Abstract
In the title compound, C21H21FN3O2P, the NH and P(=O) groups of the C(=O)NHP(=O) fragment are in a syn arrangement with respect to each other, as are the two amide H atoms of the two CH3–4-C6H4–NH moieties. In the crystal, molecules are linked through N—H⋯O(=P) and N—H⋯O(=C) hydrogen bonds, forming R 2 2(8) and R 2 2(12) rings, which are arranged in chains parallel to [010].
Related literature
For hydrogen-bond patterns in phosphoric triamides of the formula RC(O)NHP(O)[NR
1
R
2]2 and RC(O)NHP(O)[NHR
1]2, see: Toghraee et al. (2011 ▶). For different cyclic hydrogen-bond motifs, see: Pourayoubi et al. (2011 ▶).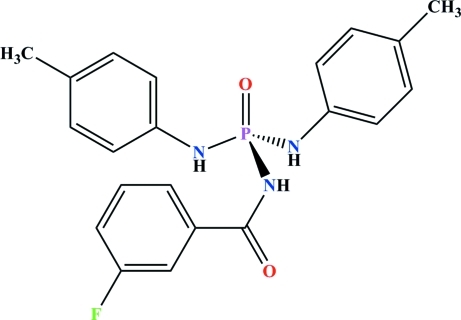
Experimental
Crystal data
C21H21FN3O2P
M r = 397.38
Monoclinic,
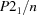
a = 10.2132 (5) Å
b = 9.8588 (4) Å
c = 20.2711 (9) Å
β = 93.621 (2)°
V = 2037.02 (16) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.17 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.25 × 0.22 × 0.14 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2007 ▶) T min = 0.662, T max = 0.745
20105 measured reflections
3844 independent reflections
3061 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.030
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.039
wR(F 2) = 0.109
S = 1.04
3844 reflections
255 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.37 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.35 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: OLEX (Dolomanov et al., 2003 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶) and enCIFer (Allen et al., 2004 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811045314/lh5349sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811045314/lh5349Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯O2i | 0.86 | 1.97 | 2.7835 (18) | 157 |
| N3—H3⋯O1ii | 0.86 | 2.06 | 2.8972 (18) | 165 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 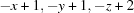 ; (ii)
; (ii) 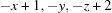 .
.
Acknowledgments
Support of this investigation by Ferdowsi University of Mashhad is gratefully acknowledged.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
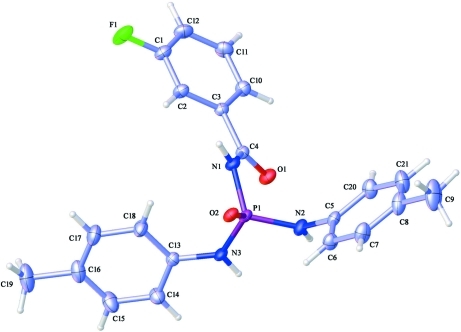
The possible hydrogen bond patterns in crystal structure of phosphoric triamides of the general formula RC(O)NHP(O)[NR1R2]2 and RC(O)NHP(O)[NHR1]2 have been analyzed recently (Toghraee et al., 2011) and the hydrogen bonds strengths in these systems were discussed based on cyclic hydrogen bond motifs (Pourayoubi et al., 2011). It was concluded that the R22(8) ring motif is generated by a pair of P(═O)···H–NC(O)NHP(O) hydrogen bonds between two neighboring molecules in the crystal packing of phosphoric triamides of the formula RC(O)NHP(O)[NR1R2]2 which contain a syn orientation of P(═O) versus N—H. In the case of phosphoric triamides of the formula RC(O)NHP(O)[NHR1]2, crystal structure is usually composed of a chain of R22(8) and R22(12) ring motifs which alternately connected to each other. However, a few other hydrogen bond patterns were also found. The R22(8) motif is formed by two P(═O)···H–NC(O)NHP(O) hydrogen bonds and the R22(12) motif by two C(═O)···H–Namide hydrogen bonds. In this work, the synthesis and crystal structure of a new phosphoric triamide, P(O)[NHC(O)C6H4(3-F)][NH–C6H4–4–CH3]2, is reported. This investigation was carried out as part of a comprehensive study on the hydrogen bonds pattern in phosphoric triamides with formula RC(O)NHP(O)[NHR1]2. The phosphorus atom has a distorted tetrahedral environment (Fig. 1). Comparison of the O–P–N angles indicates that the O–P–N1 angle is smaller than ideal tetrahedral (107.02 (7)°) and the O–P–N2 and O–P–N3 angles (113.75 (7)° and 116.29 (7)°, respectively) display larger than ideal values. This probably arises due to steric repulsion involving the P(═O) group. Moreover, there is no π···π interaction between the two para-methyl phenyl groups. The C(═O) and P(═O) groups of the C(═O)NHP(═O) moiety are in anti positions relative to each other, contrary to the syn orientation of P(═O) and NH groups. The P(═O), C(═O) and P–N bond lengths and P–N–C bond angles are in the range of the expected values. In the crystal structure, molecules are linked through P(═O)···H–NC(O)NHP(O) and C(═ O)···H–Namide hydrogen bonds (Table 1), to give a linear chain running along the b axis.
Experimental
Synthesis of 3-F–C6H4C(O)NHP(O)Cl2 A mixture of phosphorus pentachloride (3.773 g, 18.12 mmol) and 3-fluorobenzamide (2.521 g, 18.12 mmol) were refluxed in CCl4 for 8 h, and then the resulting solution was cooled to the room temperature. Formic acid (0.834 g, 18.12 mmol) was syringed dropwise into the stirring solution in 20 min and stirred for 6 h to yield the white precipitate that was filtered and dried in vacuum.
Synthesis of the title molecule To a solution of 3-F–C6H4C(O)NHP(O)Cl2 (0.256 g, 1 mmol) in CHCl3 (20 ml), a mixture of p-toluidine (0.214 g, 2 mmol) and triethylamine (0.202 g, 2 mmol) in CHCl3 (5 ml) was added dropwise at 273 K. After 4 h stirring, the solvent was evaporated in vacuum and then the resulting solid was washed with distilled water. Single crystals of title compound were obtained from a mixture of CH3OH, CH3CN and n-C6H14 after slow evaporation at room temperature. IR (KBr, cm-1): 3355 (NH), 3313 (NH), 3081 (NH), 2921, 1651 (C═O), 1615, 1588, 1513, 1440, 1386, 1267, 1235, 1210, 961, 870, 861, 817, 751.
Refinement
All H atoms were placed in calculated positions with C—H = 0.93-0.96Å; N—H = 0.86Å and were included in a riding-model approximation with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C,N) or 1.5Ueq(Cmethyl).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound. Ellipsoids are given at the 50% probability level.
Crystal data
| C21H21FN3O2P | F(000) = 832 |
| Mr = 397.38 | Dx = 1.296 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 6910 reflections |
| a = 10.2132 (5) Å | θ = 2.3–25.1° |
| b = 9.8588 (4) Å | µ = 0.17 mm−1 |
| c = 20.2711 (9) Å | T = 296 K |
| β = 93.621 (2)° | Cubic, colorless |
| V = 2037.02 (16) Å3 | 0.25 × 0.22 × 0.14 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 3844 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3061 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.030 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 25.7°, θmin = 2.9° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2007) | h = −12→12 |
| Tmin = 0.662, Tmax = 0.745 | k = −12→11 |
| 20105 measured reflections | l = −24→24 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.039 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.109 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.04 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0537P)2 + 0.6292P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3844 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.003 |
| 255 parameters | Δρmax = 0.37 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.35 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| P1 | 0.55273 (4) | 0.28199 (4) | 0.97803 (2) | 0.03501 (15) | |
| F1 | 0.00592 (13) | 0.50210 (15) | 1.10740 (8) | 0.0863 (5) | |
| O1 | 0.32311 (13) | 0.10156 (12) | 0.97315 (7) | 0.0522 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.62121 (12) | 0.41249 (11) | 0.97696 (6) | 0.0424 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.39319 (14) | 0.31600 (13) | 0.98654 (7) | 0.0384 (4) | |
| H1 | 0.3699 | 0.3994 | 0.9901 | 0.046* | |
| N2 | 0.56968 (16) | 0.18952 (15) | 0.91224 (7) | 0.0457 (4) | |
| H2 | 0.5594 | 0.1032 | 0.9149 | 0.055* | |
| N3 | 0.59807 (15) | 0.17934 (14) | 1.03822 (7) | 0.0407 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.6244 | 0.1001 | 1.0273 | 0.049* | |
| C1 | 0.0244 (2) | 0.3949 (2) | 1.06744 (11) | 0.0523 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.14869 (18) | 0.36985 (19) | 1.04838 (10) | 0.0462 (5) | |
| H2A | 0.2185 | 0.4259 | 1.0621 | 0.055* | |
| C3 | 0.16722 (17) | 0.25899 (17) | 1.00822 (9) | 0.0381 (4) | |
| C4 | 0.29931 (18) | 0.21885 (16) | 0.98807 (9) | 0.0375 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.60112 (19) | 0.24700 (18) | 0.85011 (9) | 0.0439 (4) | |
| C6 | 0.7180 (2) | 0.3164 (2) | 0.84531 (11) | 0.0558 (5) | |
| H6 | 0.7763 | 0.3256 | 0.8822 | 0.067* | |
| C7 | 0.7477 (3) | 0.3719 (3) | 0.78558 (12) | 0.0684 (7) | |
| H7 | 0.8258 | 0.4196 | 0.7831 | 0.082* | |
| C8 | 0.6657 (3) | 0.3589 (2) | 0.72965 (11) | 0.0726 (7) | |
| C9 | 0.7009 (4) | 0.4217 (3) | 0.66478 (14) | 0.1173 (13) | |
| H9A | 0.7807 | 0.3818 | 0.6512 | 0.176* | |
| H9B | 0.7130 | 0.5176 | 0.6705 | 0.176* | |
| H9C | 0.6314 | 0.4053 | 0.6316 | 0.176* | |
| C10 | 0.06158 (19) | 0.1775 (2) | 0.98825 (10) | 0.0492 (5) | |
| H10 | 0.0741 | 0.1025 | 0.9616 | 0.059* | |
| C11 | −0.0622 (2) | 0.2074 (2) | 1.00776 (12) | 0.0601 (6) | |
| H11 | −0.1329 | 0.1531 | 0.9936 | 0.072* | |
| C12 | −0.0815 (2) | 0.3170 (2) | 1.04808 (12) | 0.0591 (6) | |
| H12 | −0.1645 | 0.3374 | 1.0617 | 0.071* | |
| C13 | 0.59854 (18) | 0.20754 (18) | 1.10666 (9) | 0.0410 (4) | |
| C14 | 0.6514 (2) | 0.1138 (2) | 1.15103 (10) | 0.0577 (5) | |
| H14 | 0.6853 | 0.0331 | 1.1357 | 0.069* | |
| C15 | 0.6545 (3) | 0.1384 (3) | 1.21817 (12) | 0.0753 (7) | |
| H15 | 0.6903 | 0.0735 | 1.2473 | 0.090* | |
| C16 | 0.6059 (3) | 0.2569 (3) | 1.24288 (11) | 0.0699 (7) | |
| C17 | 0.5550 (3) | 0.3505 (3) | 1.19855 (12) | 0.0721 (7) | |
| H17 | 0.5225 | 0.4317 | 1.2142 | 0.087* | |
| C18 | 0.5505 (2) | 0.3279 (2) | 1.13088 (11) | 0.0609 (6) | |
| H18 | 0.5154 | 0.3933 | 1.1019 | 0.073* | |
| C19 | 0.6086 (4) | 0.2837 (4) | 1.31697 (12) | 0.1036 (11) | |
| H19A | 0.6172 | 0.3794 | 1.3250 | 0.155* | |
| H19B | 0.6818 | 0.2370 | 1.3386 | 0.155* | |
| H19C | 0.5286 | 0.2517 | 1.3340 | 0.155* | |
| C20 | 0.5180 (2) | 0.2333 (2) | 0.79481 (11) | 0.0633 (6) | |
| H20 | 0.4392 | 0.1869 | 0.7974 | 0.076* | |
| C21 | 0.5505 (3) | 0.2879 (3) | 0.73502 (11) | 0.0772 (8) | |
| H21 | 0.4936 | 0.2766 | 0.6978 | 0.093* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| P1 | 0.0371 (3) | 0.0248 (2) | 0.0440 (3) | 0.00215 (18) | 0.00981 (19) | −0.00342 (18) |
| F1 | 0.0618 (9) | 0.0742 (9) | 0.1262 (13) | 0.0042 (7) | 0.0322 (8) | −0.0372 (9) |
| O1 | 0.0543 (8) | 0.0277 (6) | 0.0757 (9) | −0.0005 (6) | 0.0121 (7) | −0.0088 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0414 (7) | 0.0284 (6) | 0.0589 (8) | −0.0007 (5) | 0.0146 (6) | −0.0053 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0370 (8) | 0.0245 (7) | 0.0543 (9) | 0.0032 (6) | 0.0083 (7) | −0.0023 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0605 (10) | 0.0281 (7) | 0.0503 (9) | −0.0020 (7) | 0.0171 (8) | −0.0054 (7) |
| N3 | 0.0478 (9) | 0.0273 (7) | 0.0477 (9) | 0.0088 (6) | 0.0078 (7) | −0.0044 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0467 (11) | 0.0432 (11) | 0.0681 (13) | 0.0050 (9) | 0.0131 (10) | −0.0026 (10) |
| C2 | 0.0386 (10) | 0.0372 (10) | 0.0634 (12) | −0.0022 (8) | 0.0082 (9) | −0.0043 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0394 (10) | 0.0312 (8) | 0.0441 (10) | −0.0004 (7) | 0.0050 (8) | 0.0047 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0427 (10) | 0.0277 (8) | 0.0424 (9) | −0.0009 (7) | 0.0040 (8) | −0.0001 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0524 (11) | 0.0362 (9) | 0.0443 (10) | 0.0017 (8) | 0.0137 (9) | −0.0071 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0523 (12) | 0.0636 (13) | 0.0527 (12) | −0.0067 (10) | 0.0117 (10) | −0.0048 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0773 (16) | 0.0674 (15) | 0.0634 (15) | −0.0214 (13) | 0.0275 (13) | −0.0077 (12) |
| C8 | 0.113 (2) | 0.0568 (13) | 0.0499 (13) | −0.0161 (14) | 0.0230 (14) | −0.0076 (11) |
| C9 | 0.200 (4) | 0.098 (2) | 0.0569 (16) | −0.045 (3) | 0.036 (2) | 0.0000 (16) |
| C10 | 0.0486 (12) | 0.0433 (10) | 0.0556 (12) | −0.0079 (9) | 0.0027 (9) | −0.0022 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0420 (12) | 0.0631 (14) | 0.0747 (15) | −0.0108 (10) | −0.0004 (10) | 0.0009 (12) |
| C12 | 0.0368 (11) | 0.0619 (13) | 0.0796 (15) | 0.0015 (10) | 0.0108 (10) | 0.0076 (12) |
| C13 | 0.0419 (10) | 0.0363 (9) | 0.0450 (10) | −0.0035 (8) | 0.0052 (8) | −0.0018 (8) |
| C14 | 0.0731 (15) | 0.0432 (11) | 0.0556 (13) | 0.0021 (10) | −0.0059 (11) | 0.0006 (9) |
| C15 | 0.110 (2) | 0.0598 (14) | 0.0541 (14) | −0.0110 (14) | −0.0124 (13) | 0.0081 (12) |
| C16 | 0.0890 (18) | 0.0740 (16) | 0.0471 (12) | −0.0304 (14) | 0.0079 (12) | −0.0068 (12) |
| C17 | 0.0956 (19) | 0.0633 (14) | 0.0590 (14) | −0.0005 (14) | 0.0174 (13) | −0.0187 (12) |
| C18 | 0.0824 (16) | 0.0496 (12) | 0.0512 (12) | 0.0142 (11) | 0.0073 (11) | −0.0072 (10) |
| C19 | 0.148 (3) | 0.116 (2) | 0.0475 (14) | −0.048 (2) | 0.0094 (16) | −0.0108 (15) |
| C20 | 0.0697 (15) | 0.0617 (14) | 0.0588 (13) | −0.0191 (12) | 0.0068 (11) | −0.0095 (11) |
| C21 | 0.107 (2) | 0.0759 (17) | 0.0473 (13) | −0.0201 (16) | −0.0021 (13) | −0.0073 (12) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| P1—O2 | 1.4652 (12) | C9—H9A | 0.9600 |
| P1—N3 | 1.6297 (15) | C9—H9B | 0.9600 |
| P1—N2 | 1.6336 (15) | C9—H9C | 0.9600 |
| P1—N1 | 1.6830 (14) | C10—C11 | 1.380 (3) |
| F1—C1 | 1.352 (2) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| O1—C4 | 1.224 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.377 (3) |
| N1—C4 | 1.357 (2) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| N1—H1 | 0.8600 | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| N2—C5 | 1.436 (2) | C13—C14 | 1.376 (3) |
| N2—H2 | 0.8600 | C13—C18 | 1.386 (3) |
| N3—C13 | 1.415 (2) | C14—C15 | 1.381 (3) |
| N3—H3 | 0.8600 | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C12 | 1.364 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.376 (4) |
| C1—C2 | 1.373 (3) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.383 (3) | C16—C17 | 1.367 (4) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9300 | C16—C19 | 1.523 (3) |
| C3—C10 | 1.385 (3) | C17—C18 | 1.388 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.488 (2) | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C5—C20 | 1.369 (3) | C18—H18 | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.385 (3) | C19—H19A | 0.9600 |
| C6—C7 | 1.380 (3) | C19—H19B | 0.9600 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C19—H19C | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.373 (4) | C20—C21 | 1.386 (3) |
| C7—H7 | 0.9300 | C20—H20 | 0.9300 |
| C8—C21 | 1.378 (4) | C21—H21 | 0.9300 |
| C8—C9 | 1.517 (3) | ||
| O2—P1—N3 | 116.29 (8) | C8—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| O2—P1—N2 | 113.75 (7) | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| N3—P1—N2 | 103.00 (8) | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| O2—P1—N1 | 107.02 (7) | C11—C10—C3 | 120.22 (19) |
| N3—P1—N1 | 106.15 (7) | C11—C10—H10 | 119.9 |
| N2—P1—N1 | 110.37 (8) | C3—C10—H10 | 119.9 |
| C4—N1—P1 | 123.49 (12) | C12—C11—C10 | 120.4 (2) |
| C4—N1—H1 | 118.3 | C12—C11—H11 | 119.8 |
| P1—N1—H1 | 118.3 | C10—C11—H11 | 119.8 |
| C5—N2—P1 | 122.47 (12) | C1—C12—C11 | 118.13 (19) |
| C5—N2—H2 | 118.8 | C1—C12—H12 | 120.9 |
| P1—N2—H2 | 118.8 | C11—C12—H12 | 120.9 |
| C13—N3—P1 | 126.55 (12) | C14—C13—C18 | 118.45 (19) |
| C13—N3—H3 | 116.7 | C14—C13—N3 | 119.09 (17) |
| P1—N3—H3 | 116.7 | C18—C13—N3 | 122.44 (17) |
| F1—C1—C12 | 118.31 (18) | C13—C14—C15 | 120.7 (2) |
| F1—C1—C2 | 118.40 (19) | C13—C14—H14 | 119.7 |
| C12—C1—C2 | 123.3 (2) | C15—C14—H14 | 119.7 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 118.11 (18) | C16—C15—C14 | 121.4 (2) |
| C1—C2—H2A | 120.9 | C16—C15—H15 | 119.3 |
| C3—C2—H2A | 120.9 | C14—C15—H15 | 119.3 |
| C2—C3—C10 | 119.83 (17) | C17—C16—C15 | 117.7 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 122.14 (16) | C17—C16—C19 | 120.9 (3) |
| C10—C3—C4 | 117.95 (16) | C15—C16—C19 | 121.4 (3) |
| O1—C4—N1 | 120.64 (16) | C16—C17—C18 | 121.9 (2) |
| O1—C4—C3 | 121.13 (16) | C16—C17—H17 | 119.0 |
| N1—C4—C3 | 118.22 (14) | C18—C17—H17 | 119.0 |
| C20—C5—C6 | 118.93 (19) | C13—C18—C17 | 119.8 (2) |
| C20—C5—N2 | 121.18 (18) | C13—C18—H18 | 120.1 |
| C6—C5—N2 | 119.89 (18) | C17—C18—H18 | 120.1 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 119.7 (2) | C16—C19—H19A | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—H6 | 120.1 | C16—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.1 | H19A—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 122.1 (2) | C16—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 119.0 | H19A—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 119.0 | H19B—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—C21 | 117.5 (2) | C5—C20—C21 | 120.5 (2) |
| C7—C8—C9 | 120.8 (3) | C5—C20—H20 | 119.8 |
| C21—C8—C9 | 121.7 (3) | C21—C20—H20 | 119.8 |
| C8—C9—H9A | 109.5 | C8—C21—C20 | 121.3 (2) |
| C8—C9—H9B | 109.5 | C8—C21—H21 | 119.4 |
| H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 | C20—C21—H21 | 119.4 |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···O2i | 0.86 | 1.97 | 2.7835 (18) | 157. |
| N3—H3···O1ii | 0.86 | 2.06 | 2.8972 (18) | 165. |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z+2; (ii) −x+1, −y, −z+2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: LH5349).
References
- Allen, F. H., Johnson, O., Shields, G. P., Smith, B. R. & Towler, M. (2004). J. Appl. Cryst. 37, 335–338.
- Bruker (2007). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Blake, A. J., Champness, N. R. & Schröder, M. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst. 36, 1283–1284.
- Pourayoubi, M., Tarahhomi, A., Saneei, A., Rheingold, A. L. & Golen, J. A. (2011). Acta Cryst. C67, o265–o272. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Toghraee, M., Pourayoubi, M. & Divjakovic, V. (2011). Polyhedron, 30, 1680–1690.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811045314/lh5349sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811045314/lh5349Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report