Abstract
In the title compound, C14H9BrN2O, the quinazoline unit is essentially planar, with a mean deviation of 0.058 (2) Å from the least-squares plane defined by the ten constituent ring atoms. The dihedral angle between the mean plane of the quinazoline ring system and the 4-bromophenyl ring is 47.6 (1)°. In the crystal, molecules are linked by intermolecular C—H⋯N and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming infinite chains of alternating R 2 2(6) dimers and R 2 2(14) ring motifs.
Related literature
For the synthesis of the title compound, see: Priya, Zulykama et al. (2011 ▶). For a related structure, see: Priya, Srinivasan et al. (2011 ▶). For the biological activity of quinazoline derivatives, see: Wolfe et al.(1990 ▶); Tereshima et al. (1995 ▶); Pandeya et al. (1999 ▶). For graph-set notation, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C14H9BrN2O
M r = 301.14
Monoclinic,

a = 16.961 (3) Å
b = 3.9530 (8) Å
c = 17.698 (3) Å
β = 93.168 (11)°
V = 1184.8 (4) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 3.46 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.20 × 0.20 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEXII area-detector diffractometer
10371 measured reflections
2840 independent reflections
1772 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.050
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.036
wR(F 2) = 0.094
S = 1.01
2840 reflections
163 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.34 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.54 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2008 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2008 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97 and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811040736/im2320sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811040736/im2320Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811040736/im2320Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C8—H8⋯N1i | 0.93 | 2.48 | 3.286 (4) | 146 |
| C11—H11⋯O1ii | 0.93 | 2.32 | 3.224 (4) | 165 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
TS and DV thank the TBI X-ray facility, CAS in Crystallography and Biophysics, University of Madras, India, for the data collection and TS also thanks the DST for the Inspire fellowship
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
4(3H)-Quinazolinones are an important class of fused heterocycles with a wide range of biological activities such as anti-cancer (Wolfe et al.,1990), anti-inflammatory (Tereshima et al.,1995) and anti-HIV (Pandeya et al., 1999). In addition to that, quinazolinones exibit anti-bacterial and anti-fungal activities (Priya, Zulykama et al., 2011).
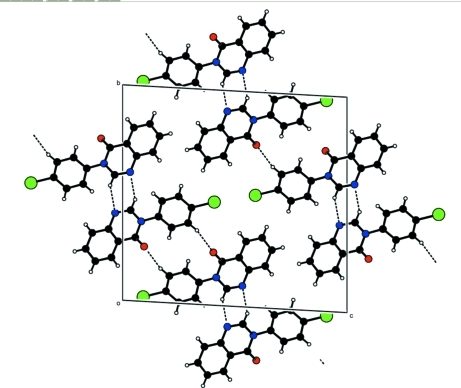
In title molecule (Fig. 1), the quinazoline unit is essentially planar, with a mean deviation of 0.058 (2) Å from the least square plane defined by the ten constituent atoms. The dihedral angle formed by the 4-bromophenyl ring and the mean plane of the quinazoline fragment is 47.6 (1)° . In the crystal packing, molecules are linked by intermolecular C–H···N and C–H···O hydrogen bonds (Table 1). These hydrogen bonds are forming infinite chains of alternating R22(6) dimer and R22(14) ring motifs (Bernstein et al., 1995) as shown in Fig. 2.
Experimental
To an ice-cold solution of 2.8 ml POCl3 in 5 ml DMF was added anthranilic acid (2 g, 0.0146 mole) and stirred for 5-10 min until TLC indicated the disappearance of anthranilic acid. The reaction mixture was then treated with an equimolar amount of p-bromo-aniline (2.511 g) and supported on anhydrous sodium sulfate (five times the weight of anthranilic acid) and exposed to microwave (BPL company) irradiation (600 W) for 2-4 min with 30 sec pulse. The reaction mixture was quenched with water (50 ml) and extracted with ethyl acetate (2 x 50 ml). The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, concentrated and purified by silica gel column chromatography (60-20 mesh) using hexane/EtOAc (7.5 : 2.5) as eluent to yield the pure product (yield: 4,397 g, 84%). Single crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction were prepared by slow evaporation of a solution of the title compound in methanol at room temperature.
Refinement
Hydrogen atoms were placed in calculated positions with C–H = 0.93 Å and refined using a riding model with fixed a isotropic displacement parameter of Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of the title compound. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level. H atoms are presented as a small spheres of arbitrary radius.
Fig. 2.
View of the C–H···N and C–H···O hydrogen bonds (dotted lines) in the crystal structure of the title compound. [Symmetry codes: (i) - x + 1, - y -1, - z; (ii) - x +1/2, y - 1/2, - z + 1/2.]
Crystal data
| C14H9BrN2O | F(000) = 600 |
| Mr = 301.14 | Dx = 1.688 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 2840 reflections |
| a = 16.961 (3) Å | θ = 1.6–28.3° |
| b = 3.9530 (8) Å | µ = 3.46 mm−1 |
| c = 17.698 (3) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 93.168 (11)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 1184.8 (4) Å3 | 0.20 × 0.20 × 0.20 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEXII area-detector diffractometer | 1772 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.050 |
| graphite | θmax = 28.3°, θmin = 1.6° |
| ω and φ scans | h = −22→14 |
| 10371 measured reflections | k = −4→5 |
| 2840 independent reflections | l = −23→23 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.036 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.094 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.01 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0381P)2 + 0.2934P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2840 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 163 parameters | Δρmax = 0.34 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.54 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.30495 (19) | −0.4078 (7) | −0.13542 (16) | 0.0457 (8) | |
| H1 | 0.3413 | −0.5172 | −0.1644 | 0.055* | |
| C2 | 0.22902 (19) | −0.3495 (8) | −0.16454 (17) | 0.0494 (8) | |
| H2 | 0.2143 | −0.4201 | −0.2134 | 0.059* | |
| C3 | 0.17450 (19) | −0.1869 (8) | −0.12177 (18) | 0.0500 (8) | |
| H3 | 0.1233 | −0.1520 | −0.1418 | 0.060* | |
| C4 | 0.19570 (17) | −0.0771 (8) | −0.04997 (17) | 0.0445 (7) | |
| H4 | 0.1591 | 0.0340 | −0.0216 | 0.053* | |
| C5 | 0.27242 (16) | −0.1327 (7) | −0.01962 (15) | 0.0354 (7) | |
| C6 | 0.32663 (17) | −0.3015 (7) | −0.06239 (15) | 0.0360 (6) | |
| N2 | 0.37065 (13) | −0.1237 (5) | 0.08283 (12) | 0.0338 (5) | |
| C9 | 0.39734 (16) | −0.0577 (7) | 0.15992 (14) | 0.0340 (6) | |
| C10 | 0.35023 (17) | −0.1470 (7) | 0.21832 (16) | 0.0424 (7) | |
| H10 | 0.3018 | −0.2522 | 0.2077 | 0.051* | |
| C11 | 0.37520 (18) | −0.0797 (7) | 0.29172 (16) | 0.0430 (7) | |
| H11 | 0.3434 | −0.1357 | 0.3310 | 0.052* | |
| C12 | 0.44731 (17) | 0.0707 (7) | 0.30707 (15) | 0.0383 (7) | |
| C13 | 0.49575 (17) | 0.1529 (7) | 0.24960 (16) | 0.0440 (7) | |
| H13 | 0.5449 | 0.2506 | 0.2607 | 0.053* | |
| C14 | 0.47056 (16) | 0.0889 (7) | 0.17584 (16) | 0.0397 (7) | |
| H14 | 0.5026 | 0.1440 | 0.1367 | 0.048* | |
| C7 | 0.29483 (16) | −0.0184 (8) | 0.05649 (15) | 0.0392 (7) | |
| C8 | 0.41999 (17) | −0.2860 (7) | 0.03558 (16) | 0.0380 (7) | |
| H8 | 0.4704 | −0.3381 | 0.0556 | 0.046* | |
| O1 | 0.25479 (13) | 0.1572 (6) | 0.09574 (12) | 0.0599 (6) | |
| N1 | 0.40348 (14) | −0.3727 (6) | −0.03334 (13) | 0.0411 (6) | |
| Br1 | 0.47919 (2) | 0.17499 (9) | 0.408526 (17) | 0.05840 (16) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.056 (2) | 0.0462 (19) | 0.0358 (15) | 0.0011 (15) | 0.0107 (14) | −0.0001 (13) |
| C2 | 0.057 (2) | 0.053 (2) | 0.0376 (15) | −0.0083 (17) | −0.0049 (15) | 0.0042 (14) |
| C3 | 0.0436 (18) | 0.056 (2) | 0.0494 (18) | −0.0026 (16) | −0.0041 (15) | 0.0095 (16) |
| C4 | 0.0351 (17) | 0.0494 (19) | 0.0493 (17) | 0.0077 (14) | 0.0058 (14) | 0.0051 (14) |
| C5 | 0.0356 (16) | 0.0347 (17) | 0.0368 (14) | 0.0037 (13) | 0.0094 (12) | 0.0068 (12) |
| C6 | 0.0361 (16) | 0.0359 (15) | 0.0367 (14) | 0.0006 (13) | 0.0081 (12) | 0.0063 (12) |
| N2 | 0.0301 (12) | 0.0408 (14) | 0.0314 (11) | 0.0064 (11) | 0.0090 (9) | 0.0002 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0335 (16) | 0.0367 (16) | 0.0325 (13) | 0.0026 (13) | 0.0077 (12) | 0.0035 (12) |
| C10 | 0.0390 (17) | 0.0477 (19) | 0.0416 (15) | −0.0047 (14) | 0.0122 (13) | 0.0043 (14) |
| C11 | 0.0467 (18) | 0.0506 (19) | 0.0331 (14) | −0.0002 (15) | 0.0153 (13) | 0.0068 (13) |
| C12 | 0.0453 (18) | 0.0410 (16) | 0.0291 (13) | 0.0023 (14) | 0.0050 (12) | 0.0026 (12) |
| C13 | 0.0379 (16) | 0.0505 (19) | 0.0434 (16) | −0.0070 (15) | 0.0018 (13) | 0.0042 (14) |
| C14 | 0.0341 (16) | 0.0474 (19) | 0.0389 (15) | −0.0011 (14) | 0.0131 (12) | 0.0086 (13) |
| C7 | 0.0316 (16) | 0.0478 (18) | 0.0390 (15) | 0.0039 (15) | 0.0083 (12) | 0.0052 (14) |
| C8 | 0.0304 (15) | 0.0447 (17) | 0.0397 (15) | 0.0077 (13) | 0.0096 (12) | 0.0039 (13) |
| O1 | 0.0482 (13) | 0.0870 (17) | 0.0452 (12) | 0.0302 (12) | 0.0080 (10) | −0.0133 (12) |
| N1 | 0.0372 (14) | 0.0494 (16) | 0.0377 (13) | 0.0062 (12) | 0.0117 (11) | −0.0007 (11) |
| Br1 | 0.0734 (3) | 0.0652 (3) | 0.03636 (18) | −0.00188 (19) | 0.00039 (15) | −0.00357 (15) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—C2 | 1.380 (4) | C9—C14 | 1.385 (4) |
| C1—C6 | 1.389 (4) | C9—C10 | 1.387 (4) |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | C10—C11 | 1.370 (4) |
| C2—C3 | 1.385 (4) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C11—C12 | 1.373 (4) |
| C3—C4 | 1.372 (4) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C12—C13 | 1.381 (4) |
| C4—C5 | 1.398 (4) | C12—Br1 | 1.892 (3) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C13—C14 | 1.374 (4) |
| C5—C6 | 1.393 (4) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C5—C7 | 1.451 (4) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C6—N1 | 1.403 (4) | C7—O1 | 1.216 (3) |
| N2—C8 | 1.374 (3) | C8—N1 | 1.283 (4) |
| N2—C7 | 1.406 (3) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| N2—C9 | 1.437 (3) | ||
| C2—C1—C6 | 119.4 (3) | C10—C9—N2 | 119.8 (2) |
| C2—C1—H1 | 120.3 | C11—C10—C9 | 119.8 (3) |
| C6—C1—H1 | 120.3 | C11—C10—H10 | 120.1 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 120.7 (3) | C9—C10—H10 | 120.1 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.6 | C10—C11—C12 | 119.8 (3) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.6 | C10—C11—H11 | 120.1 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.3 (3) | C12—C11—H11 | 120.1 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.9 | C11—C12—C13 | 121.0 (3) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.9 | C11—C12—Br1 | 119.1 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.8 (3) | C13—C12—Br1 | 119.8 (2) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.1 | C14—C13—C12 | 119.3 (3) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.1 | C14—C13—H13 | 120.3 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 119.7 (3) | C12—C13—H13 | 120.3 |
| C6—C5—C7 | 120.4 (2) | C13—C14—C9 | 119.9 (2) |
| C4—C5—C7 | 119.9 (2) | C13—C14—H14 | 120.1 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 120.1 (3) | C9—C14—H14 | 120.1 |
| C1—C6—N1 | 118.2 (3) | O1—C7—N2 | 120.6 (3) |
| C5—C6—N1 | 121.6 (2) | O1—C7—C5 | 125.6 (3) |
| C8—N2—C7 | 120.9 (2) | N2—C7—C5 | 113.8 (2) |
| C8—N2—C9 | 119.5 (2) | N1—C8—N2 | 126.5 (3) |
| C7—N2—C9 | 119.7 (2) | N1—C8—H8 | 116.7 |
| C14—C9—C10 | 120.1 (3) | N2—C8—H8 | 116.7 |
| C14—C9—N2 | 120.1 (2) | C8—N1—C6 | 116.4 (2) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.0 (4) | C10—C11—C12—Br1 | 177.9 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.9 (5) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 1.3 (5) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.6 (5) | Br1—C12—C13—C14 | −177.3 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.5 (4) | C12—C13—C14—C9 | −0.2 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—C7 | −179.7 (3) | C10—C9—C14—C13 | −1.5 (4) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −1.1 (4) | N2—C9—C14—C13 | 179.7 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—N1 | 178.2 (2) | C8—N2—C7—O1 | −171.8 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 1.3 (4) | C9—N2—C7—O1 | 7.5 (4) |
| C7—C5—C6—C1 | −179.5 (3) | C8—N2—C7—C5 | 6.9 (4) |
| C4—C5—C6—N1 | −177.9 (2) | C9—N2—C7—C5 | −173.8 (2) |
| C7—C5—C6—N1 | 1.3 (4) | C6—C5—C7—O1 | 172.8 (3) |
| C8—N2—C9—C14 | 48.8 (4) | C4—C5—C7—O1 | −8.0 (4) |
| C7—N2—C9—C14 | −130.5 (3) | C6—C5—C7—N2 | −5.9 (4) |
| C8—N2—C9—C10 | −130.0 (3) | C4—C5—C7—N2 | 173.3 (2) |
| C7—N2—C9—C10 | 50.7 (4) | C7—N2—C8—N1 | −3.4 (4) |
| C14—C9—C10—C11 | 2.1 (4) | C9—N2—C8—N1 | 177.3 (3) |
| N2—C9—C10—C11 | −179.1 (3) | N2—C8—N1—C6 | −1.7 (4) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | −1.1 (5) | C1—C6—N1—C8 | −176.6 (3) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | −0.6 (5) | C5—C6—N1—C8 | 2.7 (4) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C8—H8···N1i | 0.93 | 2.48 | 3.286 (4) | 146. |
| C11—H11···O1ii | 0.93 | 2.32 | 3.224 (4) | 165. |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y−1, −z; (ii) −x+1/2, y−1/2, −z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: IM2320).
References
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 34, 1555–1573.
- Bruker (2008). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Pandeya, S. N., Sriram, D., Nath, G. & Declera, E. (1999). Pharm. Acta Helv. 74, 11–17. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Priya, M. G. R., Srinivasan, T., Girija, K., Chandran, N. R. & Velmurugan, D. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o2310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Priya, M. G. R., Zulykama, Y., Girija, K., Murugesh, S. & Perumal, P. T. (2011). Indian J. Chem. Sect. B, 50, pp. 98–102.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Tereshima, K., Shimamura, H., Kawase, A., Tanaka, Y., Tanimura, T., Ishizuka, Y. & Sato, M. (1995). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 45, 2021–2023. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, J. F., Rathman, T. L., Sleevi, M. C., Campbell, J. S. A. & Greenwood, T. D. (1990). J. Med. Chem. 33, 161–166. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811040736/im2320sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811040736/im2320Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811040736/im2320Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report