Abstract
In the title molecule, C24H16Cl2N2O, the dihedral angles between the pyrazole ring and its N- and C-bonded phenyl rings are 7.06 (10) and 53.15 (10)°, respectively. The dihedral angle between the two pendant rings is 52.32 (10)°. The molecule exists in a trans conformation with respect to the acyclic C=C bond. In the crystal, inversion dimers occur in which each molecule is linked to the other by two C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds to the same acceptor O atom. There are also short Cl⋯Cl contacts [3.3492 (9) Å] and C—H⋯π interactions.
Related literature
For general background to and the biological activity of pyrazoles, see: Patel et al. (2004 ▶); Isloor et al. (2009 ▶); Vijesh et al. (2010 ▶); Sharma et al. (2010 ▶); Rostom et al. (2003 ▶); Ghorab et al. (2010 ▶); Amnekar & Bhusari (2010 ▶). For hydrogen-bond motifs, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶). For standard bond-length data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶).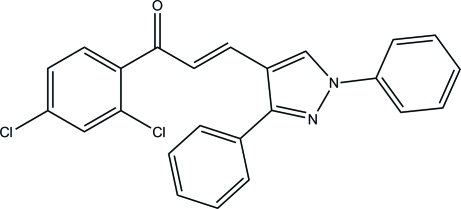
Experimental
Crystal data
C24H16Cl2N2O
M r = 419.29
Triclinic,

a = 9.6185 (8) Å
b = 10.6596 (9) Å
c = 11.8537 (10) Å
α = 67.377 (2)°
β = 75.777 (1)°
γ = 69.934 (2)°
V = 1044.64 (15) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.33 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.31 × 0.21 × 0.08 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEXII DUO CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009 ▶) T min = 0.904, T max = 0.973
22059 measured reflections
6053 independent reflections
3980 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.027
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.043
wR(F 2) = 0.134
S = 1.04
6053 reflections
262 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.22 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.27 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2009 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2009 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: SHELXTL; software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811044382/hb6456sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811044382/hb6456Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811044382/hb6456Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the C19–C24 and C13–C18 benzene rings, respectively.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C11—H11A⋯O1i | 0.93 | 2.30 | 3.230 (2) | 174 |
| C20—H20A⋯O1i | 0.93 | 2.59 | 3.509 (3) | 168 |
| C2—H2A⋯Cg1ii | 0.93 | 2.75 | 3.585 (2) | 149 |
| C23—H23A⋯Cg2iii | 0.93 | 2.90 | 3.655 (2) | 140 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
HKF and CKQ thank Universiti Sains Malaysia for the Research University Grant (No. 1001/PFIZIK/811160). AMI is thankful to the Department of Atomic Energy, Board for Research in Nuclear Sciences, Government of India, for the Young scientist award.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Pyrazoles are novel class of heterocyclic compounds possessing wide variety of application in the agrochemical and pharmaceutical industries (Patel et al., 2004). Derivatives of pyrazoles are found to show good antibacterial (Isloor et al., 2009; Vijesh et al., 2010), anti-inflammatory (Sharma et al., 2010), analgesic (Rostom et al., 2003), anticancer, radioprotective (Ghorab et al., 2010) and anti-convulsant activity (Amnekar & Bhusari, 2010). Prompted by the diverse activities of pyrazole derivatives, we have synthesized the title compound to study its crystal structure.
In the title molecule (Fig. 1), the phenyl (C1-C6) ring and the two benzene (C13-C18 and C19-C24) rings form dihedral angles of 64.29 (9), 53.15 (10) and 7.06 (10)°, respectively, with the pyrazole ring (N1/N2/C10-C12). The phenyl ring also forms dihedral angles of 65.06 (10) and 67.80 (10)° with the two benzene rings (C13-C18 and C19-C24), respectively. The benzene rings form a dihedral angle of 52.32 (10)°. The title molecule exists in trans conformation with respect to the acyclic C8═C9 bond [bond length = 1.330 (2) Å]. Bond lengths (Allen et al., 1987) and angles are within normal ranges. There is a short Cl2···Cl2 contact (symmetry code : -x, 1-y, 1-z) with distance = 3.3492 (9) Å which is shorter than the sum of van der Waals radii of the Cl atoms.
In the crystal (Fig. 2), molecules are linked into inversion dimers by intermolecular bifurcated C11–H11A···O1 and C20–H20A···O1 acceptor bonds (Table 1), generating six-membered R12(6) ring motifs (Bernstein et al., 1995). The crystal structure is further consolidated by C2–H2A···Cg1 and C23–H23A···Cg2 (Table 1) interactions, where Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of C19-C24 and C13-C18 benzene rings, respectively.
Experimental
To a cold, stirred mixture of methanol (20 ml) and sodium hydroxide (12.09 mmol), 2,4-dichloroacetophenone (4.03 mmol) was added. The reaction mixture was stirred for 10 min. 1,3-Diphenyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carbaldehyde (4.03 mmol) was added to this solution followed by tetrahydrofuran (30 ml). The solution was further stirred for 2 h at 273 K and then at room temperature for 5 h. It was then poured into ice cold water. The resulting solution was neutralized with Dil. HCl. The solid that separated was filtered, washed with water, dried and crystallized from ethanol to yield colourless blocks of (I). Yield: 1.28 g, 76.19 %. M.p.: 406-408 K.
Refinement
All H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model with C–H = 0.93 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound showing 30% probability displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms.
Fig. 2.
The crystal structure of the title compound, viewed along the a axis. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonds (dashed lines) have been omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| C24H16Cl2N2O | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 419.29 | F(000) = 432 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.333 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 9.6185 (8) Å | Cell parameters from 5364 reflections |
| b = 10.6596 (9) Å | θ = 2.4–28.8° |
| c = 11.8537 (10) Å | µ = 0.33 mm−1 |
| α = 67.377 (2)° | T = 296 K |
| β = 75.777 (1)° | Block, colourless |
| γ = 69.934 (2)° | 0.31 × 0.21 × 0.08 mm |
| V = 1044.64 (15) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEXII DUO CCD diffractometer | 6053 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3980 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.027 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 30.0°, θmin = 1.9° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009) | h = −13→13 |
| Tmin = 0.904, Tmax = 0.973 | k = −14→14 |
| 22059 measured reflections | l = −16→16 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.043 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.134 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.04 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0581P)2 + 0.1623P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 6053 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 262 parameters | Δρmax = 0.22 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.27 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.72422 (6) | 0.23879 (6) | 0.46250 (5) | 0.08035 (18) | |
| Cl2 | 0.14184 (5) | 0.45480 (9) | 0.57917 (6) | 0.1019 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.10827 (16) | 0.35212 (16) | 0.86276 (14) | 0.0787 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.22996 (13) | 0.84151 (14) | 1.00579 (11) | 0.0461 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.35901 (14) | 0.86410 (14) | 0.93127 (12) | 0.0496 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.4853 (2) | 0.3081 (2) | 0.76848 (16) | 0.0634 (5) | |
| H1A | 0.5039 | 0.2962 | 0.8459 | 0.076* | |
| C2 | 0.6034 (2) | 0.2677 (2) | 0.68476 (17) | 0.0677 (5) | |
| H2A | 0.7000 | 0.2286 | 0.7056 | 0.081* | |
| C3 | 0.57655 (18) | 0.28591 (17) | 0.57036 (15) | 0.0537 (4) | |
| C4 | 0.43478 (18) | 0.34217 (18) | 0.53839 (16) | 0.0565 (4) | |
| H4A | 0.4175 | 0.3541 | 0.4606 | 0.068* | |
| C5 | 0.31849 (17) | 0.38071 (18) | 0.62408 (16) | 0.0526 (4) | |
| C6 | 0.33961 (17) | 0.36581 (16) | 0.74104 (14) | 0.0470 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.21224 (19) | 0.40361 (18) | 0.83561 (15) | 0.0536 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.21287 (19) | 0.50151 (19) | 0.89386 (15) | 0.0570 (4) | |
| H8A | 0.1421 | 0.5086 | 0.9621 | 0.068* | |
| C9 | 0.30613 (17) | 0.58143 (16) | 0.85751 (13) | 0.0466 (3) | |
| H9A | 0.3819 | 0.5680 | 0.7937 | 0.056* | |
| C10 | 0.30113 (16) | 0.68689 (16) | 0.90744 (13) | 0.0452 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.19295 (17) | 0.73726 (17) | 0.99304 (14) | 0.0481 (3) | |
| H11A | 0.1098 | 0.7049 | 1.0343 | 0.058* | |
| C12 | 0.40123 (16) | 0.77075 (16) | 0.87221 (14) | 0.0452 (3) | |
| C13 | 0.53890 (16) | 0.76264 (17) | 0.78363 (14) | 0.0478 (3) | |
| C14 | 0.5637 (2) | 0.8813 (2) | 0.68817 (19) | 0.0703 (5) | |
| H14A | 0.4923 | 0.9684 | 0.6784 | 0.084* | |
| C15 | 0.6947 (3) | 0.8706 (3) | 0.6070 (2) | 0.0862 (7) | |
| H15A | 0.7098 | 0.9505 | 0.5420 | 0.103* | |
| C16 | 0.8019 (2) | 0.7449 (3) | 0.6209 (2) | 0.0785 (6) | |
| H16A | 0.8902 | 0.7395 | 0.5666 | 0.094* | |
| C17 | 0.7792 (2) | 0.6270 (2) | 0.71462 (19) | 0.0711 (5) | |
| H17A | 0.8523 | 0.5410 | 0.7244 | 0.085* | |
| C18 | 0.64774 (18) | 0.6348 (2) | 0.79530 (16) | 0.0580 (4) | |
| H18A | 0.6323 | 0.5535 | 0.8580 | 0.070* | |
| C19 | 0.15658 (16) | 0.92254 (17) | 1.08631 (14) | 0.0488 (4) | |
| C20 | 0.03696 (19) | 0.8896 (2) | 1.17154 (17) | 0.0612 (4) | |
| H20A | 0.0011 | 0.8173 | 1.1752 | 0.073* | |
| C21 | −0.0289 (2) | 0.9666 (3) | 1.25176 (19) | 0.0756 (6) | |
| H21A | −0.1097 | 0.9455 | 1.3097 | 0.091* | |
| C22 | 0.0236 (2) | 1.0730 (3) | 1.2467 (2) | 0.0799 (6) | |
| H22A | −0.0205 | 1.1228 | 1.3018 | 0.096* | |
| C23 | 0.1411 (2) | 1.1064 (2) | 1.1603 (2) | 0.0755 (6) | |
| H23A | 0.1757 | 1.1797 | 1.1561 | 0.091* | |
| C24 | 0.2084 (2) | 1.03114 (19) | 1.07925 (17) | 0.0609 (4) | |
| H24A | 0.2880 | 1.0538 | 1.0205 | 0.073* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0657 (3) | 0.0801 (3) | 0.0695 (3) | 0.0003 (2) | 0.0118 (2) | −0.0280 (3) |
| Cl2 | 0.0469 (3) | 0.1805 (7) | 0.1026 (4) | 0.0004 (3) | −0.0210 (3) | −0.0934 (5) |
| O1 | 0.0746 (8) | 0.1027 (10) | 0.0849 (10) | −0.0569 (8) | 0.0247 (7) | −0.0516 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0409 (6) | 0.0555 (7) | 0.0445 (7) | −0.0107 (5) | −0.0034 (5) | −0.0228 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0432 (6) | 0.0584 (8) | 0.0514 (7) | −0.0148 (6) | 0.0002 (5) | −0.0258 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0607 (10) | 0.0753 (11) | 0.0465 (9) | −0.0052 (9) | −0.0152 (8) | −0.0190 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0498 (9) | 0.0772 (12) | 0.0580 (10) | 0.0050 (8) | −0.0153 (8) | −0.0180 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0512 (8) | 0.0471 (8) | 0.0515 (9) | −0.0044 (7) | 0.0001 (7) | −0.0165 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0537 (9) | 0.0680 (10) | 0.0519 (9) | −0.0095 (8) | −0.0069 (7) | −0.0306 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0435 (8) | 0.0643 (10) | 0.0600 (9) | −0.0117 (7) | −0.0080 (7) | −0.0330 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0491 (8) | 0.0494 (8) | 0.0472 (8) | −0.0172 (6) | −0.0011 (6) | −0.0210 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0549 (9) | 0.0619 (9) | 0.0507 (9) | −0.0251 (8) | 0.0054 (7) | −0.0255 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0576 (9) | 0.0704 (10) | 0.0515 (9) | −0.0284 (8) | 0.0132 (7) | −0.0321 (8) |
| C9 | 0.0467 (8) | 0.0563 (9) | 0.0390 (7) | −0.0165 (7) | 0.0010 (6) | −0.0200 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0448 (7) | 0.0514 (8) | 0.0404 (7) | −0.0147 (6) | −0.0022 (6) | −0.0171 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0446 (7) | 0.0584 (9) | 0.0446 (8) | −0.0175 (7) | −0.0006 (6) | −0.0209 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0414 (7) | 0.0522 (8) | 0.0430 (8) | −0.0118 (6) | −0.0037 (6) | −0.0190 (6) |
| C13 | 0.0444 (8) | 0.0591 (9) | 0.0471 (8) | −0.0187 (7) | 0.0000 (6) | −0.0250 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0740 (12) | 0.0622 (11) | 0.0730 (12) | −0.0283 (9) | 0.0118 (10) | −0.0255 (9) |
| C15 | 0.0974 (16) | 0.0867 (15) | 0.0792 (14) | −0.0554 (13) | 0.0292 (12) | −0.0311 (12) |
| C16 | 0.0657 (12) | 0.1101 (17) | 0.0835 (14) | −0.0461 (12) | 0.0260 (10) | −0.0599 (14) |
| C17 | 0.0497 (9) | 0.0921 (14) | 0.0775 (13) | −0.0128 (9) | 0.0048 (9) | −0.0482 (12) |
| C18 | 0.0497 (9) | 0.0676 (10) | 0.0536 (9) | −0.0132 (8) | −0.0020 (7) | −0.0223 (8) |
| C19 | 0.0430 (7) | 0.0575 (9) | 0.0451 (8) | −0.0012 (6) | −0.0116 (6) | −0.0238 (7) |
| C20 | 0.0487 (9) | 0.0821 (12) | 0.0594 (10) | −0.0145 (8) | −0.0031 (7) | −0.0360 (9) |
| C21 | 0.0540 (10) | 0.1103 (17) | 0.0666 (12) | −0.0113 (10) | 0.0016 (9) | −0.0495 (12) |
| C22 | 0.0712 (12) | 0.0989 (16) | 0.0786 (14) | −0.0009 (11) | −0.0085 (11) | −0.0595 (13) |
| C23 | 0.0809 (13) | 0.0743 (12) | 0.0820 (14) | −0.0099 (10) | −0.0114 (11) | −0.0467 (11) |
| C24 | 0.0642 (10) | 0.0610 (10) | 0.0605 (10) | −0.0121 (8) | −0.0050 (8) | −0.0297 (8) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cl1—C3 | 1.7369 (16) | C11—H11A | 0.9300 |
| Cl2—C5 | 1.7304 (16) | C12—C13 | 1.474 (2) |
| O1—C7 | 1.2196 (19) | C13—C14 | 1.382 (2) |
| N1—C11 | 1.346 (2) | C13—C18 | 1.385 (2) |
| N1—N2 | 1.3718 (17) | C14—C15 | 1.385 (3) |
| N1—C19 | 1.4283 (19) | C14—H14A | 0.9300 |
| N2—C12 | 1.3282 (19) | C15—C16 | 1.360 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.378 (3) | C15—H15A | 0.9300 |
| C1—C6 | 1.388 (2) | C16—C17 | 1.362 (3) |
| C1—H1A | 0.9300 | C16—H16A | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.370 (3) | C17—C18 | 1.384 (2) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9300 | C17—H17A | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.371 (2) | C18—H18A | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.378 (2) | C19—C24 | 1.377 (2) |
| C4—H4A | 0.9300 | C19—C20 | 1.379 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.391 (2) | C20—C21 | 1.388 (3) |
| C6—C7 | 1.501 (2) | C20—H20A | 0.9300 |
| C7—C8 | 1.458 (2) | C21—C22 | 1.368 (3) |
| C8—C9 | 1.330 (2) | C21—H21A | 0.9300 |
| C8—H8A | 0.9300 | C22—C23 | 1.371 (3) |
| C9—C10 | 1.441 (2) | C22—H22A | 0.9300 |
| C9—H9A | 0.9300 | C23—C24 | 1.384 (3) |
| C10—C11 | 1.385 (2) | C23—H23A | 0.9300 |
| C10—C12 | 1.416 (2) | C24—H24A | 0.9300 |
| C11—N1—N2 | 111.74 (12) | N2—C12—C13 | 120.29 (14) |
| C11—N1—C19 | 128.80 (13) | C10—C12—C13 | 127.91 (13) |
| N2—N1—C19 | 119.42 (13) | C14—C13—C18 | 118.39 (15) |
| C12—N2—N1 | 104.76 (12) | C14—C13—C12 | 121.32 (15) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 122.13 (16) | C18—C13—C12 | 120.28 (15) |
| C2—C1—H1A | 118.9 | C13—C14—C15 | 119.99 (19) |
| C6—C1—H1A | 118.9 | C13—C14—H14A | 120.0 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.06 (16) | C15—C14—H14A | 120.0 |
| C3—C2—H2A | 120.5 | C16—C15—C14 | 121.0 (2) |
| C1—C2—H2A | 120.5 | C16—C15—H15A | 119.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.28 (15) | C14—C15—H15A | 119.5 |
| C2—C3—Cl1 | 119.79 (13) | C15—C16—C17 | 119.70 (18) |
| C4—C3—Cl1 | 118.92 (13) | C15—C16—H16A | 120.1 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 118.53 (15) | C17—C16—H16A | 120.1 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 120.7 | C16—C17—C18 | 120.23 (19) |
| C5—C4—H4A | 120.7 | C16—C17—H17A | 119.9 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 122.56 (14) | C18—C17—H17A | 119.9 |
| C4—C5—Cl2 | 117.16 (12) | C17—C18—C13 | 120.67 (17) |
| C6—C5—Cl2 | 120.25 (12) | C17—C18—H18A | 119.7 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 116.43 (14) | C13—C18—H18A | 119.7 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 121.05 (14) | C24—C19—C20 | 120.82 (15) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 122.46 (14) | C24—C19—N1 | 119.36 (15) |
| O1—C7—C8 | 120.46 (15) | C20—C19—N1 | 119.81 (15) |
| O1—C7—C6 | 119.38 (15) | C19—C20—C21 | 118.66 (19) |
| C8—C7—C6 | 120.16 (14) | C19—C20—H20A | 120.7 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 125.46 (15) | C21—C20—H20A | 120.7 |
| C9—C8—H8A | 117.3 | C22—C21—C20 | 120.8 (2) |
| C7—C8—H8A | 117.3 | C22—C21—H21A | 119.6 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 126.31 (14) | C20—C21—H21A | 119.6 |
| C8—C9—H9A | 116.8 | C21—C22—C23 | 120.02 (19) |
| C10—C9—H9A | 116.8 | C21—C22—H22A | 120.0 |
| C11—C10—C12 | 104.10 (13) | C23—C22—H22A | 120.0 |
| C11—C10—C9 | 128.48 (14) | C22—C23—C24 | 120.2 (2) |
| C12—C10—C9 | 127.26 (13) | C22—C23—H23A | 119.9 |
| N1—C11—C10 | 107.60 (13) | C24—C23—H23A | 119.9 |
| N1—C11—H11A | 126.2 | C19—C24—C23 | 119.49 (18) |
| C10—C11—H11A | 126.2 | C19—C24—H24A | 120.3 |
| N2—C12—C10 | 111.80 (13) | C23—C24—H24A | 120.3 |
| C11—N1—N2—C12 | −0.17 (16) | N1—N2—C12—C13 | −179.30 (13) |
| C19—N1—N2—C12 | 177.93 (12) | C11—C10—C12—N2 | 0.29 (17) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.5 (3) | C9—C10—C12—N2 | 175.95 (14) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.6 (3) | C11—C10—C12—C13 | 179.43 (15) |
| C1—C2—C3—Cl1 | 178.80 (15) | C9—C10—C12—C13 | −4.9 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.1 (3) | N2—C12—C13—C14 | −52.8 (2) |
| Cl1—C3—C4—C5 | −179.29 (13) | C10—C12—C13—C14 | 128.08 (19) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.5 (3) | N2—C12—C13—C18 | 126.52 (17) |
| C3—C4—C5—Cl2 | 178.65 (14) | C10—C12—C13—C18 | −52.6 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.1 (3) | C18—C13—C14—C15 | 0.1 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | 177.56 (17) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 179.44 (18) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.7 (3) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −1.3 (4) |
| Cl2—C5—C6—C1 | −178.70 (14) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | 1.2 (4) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −178.03 (16) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | 0.1 (3) |
| Cl2—C5—C6—C7 | 3.9 (2) | C16—C17—C18—C13 | −1.3 (3) |
| C1—C6—C7—O1 | −123.5 (2) | C14—C13—C18—C17 | 1.2 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—O1 | 53.8 (2) | C12—C13—C18—C17 | −178.17 (16) |
| C1—C6—C7—C8 | 56.8 (2) | C11—N1—C19—C24 | −176.03 (15) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | −125.95 (18) | N2—N1—C19—C24 | 6.2 (2) |
| O1—C7—C8—C9 | −168.14 (18) | C11—N1—C19—C20 | 5.2 (2) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | 11.6 (3) | N2—N1—C19—C20 | −172.51 (14) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | 174.67 (16) | C24—C19—C20—C21 | −1.1 (3) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | −7.0 (3) | N1—C19—C20—C21 | 177.64 (16) |
| C8—C9—C10—C12 | 178.37 (17) | C19—C20—C21—C22 | 0.0 (3) |
| N2—N1—C11—C10 | 0.35 (17) | C20—C21—C22—C23 | 1.0 (3) |
| C19—N1—C11—C10 | −177.52 (14) | C21—C22—C23—C24 | −1.0 (3) |
| C12—C10—C11—N1 | −0.37 (16) | C20—C19—C24—C23 | 1.2 (3) |
| C9—C10—C11—N1 | −175.96 (14) | N1—C19—C24—C23 | −177.55 (16) |
| N1—N2—C12—C10 | −0.08 (16) | C22—C23—C24—C19 | −0.1 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the C19–C24 and C13–C18 benzene rings, respectively. |
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C11—H11A···O1i | 0.93 | 2.30 | 3.230 (2) | 174 |
| C20—H20A···O1i | 0.93 | 2.59 | 3.509 (3) | 168 |
| C2—H2A···Cg1ii | 0.93 | 2.75 | 3.585 (2) | 149 |
| C23—H23A···Cg2iii | 0.93 | 2.90 | 3.655 (2) | 140 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+1, −z+2; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+2; (iii) −x+1, −y+2, −z+2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HB6456).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Amnekar, N. D. & Bhusari, K. P. (2010). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45, 149–159. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Bruker (2009). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Ghorab, M. M., Ragab, F. A., Alqasoumi, S. I., Alafeefy, A. M. & Aboulmagd, S. A. (2010). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45, 171–178. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Isloor, A. M., Kalluraya, B. & Shetty, P. (2009). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 44, 3784–3787. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Patel, M. V., Bell, R., Majest, S., Henry, R. & Kolasa, T. (2004). J. Org. Chem. 69, 7058–7065. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rostom, S. A. F., Shalaby, M. A. & El-Demellawy, M. A. (2003). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 38, 959–974. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P. K., Kumar, S., Kumar, P., Kaushik, P., Kaushik, D., Dhingra, Y. & Aneja, K. R. (2010). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45, 2650–2655. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Vijesh, A. M., Isloor, A. M., Prabhu, V., Ahmad, S. & Malladi, S. (2010). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45, 5460–5464. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811044382/hb6456sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811044382/hb6456Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811044382/hb6456Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




