Abstract
The title compound, C18H15NO3, consists of an indolizine ring system and an aromatic ring. The two ring systems are not coplanar, the dihedral angle between the two being 54.26 (7)°. In the crystal, inversion dimers are formed by weak C—H⋯O interactions. These dimeric groups are further extended to form a regular two-dimensional structure by additional weak C—H⋯O interactions.
Related literature
For background information on indolizine and its derivatives, see: Tukulula et al. (2010 ▶); James et al. (2008 ▶); Teklu et al. (2005 ▶); Shen et al. (2008 ▶, 2006 ▶). For the synthesis of the title compound, see: Wang et al. (2000 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C18H15NO3
M r = 293.31
Monoclinic,
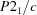
a = 10.030 (2) Å
b = 19.223 (3) Å
c = 7.9652 (17) Å
β = 103.073 (3)°
V = 1495.9 (5) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 291 K
0.24 × 0.20 × 0.18 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2000 ▶) T min = 0.979, T max = 0.984
8910 measured reflections
2604 independent reflections
1604 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.057
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.048
wR(F 2) = 0.129
S = 1.00
2604 reflections
201 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.18 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.15 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2000 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2000 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: SHELXTL; software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681104284X/im2326sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681104284X/im2326Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681104284X/im2326Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1—H1⋯O1i | 0.93 | 2.45 | 3.163 (3) | 134 |
| C14—H14⋯O3ii | 0.93 | 2.58 | 3.455 (3) | 157 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province of China (grant No. BK2008435) and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions for financial support.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Indolizine and it's derivatives have been comprehensively applied in biology and medicine due to their particular structures (Tukulula et al., 2010; James et al., 2008; Teklu et al., 2005). They can also be used as organic fluorescence probes (Shen et al., 2008; Shen et al., 2006). In our continuing studies in organic fluorescence probes, we synthesized the ethyl-3-benzoylindolizine-1-carboxylate (I).
The crystal structure of the title compound, C18H15NO3, reveals that all bond lengths and angles have normal values (Table 1 and 2). In the asymmetric unit there is one title compound molecule. The molecular structure consists of one indolizine ring A (C1—C8/N) and an aromatic ring B(C10—C15) (Fig. 1). Rings A and ring B are not coplanar with the dihedral angle between them being 54.26 (7) °.
In the crystal packing there are weak C1—H1···O1i (i: 1 - x,-y,2 - z) interactions between neighbouring molecules forming dimeric groups (Fig. 2). These dimeric groups are further extended into a tegular 2-D structure via weak C14—H14···O3ii (ii: -x,-1/2 + y,0.5 - z) interactions (Fig. 2).
Experimental
Ethyl-3-benzoylindolizine-1-carboxylate was prepared by 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition according to a procedure described in the literature (Wang, et al., 2000). A suspension of N-(benzoylmethyl)pyridinium bromide (C5H5N+–CH2COC6H5 Br-) (10 mmol), ethyl acrylate (40 mmol), Et3N (20 ml) and CrO3 (20 mmol) in DMF (40 ml) was stirred at 90°C for 2 h (monitored by TLC). The mixture was then cooled to room temperature and poured into 5% aqueous HCl (200 mL). The mixture was extracted with CH2Cl2 (2 times 50 mL) and the combined extracts were washed with water (2 times 50 mL) and dried over Na2SO4. The solvent was removed to give a solid, which was purified by chromatography [silica gel, 20% ethyl acetate in light petroleum (b.p. 60–90°C)] to yield 1.90 g (68%) (I). Yellow crystals were obtained by recrystallization from ethyl acetate at room temperature.
H-NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz) δ: 1.41 (t, 3H, CH3), 4.38 (q, 2H, CH2), 7.10 (t, 1H, H6), 7.44–7.84 (m, 7H, H7, H2 and PhH), 8.39 (d, 1H, H8), 9.98 (d, 1H, H5).
Refinement
The H atoms were placed in calculated positions and included as part of a riding model, with C—H = 0.93–0.97 Å, and with Uequiv values set at 1.2–1.5 Uequiv of the parent atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
A view of the title compound showing the atom-numbering scheme and displacement ellipsoids drawn at 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.
A view of the 2-D structure down c axis (i: 1 - x,-y,2 - z; ii: -x,-1/2 + y,0.5 - z).
Crystal data
| C18H15NO3 | F(000) = 616 |
| Mr = 293.31 | Dx = 1.302 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 1073 reflections |
| a = 10.030 (2) Å | θ = 2.3–19.4° |
| b = 19.223 (3) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 7.9652 (17) Å | T = 291 K |
| β = 103.073 (3)° | Block, yellow |
| V = 1495.9 (5) Å3 | 0.24 × 0.20 × 0.18 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer | 2604 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: sealed tube | 1604 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.057 |
| phi and ω scans | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 2.1° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2000) | h = −11→11 |
| Tmin = 0.979, Tmax = 0.984 | k = −22→20 |
| 8910 measured reflections | l = −9→9 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.048 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.129 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0588P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.00 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.010 |
| 2604 reflections | Δρmax = 0.18 e Å−3 |
| 201 parameters | Δρmin = −0.15 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL97, Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.015 (2) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger.Least-squares planes (x,y,z in crystal coordinates) and deviations from them (* indicates atom used to define plane)8.2801 (0.0047) x + 9.1394 (0.0112) y - 3.8457 (0.0039) z = 0.2003 (0.0031)* 0.0099 (0.0018) C1 * 0.0019 (0.0019) C2 * -0.0097 (0.0019) C3 * -0.0087 (0.0017) C4 * 0.0066 (0.0018) C5 * 0.0165 (0.0017) C6 * -0.0108 (0.0017) C7 * -0.0130 (0.0017) C8 * 0.0072 (0.0016) N1Rms deviation of fitted atoms = 0.0101- 0.9358 (0.0101) x - 10.1188 (0.0159) y + 6.7251 (0.0044) z = 4.3984 (0.0037)Angle to previous plane (with approximate e.s.d.) = 54.26 (0.07)* -0.0091 (0.0016) C10 * 0.0153 (0.0017) C11 * -0.0081 (0.0018) C12 * -0.0053 (0.0019) C13 * 0.0114 (0.0018) C14 * -0.0042 (0.0016) C15Rms deviation of fitted atoms = 0.0097 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.3367 (2) | 0.08044 (12) | 0.8614 (3) | 0.0535 (7) | |
| H1 | 0.4005 | 0.0494 | 0.9231 | 0.064* | |
| C2 | 0.3057 (3) | 0.13943 (12) | 0.9370 (3) | 0.0620 (7) | |
| H2 | 0.3483 | 0.1490 | 1.0509 | 0.074* | |
| C3 | 0.2092 (3) | 0.18631 (13) | 0.8436 (3) | 0.0613 (7) | |
| H3 | 0.1880 | 0.2267 | 0.8963 | 0.074* | |
| C4 | 0.1464 (2) | 0.17291 (11) | 0.6764 (3) | 0.0501 (6) | |
| H4 | 0.0825 | 0.2041 | 0.6154 | 0.060* | |
| C5 | 0.1782 (2) | 0.11209 (10) | 0.5963 (3) | 0.0426 (6) | |
| C6 | 0.1348 (2) | 0.08293 (10) | 0.4309 (3) | 0.0445 (6) | |
| C7 | 0.2020 (2) | 0.02004 (11) | 0.4333 (3) | 0.0477 (6) | |
| H7 | 0.1906 | −0.0104 | 0.3403 | 0.057* | |
| C8 | 0.2880 (2) | 0.00854 (10) | 0.5917 (3) | 0.0449 (6) | |
| C9 | 0.3887 (2) | −0.04547 (11) | 0.6464 (3) | 0.0473 (6) | |
| C10 | 0.3774 (2) | −0.10994 (10) | 0.5398 (3) | 0.0411 (6) | |
| C11 | 0.4968 (3) | −0.13982 (12) | 0.5151 (3) | 0.0536 (7) | |
| H11 | 0.5808 | −0.1192 | 0.5626 | 0.064* | |
| C12 | 0.4918 (3) | −0.20014 (12) | 0.4201 (4) | 0.0670 (8) | |
| H12 | 0.5722 | −0.2191 | 0.4002 | 0.080* | |
| C13 | 0.3690 (3) | −0.23235 (13) | 0.3550 (3) | 0.0674 (8) | |
| H13 | 0.3662 | −0.2732 | 0.2917 | 0.081* | |
| C14 | 0.2502 (3) | −0.20418 (12) | 0.3833 (3) | 0.0611 (7) | |
| H14 | 0.1671 | −0.2265 | 0.3414 | 0.073* | |
| C15 | 0.2542 (2) | −0.14261 (11) | 0.4742 (3) | 0.0497 (6) | |
| H15 | 0.1734 | −0.1231 | 0.4912 | 0.060* | |
| C16 | 0.0427 (2) | 0.11668 (12) | 0.2879 (3) | 0.0496 (6) | |
| C17 | −0.0756 (3) | 0.10378 (13) | −0.0047 (3) | 0.0640 (7) | |
| H17A | −0.0512 | 0.0856 | −0.1073 | 0.077* | |
| H17B | −0.0680 | 0.1541 | −0.0066 | 0.077* | |
| C18 | −0.2186 (3) | 0.08400 (16) | −0.0048 (4) | 0.0880 (10) | |
| H18A | −0.2252 | 0.0343 | 0.0015 | 0.132* | |
| H18B | −0.2785 | 0.1003 | −0.1089 | 0.132* | |
| H18C | −0.2446 | 0.1046 | 0.0928 | 0.132* | |
| N1 | 0.27358 (18) | 0.06663 (9) | 0.6934 (2) | 0.0438 (5) | |
| O1 | 0.48475 (18) | −0.03908 (9) | 0.7719 (2) | 0.0698 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.01794 (18) | 0.07657 (8) | 0.1471 (2) | 0.0672 (5) | |
| O3 | −0.00443 (17) | 0.17415 (8) | 0.2920 (2) | 0.0662 (5) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0636 (17) | 0.0482 (14) | 0.0423 (14) | 0.0019 (12) | −0.0016 (12) | −0.0008 (11) |
| C2 | 0.080 (2) | 0.0534 (15) | 0.0490 (16) | 0.0019 (14) | 0.0082 (14) | −0.0108 (13) |
| C3 | 0.0735 (19) | 0.0484 (15) | 0.0631 (18) | 0.0056 (13) | 0.0175 (15) | −0.0091 (13) |
| C4 | 0.0506 (15) | 0.0421 (13) | 0.0576 (17) | 0.0043 (11) | 0.0123 (13) | 0.0015 (12) |
| C5 | 0.0403 (14) | 0.0374 (12) | 0.0488 (14) | 0.0011 (10) | 0.0075 (12) | 0.0033 (11) |
| C6 | 0.0471 (15) | 0.0389 (12) | 0.0440 (14) | 0.0024 (11) | 0.0033 (11) | −0.0009 (11) |
| C7 | 0.0532 (16) | 0.0408 (13) | 0.0445 (15) | −0.0015 (11) | 0.0015 (12) | −0.0058 (10) |
| C8 | 0.0510 (15) | 0.0372 (12) | 0.0431 (14) | 0.0017 (11) | 0.0035 (12) | −0.0031 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0464 (15) | 0.0434 (13) | 0.0485 (15) | 0.0003 (11) | 0.0028 (13) | 0.0015 (11) |
| C10 | 0.0458 (15) | 0.0342 (12) | 0.0406 (13) | 0.0014 (11) | 0.0040 (11) | 0.0066 (10) |
| C11 | 0.0483 (16) | 0.0473 (14) | 0.0643 (17) | 0.0002 (12) | 0.0109 (13) | 0.0001 (12) |
| C12 | 0.0695 (19) | 0.0521 (16) | 0.084 (2) | 0.0083 (14) | 0.0271 (16) | −0.0052 (15) |
| C13 | 0.084 (2) | 0.0468 (15) | 0.0695 (19) | −0.0001 (16) | 0.0127 (17) | −0.0128 (13) |
| C14 | 0.0613 (18) | 0.0481 (15) | 0.0678 (18) | −0.0107 (13) | 0.0020 (14) | −0.0026 (13) |
| C15 | 0.0471 (16) | 0.0444 (13) | 0.0550 (16) | 0.0025 (11) | 0.0061 (13) | 0.0017 (12) |
| C16 | 0.0505 (16) | 0.0441 (14) | 0.0505 (16) | 0.0011 (12) | 0.0037 (12) | 0.0040 (12) |
| C17 | 0.069 (2) | 0.0711 (17) | 0.0429 (15) | 0.0018 (15) | −0.0064 (14) | 0.0072 (13) |
| C18 | 0.072 (2) | 0.113 (2) | 0.074 (2) | −0.0102 (18) | 0.0051 (17) | 0.0196 (18) |
| N1 | 0.0485 (12) | 0.0381 (10) | 0.0412 (11) | −0.0003 (9) | 0.0027 (9) | −0.0013 (8) |
| O1 | 0.0645 (12) | 0.0669 (12) | 0.0635 (12) | 0.0164 (9) | −0.0162 (10) | −0.0144 (9) |
| O2 | 0.0783 (13) | 0.0639 (11) | 0.0487 (11) | 0.0165 (9) | −0.0083 (9) | −0.0023 (9) |
| O3 | 0.0722 (13) | 0.0488 (10) | 0.0679 (13) | 0.0143 (9) | −0.0041 (10) | 0.0056 (9) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—C2 | 1.353 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.382 (3) |
| C1—N1 | 1.370 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.379 (3) |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.406 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.372 (3) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.363 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.373 (3) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.403 (3) | C14—C15 | 1.383 (3) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C5—N1 | 1.393 (3) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.407 (3) | C16—O3 | 1.205 (3) |
| C6—C7 | 1.382 (3) | C16—O2 | 1.337 (3) |
| C6—C16 | 1.448 (3) | C17—O2 | 1.450 (3) |
| C7—C8 | 1.376 (3) | C17—C18 | 1.484 (3) |
| C7—H7 | 0.9300 | C17—H17A | 0.9700 |
| C8—N1 | 1.406 (2) | C17—H17B | 0.9700 |
| C8—C9 | 1.445 (3) | C18—H18A | 0.9600 |
| C9—O1 | 1.228 (3) | C18—H18B | 0.9600 |
| C9—C10 | 1.492 (3) | C18—H18C | 0.9600 |
| C10—C15 | 1.379 (3) | ||
| C2—C1—N1 | 119.7 (2) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.9 |
| C2—C1—H1 | 120.2 | C13—C12—C11 | 120.4 (2) |
| N1—C1—H1 | 120.2 | C13—C12—H12 | 119.8 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 120.1 (2) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.8 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.9 | C12—C13—C14 | 119.9 (2) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.9 | C12—C13—H13 | 120.1 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.4 (2) | C14—C13—H13 | 120.1 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.8 | C13—C14—C15 | 120.0 (2) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.8 | C13—C14—H14 | 120.0 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.0 (2) | C15—C14—H14 | 120.0 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.0 | C10—C15—C14 | 120.3 (2) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.0 | C10—C15—H15 | 119.8 |
| N1—C5—C4 | 117.9 (2) | C14—C15—H15 | 119.8 |
| N1—C5—C6 | 107.35 (18) | O3—C16—O2 | 123.5 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 134.7 (2) | O3—C16—C6 | 125.0 (2) |
| C7—C6—C5 | 106.80 (19) | O2—C16—C6 | 111.5 (2) |
| C7—C6—C16 | 128.7 (2) | O2—C17—C18 | 110.6 (2) |
| C5—C6—C16 | 124.45 (19) | O2—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 110.83 (19) | C18—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 124.6 | O2—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 124.6 | C18—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—N1 | 106.01 (18) | H17A—C17—H17B | 108.1 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 129.9 (2) | C17—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| N1—C8—C9 | 123.6 (2) | C17—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| O1—C9—C8 | 122.7 (2) | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| O1—C9—C10 | 119.4 (2) | C17—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 117.9 (2) | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C15—C10—C11 | 119.2 (2) | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C15—C10—C9 | 122.7 (2) | C1—N1—C5 | 121.86 (18) |
| C11—C10—C9 | 118.0 (2) | C1—N1—C8 | 129.14 (19) |
| C12—C11—C10 | 120.2 (2) | C5—N1—C8 | 109.00 (18) |
| C12—C11—H11 | 119.9 | C16—O2—C17 | 116.98 (18) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 0.0 (4) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −2.4 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.2 (4) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.5 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.1 (4) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 1.4 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | 0.6 (3) | C11—C10—C15—C14 | −0.6 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −179.7 (2) | C9—C10—C15—C14 | −176.8 (2) |
| N1—C5—C6—C7 | 1.5 (2) | C13—C14—C15—C10 | −1.3 (4) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −178.2 (2) | C7—C6—C16—O3 | −174.1 (2) |
| N1—C5—C6—C16 | −175.5 (2) | C5—C6—C16—O3 | 2.2 (4) |
| C4—C5—C6—C16 | 4.8 (4) | C7—C6—C16—O2 | 4.5 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | −1.1 (3) | C5—C6—C16—O2 | −179.2 (2) |
| C16—C6—C7—C8 | 175.7 (2) | C2—C1—N1—C5 | 0.5 (3) |
| C6—C7—C8—N1 | 0.3 (3) | C2—C1—N1—C8 | −178.6 (2) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | −172.0 (2) | C4—C5—N1—C1 | −0.8 (3) |
| C7—C8—C9—O1 | 157.9 (2) | C6—C5—N1—C1 | 179.45 (18) |
| N1—C8—C9—O1 | −13.2 (4) | C4—C5—N1—C8 | 178.43 (18) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | −19.2 (4) | C6—C5—N1—C8 | −1.3 (2) |
| N1—C8—C9—C10 | 169.63 (18) | C7—C8—N1—C1 | 179.8 (2) |
| O1—C9—C10—C15 | 139.8 (2) | C9—C8—N1—C1 | −7.3 (3) |
| C8—C9—C10—C15 | −43.0 (3) | C7—C8—N1—C5 | 0.6 (2) |
| O1—C9—C10—C11 | −36.4 (3) | C9—C8—N1—C5 | 173.6 (2) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | 140.8 (2) | O3—C16—O2—C17 | −2.7 (3) |
| C15—C10—C11—C12 | 2.5 (3) | C6—C16—O2—C17 | 178.65 (19) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | 178.8 (2) | C18—C17—O2—C16 | −89.0 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C1—H1···O1i | 0.93 | 2.45 | 3.163 (3) | 134 |
| C14—H14···O3ii | 0.93 | 2.58 | 3.455 (3) | 157 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y, −z+2; (ii) −x, y−1/2, −z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: IM2326).
References
- Bruker (2000). SMART, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- James, D. A., Koya, K., Li, H., Liang, G. Q., Xia, Z. Q., Ying, W. W., Wu, Y. M. & Sun, L. J. (2008). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 18, 1784–1787. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.-M., Wang, B.-X., Feng, Y.-Y., Shen, Z.-Y., Shen, J., Li, C. & Hu, H.-W. (2006). Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 27, 651–653.
- Shen, Z.-Y., Wang, B.-X., Shen, J. & Hu, H.-W. (2008). Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 29, 916–918.
- Teklu, S., Gundersen, L. L., Larsen, T., Malterud, K. E. & Rise, F. (2005). Med. Chem. 13, 3127–3139. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Tukulula, M., Klein, R. & Kaye, P. T. (2010). Synth. Commun. 40, 2018–2028.
- Wang, B.-X., Hu, J.-X., Zhang, X.-C., Hu, Y.-F. & Hu, H.-W. (2000). J. Heterocycl. Chem. 37, 1533–1537.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681104284X/im2326sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681104284X/im2326Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681104284X/im2326Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




