Abstract
The title compound, [Cu(C2O4)(C5H8N2)2]n, is composed of one-dimensional linear chains running parallel to the a axis. In the chain, trans-[Cu(imidazole)2]2+ units are sequentially bridged by bis-bidentate oxalate ligands, resulting in an octahedral CuO4N2 donor set. The Cu⋯Cu separation through the oxalate bridge is 5.620 (5) Å. Both the Cu atoms and the C—C bond of the oxalate bridge are bisected by inversion centres.
Related literature
For general background on ferroelectric organic compounds with framework structures, see: Fu et al. (2009 ▶); Ye et al. (2006 ▶); Zhang et al. (2008 ▶, 2010 ▶).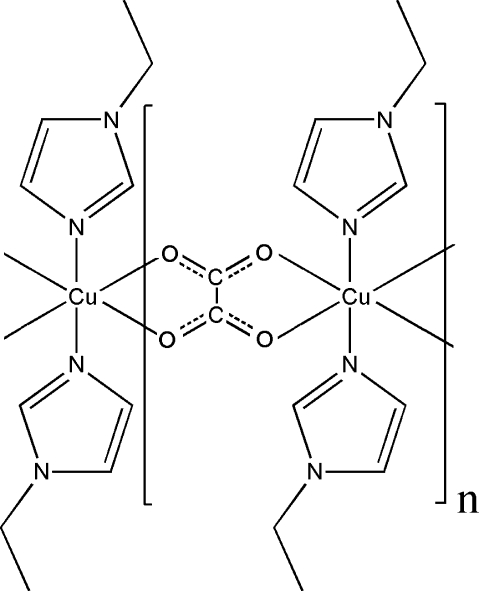
Experimental
Crystal data
[Cu(C2O4)(C5H8N2)2]
M r = 343.83
Monoclinic,
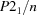
a = 5.6200 (11) Å
b = 8.8577 (18) Å
c = 14.481 (3) Å
β = 96.55 (3)°
V = 716.2 (2) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 1.55 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.30 × 0.25 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Rigaku SCXmini diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.635, T max = 0.734
7300 measured reflections
1653 independent reflections
1267 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.062
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.040
wR(F 2) = 0.092
S = 1.05
1653 reflections
98 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.48 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.33 e Å−3
Data collection: CrystalClear (Rigaku, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: CrystalClear; data reduction: CrystalClear; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811043121/bg2425sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811043121/bg2425Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Southeast University.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
As part of our ongoing study of potential ferroelectric materials we have determined the structure of the present copper complex and examined its dielectric behaviour with temperature. This is the usual method for detecting these materials (Fu et al., 2009; Ye et al., 2006; Zhang et al., 2008; Zhang et al., 2010). Unfortunately, the dielectric constant for the title compound, Cu[C5H8N]2C2O4, (I) does not show any behavior indicating the onset of a ferroelectric phase change over the range 80 K to 298 K (m.p.319–329).
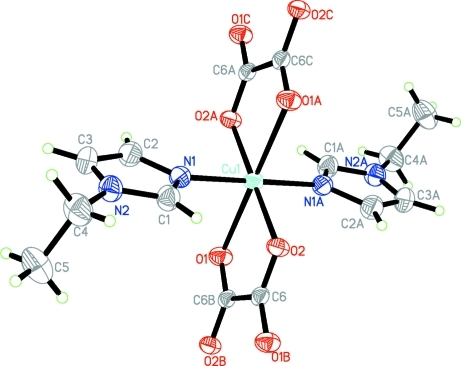
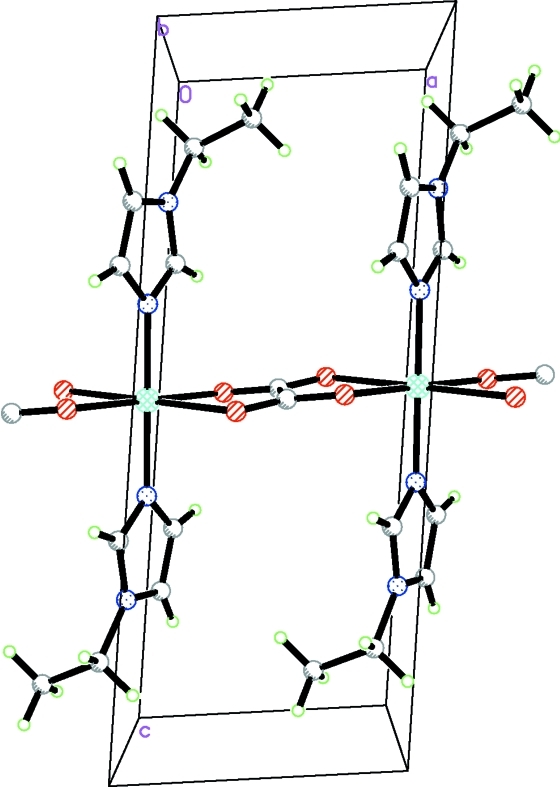
The Cu atoms are located on crystallographic inversion centers, and are coordinated to four oxygen atoms of two bridging oxalato ligands, also bisected by inversion centres, and two endocyclic nitrogen atoms from two crystallograhically related imidazole molecules, resulting in octahedral MO4N2 donor sets. Fig. 2 suggests the way in which oxalato-bridged chains build up. The Cu — Cu intrachain separation is 5.620 (5) Å.
Experimental
A mixture of 1-ethyl imidazole (1.9 g, 20 mmol), cupric oxalate (1.5 g, 10 mmol) in water was stirred for several days at ambient temperature; blue block crystals were obtained on standing.
Refinement
All H atoms were placed in geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms with C—H = 0.93–0.96 Å, and with Uĩso(H) = 1.2 Uĩso(C) or 1.5 Uĩso(C) for ethy H atoms..
Figures
Fig. 1.
Ellipsoid plot of (I), ( 50% probability level). Symmetry codes A: -x, 1-y, 1-z. B: 1-x, 1-y, 1-z. C: -1+x, y, z.
Fig. 2.
Packing diagram of the title compound showing the way in which chains are built up.
Crystal data
| [Cu(C2O4)(C5H8N2)2] | F(000) = 354 |
| Mr = 343.83 | Dx = 1.594 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 1653 reflections |
| a = 5.6200 (11) Å | θ = 2.3–27.5° |
| b = 8.8577 (18) Å | µ = 1.55 mm−1 |
| c = 14.481 (3) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 96.55 (3)° | Block, blue |
| V = 716.2 (2) Å3 | 0.30 × 0.25 × 0.20 mm |
| Z = 2 |
Data collection
| Rigaku SCXmini diffractometer | 1267 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.062 |
| graphite | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 3.7° |
| ω scans | h = −7→7 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku, 2005) | k = −11→11 |
| Tmin = 0.635, Tmax = 0.734 | l = −18→18 |
| 7300 measured reflections | 2 standard reflections every 150 reflections |
| 1653 independent reflections | intensity decay: none |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.040 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.092 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0361P)2 + 0.3394P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 1653 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 98 parameters | Δρmax = 0.48 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.33 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cu1 | 0.0000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.02341 (16) | |
| C1 | 0.0677 (5) | 0.4366 (4) | 0.3025 (2) | 0.0326 (7) | |
| H1 | 0.1452 | 0.3463 | 0.3194 | 0.039* | |
| C2 | −0.1151 (5) | 0.6469 (4) | 0.3090 (2) | 0.0365 (7) | |
| H2 | −0.1900 | 0.7304 | 0.3318 | 0.044* | |
| C3 | −0.0853 (6) | 0.6229 (4) | 0.2184 (2) | 0.0397 (8) | |
| H3 | −0.1337 | 0.6861 | 0.1685 | 0.048* | |
| C4 | 0.1083 (6) | 0.4132 (4) | 0.1331 (2) | 0.0439 (8) | |
| H4A | −0.0227 | 0.4136 | 0.0833 | 0.053* | |
| H4B | 0.1477 | 0.3088 | 0.1482 | 0.053* | |
| C5 | 0.3213 (7) | 0.4885 (4) | 0.0999 (3) | 0.0534 (9) | |
| H5A | 0.2801 | 0.5899 | 0.0809 | 0.080* | |
| H5B | 0.3701 | 0.4333 | 0.0482 | 0.080* | |
| H5C | 0.4505 | 0.4906 | 0.1494 | 0.080* | |
| C6 | 0.4839 (4) | 0.4123 (3) | 0.49195 (17) | 0.0210 (5) | |
| N1 | −0.0177 (4) | 0.5292 (3) | 0.36168 (15) | 0.0282 (6) | |
| N2 | 0.0296 (4) | 0.4876 (3) | 0.21516 (16) | 0.0339 (6) | |
| O1 | 0.3372 (3) | 0.6619 (2) | 0.52150 (13) | 0.0291 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.2754 (3) | 0.3599 (2) | 0.49398 (12) | 0.0259 (4) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cu1 | 0.0188 (2) | 0.0301 (3) | 0.0218 (2) | 0.0016 (2) | 0.00409 (16) | −0.0002 (2) |
| C1 | 0.0357 (16) | 0.0345 (16) | 0.0279 (16) | 0.0039 (14) | 0.0056 (13) | 0.0016 (13) |
| C2 | 0.0367 (16) | 0.0403 (18) | 0.0333 (16) | 0.0065 (14) | 0.0067 (13) | 0.0027 (14) |
| C3 | 0.0414 (17) | 0.0478 (19) | 0.0291 (16) | 0.0012 (16) | 0.0010 (13) | 0.0095 (15) |
| C4 | 0.050 (2) | 0.056 (2) | 0.0266 (16) | −0.0079 (17) | 0.0082 (14) | −0.0087 (15) |
| C5 | 0.063 (2) | 0.050 (2) | 0.052 (2) | −0.0054 (19) | 0.0277 (19) | 0.0000 (18) |
| C6 | 0.0211 (12) | 0.0244 (14) | 0.0172 (12) | 0.0034 (12) | 0.0008 (10) | 0.0010 (11) |
| N1 | 0.0265 (12) | 0.0336 (15) | 0.0248 (12) | 0.0027 (10) | 0.0048 (10) | 0.0015 (10) |
| N2 | 0.0358 (13) | 0.0422 (15) | 0.0238 (12) | −0.0023 (12) | 0.0042 (10) | −0.0010 (11) |
| O1 | 0.0235 (9) | 0.0270 (11) | 0.0374 (11) | 0.0020 (8) | 0.0069 (8) | −0.0030 (9) |
| O2 | 0.0197 (9) | 0.0269 (10) | 0.0316 (10) | −0.0014 (8) | 0.0054 (8) | −0.0003 (9) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cu1—O2 | 1.9935 (18) | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| Cu1—O2i | 1.9935 (18) | C4—N2 | 1.470 (4) |
| Cu1—N1 | 2.011 (2) | C4—C5 | 1.497 (4) |
| Cu1—N1i | 2.011 (2) | C4—H4A | 0.9700 |
| Cu1—O1i | 2.3684 (18) | C4—H4B | 0.9700 |
| Cu1—O1 | 2.3684 (19) | C5—H5A | 0.9600 |
| C1—N1 | 1.316 (4) | C5—H5B | 0.9600 |
| C1—N2 | 1.337 (4) | C5—H5C | 0.9600 |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | C6—O1ii | 1.235 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.359 (4) | C6—O2 | 1.264 (3) |
| C2—N1 | 1.368 (4) | C6—C6ii | 1.579 (5) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | O1—C6ii | 1.235 (3) |
| C3—N2 | 1.365 (4) | ||
| O2—Cu1—O2i | 180.000 (1) | N2—C4—C5 | 112.7 (3) |
| O2—Cu1—N1 | 89.27 (8) | N2—C4—H4A | 109.1 |
| O2i—Cu1—N1 | 90.73 (8) | C5—C4—H4A | 109.1 |
| O2—Cu1—N1i | 90.73 (8) | N2—C4—H4B | 109.1 |
| O2i—Cu1—N1i | 89.27 (8) | C5—C4—H4B | 109.1 |
| N1—Cu1—N1i | 180.000 (1) | H4A—C4—H4B | 107.8 |
| O2—Cu1—O1i | 103.35 (7) | C4—C5—H5A | 109.5 |
| O2i—Cu1—O1i | 76.65 (7) | C4—C5—H5B | 109.5 |
| N1—Cu1—O1i | 89.94 (8) | H5A—C5—H5B | 109.5 |
| N1i—Cu1—O1i | 90.06 (8) | C4—C5—H5C | 109.5 |
| O2—Cu1—O1 | 76.65 (7) | H5A—C5—H5C | 109.5 |
| O2i—Cu1—O1 | 103.35 (7) | H5B—C5—H5C | 109.5 |
| N1—Cu1—O1 | 90.06 (8) | O1ii—C6—O2 | 125.6 (2) |
| N1i—Cu1—O1 | 89.94 (8) | O1ii—C6—C6ii | 117.7 (3) |
| O1i—Cu1—O1 | 180.00 (7) | O2—C6—C6ii | 116.7 (3) |
| N1—C1—N2 | 112.0 (3) | C1—N1—C2 | 105.3 (2) |
| N1—C1—H1 | 124.0 | C1—N1—Cu1 | 126.0 (2) |
| N2—C1—H1 | 124.0 | C2—N1—Cu1 | 128.6 (2) |
| C3—C2—N1 | 109.5 (3) | C1—N2—C3 | 106.8 (2) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 125.2 | C1—N2—C4 | 125.6 (3) |
| N1—C2—H2 | 125.2 | C3—N2—C4 | 127.5 (3) |
| C2—C3—N2 | 106.3 (3) | C6ii—O1—Cu1 | 108.12 (16) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 126.8 | C6—O2—Cu1 | 119.93 (16) |
| N2—C3—H3 | 126.8 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+1, −z+1; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BG2425).
References
- Fu, D.-W., Ge, J.-Z., Dai, J., Ye, H.-Y. & Qu, Z.-R. (2009). Inorg. Chem. Commun. 12, 994–997.
- Rigaku (2005). CrystalClear Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ye, Q., Song, Y.-M., Wang, G.-X., Chen, K. & Fu, D.-W. (2006). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 6554–6555. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W., Xiong, R.-G. & Huang, S.-P. D. (2008). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 10468–10469. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W., Ye, H.-Y., Cai, H.-L., Ge, J.-Z. & Xiong, R.-G. (2010). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 7300–7302. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811043121/bg2425sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811043121/bg2425Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report