1.687 (2) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| S2—C19 | 1.692 (2) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| S3—C22 | 1.723 (2) | C13—C14 | 1.384 (3) |
| S4—C22 | 1.649 (2) | C13—C18 | 1.386 (3) |
| P—C7 | 1.818 (2) | C14—C15 | 1.384 (4) |
| P—C13 | 1.819 (2) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| P—C1 | 1.827 (2) | C15—C16 | 1.367 (5) |
| C1—C2 | 1.383 (3) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C6 | 1.384 (3) | C16—C17 | 1.369 (4) |
| C2—C3 | 1.386 (4) | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C17—C18 | 1.375 (4) |
| C3—C4 | 1.359 (4) | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C18—H18 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.373 (4) | C19—O20 | 1.301 (3) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | O20—C21 | 1.455 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.387 (4) | C21—H21A | 0.9600 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C21—H21B | 0.9600 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C21—H21C | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.371 (3) | C22—O23 | 1.316 (3) |
| C7—C12 | 1.381 (3) | O23—C24 | 1.447 (3) |
| C8—C9 | 1.377 (4) | C24—H24A | 0.9600 |
| C8—H8 | 0.9300 | C24—H24B | 0.9600 |
| C9—C10 | 1.359 (4) | C24—H24C | 0.9600 |
| P—Pd—S3 | 88.08 (2) | C10—C11—C12 | 120.6 (3) |
| P—Pd—S2 | 95.32 (2) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.7 |
| S3—Pd—S2 | 175.72 (2) | C12—C11—H11 | 119.7 |
| P—Pd—S1 | 168.78 (2) | C11—C12—C7 | 120.3 (3) |
| S3—Pd—S1 | 101.78 (2) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.8 |
| S2—Pd—S1 | 74.60 (2) | C7—C12—H12 | 119.8 |
| C19—S1—Pd | 85.06 (8) | C14—C13—C18 | 119.3 (2) |
| C19—S2—Pd | 85.56 (8) | C14—C13—P | 122.88 (19) |
| C22—S3—Pd | 115.44 (8) | C18—C13—P | 117.85 (18) |
| C7—P—C13 | 105.95 (10) | C15—C14—C13 | 119.7 (3) |
| C7—P—C1 | 104.63 (10) | C15—C14—H14 | 120.2 |
| C13—P—C1 | 104.52 (10) | C13—C14—H14 | 120.2 |
| C7—P—Pd | 110.69 (8) | C16—C15—C14 | 120.4 (3) |
| C13—P—Pd | 114.35 (7) | C16—C15—H15 | 119.8 |
| C1—P—Pd | 115.78 (7) | C14—C15—H15 | 119.8 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 118.7 (2) | C15—C16—C17 | 120.3 (3) |
| C2—C1—P | 121.55 (18) | C15—C16—H16 | 119.9 |
| C6—C1—P | 119.78 (18) | C17—C16—H16 | 119.9 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 120.4 (2) | C16—C17—C18 | 120.0 (3) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.8 | C16—C17—H17 | 120.0 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.8 | C18—C17—H17 | 120.0 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.3 (3) | C17—C18—C13 | 120.3 (3) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.9 | C17—C18—H18 | 119.8 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.9 | C13—C18—H18 | 119.8 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.4 (3) | O20—C19—S1 | 119.69 (17) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.8 | O20—C19—S2 | 125.54 (17) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.8 | S1—C19—S2 | 114.77 (13) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.7 (3) | C19—O20—C21 | 118.96 (19) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.2 | O20—C21—H21A | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.2 | O20—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 120.6 (2) | H21A—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 119.7 | O20—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.7 | H21A—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C12 | 118.7 (2) | H21B—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—P | 119.16 (18) | O23—C22—S4 | 123.92 (17) |
| C12—C7—P | 122.1 (2) | O23—C22—S3 | 115.46 (16) |
| C7—C8—C9 | 120.1 (3) | S4—C22—S3 | 120.60 (14) |
| C7—C8—H8 | 120.0 | C22—O23—C24 | 119.4 (2) |
| C9—C8—H8 | 120.0 | O23—C24—H24A | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 121.1 (3) | O23—C24—H24B | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—H9 | 119.5 | H24A—C24—H24B | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 119.5 | O23—C24—H24C | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—C11 | 119.2 (3) | H24A—C24—H24C | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—H10 | 120.4 | H24B—C24—H24C | 109.5 |
| C11—C10—H10 | 120.4 | ||
| P—Pd—S1—C19 | 26.14 (14) | C13—P—C7—C12 | 81.9 (3) |
| S3—Pd—S1—C19 | 177.19 (8) | C1—P—C7—C12 | −28.2 (3) |
| S2—Pd—S1—C19 | −0.47 (8) | Pd—P—C7—C12 | −153.6 (2) |
| P—Pd—S2—C19 | −174.52 (8) | C12—C7—C8—C9 | −0.8 (4) |
| S3—Pd—S2—C19 | −32.0 (3) | P—C7—C8—C9 | 176.9 (2) |
| S1—Pd—S2—C19 | 0.46 (8) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 1.2 (4) |
| P—Pd—S3—C22 | 174.99 (9) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −0.1 (5) |
| S2—Pd—S3—C22 | 32.3 (3) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −1.4 (5) |
| S1—Pd—S3—C22 | 0.40 (9) | C10—C11—C12—C7 | 1.8 (6) |
| S3—Pd—P—C7 | −85.16 (8) | C8—C7—C12—C11 | −0.7 (5) |
| S2—Pd—P—C7 | 92.24 (8) | P—C7—C12—C11 | −178.3 (3) |
| S1—Pd—P—C7 | 66.54 (14) | C7—P—C13—C14 | −7.9 (2) |
| S3—Pd—P—C13 | 34.40 (8) | C1—P—C13—C14 | 102.3 (2) |
| S2—Pd—P—C13 | −148.20 (8) | Pd—P—C13—C14 | −130.10 (18) |
| S1—Pd—P—C13 | −173.90 (12) | C7—P—C13—C18 | 171.35 (18) |
| S3—Pd—P—C1 | 156.01 (8) | C1—P—C13—C18 | −78.4 (2) |
| S2—Pd—P—C1 | −26.60 (8) | Pd—P—C13—C18 | 49.2 (2) |
| S1—Pd—P—C1 | −52.30 (14) | C18—C13—C14—C15 | 0.1 (4) |
| C7—P—C1—C2 | 127.6 (2) | P—C13—C14—C15 | 179.3 (2) |
| C13—P—C1—C2 | 16.5 (2) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.8 (4) |
| Pd—P—C1—C2 | −110.26 (19) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | −0.2 (5) |
| C7—P—C1—C6 | −53.8 (2) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | −1.3 (5) |
| C13—P—C1—C6 | −164.93 (19) | C16—C17—C18—C13 | 2.2 (4) |
| Pd—P—C1—C6 | 68.3 (2) | C14—C13—C18—C17 | −1.5 (4) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.4 (4) | P—C13—C18—C17 | 179.2 (2) |
| P—C1—C2—C3 | 178.2 (2) | Pd—S1—C19—O20 | −179.27 (18) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.3 (5) | Pd—S1—C19—S2 | 0.68 (11) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.1 (5) | Pd—S2—C19—O20 | 179.3 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.4 (5) | Pd—S2—C19—S1 | −0.69 (11) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.0 (4) | S1—C19—O20—C21 | −175.44 (16) |
| P—C1—C6—C5 | −178.6 (2) | S2—C19—O20—C21 | 4.6 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.4 (4) | Pd—S3—C22—O23 | 9.4 (2) |
| C13—P—C7—C8 | −95.7 (2) | Pd—S3—C22—S4 | −172.25 (10) |
| C1—P—C7—C8 | 154.22 (19) | S4—C22—O23—C24 | −6.8 (4) |
| Pd—P—C7—C8 | 28.8 (2) | S3—C22—O23—C24 | 171.4 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C18—H18···O20i | 0.93 | 2.64 | 3.211 | 120. |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+2, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BT5655).
References
- Allen, F. H. (2002). Acta Cryst. B58, 380–388. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (1999). SMART, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc. Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Friebolin, W., Schilling, G., Zöller, M. & Amtmann, E. (2005). J. Med. Chem. 48, 7925–7931. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Karlin, D. K. (2005). Editor. Progress in Inorganic Chemistry, Vol. 53. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Tiekink, E. R. T. (2003). CrystEngComm, 5, 101–113.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811040487/bt5655sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811040487/bt5655Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



