Abstract
Over the centuries, a significant part of the Brazilian fauna is widely sold, more specifically in retail stores or street markets. The objective was to characterize the sale of medicinal animals in five large northeast cities. Information about the sale of zootherapeutic items was obtained in the cities of Aracaju-SE, Fortaleza-CE, Maceio-AL, Recife-PE, and Salvador-BA. A total of 68 animal species were sold for medicinal purposes in the cities studied; these are the first results on the use and sale of zootherapeutics in the markets of Aracaju, Fortaleza, and Salvador and first recorded on the medicinal use of the Achatina fulica, Trachycardium muricatum, Philodryas olfersii, Desmodus rotundus, and Leptodactylus vastus. Knowledge of the fauna utilized popular medicine is indispensable for conservation, demonstrating that research on this subject is necessary to determine appropriate practices for the management of the fauna.
1. Introduction
Brazil has a rich diversity of animal species, which, along with its extensive cultural diversity, is reflected in a complex knowledge of the uses of faunistic resources [1–3]. Over the centuries, a significant part of the fauna has been utilized for alternative therapeutic agents by different people of the country [1, 4], a practice that has been perpetuated since colonial times and currently is widely spread among rural and urban communities in various regions of Brazil [5, 6]. In the cities, zootherapeutic products are widely sold, more specifically in retail stores or street markets as noted by recent ethnozoological studies [1, 4, 7–12].
Studies carried out in stores and street markets for the purpose of evaluating the commerce of medicinal animals are scarce [13]. Albuquerque et al. [14] affirm that these outlets can, on a small scale, represent the biodiversity of a region, making it possible to identify areas of extensive exploitation, which can provide information to help monitor the regional biodiversity. From an ecological perspective, the sale of plants and animals at these locations makes them important, since the demand for these resources can have direct and indirect implications on the diversity exploited. Thus, as pointed out by Almeida and Albuquerque [7], the information obtained in these commercial centers can be utilized for the formulation of rational strategies in the commercialization and use of these resources.
Considering that various animal species sold for medicinal use are on lists of threatened species [15], the ecological implications associated with this modality of exploitation of fauna are evident. Whiting et al. [16] noted that biologists and ecologists have neglected information about traditional commerce in devising strategies for the conservation of the species utilized for the production of traditional remedies. Therefore, ethnozoological studies are important, because they provide information about the species utilized for traditional purposes (medicinal, religious, food, etc.), which can contribute to the development of actions that allow the maintenance of faunistic resources [7, 13, 17].
In Northeast Brazil, the commerce of zootherapeutic products is common. Recent studies conducted in 10 cities in the region [5, 12, 18–22] demonstrated the existence of intense use and commercialization routes of animals for medicinal purposes among these cities. However, there are still gaps concerning the richness of traded species, which makes it difficult to evaluate the magnitude and impact of this commerce on natural populations of the animals involved, as well as potential implications of such uses for the public health of local users.
Despite the existence of information on the sale of animals for medicinal purposes in some important cities of Northeast Brazil, such as Aracaju-SE, Fortaleza-CE, and Salvador-BA, there are no published data available. For the cities of Maceio-AL and Recife-PE, although the commerce of medicinal fauna has been previously investigated, the list of species presented does not include all taxonomic groups but shows few animals identified at the species level.
The objective of the present study was to characterize the sale of medicinal animals in five large northeast cities. More specifically, the work aimed to (i) list which animals are sold for medicinal purposes in the capitals of the states of Sergipe (Aracaju), Ceará (Fortaleza), Alagoas (Maceió), Pernambuco (Recife), and Bahia (Salvador); (ii) evaluate the versatility of the animal species by calculating the relative importance; (iii) test the idea of utilitarian redundancy; (iv) compare the degree of similarity between the localities sampled; (v) estimate the richness and diversity of species traded; and based on this information, discuss aspects related to conservation and public health associated with the medicinal fauna commerce in Brazil.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Area of Study
Information about the use and sale of zootherapeutic products was obtained in the cities of Aracaju-SE, Fortaleza-CE, Maceio-AL, Recife-PE, and Salvador-BA (Figure 1). In Maceio and Recife, prior studies on the sale of zootherapeutic products have been carried out [5, 22], where the first involved only one taxonomic group (reptiles) and both works did not show information on the number citations among the vendors, which prompted us to include these cities in our research.
Figure 1.
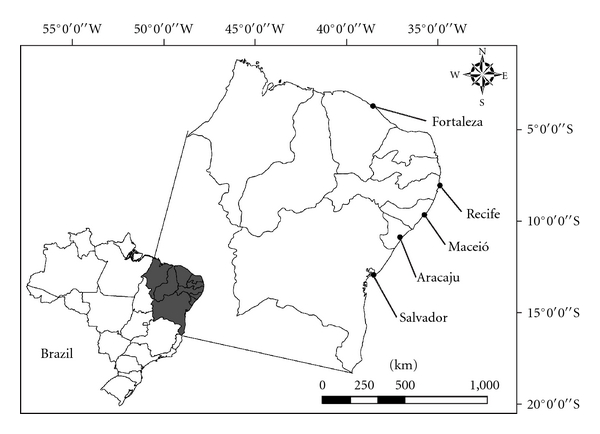
Map locating the cities studied in Northeastern Brazil.
2.2. Procedures
Field work was undertaken during the period from January to November of 2010, in public markets of Aracaju (Mercado Central), Fortaleza (Mercado Central, São Sebastião, and Praia do Futuro), Maceió (Mercado da Produção), Recife (Mercado São José, Afogados, Água Fria, Encruzilhada, and Casa Amarela), and Salvador (Feira de São Joaquim, Sete Portas, and Itapuã).
To obtain the information we interviewed 102 (65 men and 37 women) merchants about the use and commercialization of medicinal animals, being 12 in the Aracaju city (11 men and 1 woman), 29 in Fortaleza (17 men and 12 women), 17 in Maceió (7 men and 10 women), 21 in Recife (16 men and 5 women), and 23 in Salvador (14 men and 9 women).
Sampling was nonrandom intentional, in which the interviewees were predefined [23], composed only of people who actually sold zootherapeutic products. Semistructured questionnaires were used, complemented by free interviews and informal conversations. The questionnaires contained questions on the animal species used for medicinal purposes, their respective uses, preparations, and parts utilized.
To respect intellectual property rights, we adopted the following protocol in the field: before the survey, we introduced ourselves, explained the nature and objectives of our research, and asked the respondents for permission to record the information. The ethical approval for the study was obtained from the Ethics Committee of Universidade Federal da Paraíba (Protocol: CEP/HULW no. 065/10).
Vernacular names of species were recorded as quoted during the interviews. Zoological material was identified with the aid of specialists, through examination of voucher specimens donated by the interviewees or purchased at the surveyed markets, and through photographs taken during interviews of the animal species or their parts. Whenever necessary, these procedures were supplemented by checking vernacular names provided by traders against the scientific names, with the aid of taxonomists familiar with the study areas.
2.3. Data Analysis
The ailments treated by zootherapeutics were grouped into categories based on the model used by the “Centro Brasileiro de Classificação de Doenças” (Brazilian Center for the Classification of Diseases) [24].
To estimate the level of agreement between interviewees over which animals to use for each category, we calculated the informant consensus factor (ICF), adapted from Heinrich et al. [25] that looks at the variability of animals used for each treatment, and therefore the consensus between practitioners. This factor estimates the relationship between the “number of use reports in each category (nar) minus the number of taxa used (na)” and the “number of use reports in each category minus 1.” ICF is thus calculated using the following formula:
| (1) |
The product of this factor ranges from 0 to 1. A high value (close to 1) indicates a high consensus, where relatively few taxa (usually species) are used by a large proportion of people, while a low value indicates that the informants disagree on the taxa to be used for treating a particular illness.
2.4. Relative Importance (RI)
The relative importance (RI) of the species cited was calculated (adapted from Bennett and Prance [26]). Relative importance was calculated according to the following formula, with “2,” being the highest possible value, indicating the most versatile species. The most versatile species are those that have the greatest number of medicinal properties: RI = NCS + NP, where NCS (number of body systems) is the number of body systems treated by a given species (NCSS) divided by the total number of body systems treated by the most versatile species (NCSSV). The number of properties (NP) is obtained by the relationship between the number of properties attributed to a species (NPS) divided by the total number of properties attributed to the most versatile species (NPSV).
2.5. Utilitarian Redundancy of the Diseases and/or Symptoms
Utilitarian redundancy of zootherapeutic products was tested according to the model adapted from Albuquerque and Oliveira [27]. According to these authors, the idea of utilitarian redundancy is based on the theory of ecological redundancy (this theory indicates that all species present specific functions in the ecosystem, but some can show similar functions, minimizing damages in the ecosystem due the extinction) (see [28, 29]). Therefore, the notion of functional redundancy relies on the presumption that some species are utilized for the treatment of more than one disease and/or symptom, such that the inclusion of more than one species within a disease category can be a mechanism of reducing the impact on the animals sold for medicinal purposes.
To evaluate this hypothesis, each disease and/or symptom was categorized according to the level of redundancy of the species used: highly redundant (≥15% of the number of species utilized), redundant (15% < the number of species ≥5%), and not very redundant (<5% of the species). In order to evaluate the idea of utilitarian redundancy in a possibly better manner, the diseases and/or symptoms were not reclassified, and thus the names cited by the informants were kept.
2.6. Coefficient of Similarity
The composition of the species cited was compared between the cities studied by means of the similarity index based on data of multiple incidence. The similarity between the localities was estimated using the distance coefficient of Bray-Curtis [30]. The similarity matrix was constructed and grouping analysis performed in the past program [31].
2.7. Estimate of Species Richness
Initially, incidence data (presence or absence) of the species in the markets of Aracaju, Fortaleza, Maceio, Recife, and Salvador were used to estimate the richness of medicinal species sold in each city. The term richness of species refers to the number of species living in the determined area [32]. However, due to the difficulty to access the total number of species, indexes of estimated richness are important tools to identify the most probable number of species living on the ecosystem, community, or, as our work, on the public markets. Species richness was calculated utilizing the estimators CHAO 2, ICE, Jackknife 1, and Jackknife 2 (see [30]), with the program Estimate S 8.2.0 [33]. These indices have been utilized in ethnobotanical and ethnozoological studies [16, 34].
3. Results and Discussion
In the cities studied, the trade in animal-based medications was shown to be common practice. A total of 68 animal species, distributed in 47 families, were sold for medicinal purposes in the cities studied (Table 1). The most representative taxa were mammals (20), reptiles (17), and birds (12) (see Figure 2). These are the first results on the use and sale of animals for traditional medicine in the markets of Aracaju, Fortaleza, and Salvador, where the commercialization of respectively 19, 28, and 36 species was recorded. For the cities of Recife and Maceio, the number of species recorded was higher than that documented in previous works. In Recife, Silva et al. [5] recorded the commerce of 18 medicinal species, while in Maceió, Freire [22] reported the use of 17 species of reptiles sold for medicinal purposes. In the present study, we recorded 31 and 27 species in Recife and Maceió, respectively.
Table 1.
Animal species commercialized for medicinal purposes in the municipalities of Aracaju-SE, Fortaleza-CE, Maceió-AL, Recife-PE, and Salvador-BA.
| Family/species/local name | Part used | Disease (or illness) | RI total | Number of citations per city/RI per city | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aracaju | Fortaleza | Maceió | Recife | Salvador | ||||
| Molluscs | ||||||||
| Achatinidae | ||||||||
| Achatina fulica (Ferussac, 1821), giant east African snail, caramujo gigante africano | Shell | Stroke | 0.12 | — | — | — | — | 5/0.14 |
| Cardiidae | ||||||||
| Trachycardium muricatum (Linnaeus, 1758), yellow pricklycockle, rala-côco | Shell | Stroke | 0.12 | — | — | — | — | 2/0.14 |
| Strombidae | ||||||||
|
Strombus pugilis Linnaeus, 1758, west Indian fighting conch, estrombo-lutador- das-Índias-Ocidentais |
Shell | Stroke and “simpatias” | 0.23 | 2/0.56 | — | — | — | 1/0.14 |
|
| ||||||||
| Insects | ||||||||
| Apidae | ||||||||
| Apis mellifera (Linnaeus, 1758), honey bee, abelha italiana | Honey and wax | Bronchitis, cough, flu, nasal congestion, asthma, sore throat, stomach ache, diarrhea, and cracks in the feet | 0.62 | 4/0.78 | 22/1.02 | 4/0.32 | 10/0.34 | 6/0.36 |
| Melipona subnitida (Ducke, 1910), stingless bee, jandaíra | Honey and wax | Sore throat, cough, and diarrhea | 0.18 | — | 4/0.55 | — | — | — |
| Melipona scutellaris Latreille, 1811, stingless bee, uruçu | Honey and wax | Asthma, cough, flu, nasal congestion, earache, stomach ache, diarrhea, and gastritis | 0.59 | — | — | 4/1.09 | 1/0.18 | — |
| Partamona cupira (Smith, 1863), stingless bee, abelha cupira | Honey and wax | Sore throat, flu, cough, nasal congestion, and diarrhea | 0.33 | — | 2/0.55 | 2/0.43 | 1/0.34 | — |
| Blattidae | ||||||||
| Periplaneta americana (Linnaeus, 1758), cockroach, barata | Wings and whole animal | Asthma and earache | 0.23 | 2/0.56 | — | — | — | — |
| Termitidae | ||||||||
| Nasutitermes corniger (Motschulsky, 1855), térmite, cupim de aroeira | Whole animal | Asthma, cough, flu, and sore throat | 0.21 | — | 4/0.45 | — | — | — |
|
| ||||||||
| Equinoderms | ||||||||
| Echinasteridae | ||||||||
| Echinaster echinophorus (Lamarck, 1816), starfish, estrela do mar | Whole animal | Asthma, flu, stroke, “simpatias,” erysipelas, cancer, and thrombosis | 0.64 | 7/0.83 | — | 3/0.44 | — | 6/0.60 |
| Oreasteridae | ||||||||
| Oreaster reticulatus (Linnaeus 1758), starfish, estrela do mar | Whole animal | Asthma, stroke, erysipelas, cancer, “simpatias,” and evil eyes | 0.61 | 6/0.83 | 1/0.24 | 3/0.54 | 6/0.59 | 4/0.56 |
|
| ||||||||
| Fishes | ||||||||
| Erythrinidae | ||||||||
| Hoplias malabaricus (Bloch, 1794), trhaira, traíra | Fat | Earache, healing, strain, sore throat, cough, asthma, swelling, urinary infection, and infections | 0.79 | 2/1.39 | 4/1.17 | — | — | — |
| Gymnotidae | ||||||||
| Electrophorus electricus, (Linnaeus, 1766), electric eel, peixe-elétrico, LR | Fat | Rheumatism, osteoporosis, crack in the feet, pains, inflammation, sore throat, asthma, cough, sinusitis, flu, swelling, itch, wound, earache, toothache, burns, muscular pain, bruises, strain, headache, joint pain, erysipelas, snake bites, skin diseases, healing, and boils | 1.51 | 1/0.67 | 4/1.79 | 2/1.41 | 1/0.64 | 3/1.26 |
| Syngnathidae | ||||||||
| Hippocampus reidi (Ginsburg, 1933), longsnout seahorse, cavalo-marinho, DD | Whole animal | Asthma, flu, stroke, erysipelas, toothache, circulatory problems, and thrombosis | 0.64 | 4/0.39 | 4/0.24 | 4/0.54 | 7/0.28 | 9/0.78 |
| Unidentified family | ||||||||
| Shark, tubarão | Cartilage | Rheumatism | 0.12 | — | 1/0.24 | — | — | — |
| Unidentified family | ||||||||
| Stingray, Raia | Fat | Sore throat, pains, rheumatism, burns, asthma, and infections | 0.53 | — | 1/1.26 | — | — | — |
|
| ||||||||
| Amphibians | ||||||||
| Bufonidae | ||||||||
| Rhinella jimi (Stevaux, 2002), cururu toad, sapo cururu, LR | Skin and fat | Sore throat, asthma, flu, cough, rheumatism, inflammation, backache, osteoporosis, arthrosis, arthritis, strain, diarrhea, “simpatias,” toothache, cancer, infections, and earache | 1.13 | 1/0.67 | 7/1.45 | — | 1/0.94 | 1/0.18 |
| Leptodactylidae | ||||||||
| Leptodactylus labyrinthicus (Spix, 1824), South American pepper frog, rã-pimenta, LR | Fat | Sore throat, cough, and asthma | 0.18 | — | 2/0.38 | — | — | — |
| Leptodactylus vastus Lutz, 1930, South American pepper frog, rã-pimenta, LR | Fat | Sore throat, cough, asthma, arthritis, and backache | 0.33 | — | 3/0.69 | — | — | — |
|
| ||||||||
| Reptiles | ||||||||
| Chelidae | ||||||||
| Tortoise, cágado_Fortaleza | Fat | Rheumatism, cracks in the feet, arthrosis, backache, sore throat, and swelling | 0.53 | — | 2/1.10 | — | — | — |
| Tortoise, cágado_Recife | Carapace | Asthma, burns, and rheumatism | 0.35 | — | — | — | 1/0.53 | — |
| Cheloniidae | ||||||||
| Chelonia mydas (Linnaeus, 1758), green turtle, tartaruga verde, EM | Fat and carapace | Sore throat, rheumatism, swelling, inflammation, burns, healing, cough, asthma, arthritis, backache, cancer, backache, stroke, thrombosis, erysipelas, stomach ache, and infections | 1.18 | — | 4/1.38 | — | — | 1/0.92 |
| Testudinidae | ||||||||
| Chelonoidis sp, tortoise, jabuti | Fat | Sore throat, cough, asthma, earache, backache, and inflammations | 0.53 | — | 1/1.17 | — | — | — |
| Iguanidae | ||||||||
| Iguana iguana (Linnaeus, 1758), common green iguana, camaleão, DD | Fat and tail | Earache, deafness, sore throat, inflammations, swelling, wounds, burns, and acne | 0.67 | — | — | 3/0.71 | 1/1.05 | — |
| Teiidae | ||||||||
| Cnemidophorus ocellifer (Spix, 1825), spix's whiptail, calango | Whole animal | Stroke, thrombosis, cancer, and hemorrhoids | 0.30 | — | — | 2/0.71 | — | — |
| Tupinambis merianae (Duméril and Bibron, 1839), teju lizard, téju, LR | Fat, skin, and tail | Sore throat, pneumonia, sinusitis, flu, bronchitis, asthma, cough, rheumatism, swelling, strain, inflammations, earache, deafness, backache, arthrosis, arthritis, burns, osteoporosis, healing, muscular pain, cracks in the feet, toothache, headache, itch, lung problems, infections, pains, injuries, gastritis, snake bites, and skin diseases | 1.67 | 1/2.00 | 12/1.83 | 3/1.79 | 8/1.82 | 5/1.66 |
| Boidae | ||||||||
| Boa constrictor (Linnaeus, 1758), boa, jibóia, DD | Skin, fat, bone, and feces | Sore throat, cough, toothache, rheumatism, inflammations, asthma, flu, arthrosis, osteoporosis, cracks in the feet pains, arthritis, backache, healing, “simpatias,” swelling, bruises, cancer, tuberculosis, pneumonia, edemas, and stomach ache | 1.29 | 2/1.67 | 8/1.60 | 3/1.52 | — | 2/0.86 |
| Epicrates cenchria (Linnaeus, 1758), rainbow boa, salamanta, DD | Fat | Sore throat, rheumatism, swelling, backache, arthrosis, burns, and toothache | 0.56 | — | 1/1.17 | — | — | — |
| Colubridae | ||||||||
| Philodryas olfersii (Lichtenstein, 1823), Lichtenstein's green racer, cobra verde | Whole animal | Stroke | 0.12 | — | — | — | — | 1/0.18 |
| Spilotes pullatus (Linnaeus, 1758), yellow rat snake, caninana, | Bone and fat | Sore throat, cancer, and inflammations | 0.35 | — | — | — | — | 1/0.42 |
| Elapidae | ||||||||
| Micrurus ibiboboca (Merrem, 1820), caatinga coral snake, cobra-coral | Fat | Rheumatism, asthma, toothache, sore throat, cough, osteoporosis, swelling, inflammations, arthritis, and healing | 0.57 | — | — | 3/0.97 | — | — |
| Caudisona durissa (Linnaeus, 1758), rattlesnake, cascavel, LR | Fat, rattle, bone, and skin | Backache, rheumatism, cracks in the feet, osteoporosis, swelling, inflammation, arthritis, arthrosis, asthma, sore throat, earache, healing, burns, toothache, cough, bronchitis, snake bites, stroke, muscular pain, injuries, epilepsy, cancer, tuberculosis, “simpatias,” “evil eyes,” “attract partners,” and “attract money” | 1.70 | 2/1.67 | 3/1.38 | 2/2.00 | 4/1.88 | 3/0.96 |
| Unidentified family | ||||||||
| Alligator, jacaré_Aracaju | Skin | Stroke, asthma, bronchitis, and rheumatism | 0.38 | 3/0.94 | — | — | — | — |
| Alligator, jacaré_Maceió | Skin | Stroke, bronchitis, backache, toothache, snake bite, and rheumatism | 0.53 | — | — | 2/0.98 | — | — |
| Alligator, jacaré_Recife | Fat and skin | Sinusitis, bronchitis, asthma, sore throat, toothache, burns, thrombosis, cancer, and diarrhea | 0.71 | — | — | — | 4/1.35 | — |
| Alligator, jacaré_Salvador | Skin | Asthma, stroke, tuberculosis, sexual impotence, snake bites, inflammations, menstrual cramps, headache, and stomach ache | 1.07 | — | — | — | — | 6/1.24 |
|
| ||||||||
| Birds | ||||||||
| Anatidae | ||||||||
| Anser anser (Linnaeus, 1758), greylag goose, ganso | Fat | Flu, cough and sore throat | 0.18 | — | — | — | 1/0.28 | — |
| Anas platyrhynchos Linnaeus, 1758, mallard, pato | Fat and eggs | Asthma, sore throat, sinusitis, and sexual impotence | 0.30 | — | — | — | — | 2/0.54 |
| Ciconiidae | ||||||||
| Coragyps atratus (Bechstein, 1793), black vulture, urubu, LR | Fat, liver, and e feather | “Simpatias,” alcoholism, and asthma | 0.35 | — | 1/0.24 | 4/0.44 | 2/0.18 | — |
| Columbidae | ||||||||
| Columba livia Gmelin, 1789, common pigeon, Pombo | Fat | Sore throat, sinusitis, cough, and asthma | 0.21 | — | — | — | — | 2/0.26 |
| Phasianidae | ||||||||
| Gallus gallus, (Linnaeus, 1758), chicken, galinha | Fat and spur | Cough, sore throat, flu, sinusitis, sexual impotence, swelling, nasal congestion, fever, diarrhea, earache, skin diseases, strain, burns, menstrual cramps, inflammations, pains, bruise, and cracks in the feet | 1.33 | 2/0.89 | 2/0.55 | — | 2/0.34 | 4/1.62 |
| Numida meleagris (Linnaeus, 1758), helmeted guineafowl, galinha d'angola | Fat | Nasal congestion, flu, rheumatism, asthma, strain, burns, and healing | 0.48 | — | — | — | — | 1/0.58 |
| Pavo cristatus (Linnaeus, 1758), common peafowl, pavão | Fat and feather | Snake bite, asthma, and sore throat | 0.26 | — | — | 1/0.44 | — | 1/0.28 |
| Rheidae | ||||||||
| Rhea americana (Linnaeus, 1758), greater rhea, ema, NT | Fat | Acne, rheumatism, cracks in the feet, burns, and nasal congestion | 0.49 | — | — | — | 1/0.76 | — |
| Unidentified family | ||||||||
| Owl, coruja_Fortaleza | Fat | “Simpatias” | 0.12 | — | 1/0.24 | — | — | — |
| Owl, coruja_Salvador | Fat | Sore throat, rheumatism, toothache, sinusitis, pains, and infections | 0.44 | — | — | — | — | 1/0.54 |
| Unidentified family | ||||||||
| Pheasant, faisão | Fat | Sore throat, rheumatism, toothache, sinusitis, and pains | 0.41 | — | — | — | — | 1/0.50 |
| Unidentified family | ||||||||
| Hawk, gavião | Fat | Asthma, cough, sore throat, fever, diarrhea, and earache | 0.53 | — | — | — | — | 1/0.64 |
|
| ||||||||
| Mammals | ||||||||
| Agoutidae | ||||||||
| Cuniculus paca (Linnaeus, 1766), spotted paca, paca, LR | Penis | Sexual impotence | 0.12 | — | — | — | — | 1/0.14 |
| Bovidae | ||||||||
| Bos taurus (Linnaeus, 1758), cow, boi | Fat, tail, skin, horn, and fel (bile) | Asthma, sore throat, flu, stroke, bronchitis, thrombosis, swelling, diarrhea, sexual impotence, “evil eyes,” and “simpatias” | 0.77 | — | 4/0.24 | 4/0.60 | 2/0.53 | 5/0.82 |
| Bubalus bubalis (Linnaeus, 1758), water buffalo, buffalo | Tail and horn | Asthma, stroke, and “evil eyes” | 0.35 | — | — | — | 1/0.41 | — |
| Capra hircus (Linnaeus, 1758), domestic goat, bode | Fat and brain | Cracks in the feet, burns, sore throat, asthma, sinusitis, pain, toothache, rheumatism, osteoporosis, infections, inflammations, bruise, erysipelas, strain, and sexual impotence | 0.98 | 1/0.56 | — | 2/1.04 | 1/0.76 | 2/0.72 |
| Ovis aries (Linnaeus, 1758), sheep, carneiro | Fat | Rheumatism, cracks in the feet, sore throat, osteoporosis, arthritis, arthrosis, healing, inflammations, cough, swelling, flu, asthma, burns, pains, muscular pain, acne, circulatory problems, joint pain, bruise, strain, and toothache | 1.09 | 2/1.11 | 5/1.31 | 3/1.36 | 12/1.57 | 1/0.46 |
| Bradypodidae | ||||||||
| Bradypus sp., sloth, preguiça | Fat, nail, and skin | Thrombosis, stroke, asthma, sore throat, “evil eyes,” and circulatory problems | 0,44 | — | — | 4/0.71 | 2/0.64 | — |
| Canidae | ||||||||
| Canis lupus (Linnaeus, 1758), dog, cachorro | Fat | “Simpatias” | 0.12 | — | 1/0.24 | — | — | — |
| Cerdocyon thous (Linnaeus, 1766), fox, raposa, LR | Fat | Flu, asthma, pains, inflammations, snake bites, strain, rheumatism, and sore throat | 0.59 | — | — | 4/1.09 | 1/0.18 | — |
| Cervidae | ||||||||
| Mazama gouazoubira (G. Fischer, 1814), gray brocket, veado, VU | Tail, horne, and tíbia | “Simpatias,” asthma, sore throat, cough, arthritis, and rheumatism | 0.44 | — | 2/0.93 | 3/1.20 | 4/0.95 | 2/0.48 |
| Dasypodidae | ||||||||
| Dasypus novemcinctus (Linnaeus, 1758), nine-banded armadillo, tatu galinha, LR | Fat and tail | Deafness, earache, asthma, burns, sinusitis, cough, pains, inflammations, urinary infection, strain, and rheumatism | 0.85 | — | — | 1/0.71 | 1/1.15 | — |
| Euphractus sexcinctus (Linnaeus, 1758), six-banded armadillo, tatu-peba, LR | Fat, tail, and legs | Deafness, earache, asthma, burns, sinusitis, cough, pains, inflammations, strain, rheumatism, “evil eyes,” urinary infection, sexual impotence, injuries, tuberculosis, infections, and osteoporosis | 1.22 | — | — | 1/0.71 | 1/1.20 | 3/1.22 |
| Delphinidae | ||||||||
| Sotalia guianensis (P.-J. van Bénéden, 1864), Guianan river dolphin, boto, DD | Fat, penis, eyes, and blood | “Simpatias,” “attract partners,” asthma, rheumatism, osteoporosis, burns, sexual impotence, swelling, inflammations, arthrosis, toothache, headache, stomach ache, earache, erysipelas, flu, cough, sore throat, muscular pain, menstrual cramps, cancer, tuberculosis, pneumonia, thrombosis, snake bites, skin diseases, healing, and backache | 1.90 | 1/1.22 | 1/0.24 | 7/1.58 | 6/1.79 | 6/1.58 |
| Erethizontidae | ||||||||
| Coendou prehensilis (Linnaeus, 1758), Brazilian porcupine, porco-espinho, coandú, LR | Spine | Asthma, bronchitis, cough, thrombosis, cancer, eczema, acne, toothache, stroke, “attract money,” and earache | 0.94 | 1/0.83 | — | 3/0.54 | 1/0.71 | 6/0.64 |
| Felidae | ||||||||
| Leopardus pardalis (Linnaeus, 1758), ocelot, jaguatirica, gato maracajá, DD | Eyes | Asthma, “evil eyes,” and sexual impotence | 0.35 | — | — | — | 1/0.53 | — |
| Myrmecophagidae | ||||||||
| Myrmecophaga tridactyla (Linnaeus, 1758), Anteater, tamanduá bandeira | Skin | Stroke | 0.12 | — | — | — | — | 1/0.14 |
| Phyllostomidae | ||||||||
| Desmodus rotundus (E. Geoffroy, 1810), vampire bat, morcego, DD | Whole animal | Asthma, stroke, and rheumatism | 0.35 | — | — | — | — | 3/0.42 |
| Suidae | ||||||||
| Sus scrofa (Linnaeus, 1758), pig, porco | Fat | Acne, boils, and bronchitis | 0.26 | — | — | — | 1/0.41 | — |
| Trichechidae | ||||||||
| Trichechus manatus (Linnaeus, 1758), manatee, peixe-boi, CR | Fat | Burns, earache, swelling, wounds, menstrual cramps, bruises, asthma, flu, toothache, inflammations, pains, rheumatism, arthrosis, arthritis, backache, osteoporosis, cancer, thrombosis, sore throat, sinusitis, erysipelas, snake bites, skin diseases, healing, headache, cracks in the feet, and sexual impotence | 1.87 | 1/1.22 | — | 4/1.63 | 2/1.28 | 3/2.00 |
| Unidentified family | ||||||||
| Whale, baleia_Recife | Fat | Sore throat and menstrual cramps | 0.23 | — | — | — | 1/0.36 | — |
| Whale, baleia_Salvador | Fat | Rheumatism and menstrual cramps | 0.23 | — | — | — | — | 2/0.28 |
Legends: RI: relative importance; CR: critically endangered; EN: endangered; VU: vulnerable; NT: near threatened; LR: lower risk; DD: deficient data.
Figure 2.
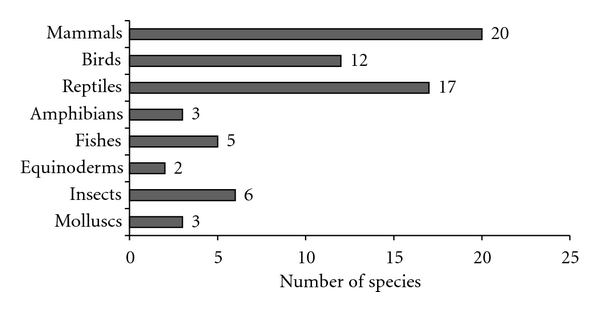
Number of animal species used as remedies per taxonomic category in Northeastern Brazil.
The increase in the number of species cited for medicinal purposes, sold in the markets of Recife and Maceio may be the result of the structure of the traditional medicine systems of the public markets, because these are open and dynamic systems, which are inclined to increase in species over the years, although with a tendency to maintain the species of greater importance [14]. These authors studied the sale of medicinal plants in the same market in different periods (1995 and 2002) and found an increase of 58 species in a period of seven years (1995 = 78 species and 2002 =136 species), but species of high relative importance continued to be present in the markets evaluated.
Similarly, the data obtained in the present study corroborated the results of Albuquerque et al. [14] for the commerce of medicinal plants. We found an increase in the composition of animal species in the markets of Recife and Maceio, where the sale of species of high relative importance was maintained, such as Caudisona durissa and Tupinambis merianae, which were recorded in the two periods in which the studies were performed.
In general, the diversity of medicinal species recorded in the present study confirms the importance of the fauna as a therapeutic resource in urban areas, corroborating previous studies that indicated the commercialization of zootherapeutic products as a common activity in various Brazilian cities (see [8, 12, 17–21]). Compared to other studies of markets in Northeast Brazil, the number of medicinal species traded in the cities studied is substantial. In Feira de Santana, BA, for example, a total of 16 animal species were reported being sold for medicinal purposes in the public markets of the city [18], in Santa Cruz do Capibaribe, PE, 37 species [19], in Caruaru, PE, 36 species [20], in the cities of Crato and Juazeiro do Norte 31 species [12], and in the metropolitan region of Natal, 23 species [21].
The majority of the medicinal species sold in the cities studied are the same as those sold and/or utilized in other cities in Northeast Brazil, with the exception of five medicinal species not previously recorded (Figure 3): Achatina fulica, Trachycardium muricatum, Philodryas olfersii, Desmodus rotundus, and Leptodactylus vastus. Of these species, four were cited only in the Salvador markets (A. fulica [cited by five informants], T. muricatum [cited by two informants], P. olfersii [cited by one informant], and D. rotundus [cited by three informants]) and only one in the Fortaleza markets (L. vastus [cited by three informants]).
Figure 3.
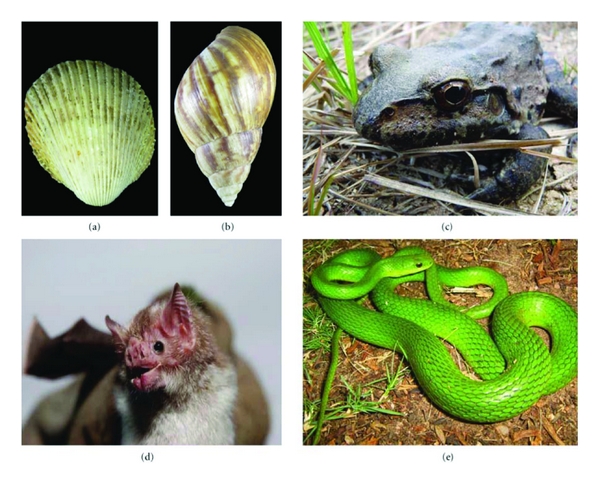
New records of species used in traditional medicine. (a) Trachycardium muricatum, (b) Achatina fulica, (c) Leptodactylus vastus, (d) Desmodus rotundus, (e) Philodryas olfersii (Photos: (a), (b) Joafrâncio P. Araújo; (c) Hugo Fernandes-Ferreira; (d) Patrício A. da Rocha; (e) Samuel C. Ribeiro).
The species of molluscs A. fulica and T. muricatum are utilized in the treatment of stroke. The fat of L. vastus is administered for the treatment of sore throat, cough, asthma, arthritis, and backache. The snake P. olfersii is utilized for the treatment of stroke and the bat D. rotundus is administered for the treatment of stroke, asthma, and rheumatism.
The species with the highest number of citations were Apis mellifera (n = 46), Tupinambis merianae (n = 28), Hippocampus reidi (n = 27), Bos taurus (n = 23), Oreaster reticulatus (n = 20). In other studies on the trade of zootherapeutic products in stores and street markets, these species are also often utilized in the production of traditional remedies [8, 12, 17–21].
Of the species recorded in the present work, the majority represent wild animals (82.4%). Only 12 species of domestic animals are sold as medicinal products, and they are Anser anser, Anas platyrhynchos, Numida meleagris, Gallus domesticus, Pavo cristatus, Ovis aries, Capra hircus, Bos taurus, Bubalus bubalis, Canis lupus, and Sus scrofa. These results corroborate the tendency observed in other studies, which have demonstrated that wild animals compose the greater part of the medicinal fauna utilized in popular medicine in Brazil [8, 12, 17–21] and in the world [35–40].
All animals cited occur in ecosystems close to the cities studied, with the exception of Electrophorus electricus. This species occurs in the Northeast Brazil region, only in the state of Maranhão [41]. Thus, the results indicate a tendency of the commercialization of animals that occurs in the proximity of the localities sampled. This demonstrates the importance of the local fauna in supplying the products utilized in the preparation of traditional remedies, which would reduce the costs for the acquisition and commercialization of zootherapeutic products, but this hypothesis needs to be adequately tested. These data corroborate other works conducted in markets in Northeast Brazil [7–9, 12, 17, 42], which also recorded a predominance of the use of animals of the local fauna for trade, showing the importance of the biodiversity of each region as a resource for zootherapy.
Various parts and metabolic secretions of the animals are utilized in the preparation of medications (Figure 4), and they are skin, fat, honey, wax, shell, wings, spines, rattle, blood, feces, horn, feathers, hoof, tibia, cartilage, eye, tail, liver, claw, foot, eggs, bile, and bone. Animals such as A. fulica, T. muricatum, P. olfersii, D. rotundus, O. reticulates, and H. reidi can be used whole.
Figure 4.
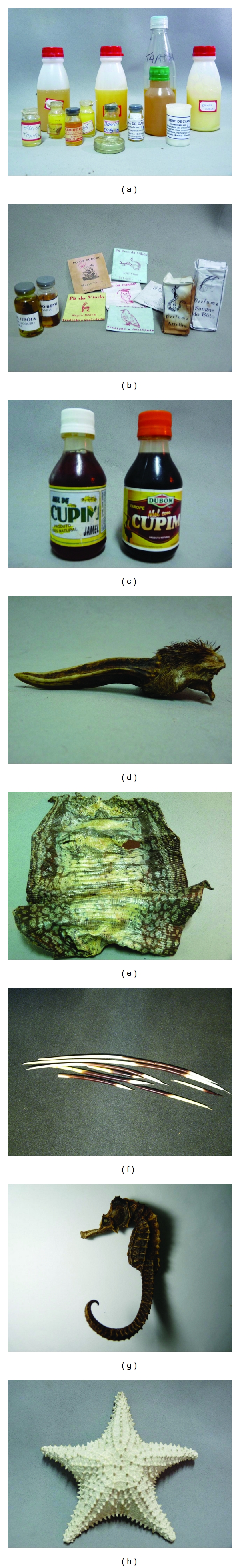
Examples of animal products used as remedies sold in Aracaju-SE, Fortaleza-CE, Maceió-AL, Recife-PE, and Salvador-BA public markets. (a) Body fat; (b) metabolism secretion such as blood, feces, and urine; (c) honey of Nasutitermes corniger; (d) horn of Mazama gouazoubira; (e) skin of Tupinambis merianae; (f) spine of Coendou prehensilis; (g) dried Seahorses (Hippocampus reidi); (h) dried starfish (Oreaster reticulatus). (Photos: Hugo Fernandes-Ferreira).
Among the products cited by the informants, fat was cited most often, which can be extracted from the following animals: H. malabaricus, E. electricus, R. jimi, C. mydas, T. Merianae, and B. constrictor. The frequent utilization of fat can be attributed to the fact that the main animals utilized are vertebrates, which have a large quantity of fat in their body [19]. Another possible explanation for the marked use of body fat for medicinal purposes can be due its chemical composition. Body fat consists mainly of fatty acids, which have an extensive proven medicinal applicability [43–45], such that this intense use and/or medicinal trade can be the result of the empirical observation of the efficacy of fat by human users of this zootherapeutic product.
The medicinal animals listed in the present study are applied for the treatment of 58 diseases and/or symptoms (Table 2). The categories with the higher values of ICF were diseases of the respiratory tract (0.91), diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue (0.89), and undefined diseases (0.88). These high values of consensus for these categories were also found in other works carried out in the public markets of North and Northeast Brazil [8, 9, 12, 19, 20].
Table 2.
Categories of diseases treated with animal-based medicines that are sold in public markets in Aracaju-SE, Fortaleza-CE, Maceió-AL, Recife-PE, and Salvador-BA, according to the “Centro Brasileiro de Classificação de Doenças” (1993).
| Categories | Diseases cited “by the vendors” | Total |
|---|---|---|
| A | “Attract money,” “attract partner,” “simpatias,” “evil eyes,” itch, bruise, pain, skin disease, edema, weakness, swelling, inflammations, infections, circulation problems, and lung problems | 15 |
| B | Asthma, bronchitis, nasal congestion, sore throat, flu, pneumonia, sinusitis, and cough | 8 |
| C | Arthritis, arthrosis, healing, backache, toothache, joint pain, osteoporosis, and rheumatism | 8 |
| D | Earache and deafness | 2 |
| E | Alcoholism, injuries, muscular pain, strain, snake bites, and burns | 6 |
| F | Stomach ache and gastritis | 2 |
| G | Acne, boils, eczema, and cracks in the feet | 4 |
| H | Sexual impotence | 1 |
| I | Stroke, thrombosis, and hemorrhoids | 3 |
| J | Urinary infection and menstrual cramps | 2 |
| K | Headache and epilepsy | 2 |
| L | Diarrhea, erysipelas, and tuberculosis | 3 |
| M | Cancer | 1 |
| N | Fever | 1 |
|
| ||
| Total | 58 | |
A: undefined illnesses; B: diseases of the respiratory system; C: diseases of the osteomuscular system and conjunctive tissue; D: diseases of the ear; E: lesions caused by poisoning and other external causes; F: diseases of the digestive system; G: diseases of the skin and the subcutaneous tissue; H: mental and behavioural perturbations; I: diseases of the circulatory system; J: diseases of the urogenital system; K: diseases of the nervous system; L: diseases caused by parasites; M: neoplasias (tumours); N: symptoms not categorized in other part or section.
A total of 1575 citations of uses for medicinal animals were cataloged (Table 3). The categories with highest number of citations were diseases of the respiratory tract (613 citations; 56 species), diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue (269 citations; 29 species), and undefined diseases (259 citations; 38 species). The diseases with highest number of citations were asthma (226 citations; 14.3%), sore throat (158 citations; 10.1%), and cough (111 citations; 7.1%). Other works carried out in the Northeast also indicate that these diseases are widely treated with medicinal animals [7–9, 12, 19, 20, 40].
Table 3.
Consensus factors of the informants for the categories described.
| Categories | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | |
| All localities combined | ||||||||||||||
| Species used | 38 | 56 | 29 | 20 | 22 | 11 | 19 | 9 | 22 | 8 | 6 | 17 | 11 | 2 |
| Percentage of species used (%) | 55.8 | 82.3 | 42.6 | 29.4 | 32.3 | 16.2 | 27.9 | 13.2 | 32.3 | 11.7 | 8.8 | 25 | 16.2 | 2.9 |
| Use citations | 259 | 613 | 269 | 51 | 107 | 25 | 42 | 22 | 98 | 17 | 20 | 30 | 20 | 2 |
| Percentage of use citations (%) | 16.4 | 38.9 | 17.1 | 3.2 | 6.8 | 1.6 | 2.6 | 1.4 | 6.2 | 1.1 | 1.3 | 1.9 | 1.3 | 0.12 |
| ICF | 0.88 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.62 | 0.8 | 0.58 | 0.56 | 0.61 | 0.78 | 0.56 | 0.73 | 0.44 | 0.47 | — |
| Aracaju-SE | ||||||||||||||
| Species used | 10 | 12 | 9 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 5 | — | — | — | — | — |
| Percentage of species used (%) | 52.6 | 63.1 | 47.3 | 21 | 15.8 | 15.8 | 10.5 | 5.3 | 26.3 | — | — | — | — | — |
| Use citations | 27 | 45 | 28 | 5 | 8 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 13 | — | — | — | — | — |
| Percentage of use citations (%) | 20.1 | 33.6 | 20.9 | 3.7 | 5.9 | 3 | 2.2 | 0.7 | 9.7 | — | — | — | — | — |
| ICF | 0.65 | 0.75 | 0.7 | 0.25 | 0.71 | 0.33 | 0.5 | — | 0.66 | — | — | — | — | — |
| Fortaleza-CE | ||||||||||||||
| Species used | 19 | 23 | 12 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 6 | 1 | — | 1 | — | — | — | — |
| Percentage of species used (%) | 67.8 | 82.1 | 42.8 | 14.3 | 14.3 | 10.8 | 21.4 | 3.6 | — | 3.6 | — | — | — | — |
| Use citations | 69 | 155 | 79 | 7 | 4 | 9 | 10 | 1 | — | 1 | — | — | — | — |
| Percentage of use citations (%) | 20.6 | 46.3 | 23.6 | 2 | 1.2 | 2.7 | 3 | 0.3 | — | 0.3 | — | — | — | — |
| ICF | 0.74 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.5 | — | 0.75 | 0.44 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Maceió-AL | ||||||||||||||
| Species used | 14 | 26 | 12 | 7 | 6 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 8 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 1 | — |
| Percentage of species used (%) | 51.8 | 96.3 | 44.4 | 25.9 | 22.2 | 7.4 | 22.2 | 3.7 | 29.6 | 11.1 | 3.7 | 14.8 | 3.7 | — |
| Use citations | 59 | 150 | 98 | 17 | 20 | 4 | 11 | 4 | 24 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 2 | — |
| Percentage of use citations (%) | 14.5 | 37 | 24.1 | 4.2 | 5 | 0.9 | 2.7 | 0.9 | 5.9 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 1.2 | 0.4 | — |
| ICF | 0.78 | 0.83 | 0.88 | 0.62 | 0.73 | 0.66 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.69 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.25 | 1 | — |
| Recife-PE | ||||||||||||||
| Species used | 17 | 24 | 12 | 9 | 9 | 2 | 7 | 3 | 8 | 3 | — | 1 | 2 | — |
| Percentage of species used (%) | 54.8 | 77.4 | 38.7 | 29 | 29 | 6.4 | 22.5 | 9.8 | 25.8 | 9.8 | — | 3.2 | 6.4 | — |
| Use citations | 59 | 136 | 30 | 14 | 47 | 3 | 14 | 4 | 13 | 4 | — | 5 | 3 | — |
| Percentage of use citations (%) | 17.7 | 40.9 | 9 | 4.2 | 14.1 | 0.9 | 4.2 | 1.2 | 3.9 | 1.2 | — | 1.5 | 0.9 | — |
| ICF | 0.72 | 0.83 | 0.62 | 0.39 | 0.82 | 0.5 | 0.54 | 0.33 | 0.41 | 0.33 | — | 0.75 | 0.5 | — |
| Salvador-BA | ||||||||||||||
| Species used | 15 | 26 | 13 | 4 | 10 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 15 | 4 | 6 | 14 | 7 | 2 |
| Percentage of species used (%) | 41.6 | 72.2 | 36.1 | 11.1 | 27.7 | 8.3 | 16.6 | 16.6 | 41.6 | 11.1 | 16.6 | 38.8 | 19.4 | 5.5 |
| Use citations | 46 | 127 | 34 | 4 | 28 | 4 | 7 | 12 | 48 | 8 | 14 | 20 | 15 | 2 |
| Percentage of use citations (%) | 12.4 | 34.4 | 9.2 | 1.1 | 7.6 | 1.1 | 1.9 | 3.2 | 13 | 2.7 | 3.8 | 0.5 | 4.1 | 0.5 |
| ICF | 0.69 | 0.8 | 0.63 | 0.57 | 0.66 | 0.5 | 0.17 | 0.64 | 0.7 | 0.57 | 0.61 | 0.32 | 0.5 | — |
A: undefined illnesses; B: diseases of the respiratory system; C: diseases of the osteomuscular system and conjunctive tissue; D: diseases of the ear; E: lesions caused by poisoning and other external causes; F: diseases of the digestive system; G: diseases of the skin and the subcutaneous tissue; H: mental and behavioural perturbations; I: diseases of the circulatory system; J: diseases of the urogenital system; K: diseases of the nervous system; L: diseases caused by parasites; M: neoplasias (tumours); N: symptoms not categorized in other part or section.
Even with the high number of citations to illnesses treated with animal products commercialized in Brazil, there are few laboratory studies testing its efficacy. Ferreira et al. [45] indicate that the body fat of Boa constrictor does not present a clinically relevant bacterial activity, but when combined with antibiotics, the fat demonstrated a significant synergistic activity. Similar results are reported to the decoction of the lizard Tropidurus hispidus and the termite Nasutitermes corniger (see [46–48]). But et al. [49] report the antifever activity of the preparations using the horn of Bos taurus. Murari et al. [50] and Ferreira et al. [44] report that extracts of Pavo cristatus and the body fat of Tupinambis merianae demonstrated anti-inflammatory activity. Tempone et al. [51] showed that steroids from the skin of Rhinella jimi are active against leishmaniasis and trypanosomiasis. Besides the high number of animal species commercialized with medicinal uses in Brazil, studies about the improved biological activity of theses products are still preliminary and insufficient. So, the development of more studies is necessary to understand, evaluate, and validate the traditional and medicinal knowledge associated with the use of animal products.
Zootherapeutic remedies can be prepared in the following ways: (a) whole animals or body parts are utilized by maceration, where the resultant powder is ingested in the form of teas or together with food, and (b) body secretions and fat are administered as an ointment or ingested.
According to the informants, 60 species (88.2%) are of multiple uses, that is, they are administered in the treatment of more than one disease and/or symptom. The most versatile species, that is, with the highest RI values are Sotalia guianensis (1.90), Trichechus manatus (1.87), Caudisona durissa (1.70), and Tupinambis merianae (1.67). Alves et al. [20] and Almeida and Albuquerque [7] also cite C. durissa and T. merianae as versatile medicinal species in other studies carried out on the commerce of zootherapeutic products.
In contrast, the results obtained in this study show that the same disease and/or symptom can be treated with more than one animal species, demonstrating utilitarian redundancy as proposed by Albuquerque and Oliveira [27]. Among the diseases treated with zootherapeutic products in the cities sampled in the present work, 19 are “highly redundant,” 23 are “redundant,” and 15 are “not very redundant.” Diseases such as asthma, sore throat, rheumatism, and cough are examples of categories “highly redundant.”
As shown in Figure 5, many species are included in the categories “highly redundant” and “redundant” (67 and 50, resp.), while few species are included in the category “not very redundant” (17 species). Based on the model of utilitarian redundancy, the pressure probably caused in the commercialized species in the markets evaluated is small, because the majority of the species are listed in the categories “highly redundant” and “redundant,” where they also have various alternative therapeutic uses. In general, 23 species are on the red list of the IUCN [52], where six are in the category data deficient, 12 in the category low risk, and one in each of the following categories: near threatened, vulnerable, endangered, and critically endangered. In addition, the proportion of species considered threatened did not differ between the redundancy categories analyzed (chi squared = 0.435; P > 0.05).
Figure 5.
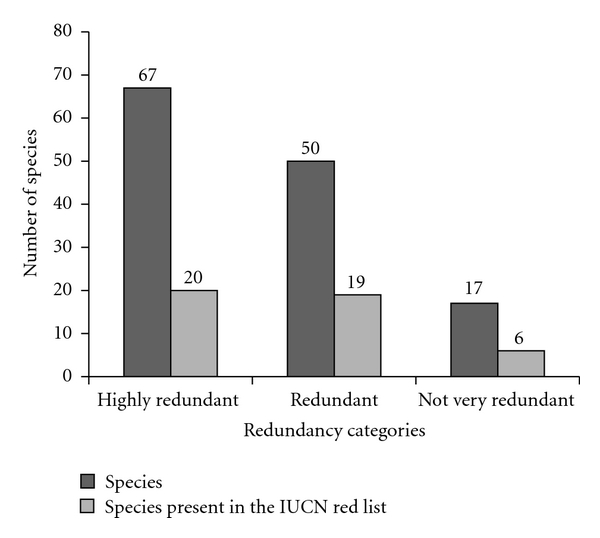
Distribution of the number of species cited per utilitarian redundancy category according to informants of the Aracaju-SE, Fortaleza-CE, Maceió-AL, Recife-PE, and Salvador-BA.
According to Albuquerque and Oliveira [27], the model of utilitarian redundancy suggests that the inclusion of species in the same therapeutic category can lead to reducing the pressure on the medicinal use of animals, such that species included in redundant categories would have options of equivalent products in other species. In this context, the species included in the category “not very redundant” should be prioritized in the development of conservation strategies, because there would not be equivalent species for medicinal use. However, the species in the more concerning categories of the IUCN red list (Rhea Americana: near threatened; Mazama gouazoubira: vulnerable; Chelonia mydas: endangered; Trichechus manatus: critically endangered) were not reported as medicines to the treatment of the “not very redundant” diseases, reinforcing our point of view that the commercialization of animals to medicinal uses do not cause a great pressure over the wild livestocks of animals.
However, this interpretation, about prioritized in the development of conservation strategies, should be taken with caution, since Albuquerque and Oliveira [27] emphasized that even in a redundant category, if there are species that have a greater local preference, the pressure of use would certainly be shifted to them. In addition, the idea of redundancy can be applied to the resilience of the local medical system, that is, highly redundant categories would be, in principle, more resilient than those not very redundant.
In relation to the similarity of the cities sampled (Aracaju, Fortaleza, Maceio, Recife, and Salvador), grouping analysis showed that the greater degree of similarity observed was between Maceio and Recife (Figure 6). In the grouping analysis, we can see that the cities close to each other showed greater similarity with regard to the animal species commercialized. Based on these results, these groupings can likely be a reflection of the presence of similar ecosystems in the cities sampled or the presence of more intense commercial routes of zootherapeutic products between closer cities.
Figure 6.
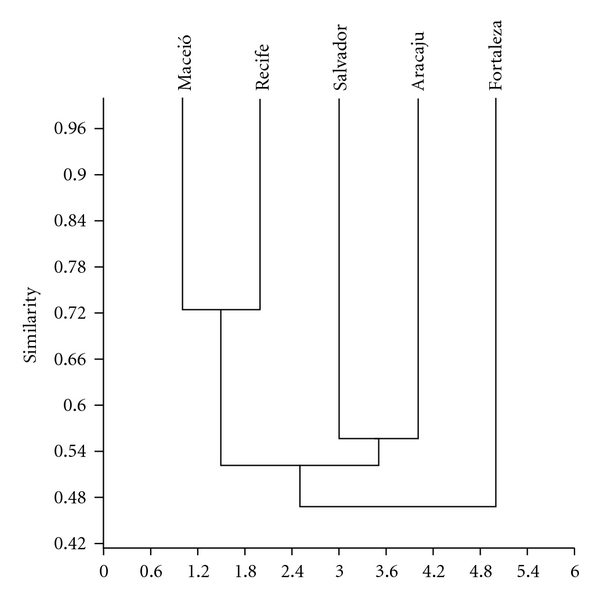
Cluster analysis of the species cited in the surveyed cities. (Correlation coefficient: R = 0.93).
Data on the commerce of medicinal animals are difficult to obtain, because many of the venders do not admit that they utilize or sell products originating from the fauna knowing that it can be illegal [17]. Therefore, the use of estimators of species richness represents an important tool. Our analyses demonstrate this, pointing out that the number of species commercialized tends to be greater than that recorded (Table 4 and Figure 7).
Table 4.
Comparison of observed species richness in Aracaju-SE, Fortaleza-CE, Maceió-AL, Recife-PE, and Salvador-BA public markets and the estimated species richness predicted by the estimators.
| Cities | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aracaju | Fortaleza | Maceió | Recife | Salvador | |
| Sobs | 19 | 28 | 27 | 31 | 36 |
| Estimators | |||||
| ICE | 25 | 34 | 28 | 49 | 48 |
| Chao2 | 21 | 33 | 28 | 43 | 45 |
| Jack1 | 25 | 36 | 29 | 44 | 49 |
| Jack2 | 25 | 40 | 29 | 51 | 55 |
Sobs: observed species.
Figure 7.
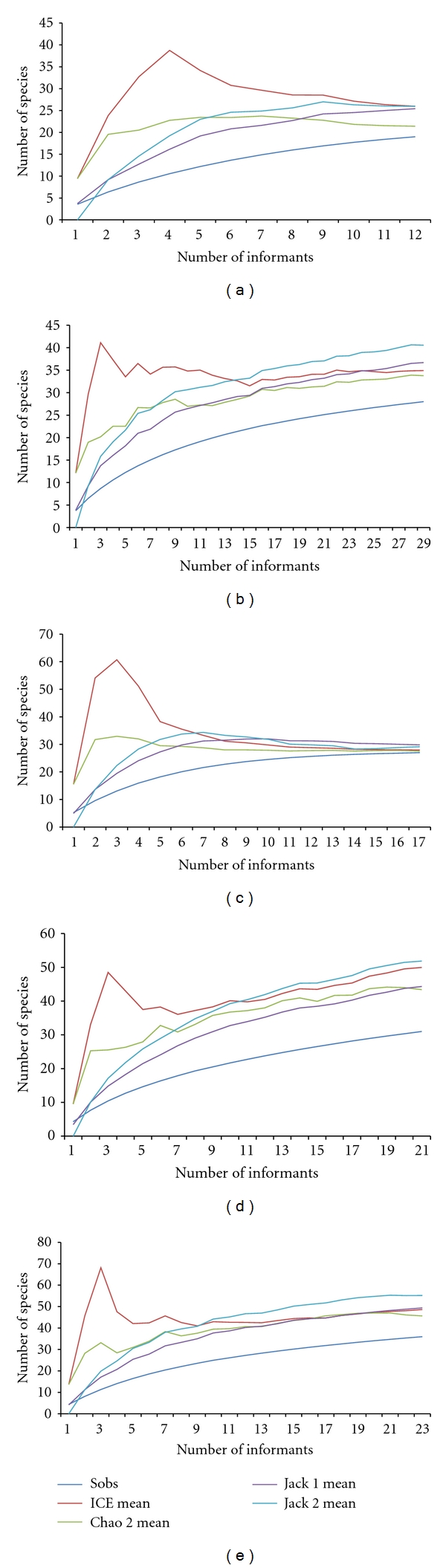
Graphs showing the values obtained with the richness estimators species assessed for each market. (a) Aracaju; (b) Fortaleza; (c) Maceió; (d) Recife; (e) Salvador.
It was observed that for Aracaju, Fortaleza, Recife, and Salvador the estimators indicated the existence of more traded species than that recorded in the present work. In accordance with the study by Whiting et al. [16], in the market in Faraday, South Africa, the richness estimator Jack 2 was better for use in studies on zootherapeutic products. According to these authors, Jack 2 yielded values closer to the number of species observed. However, based on our results obtained with the estimators ICE and CHAO 2 for the data on the sale of animals in Maceio (see Table 4), we can infer that these two estimators are also reliable, because we obtained values close to those obtained through informants in the markets of Maceió.
The values obtained with richness estimators show that the richness of species sold for traditional medicines in Northeast Brazil is high. However, the scarcity of studies on zootherapy in the country, as all over the world, has led to the importance of the zootherapeutic resources being underestimated in the country.
Estimates of species richness were utilized in ethnobiological studies conducted by Begossi [34]. In the case of research on the use and/or commerce of animals or plants, this tool has been little exploited. According to Williams et al. [53], the use of indices of species richness and diversity in ethnobiological research can serve to (i) evaluate the amount of biodiversity human populations exploit; (ii) make it possible to compare communities (or markets) using quantitative data; (iii) infer the minimal number of species necessary for the maintenance of the uses by traditional communities. In summary, the use of these indices open new perspectives for ethnozoological studies, since they can provide estimates on the richness and diversity of animal species utilized, especially considering the difficulty in obtaining information about the trade of wild animals, which are generally carried out in a clandestine manner.
In the present work, we recorded at least 68 species sold in the cities studied. Of these species, 23 (33.8%) are on the red list of threatened species [52]. The categories in which these species are included are from data deficient up to endangered. Even for some species not considered in high risk categories, the medicinal use and trade are cited as one of the causes of threat and/or population decline for only one species (H. reidi). For the majority of commercialized species, however, medicinal trade is not considered a form of threat, although it represents an additional pressure, which should be monitored, especially for species that are extensively exploited.
It is important to point out that the medicinal use of animals cannot be considered the only threat to the conservation of the species utilized for these purposes. Some authors [54] point out that the remedies based on animals are mainly formed of subproducts that do not serve other purposes other than medicinal, and therefore, the true reason for hunting them may not be for medicinal use, such in the case of food.
Understanding the aspects that involved the commerce of medicinal animals is important for the formulation of management plans for sustainable use of medicinal animal species [3]. Some works on the sale of medicinal animals indicate a concern with respect to the maintenance of these faunistic resources, taking into consideration that in Brazil the sale of medicinal animals in stores and street markets is not monitored [13].
In other countries, some published works indicate that the trade of fauna for various purposes, including medicinal, is one of the main causes of threats to wild populations. Servheen [55] pointed out that 14 species of bears, on the IUCN red list, are traded in and outside of China for medicinal use without the monitoring of the number of individuals sold. According to Lee [56], the use of rhinoceros horn in traditional medicine has been indicated as one of the main causes for the population decline of these animals. Alves et al. [3], providing an overview of the global use of primates in traditional folk medicines, noted that >100 species were traded for this purpose, and as noted by Ahmed [57] unchecked exploitation is leading to decreasing populations of primates utilized in traditional medicine in India. In Indonesia, Lee et al. [58] pointed out that the sale of mammals for various purposes, including medicinal, is one of the causes for declines in mammal populations. Athiyaman [59] reported that species of tigers are among the animals most endangered due to its trade for medicinal purposes without monitoring. Zhang et al. [60] stated that in China one of the major causes for the decline in species is illegal trade for food, craftwork, and medicinal purposes.
In Brazil, there is still no information that indicates the decline of species due to traditional medicine trade, although this activity has been indicated as one of the causes of a population decline of H. reidi [61, 62]. Although the intense commercialization of animals for medicinal purposes does not represent a significant impact for most of the species, such uses should be considered in strategies of management and conservation, particularly for those medicinal animals that are exploited more and on the list of threatened species [15].
Considering that animals represent an important source of remedies used in traditional medicines, zootherapy has become extremely relevant from a conservationist viewpoint [3]. In all the world, populations of various species have been utilized and the demand created by traditional medicine is probably one the causes of overexploitation found for some species of large mammals [1, 55, 57, 63].
According to Alves and Rosa [1], the ecological aspects associated with zootherapy represent one of the main reasons for studying the use of animals for medicinal purposes. However, it has not been possible to evaluate the magnitude of the impact of the medicinal use of the fauna, since the ways in which animals are used vary greatly [41], and the zootherapeutic products can be obtained indirectly from hunting for other purposes [11, 64]. Therefore, medicinal demand should be considered within a greater context of use of the fauna. The frequent commercialization of zootherapeutic products derived from particular species and their respective conservation status demonstrate that some animals deserve special attention.
In general, the use and commercialization of medicinal animals in Northeast Brazil is a reality consisting of an alternative for the treatment of various diseases, as well as representing an important source of income for various people. Knowledge of the fauna utilized popular medicine is indispensable for conservation, demonstrating that research on this subject is necessary to determine appropriate practices for the management of the fauna, thereby allowing the maintenance of the medicinal resources utilized and of the medicinal knowledge associated with these resources.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the CAPES for the scholarships to Felipe S. Ferreira. Many thanks to A. Leiva for reviewing the paper. They also thank the informants who contributed with the information to this research.
References
- 1.Alves RRN, Rosa IL. Why study the use of animal products in traditional medicines? Journal of Ethnobiology and Ethnomedicine. 2005;1, article 5 doi: 10.1186/1746-4269-1-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rodrigues E. Plants and animals utilized as medicines in the Jaú National Park (JNP), Brazilian Amazon. Phytotherapy Research. 2006;20(5):378–391. doi: 10.1002/ptr.1866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Alves RRN, Souto W, Barboza RRD. Primates in traditional folk medicine: a world overview. Mammal Review. 2010;40(2):155–180. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Alves RRN, Rosa IL. From cnidarians to mammals: the use of animals as remedies in fishing communities in NE Brazil. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2006;107(2):259–276. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2006.03.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Silva MLV, Alves ÂGC, Almeida AV. A zooterapia no Recife [Pernambuco]: uma articulação entre as práticas ea história. Biotemas. 2004;17:95–116. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Almeida AV. Zooterapia indígena brasileira do século XVII nas obras de Guilherme Piso, Georg Marcgrave e Joannes de Laet. Sitientibus. 2007;7:261–272. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Almeida CBR, Albuquerque UP. Uso e conservação de plantas e animais medicevais no estado de pernambuco (nordeste do Brasil): um estudo de caso. Interciencia. 2002;27(6):276–285. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Alves RRN, Rosa IL. Zootherapy goes to town: the use of animal-based remedies in urban areas of NE and N Brazil. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2007;113(3):541–555. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2007.07.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Alves RRN, Rosa IL. Zootherapeutic practices among fishing communities in North and Northeast Brazil: a comparison. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2007;111(1):82–103. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2006.10.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Alves RRN, Pereira Filho GA. Commercialization and use of snakes in North and Northeastern Brazil: implications for conservation and management. Biodiversity and Conservation. 2007;16(4):969–985. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Alves RRN, Silva CC, Barboza RRD, Souto MSW. Zootherapy as an alternative therapeutic in South America. Journal of Alternative Medicine Research. 2009;1:21–47. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ferreira FS, Brito AV, Ribeiro SC, Saraiva AAF, Almeida WO, Alves RRN. Animal-based folk remedies sold in public markets in Crato and Juazeiro do Norte, Ceará, Brazil. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2009;9, article 17 doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-9-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Alves RRN. Fauna used in popular medicine in Northeast Brazil. Journal of Ethnobiology and Ethnomedicine. 2009;5, article 1 doi: 10.1186/1746-4269-5-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Albuquerque UP, Monteiro JM, Ramos MA, Amorim ELC. Medicinal and magic plants from a public market in northeastern Brazil. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2007;110(1):76–91. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2006.09.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Alves RRN, Rosa IL, Santana GG. The role of animal-derived remedies as complementary medicine in Brazil. BioScience. 2007;57(11):949–955. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Whiting MJ, Williams VL, Hibbitts TJ. Animals traded for traditional medicine at the Faraday market in South Africa: species diversity and conservation implications. Journal of Zoology. 2011;284(2):84–96. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Alves RRN, Rosa IL. Trade of animals used in Brazilian traditional medicine: trends and implications for conservation. Human Ecology. 2010;38(5):691–704. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Costa-Neto EM. Healing with animals in Feira de Santana City, Bahia, Brazil. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 1999;65(3):225–230. doi: 10.1016/s0378-8741(98)00158-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Alves RRN, Lima HN, Tavares MC, Souto WMS, Barboza RRD, Vasconcellos A. Animal-based remedies as complementary medicines in Santa Cruz do Capibaribe, Brazil. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2008;8, article 44 doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-8-44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Alves RRN, Léo-Neto NA, Brooks SE, Albuquerque UP. Commercialization of animal-derived remedies as complementary medicine in the semi-arid region of Northeastern Brazil. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2009;124(3):600–608. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2009.04.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Oliveira ES, Torres DF, Brooks SE, Alves RRN. The medicinal animal markets in the metropolitan region of Natal City, northeastern Brazil. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2010;130(1):54–60. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.04.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Freire FC. Répteis Utilizados na Medicina Popular no Estado de Alagoas. Monografia de Graduação, Universidade Federal de Alagoas; 1996. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Albuquerque UP, Lucena RFP, Lins Neto EMF. Seleção dos participantes da pesquisa. In: Albuquerque UP, Lucena RFP, Cunha LVFC, editors. Métodos e Técnicas na Pesquisa Etnobiológica e Etnoecológica. Recife, Brazil: Nupeea; 2010. pp. 21–38. [Google Scholar]
- 24.CBCD. Classificação Estatística Internacional de Doenças e Problemas Relacionados à Saúde Décima Revisão, vol. I. Organização Mundial da Saúde [OMS]. Organização Pan-Americana de Saúde—OPAS. 1993, http://www.datasus.gov.br/cid10/webhelp/cid10.htm.
- 25.Heinrich M, Ankli A, Frei B, Weimann C, Sticher O. Medicinal plants in Mexico: healers’ consensus and cultural importance. Social Science and Medicine. 1998;47(11):1859–1871. doi: 10.1016/s0277-9536(98)00181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bennett BC, Prance GT. Introduced plants in the indigenous pharmacopoeia of northern South America. Economic Botany. 2000;54(1):90–102. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Albuquerque UP, Oliveira RF. Is the use-impact on native caatinga species in Brazil reduced by the high species richness of medicinal plants? Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2007;113(1):156–170. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2007.05.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wellnitz T, LeRoy Poff N. Functional redundancy in heterogeneous environments: implications for conservation. Ecology Letters. 2001;4(3):177–179. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Scarff FR, Bradley S. Ecosystem function and species loss—a microcosm study. Journal of Biogeography. 2002;29(5-6):641–651. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Krebs CJ. Ecological Methodology. New York, NY, USA: Harper and Row; 1989. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hammer Ø, Harper DAT, Ryan PD. Past: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontologia Electronica. 2001;4(1):1–9. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wilsey BJ, Chalcraft DR, Bowles CM, Willig MR. Relationships among indices suggest that richness is an incomplete surrogate for grassland biodiversity. Ecology. 2005;86(5):1178–1184. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Colwell RK. EstimateS 8.2: Statistical Estimation of Species Richness and Shared Species from Samples. User's Guide and Application. Storrs, Conn, USA: Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, University of Connecticut; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Begossi A. Use of ecological methods in ethnobotany: diversity indices. Economic Botany. 1996;50(3):280–289. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lev E. Traditional healing with animals (zootherapy): medieval to present-day Levantine practice. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2003;85(1):107–118. doi: 10.1016/s0378-8741(02)00377-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Mahawar MM, Jaroli DP. Animals and their products utilized as medicines by the inhabitants surrounding the Ranthambhore National Park, India. Journal of Ethnobiology and Ethnomedicine. 2006;2, article 46 doi: 10.1186/1746-4269-2-46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Mahawar MM, Jaroli DP. Traditional knowledge on zootherapeutic uses by the Saharia tribe of Rajasthan, India. Journal of Ethnobiology and Ethnomedicine. 2007;3, article 25 doi: 10.1186/1746-4269-3-25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mahawar MM, Jaroli DP. Traditional zootherapeutic studies in India: a review. Journal of Ethnobiology and Ethnomedicine. 2008;4, article 17 doi: 10.1186/1746-4269-4-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Alves RRN, Alves HN. The faunal drugstore: animal-based remedies used in traditional medicines in Latin America. Journal of Ethnobiology and Ethnomedicine. 2011;7, article 9 doi: 10.1186/1746-4269-7-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Negi CS, Palyal VS. Traditional uses of animal and animal products in medicine and rituals by the Shoka Tribes of District Pithoragarh, Uttaranchal, India. Studies on Ethnomedicine. 2007;1:51–53. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Soares EC. Peixes do Mearim. Instituto Geia, 2005.
- 42.Andrade JN, Costa-Neto EM. O comércio de produtos zooterápicos na cidade de Feira de Santana, Bahia, Brasil. Sitientibus Série Ciências Biológicas. 2006;6:37–43. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ferreira FS, Brito SV, Costa JGM, Alves RRN, Coutinho HDM, Almeida WO. Is the body fat of the lizard Tupinambis merianae effective against bacterial infections? Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2009;126(2):233–237. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2009.08.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ferreira FS, Brito SV, Saraiva RA, et al. Topical anti-inflammatory activity of body fat from the lizard Tupinambis merianae. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2010;130(3):514–520. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.05.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Ferreira FS, Silva NLG, Matias EFF, et al. Potentiation of aminoglycoside antibiotic activity using the body fat from the snake Boa constrictor . Revista Brasileira Farmacognosia. 2011;21(3):503–509. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Coutinho HDM, Santos IJM, Matias EFF, et al. Evaluation of the antimicrobial activity of the decoction of Tropidurus hispidus (Spix, 1825) and Tropidurus semitaeniatus (Spix, 1825) used by the traditional medicine. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2012;2012:6 pages. doi: 10.1155/2012/747969. Article ID 747969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Coutinho HDM, Vasconcellos A, Lima MA, Almeida-Filho GG, Alves RRN. Termite usage associated with antibiotic therapy: enhancement of aminoglycoside antibiotic activity by natural products of Nasutitermes corniger (Motschulsky 1855) BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2009;9, article 1472:35–40. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-9-35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Coutinho HDM, Vasconcellos A, Freire-Pessôa HL, Gadelha CA, Gadelha TS, Almeida-Filho GG. Natural products from the termite Nasutitermes corniger lowers aminoglycoside minimum inhibitory concentrations. Pharmacognosy Magazine. 2010;6(21):1–4. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.59958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.But PP, Lung L, Tam Y. Ethnopharmacology of rhinoceros horn. I: antipyretic effects of rhinoceros horn and other animal horns. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 1990;30(2):157–168. doi: 10.1016/0378-8741(90)90005-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Murari SK, Frey FJ, Frey BM, Gowda TV, Vishwanath BS. Use of Pavo cristatus feather extract for the better management of snakebites: neutralization of inflammatory reactions. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2005;99(2):229–237. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2005.02.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Tempone AG, Pimenta DC, Lebrun I, et al. Antileishmanial and antitrypanosomal activity of bufadienolides isolated from the toad Rhinella jimi parotoid macrogland secretion. Toxicon. 2008;52(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2008.05.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.IUCN. IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria, Version 3.1. Prepared by the IUCN Species Survival Commission. In: IUCN Gland, Switzerland, and Cambridge, United Kingdom, 2010.
- 53.Williams VL, Witkowski ETF, Balkwill K. The use of incidence-based species richness estimators, species accumulation curves and similarity measures to appraise ethnobotanical inventories from South Africa. Biodiversity and Conservation. 2007;16(9):2495–2513. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Moura FBP, Marques JGW. Folk medicine using animals in the Chapada Diamantina: incidental medicine? Ciencia e Saude Coletiva. 2008;13(2):2179–2188. doi: 10.1590/s1413-81232008000900023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Servheen C. The trade in bears and bear parts. In: Servheen SHaBP C, editor. Bears: Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan. 1999. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Lee SKH. Trade in Traditional Medicine Using Endangered Species: An International Context. 1999. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Ahmed A. Illegal trade and utilization of primates in India. ENVIS Bulletin. 2001:177–184. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Lee RJ, Gorog AJ, Dwiyahreni A, et al. Wildlife trade and implications for law enforcement in Indonesia: a case study from North Sulawesi. Biological Conservation. 2005;123(4):477–488. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Athiyaman A. An exploration into modeling sustainable consumption: the case of animal-based traditional medicines. Academy of Marketing Studies. 2008;2:16–23. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Zhang L, Hua N, Sun S. Wildlife trade, consumption and conservation awareness in southwest China. Biodiversity and Conservation. 2008;17(6):1493–1516. doi: 10.1007/s10531-008-9358-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Rosa I, Alves R, Bonifácio K, et al. Fishers’ knowledge and seahorse conservation in Brazil. Journal of Ethnobiology and Ethnomedicine. 2005;1, article 12 doi: 10.1186/1746-4269-1-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Rosa IL, Oliveira TPR, Osório FM, et al. Fisheries and trade of seahorses in Brazil: historical perspective, current trends, and future directions. Biodiversity and Conservation. 2011;20(9):1951–1971. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Still J. Use of animal products in traditional Chinese medicine: environmental impact and health hazards. Complementary Therapies in Medicine. 2003;11(2):118–122. doi: 10.1016/s0965-2299(03)00055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Alves RRN, Souto WMS. Ethnozoology in Brazil: current status and perspectives. Journal of Ethnobiology and Ethnomedicine. 2011;7, article 22 doi: 10.1186/1746-4269-7-22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


