Abstract
The NiIII atom in the anion of the title complex, (C9H14N)[Ni(C4N2S2)2], is coordinated by four S atoms of two maleonitriledithiolate ligands, and exhibits a square-planar coordination geometry.
Related literature
For background to designed functional materials, see: Nishijo et al. (2000 ▶); Robertson & Cronin (2002 ▶); Ni et al. (2005 ▶). For related structures, see: Ni et al. (2004 ▶); Ren et al. (2004 ▶, 2008 ▶); Duan et al. (2010 ▶). For the synthesis of disodium maleonitriledithiolate and 1-butane-pyridinium bromide, see: Davison & Holm (1967 ▶); Yao et al. (2008 ▶).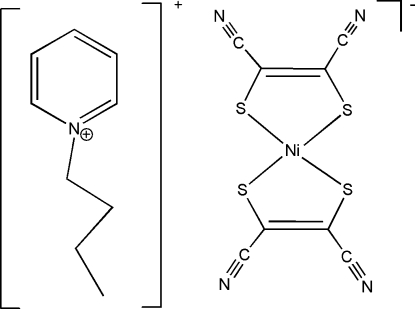
Experimental
Crystal data
(C9H14N)[Ni(C4N2S2)2]
M r = 475.30
Triclinic,

a = 9.2764 (11) Å
b = 9.9863 (11) Å
c = 12.7115 (15) Å
α = 81.695 (9)°
β = 75.882 (10)°
γ = 64.480 (11)°
V = 1029.5 (2) Å3
Z = 2
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 5.25 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.3 × 0.1 × 0.1 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2002) ▶ T min = 0.559, T max = 0.591
7461 measured reflections
3196 independent reflections
2499 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.018
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.036
wR(F 2) = 0.109
S = 1.04
3196 reflections
245 parameters
1 restraint
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.36 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.33 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2000 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2000 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: SHELXTL; software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811042103/tk2798sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811042103/tk2798Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Selected bond lengths (Å).
| Ni1—S1 | 2.1501 (8) |
| Ni1—S2 | 2.1436 (8) |
| Ni1—S3 | 2.1458 (8) |
| Ni1—S4 | 2.1461 (8) |
Acknowledgments
The author thanks the Nanjing Xiaozhuang College of Jiangsu Province, P. R. China, for financial support (grant No. 2010KYQN28).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Supramolecular chemistry and molecular crystal engineering, which is the planning and utilization of crystal-oriented syntheses for the bottom-up construction of functional molecular solids from molecules and ions, are powerful tools for the assembly of designed functional materials (Robertson & Cronin, 2002). Bis-1,2-dithiolene complexes of transition metals have been widely studied due to their novel properties and applications in the areas of near-infrared (near-IR) dyes, conducting, magnetic and non-linear optical materials (Nishijo et al., 2000; Ni et al., 2005). These applications arise due to a combination of functional properties, specific geometries and intermolecular interactions. Herein, we report the crystal structure of the title compound (I).
The molecular structure of (I) is illustrated in Fig. 1. and selected bond distances are given in Table 1. The asymmmetric units comprises one [Ni(mnt)2]- monoanion and one 1-butyl-pyridinium cation. The Ni ion in the [Ni(mnt)2]- anion is coordinated by four sulfur atoms of two mnt2- ligands, and exhibits square-planar coordination geometry. The bond lengths in the anion are in good agreement with those found in other [Ni(mnt)2]- compounds (Ni et al., 2004; Ren et al., 2004; Duan et al., 2010; Ren et al., 2008).
Experimental
All reagents and chemicals were purchased from commerical sources and used without further purification. The starting materials disodium maleonitriledithiolate (Davison et al., 1967) and 1-butyl-pyridinium bromide (Yao et al., 2008) were synthesized following the literature procedures. Disodium maleonitriledithiolate (456 mg, 2.5 mmol) and nickel chloride hexahydrate (297 mg, 1.25 mmol) were mixed under stirring in water (20 ml) at room temperature. Subsequently, a solution of 1-butyl-pyridinium bromide (1.5 mmol) in methanol (10 ml) was added to the mixture. The red precipitate that was immediately formed was filtered off and washed with methanol. Then, a methanol solution of I2 (205 mg, 0.8 mmol) was added slowly. After stirring for 40 minutes, the mixture was allowed to stand overnight. The microcrystals formed were recrystallized from acetone to give black blocks.
Refinement
The C-bound H atoms were geometrically placed (C—H = 0.93–0.97 Å) and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = 1.2–1.5Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structures of the ionic components of (I), showing the atom-numbering scheme and displacement ellipsoids at the 30% probability level.
Crystal data
| (C9H14N)[Ni(C4N2S2)2] | V = 1029.5 (2) Å3 |
| Mr = 475.30 | Z = 2 |
| Triclinic, P1 | F(000) = 486 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Dx = 1.533 Mg m−3 |
| a = 9.2764 (11) Å | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| b = 9.9863 (11) Å | µ = 5.25 mm−1 |
| c = 12.7115 (15) Å | T = 293 K |
| α = 81.695 (9)° | Block, black |
| β = 75.882 (10)° | 0.3 × 0.1 × 0.1 mm |
| γ = 64.480 (11)° |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer | 3196 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2499 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.018 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 62.6°, θmin = 3.6° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2002) | h = −10→9 |
| Tmin = 0.559, Tmax = 0.591 | k = −11→11 |
| 7461 measured reflections | l = −14→12 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.036 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.109 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.04 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0752P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3196 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 245 parameters | Δρmax = 0.36 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Δρmin = −0.33 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Ni1 | 0.17351 (5) | 0.21297 (4) | 0.32522 (3) | 0.05459 (18) | |
| S1 | −0.01043 (8) | 0.19088 (7) | 0.45807 (6) | 0.0601 (2) | |
| S2 | 0.04693 (8) | 0.45024 (7) | 0.31675 (6) | 0.0634 (2) | |
| S3 | 0.34944 (8) | 0.23715 (8) | 0.18766 (6) | 0.0646 (2) | |
| S4 | 0.30030 (9) | −0.02462 (7) | 0.33157 (6) | 0.0681 (2) | |
| N1 | −0.3268 (3) | 0.7577 (3) | 0.4479 (2) | 0.0791 (7) | |
| N2 | −0.4145 (3) | 0.4193 (3) | 0.6218 (2) | 0.0862 (8) | |
| N3 | 0.6747 (3) | −0.3235 (3) | 0.1797 (2) | 0.0886 (8) | |
| N4 | 0.7294 (3) | 0.0134 (3) | 0.0023 (2) | 0.0882 (8) | |
| N5 | 0.1415 (3) | 0.7746 (2) | 0.81191 (17) | 0.0575 (5) | |
| C1 | −0.2966 (3) | 0.3967 (3) | 0.5591 (2) | 0.0611 (7) | |
| C2 | −0.1507 (3) | 0.3709 (3) | 0.4772 (2) | 0.0531 (6) | |
| C3 | −0.2387 (3) | 0.6364 (3) | 0.4331 (2) | 0.0599 (7) | |
| C4 | −0.1257 (3) | 0.4844 (3) | 0.4169 (2) | 0.0550 (6) | |
| C5 | 0.6208 (3) | 0.0325 (3) | 0.0733 (2) | 0.0652 (7) | |
| C6 | 0.4856 (3) | 0.0568 (3) | 0.1630 (2) | 0.0565 (6) | |
| C7 | 0.4645 (3) | −0.0567 (3) | 0.2251 (2) | 0.0569 (6) | |
| C8 | 0.5794 (3) | −0.2072 (3) | 0.2023 (2) | 0.0659 (7) | |
| C9 | 0.2814 (3) | 0.6993 (3) | 0.7434 (2) | 0.0650 (7) | |
| H9 | 0.3298 | 0.5961 | 0.7497 | 0.078* | |
| C10 | 0.3530 (4) | 0.7722 (3) | 0.6651 (2) | 0.0731 (8) | |
| H10 | 0.4497 | 0.7186 | 0.6182 | 0.088* | |
| C11 | 0.2837 (4) | 0.9231 (4) | 0.6549 (2) | 0.0777 (9) | |
| H11 | 0.3331 | 0.9734 | 0.6020 | 0.093* | |
| C12 | 0.1386 (4) | 1.0006 (3) | 0.7248 (3) | 0.0782 (9) | |
| H12 | 0.0884 | 1.1037 | 0.7190 | 0.094* | |
| C13 | 0.0705 (4) | 0.9233 (3) | 0.8022 (2) | 0.0686 (8) | |
| H13 | −0.0272 | 0.9748 | 0.8491 | 0.082* | |
| C14 | 0.0666 (4) | 0.6954 (3) | 0.8999 (2) | 0.0675 (7) | |
| H14A | 0.1108 | 0.5915 | 0.8837 | 0.081* | |
| H14B | −0.0502 | 0.7374 | 0.9038 | 0.081* | |
| C15 | 0.0995 (4) | 0.7078 (4) | 1.0100 (2) | 0.0785 (9) | |
| H15A | 0.0642 | 0.8119 | 1.0222 | 0.094* | |
| H15B | 0.0340 | 0.6697 | 1.0668 | 0.094* | |
| C16 | 0.2730 (4) | 0.6270 (4) | 1.0199 (3) | 0.0827 (9) | |
| H16A | 0.3399 | 0.6628 | 0.9625 | 0.099* | |
| H16B | 0.3082 | 0.5220 | 1.0108 | 0.099* | |
| C17 | 0.2978 (4) | 0.6479 (4) | 1.1299 (3) | 0.0867 (10) | |
| H17A | 0.2674 | 0.7513 | 1.1377 | 0.130* | |
| H17B | 0.4104 | 0.5924 | 1.1341 | 0.130* | |
| H17C | 0.2311 | 0.6131 | 1.1868 | 0.130* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Ni1 | 0.0448 (3) | 0.0471 (3) | 0.0603 (3) | −0.0124 (2) | −0.0012 (2) | −0.0050 (2) |
| S1 | 0.0525 (4) | 0.0452 (4) | 0.0670 (4) | −0.0135 (3) | 0.0015 (3) | −0.0008 (3) |
| S2 | 0.0567 (4) | 0.0489 (4) | 0.0689 (4) | −0.0174 (3) | 0.0060 (3) | −0.0021 (3) |
| S3 | 0.0525 (4) | 0.0501 (4) | 0.0736 (4) | −0.0146 (3) | 0.0055 (3) | −0.0022 (3) |
| S4 | 0.0579 (4) | 0.0488 (4) | 0.0742 (5) | −0.0127 (3) | 0.0096 (4) | −0.0021 (3) |
| N1 | 0.0769 (17) | 0.0505 (15) | 0.0934 (19) | −0.0155 (13) | −0.0048 (14) | −0.0097 (13) |
| N2 | 0.0728 (18) | 0.0701 (17) | 0.0859 (18) | −0.0194 (14) | 0.0192 (15) | −0.0071 (14) |
| N3 | 0.0788 (18) | 0.0535 (16) | 0.103 (2) | −0.0110 (14) | 0.0082 (15) | −0.0122 (14) |
| N4 | 0.0702 (18) | 0.0761 (18) | 0.0905 (19) | −0.0213 (14) | 0.0174 (16) | −0.0071 (15) |
| N5 | 0.0505 (12) | 0.0568 (13) | 0.0561 (12) | −0.0137 (10) | −0.0055 (10) | −0.0116 (10) |
| C1 | 0.0588 (17) | 0.0468 (14) | 0.0640 (16) | −0.0144 (12) | −0.0012 (14) | −0.0049 (12) |
| C2 | 0.0487 (14) | 0.0487 (14) | 0.0529 (13) | −0.0139 (11) | −0.0031 (12) | −0.0079 (11) |
| C3 | 0.0610 (17) | 0.0499 (17) | 0.0608 (15) | −0.0200 (13) | −0.0031 (13) | −0.0034 (12) |
| C4 | 0.0512 (15) | 0.0477 (14) | 0.0581 (14) | −0.0143 (11) | −0.0040 (12) | −0.0104 (12) |
| C5 | 0.0555 (17) | 0.0548 (16) | 0.0709 (18) | −0.0164 (13) | 0.0016 (15) | −0.0049 (13) |
| C6 | 0.0425 (14) | 0.0557 (15) | 0.0617 (15) | −0.0135 (11) | −0.0023 (12) | −0.0097 (12) |
| C7 | 0.0469 (14) | 0.0512 (15) | 0.0615 (15) | −0.0125 (12) | −0.0024 (12) | −0.0091 (12) |
| C8 | 0.0583 (17) | 0.0542 (17) | 0.0709 (17) | −0.0181 (14) | 0.0033 (14) | −0.0048 (14) |
| C9 | 0.0559 (17) | 0.0590 (16) | 0.0660 (17) | −0.0105 (13) | −0.0073 (14) | −0.0122 (14) |
| C10 | 0.0630 (18) | 0.075 (2) | 0.0645 (17) | −0.0190 (16) | 0.0043 (15) | −0.0130 (15) |
| C11 | 0.086 (2) | 0.081 (2) | 0.0653 (17) | −0.0384 (18) | −0.0079 (17) | 0.0008 (16) |
| C12 | 0.090 (2) | 0.0564 (17) | 0.0769 (19) | −0.0210 (16) | −0.0151 (18) | −0.0030 (15) |
| C13 | 0.0653 (18) | 0.0539 (16) | 0.0689 (17) | −0.0092 (14) | −0.0057 (15) | −0.0130 (14) |
| C14 | 0.0621 (18) | 0.0705 (18) | 0.0689 (17) | −0.0297 (15) | −0.0060 (14) | −0.0053 (14) |
| C15 | 0.072 (2) | 0.078 (2) | 0.0735 (18) | −0.0302 (16) | 0.0003 (16) | 0.0052 (16) |
| C16 | 0.083 (2) | 0.071 (2) | 0.082 (2) | −0.0255 (17) | −0.0114 (18) | 0.0043 (16) |
| C17 | 0.096 (2) | 0.093 (2) | 0.079 (2) | −0.046 (2) | −0.0262 (19) | 0.0118 (18) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Ni1—S1 | 2.1501 (8) | C9—C10 | 1.359 (4) |
| Ni1—S2 | 2.1436 (8) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| Ni1—S3 | 2.1458 (8) | C10—C11 | 1.361 (4) |
| Ni1—S4 | 2.1461 (8) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| S1—C2 | 1.715 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.384 (4) |
| S2—C4 | 1.721 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| S3—C6 | 1.717 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.364 (4) |
| S4—C7 | 1.719 (3) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C3 | 1.145 (3) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| N2—C1 | 1.139 (4) | C14—C15 | 1.536 (4) |
| N3—C8 | 1.141 (4) | C14—H14A | 0.9700 |
| N4—C5 | 1.143 (3) | C14—H14B | 0.9700 |
| N5—C13 | 1.341 (4) | C15—C16 | 1.485 (4) |
| N5—C9 | 1.344 (3) | C15—H15A | 0.9700 |
| N5—C14 | 1.483 (3) | C15—H15B | 0.9700 |
| C1—C2 | 1.439 (4) | C16—C17 | 1.527 (5) |
| C2—C4 | 1.348 (4) | C16—H16A | 0.9700 |
| C3—C4 | 1.435 (4) | C16—H16B | 0.9700 |
| C5—C6 | 1.432 (4) | C17—H17A | 0.9600 |
| C6—C7 | 1.343 (4) | C17—H17B | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.440 (4) | C17—H17C | 0.9600 |
| S2—Ni1—S3 | 86.97 (3) | C11—C10—H10 | 119.8 |
| S2—Ni1—S4 | 179.28 (3) | C10—C11—C12 | 118.9 (3) |
| S3—Ni1—S4 | 92.59 (3) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.6 |
| S2—Ni1—S1 | 92.34 (3) | C12—C11—H11 | 120.6 |
| S3—Ni1—S1 | 177.33 (3) | C13—C12—C11 | 119.0 (3) |
| S4—Ni1—S1 | 88.08 (3) | C13—C12—H12 | 120.5 |
| C2—S1—Ni1 | 103.03 (9) | C11—C12—H12 | 120.5 |
| C4—S2—Ni1 | 103.36 (9) | N5—C13—C12 | 121.3 (3) |
| C6—S3—Ni1 | 102.87 (10) | N5—C13—H13 | 119.3 |
| C7—S4—Ni1 | 102.92 (9) | C12—C13—H13 | 119.3 |
| C13—N5—C9 | 119.7 (3) | N5—C14—C15 | 111.1 (2) |
| C13—N5—C14 | 119.5 (2) | N5—C14—H14A | 109.4 |
| C9—N5—C14 | 120.7 (2) | C15—C14—H14A | 109.4 |
| N2—C1—C2 | 178.1 (3) | N5—C14—H14B | 109.4 |
| C4—C2—C1 | 121.1 (2) | C15—C14—H14B | 109.4 |
| C4—C2—S1 | 121.02 (19) | H14A—C14—H14B | 108.0 |
| C1—C2—S1 | 117.88 (19) | C16—C15—C14 | 114.5 (3) |
| N1—C3—C4 | 178.3 (3) | C16—C15—H15A | 108.6 |
| C2—C4—C3 | 122.3 (2) | C14—C15—H15A | 108.6 |
| C2—C4—S2 | 120.21 (19) | C16—C15—H15B | 108.6 |
| C3—C4—S2 | 117.5 (2) | C14—C15—H15B | 108.6 |
| N4—C5—C6 | 179.3 (3) | H15A—C15—H15B | 107.6 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 121.6 (2) | C15—C16—C17 | 111.7 (3) |
| C7—C6—S3 | 120.9 (2) | C15—C16—H16A | 109.3 |
| C5—C6—S3 | 117.5 (2) | C17—C16—H16A | 109.3 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 120.0 (2) | C15—C16—H16B | 109.3 |
| C6—C7—S4 | 120.7 (2) | C17—C16—H16B | 109.3 |
| C8—C7—S4 | 119.3 (2) | H16A—C16—H16B | 107.9 |
| N3—C8—C7 | 176.4 (3) | C16—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| N5—C9—C10 | 120.7 (3) | C16—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| N5—C9—H9 | 119.6 | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—H9 | 119.6 | C16—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—C11 | 120.3 (3) | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—H10 | 119.8 | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: TK2798).
References
- Bruker (2000). SMART and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Davison, A. & Holm, H. R. (1967). Inorg. Synth. 10, 8–26.
- Duan, H. B., Ren, X. M. & Meng, Q. J. (2010). Coord. Chem. Rev. 254, 1509–1522.
- Ni, C. L., Dang, D. B., Song, Y., Song, G., Li, Y. Z., Ni, Z. P., Tian, Z. F., Wen, L. L. & Meng, Q. J. (2004). Chem. Phys. Lett. 396, 353–358.
- Ni, Z. P., Ren, X. M., Ma, J., Xie, J. L., Ni, C. L., Chen, Z. D. & Meng, Q. J. (2005). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 14330–14338. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Nishijo, J., Ogura, E., Yamaura, J., Miyazaki, A., Enoki, T., Takano, T., Kuwatani, Y. & Lyoda, M. (2000). Solid State Commun. 116, 661–664.
- Ren, X. M., Okudera, H., Kremer, R. K., Song, Y., He, C., Meng, Q. J. & Wu, P. H. (2004). Inorg. Chem. 43, 2569–2576. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ren, X. M., Sui, Y. X., Liu, G. X. & Xie, J. L. (2008). J. Phys. Chem. A, 112, 8009–8014. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Robertson, N. & Cronin, L. (2002). Coord. Chem. Rev. 227, 93–127.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2002). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Yao, B. Q., Sun, J. S., Tian, Z. F., Ren, X. M., Gu, D. W., Shen, L. J. & Xie, J. L. (2008). Polyhedron, 27, 2833–2844.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811042103/tk2798sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811042103/tk2798Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



