Abstract
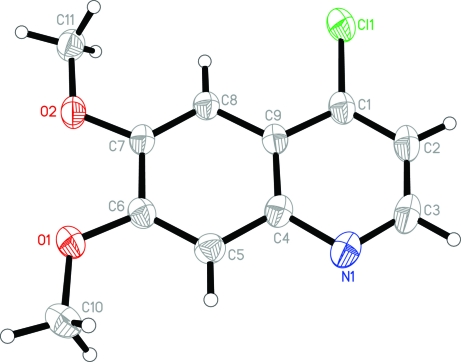
The title molecule, C11H10ClNO2, is almost planar with the C atoms of the methoxy groups deviating by −0.082 (2) and 0.020 (2) Å from the least-squares plane defined by the atoms of the quinoline ring system (r.m.s. deviation = 0.002 Å). An intramolecular C—H⋯Cl interaction generates an S(5) ring motif.
Related literature
For related structures, see: Davies & Bond (2001 ▶); Yathirajan et al. (2007 ▶). For biological properties of quinoline derivatives, see: Franck et al. (2004 ▶); Moret et al. (2006 ▶); Furuta et al. (2006 ▶); Ilovich et al. (2008 ▶). For hydrogen-bond motifs, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C11H10ClNO2
M r = 223.65
Monoclinic,
a = 12.5530 (17) Å
b = 4.6499 (7) Å
c = 18.274 (3) Å
β = 105.786 (2)°
V = 1026.4 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.35 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.3 × 0.2 × 0.2 mm
Data collection
Rigaku SCXmini diffractometer
6840 measured reflections
1808 independent reflections
1542 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.034
3 standard reflections every 150 reflections intensity decay: none
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.037
wR(F 2) = 0.115
S = 1.08
1808 reflections
139 parameters
1 restraint
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.29 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3
Data collection: CrystalClear (Rigaku, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: CrystalClear; data reduction: CrystalClear; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811042589/lr2029sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811042589/lr2029Isup3.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811042589/lr2029Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C8—H8⋯Cl1 | 0.93 | 2.70 | 3.0827 (17) | 105 |
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge financial support by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK2009293) and the Educational Commission of Jiangsu Province (JHB 2011–2).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Quinoline derivatives have been interesting to researchers for many years because a large number of natural products contain these heterocycles and also because their varied biological activities ( Franck et al. 2004; Moret et al. 2006; Furuta et al. 2006 & Ilovich et al. 2008).
Prompted by the properties of quinoline derivatives, the title compound, C11H10ClNO2, has been synthesized. Bond lengths and angles are in the usual range (Davies & Bond 2001 & Yathirajan et al. 2007) and the whole molecule is almost planar with the carbon atoms of the methoxyl groups deviating 0.08 (C10) and 0.02Å (C11) from the least-square plane defined by the atoms of the quinoline ring. There are intramolecular C8 — H8 ···Cl1 interactions (Table 1) generating S(5) ring motifs (Bernstein et al. 1995) . Figure 1 shows the molecular structure of the title compound and Figure 2 is a partial paking view of the crystal structure down the b axis.
Experimental
A mixture of 6,7- dimethoxynaphthalen-1-ol (20.4 g, 100 mmol) and POCl3 (60 ml, 640 mmol) was heated under reflux for 6 h. The excess of phosporus oxychoride was distilled out under reduced pressure. 200 g crush ice was added to the residue followed by 50% aqueous NaOH until the pH was adjusted to 8. The resulting solid was collected by filtration and washed with water to give the crude product. Purification of the crude product by a column chromatography (petroleum ether: EtOAc = 8:1 v.v) afforded the title compound (15.6 g, 70%) as pink crystals.The purity of the product, 4- chloro- 6, 7- dimethoxy- quinoline, was determined using a reversed- phase C-18 analytical HPLC column (99% purity). Crystals of the title compound suitable for X– ray diffraction were obtained by slow evaporation of methanol solution at room temperature. m. p. 403- 404 K; 1H NMR (DMSO– d6): δ8.57 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 1H), 7.40 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, 1H), 7.37 (s, 1H), 7.32 (s, 1H), 4.04 (s, 3H), 4.03 (s. 3H). MS (ESI, m/z): 224 (M+1).
Refinement
All H atoms were placed at calculated positions; C—H = 0.93 Å for aromatic H, C—H = 0.96 Å for methoxyl H. They were refined using a riding model with Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq (C) and Uiso(H) =1.5 Ueq (C), respectively.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.
Partial packing view of the title compound, viewed down the b axis.
Crystal data
| C11H10ClNO2 | F(000) = 464 |
| Mr = 223.65 | Dx = 1.447 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 12.5530 (17) Å | Cell parameters from 30 reflections |
| b = 4.6499 (7) Å | θ = 3–25° |
| c = 18.274 (3) Å | µ = 0.35 mm−1 |
| β = 105.786 (2)° | T = 296 K |
| V = 1026.4 (3) Å3 | Block, pink |
| Z = 4 | 0.3 × 0.2 × 0.2 mm |
Data collection
| Rigaku SCXmini diffractometer | Rint = 0.034 |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 1.7° |
| graphite | h = −14→14 |
| ω scans | k = −5→5 |
| 6840 measured reflections | l = −21→21 |
| 1808 independent reflections | 3 standard reflections every 150 reflections |
| 1542 reflections with I > 2σ(I) | intensity decay: none |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.037 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.115 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0662P)2 + 0.1562P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.08 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 1808 reflections | Δρmax = 0.29 e Å−3 |
| 139 parameters | Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.029 (4) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.18445 (16) | 0.9064 (4) | 0.34245 (10) | 0.0508 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.23248 (18) | 0.7745 (5) | 0.40978 (11) | 0.0608 (5) | |
| H2 | 0.2071 | 0.8077 | 0.4523 | 0.073* | |
| C3 | 0.32020 (19) | 0.5895 (5) | 0.41333 (12) | 0.0668 (6) | |
| H3 | 0.3522 | 0.4999 | 0.4596 | 0.080* | |
| C4 | 0.31375 (16) | 0.6656 (4) | 0.28823 (10) | 0.0486 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.35750 (15) | 0.6077 (4) | 0.22615 (11) | 0.0503 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.4173 | 0.4832 | 0.2326 | 0.060* | |
| C6 | 0.31298 (14) | 0.7325 (4) | 0.15691 (10) | 0.0469 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.22217 (14) | 0.9277 (4) | 0.14727 (9) | 0.0443 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.17947 (14) | 0.9890 (4) | 0.20641 (9) | 0.0441 (4) | |
| H8 | 0.1208 | 1.1173 | 0.1997 | 0.053* | |
| C9 | 0.22416 (14) | 0.8581 (3) | 0.27829 (9) | 0.0437 (4) | |
| C10 | 0.43422 (17) | 0.4878 (5) | 0.09810 (13) | 0.0659 (6) | |
| H10A | 0.4997 | 0.5563 | 0.1344 | 0.099* | |
| H10B | 0.4482 | 0.4703 | 0.0492 | 0.099* | |
| H10C | 0.4142 | 0.3033 | 0.1139 | 0.099* | |
| C11 | 0.09705 (17) | 1.2379 (5) | 0.06201 (12) | 0.0580 (5) | |
| H11A | 0.0339 | 1.1499 | 0.0729 | 0.087* | |
| H11B | 0.0780 | 1.2972 | 0.0097 | 0.087* | |
| H11C | 0.1195 | 1.4025 | 0.0942 | 0.087* | |
| Cl1 | 0.07193 (4) | 1.13418 (12) | 0.33477 (3) | 0.0656 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.36194 (14) | 0.5307 (4) | 0.35576 (9) | 0.0623 (5) | |
| O1 | 0.34547 (11) | 0.6869 (3) | 0.09331 (7) | 0.0585 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.18526 (11) | 1.0371 (3) | 0.07552 (7) | 0.0561 (4) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0588 (11) | 0.0528 (10) | 0.0423 (10) | −0.0142 (9) | 0.0164 (8) | −0.0043 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0742 (13) | 0.0699 (12) | 0.0404 (11) | −0.0112 (10) | 0.0193 (10) | 0.0013 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0824 (14) | 0.0736 (13) | 0.0398 (11) | −0.0076 (11) | 0.0088 (10) | 0.0115 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0543 (10) | 0.0463 (10) | 0.0428 (10) | −0.0079 (8) | 0.0094 (8) | 0.0014 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0505 (10) | 0.0487 (10) | 0.0506 (11) | 0.0030 (8) | 0.0120 (8) | 0.0001 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0498 (10) | 0.0491 (9) | 0.0438 (10) | −0.0047 (8) | 0.0162 (8) | −0.0054 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0504 (10) | 0.0460 (9) | 0.0363 (9) | −0.0045 (7) | 0.0114 (7) | −0.0014 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0467 (9) | 0.0452 (9) | 0.0405 (9) | −0.0029 (7) | 0.0121 (7) | −0.0012 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0487 (9) | 0.0445 (9) | 0.0381 (9) | −0.0113 (7) | 0.0123 (7) | −0.0036 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0635 (12) | 0.0696 (13) | 0.0717 (14) | 0.0061 (11) | 0.0303 (10) | −0.0091 (11) |
| C11 | 0.0643 (12) | 0.0611 (11) | 0.0474 (11) | 0.0071 (10) | 0.0134 (9) | 0.0054 (9) |
| Cl1 | 0.0735 (4) | 0.0778 (4) | 0.0532 (4) | 0.0040 (3) | 0.0302 (3) | −0.0051 (2) |
| N1 | 0.0685 (11) | 0.0630 (10) | 0.0506 (10) | −0.0002 (8) | 0.0083 (8) | 0.0112 (8) |
| O1 | 0.0633 (8) | 0.0695 (9) | 0.0478 (8) | 0.0123 (7) | 0.0239 (6) | −0.0024 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0675 (8) | 0.0654 (8) | 0.0380 (7) | 0.0129 (7) | 0.0188 (6) | 0.0068 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—C2 | 1.360 (3) | C6—C7 | 1.430 (3) |
| C1—C9 | 1.411 (3) | C7—C8 | 1.361 (2) |
| C1—Cl1 | 1.740 (2) | C7—O2 | 1.365 (2) |
| C2—C3 | 1.385 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.418 (2) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| C3—N1 | 1.325 (3) | C10—O1 | 1.433 (2) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C10—H10A | 0.9600 |
| C4—N1 | 1.370 (2) | C10—H10B | 0.9600 |
| C4—C9 | 1.410 (3) | C10—H10C | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.414 (3) | C11—O2 | 1.418 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.366 (3) | C11—H11A | 0.9600 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C11—H11B | 0.9600 |
| C6—O1 | 1.349 (2) | C11—H11C | 0.9600 |
| C2—C1—C9 | 120.67 (19) | C7—C8—C9 | 120.25 (17) |
| C2—C1—Cl1 | 119.85 (16) | C7—C8—H8 | 119.9 |
| C9—C1—Cl1 | 119.48 (14) | C9—C8—H8 | 119.9 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 118.27 (19) | C4—C9—C1 | 116.33 (16) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.9 | C4—C9—C8 | 119.53 (16) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.9 | C1—C9—C8 | 124.14 (17) |
| N1—C3—C2 | 124.90 (18) | O1—C10—H10A | 109.5 |
| N1—C3—H3 | 117.6 | O1—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 117.6 | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| N1—C4—C9 | 123.24 (18) | O1—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| N1—C4—C5 | 117.57 (17) | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C9—C4—C5 | 119.19 (16) | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 120.80 (17) | O2—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.6 | O2—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.6 | H11A—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| O1—C6—C5 | 126.01 (17) | O2—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| O1—C6—C7 | 114.29 (15) | H11A—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 119.69 (17) | H11B—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—O2 | 125.52 (16) | C3—N1—C4 | 116.59 (18) |
| C8—C7—C6 | 120.54 (15) | C6—O1—C10 | 117.47 (15) |
| O2—C7—C6 | 113.94 (15) | C7—O2—C11 | 117.24 (14) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C8—H8···Cl1 | 0.93 | 2.70 | 3.0827 (17) | 105 |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: LR2029).
References
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Davies, J. E. & Bond, A. D. (2001). Acta Cryst. E57, o947–o949.
- Franck, X., Fournet, A., Prina, E., Mahieuxe, R., Hocquemiller, R. & Fiqadere, B. (2004). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 14, 3635–3638. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Furuta, T., Sakai, T., Senga, T., Osawa, T., Kubo, K., Shimizu, T., Suzuki, R., Yoshino, T., Endo, M. & Miwa, A. (2006). J. Med. Chem. 49, 2186–2192. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ilovich, O., Jacobson, O., Aviv, Y., Litchi, A., Chisin, R. & Mishani, E. (2008). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 16, 4242–4251. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Moret, V., Dereudre-Bosquet, N., Clayette, P., Laras, Y., Pietrancosta, N., Rolland, A., Weck, C., Marc, S. & Kraus, J. L. (2006). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 16, 5988–5992. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rigaku (2005). CrystalClear Rigaku Americas Corporation, The Woodlands, Texas, USA.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Yathirajan, H. S., Sreevidya, T. V., Prathap, M., Narayana, B. & Bolte, M. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o763–o765.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811042589/lr2029sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811042589/lr2029Isup3.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811042589/lr2029Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report