Abstract
In the crystal structure of the title compound, C13H8BrNO4, molecules are linked into chains along [101] by weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and Br⋯O contacts [3.140 (4) Å]. The planes of the nitrated and brominated aryl rings form a dihedral angle of 64.98 (10)°, indicating a twist in the molecule.
Related literature
For background to the applications of aromatic esters containing nitro groups, see: Jefford & Zaslona (1985 ▶). For molecular and supramolecular structures of nitroaryl compounds, see: Wardell et al. (2005 ▶); Jefford et al., (1986 ▶). For halogen bonding, see: Politzer et al. (2010 ▶); Ritter (2009 ▶). For hydrogen bonding, see: Nardelli (1995 ▶) and for hydrogen-bond graph-set motifs, see: Etter (1990 ▶).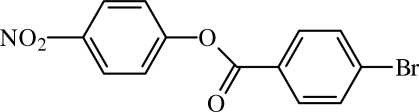
Experimental
Crystal data
C13H8BrNO4
M r = 322.11
Monoclinic,

a = 8.8177 (4) Å
b = 9.5279 (5) Å
c = 14.9394 (5) Å
β = 99.024 (3)°
V = 1239.59 (10) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 3.33 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.55 × 0.31 × 0.23 mm
Data collection
Bruker–Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.250, T max = 0.361
9341 measured reflections
2648 independent reflections
1918 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.070
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.048
wR(F 2) = 0.137
S = 1.02
2648 reflections
172 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.80 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.68 e Å−3
Data collection: COLLECT (Nonius, 1998 ▶); cell refinement: SCALEPACK (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶); data reduction: DENZO (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶) and SCALEPACK; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and Mercury (Macrae et al., 2006 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811043923/hg5114sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811043923/hg5114Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811043923/hg5114Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C10—H10⋯O4i | 0.93 | 2.69 | 3.543 (6) | 153 |
| C3—H3⋯O3ii | 0.93 | 2.60 | 3.335 (5) | 136 |
| C13—H13⋯O3iii | 0.93 | 2.67 | 3.460 (5) | 143 |
| C12—H12⋯O1iv | 0.93 | 2.50 | 3.237 (5) | 137 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  .
.
Acknowledgments
Thanks are given to the Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC) of Spain for the award of a license for the use of the Cambridge Crystallographic Database (CSD; Allen, 2002 ▶). The author also thanks the Universidad del Valle, Colombia, for partial financial support.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Aromatic esters containing nitro groups in their aromatic rings can be used as precursors for the preparation of compounds with potential analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties (Jefford & Zaslona, 1985). Molecular and supramolecular structures of a wide range of nitroaryl compounds have been reported (Wardell et al., 2005 and Jefford et al., 1986).
In order to complement the structural information on nitroaryl compounds the title ester, 4-nitrophenyl bromobenzoate (I) was synthesized. A perspective view of the molecule of the title compound, showing the atomic numbering scheme, is given in Fig. 1. The central ester fragment between atoms C4 and C8 is effectively planar. The nitrated and brominated aryl rings form a dihedral angle of 64.98 (10)°, indicating a twist in the molecule. The nitro group forms a dihedral angle of 2.7 (5)° with the adjacent aryl ring. Halogen bonding, an electrostatically driven higly directional noncovalent interaction, that can be important for its potential in the development of new materials and pharmaceutical compounds (Politzer et al., 2010 and Ritter, 2009) can be observed in the present structure. Indeed, the Br···O contacts along [101] with a Br1···O3iii, (iii: x - 1,+y,+z + 1) distance of 3.140 (4) Å, showing the formation of an infinite chain is detected (see Fig. 2). Other C—H···O weak hydrogen bonds (see Table 1, Nardelli, 1995) that complement the crystal packing can also be seen in this figure. The propagation of these interactions forms R33(30), R44(24) and R22(14) rings (Etter, 1990) along this direction.
Experimental
Solution containing equimolar quantities (3.2 mmol) of 4-bromobenzoyl chloride and 4-nitrophenol in acetonitrile (60 ml) was gradually heated under reflux for 2 h. At room temperature, triethylamine was added, to get a solid which was poured in cold water. The solid was recrystallized in dichlorometane to yield excellent yellow crystals suitable for single-crystal X-ray diffraction. M.p. 431 (1) K.
Refinement
The H-atoms were placed geometrically [C—H= 0.93 Å, Uiso(H) (1.2 times Ueq of the parent atom].
Figures
Fig. 1.
An ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997) plot of (I) with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms are shown as spheres of arbitrary radius.
Fig. 2.
Part of the crystal structure of (I), showing the formation of a one dimensional sheet along [101]. Symmetry code: (i) -x,-y,-z + 1; (ii) -x,+y + 1/2,-z + 1/2; (iii) x - 1,+y,+z + 1.
Crystal data
| C13H8BrNO4 | F(000) = 640 |
| Mr = 322.11 | Dx = 1.726 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Melting point: 431(1) K |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 8.8177 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 5487 reflections |
| b = 9.5279 (5) Å | θ = 2.9–27.1° |
| c = 14.9394 (5) Å | µ = 3.33 mm−1 |
| β = 99.024 (3)° | T = 293 K |
| V = 1239.59 (10) Å3 | Block, pale-yellow |
| Z = 4 | 0.55 × 0.31 × 0.23 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker–Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer | 2648 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1918 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.070 |
| ω scans | θmax = 27.1°, θmin = 3.5° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −10→11 |
| Tmin = 0.250, Tmax = 0.361 | k = −11→11 |
| 9341 measured reflections | l = −19→16 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.048 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.137 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.02 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0723P)2 + 0.6227P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2648 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 172 parameters | Δρmax = 0.80 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.68 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br | 1.07826 (4) | 0.25892 (4) | 1.01950 (2) | 0.0659 (2) | |
| O2 | 0.6701 (3) | 0.1952 (3) | 0.59586 (16) | 0.0569 (6) | |
| C1 | 0.9755 (4) | 0.2726 (4) | 0.8984 (2) | 0.0507 (8) | |
| O1 | 0.7563 (3) | 0.4159 (3) | 0.58276 (16) | 0.0606 (6) | |
| C4 | 0.8266 (4) | 0.2946 (3) | 0.7227 (2) | 0.0457 (7) | |
| C8 | 0.5953 (4) | 0.1968 (4) | 0.5064 (2) | 0.0480 (7) | |
| C11 | 0.4518 (4) | 0.1846 (4) | 0.3321 (2) | 0.0504 (8) | |
| C10 | 0.5615 (4) | 0.0861 (4) | 0.3623 (2) | 0.0552 (8) | |
| H10 | 0.5859 | 0.0161 | 0.3235 | 0.066* | |
| N1 | 0.3778 (5) | 0.1834 (4) | 0.2373 (2) | 0.0694 (9) | |
| C7 | 0.7503 (4) | 0.3138 (4) | 0.6281 (2) | 0.0485 (7) | |
| C5 | 0.9242 (4) | 0.4006 (4) | 0.7604 (3) | 0.0594 (9) | |
| H5 | 0.9388 | 0.4796 | 0.7261 | 0.071* | |
| C2 | 0.8757 (4) | 0.1668 (4) | 0.8629 (2) | 0.0527 (8) | |
| H2 | 0.8587 | 0.0893 | 0.8978 | 0.063* | |
| C3 | 0.8023 (4) | 0.1793 (3) | 0.7748 (2) | 0.0499 (8) | |
| H3 | 0.7354 | 0.1090 | 0.7499 | 0.060* | |
| C6 | 0.9997 (5) | 0.3897 (4) | 0.8482 (2) | 0.0631 (10) | |
| H6 | 1.0659 | 0.4603 | 0.8732 | 0.076* | |
| C9 | 0.6350 (4) | 0.0922 (3) | 0.4507 (2) | 0.0535 (8) | |
| H9 | 0.7101 | 0.0268 | 0.4724 | 0.064* | |
| C13 | 0.4817 (4) | 0.2937 (4) | 0.4769 (2) | 0.0554 (8) | |
| H13 | 0.4546 | 0.3616 | 0.5162 | 0.066* | |
| O3 | 0.4181 (5) | 0.0922 (4) | 0.18766 (19) | 0.0955 (11) | |
| C12 | 0.4100 (5) | 0.2880 (4) | 0.3889 (3) | 0.0580 (9) | |
| H12 | 0.3340 | 0.3527 | 0.3674 | 0.070* | |
| O4 | 0.2819 (6) | 0.2721 (4) | 0.2116 (3) | 0.1064 (14) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br | 0.0611 (3) | 0.0868 (3) | 0.0476 (3) | −0.00760 (19) | 0.00100 (18) | −0.00065 (17) |
| O2 | 0.0682 (16) | 0.0504 (12) | 0.0479 (13) | −0.0114 (12) | −0.0034 (11) | 0.0040 (11) |
| C1 | 0.0421 (17) | 0.062 (2) | 0.0475 (18) | 0.0014 (14) | 0.0051 (14) | −0.0012 (14) |
| O1 | 0.0684 (17) | 0.0519 (14) | 0.0599 (14) | −0.0047 (11) | 0.0054 (12) | 0.0080 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0445 (17) | 0.0475 (16) | 0.0456 (17) | 0.0002 (14) | 0.0079 (14) | −0.0012 (14) |
| C8 | 0.0480 (19) | 0.0511 (17) | 0.0434 (16) | −0.0075 (14) | 0.0029 (14) | 0.0044 (14) |
| C11 | 0.059 (2) | 0.0515 (18) | 0.0408 (16) | −0.0151 (16) | 0.0091 (15) | 0.0008 (14) |
| C10 | 0.067 (2) | 0.0478 (18) | 0.0534 (19) | −0.0115 (16) | 0.0189 (17) | −0.0075 (14) |
| N1 | 0.094 (3) | 0.067 (2) | 0.0456 (17) | −0.030 (2) | 0.0054 (17) | 0.0047 (16) |
| C7 | 0.0460 (18) | 0.0476 (18) | 0.0531 (19) | −0.0014 (14) | 0.0112 (15) | −0.0003 (15) |
| C5 | 0.060 (2) | 0.058 (2) | 0.059 (2) | −0.0160 (17) | 0.0039 (16) | 0.0070 (16) |
| C2 | 0.058 (2) | 0.0476 (18) | 0.0524 (18) | 0.0002 (15) | 0.0073 (16) | −0.0007 (14) |
| C3 | 0.054 (2) | 0.0441 (17) | 0.0509 (18) | −0.0044 (14) | 0.0059 (15) | −0.0034 (14) |
| C6 | 0.061 (2) | 0.067 (2) | 0.059 (2) | −0.0197 (18) | 0.0020 (18) | −0.0030 (17) |
| C9 | 0.057 (2) | 0.0445 (17) | 0.059 (2) | −0.0004 (15) | 0.0105 (16) | 0.0020 (14) |
| C13 | 0.056 (2) | 0.0594 (19) | 0.050 (2) | 0.0043 (17) | 0.0057 (16) | −0.0083 (16) |
| O3 | 0.148 (3) | 0.092 (2) | 0.0467 (15) | −0.027 (2) | 0.0140 (18) | −0.0131 (15) |
| C12 | 0.057 (2) | 0.062 (2) | 0.053 (2) | 0.0049 (17) | 0.0034 (17) | 0.0015 (16) |
| O4 | 0.137 (4) | 0.105 (3) | 0.063 (2) | 0.011 (2) | −0.028 (2) | 0.0082 (17) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Br—C1 | 1.896 (4) | C10—C9 | 1.379 (5) |
| O2—C7 | 1.379 (4) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| O2—C8 | 1.394 (4) | N1—O4 | 1.214 (5) |
| C1—C6 | 1.380 (5) | N1—O3 | 1.230 (5) |
| C1—C2 | 1.387 (5) | C5—C6 | 1.379 (5) |
| O1—C7 | 1.192 (4) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C3 | 1.383 (5) | C2—C3 | 1.378 (5) |
| C4—C5 | 1.388 (5) | C2—H2 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C7 | 1.477 (5) | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| C8—C9 | 1.378 (5) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| C8—C13 | 1.383 (5) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| C11—C10 | 1.372 (5) | C13—C12 | 1.367 (5) |
| C11—C12 | 1.387 (5) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C11—N1 | 1.465 (4) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C7—O2—C8 | 117.8 (3) | C6—C5—C4 | 120.5 (3) |
| C6—C1—C2 | 121.5 (3) | C6—C5—H5 | 119.8 |
| C6—C1—Br | 118.9 (3) | C4—C5—H5 | 119.8 |
| C2—C1—Br | 119.6 (3) | C3—C2—C1 | 118.5 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.4 (3) | C3—C2—H2 | 120.7 |
| C3—C4—C7 | 123.3 (3) | C1—C2—H2 | 120.7 |
| C5—C4—C7 | 117.3 (3) | C2—C3—C4 | 121.0 (3) |
| C9—C8—C13 | 122.0 (3) | C2—C3—H3 | 119.5 |
| C9—C8—O2 | 116.4 (3) | C4—C3—H3 | 119.5 |
| C13—C8—O2 | 121.5 (3) | C5—C6—C1 | 119.0 (3) |
| C10—C11—C12 | 121.8 (3) | C5—C6—H6 | 120.5 |
| C10—C11—N1 | 119.8 (3) | C1—C6—H6 | 120.5 |
| C12—C11—N1 | 118.4 (4) | C8—C9—C10 | 118.9 (3) |
| C11—C10—C9 | 119.1 (3) | C8—C9—H9 | 120.5 |
| C11—C10—H10 | 120.4 | C10—C9—H9 | 120.5 |
| C9—C10—H10 | 120.4 | C12—C13—C8 | 118.9 (3) |
| O4—N1—O3 | 123.6 (4) | C12—C13—H13 | 120.5 |
| O4—N1—C11 | 118.9 (4) | C8—C13—H13 | 120.5 |
| O3—N1—C11 | 117.5 (4) | C13—C12—C11 | 119.2 (4) |
| O1—C7—O2 | 122.4 (3) | C13—C12—H12 | 120.4 |
| O1—C7—C4 | 126.2 (3) | C11—C12—H12 | 120.4 |
| O2—C7—C4 | 111.4 (3) | ||
| C7—O2—C8—C9 | 123.0 (3) | C6—C1—C2—C3 | 1.3 (5) |
| C7—O2—C8—C13 | −60.4 (4) | Br—C1—C2—C3 | 179.9 (3) |
| C12—C11—C10—C9 | −1.7 (5) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.3 (5) |
| N1—C11—C10—C9 | 177.2 (3) | C5—C4—C3—C2 | −1.2 (5) |
| C10—C11—N1—O4 | −179.4 (4) | C7—C4—C3—C2 | −179.6 (3) |
| C12—C11—N1—O4 | −0.4 (6) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.7 (6) |
| C10—C11—N1—O3 | 0.0 (5) | C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.9 (6) |
| C12—C11—N1—O3 | 178.9 (4) | Br—C1—C6—C5 | −179.5 (3) |
| C8—O2—C7—O1 | 0.6 (5) | C13—C8—C9—C10 | 1.5 (5) |
| C8—O2—C7—C4 | −178.4 (3) | O2—C8—C9—C10 | 178.1 (3) |
| C3—C4—C7—O1 | 173.0 (4) | C11—C10—C9—C8 | 0.4 (5) |
| C5—C4—C7—O1 | −5.4 (5) | C9—C8—C13—C12 | −2.0 (6) |
| C3—C4—C7—O2 | −8.0 (5) | O2—C8—C13—C12 | −178.5 (3) |
| C5—C4—C7—O2 | 173.5 (3) | C8—C13—C12—C11 | 0.7 (6) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 1.7 (6) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 1.2 (6) |
| C7—C4—C5—C6 | −179.8 (4) | N1—C11—C12—C13 | −177.7 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C10—H10···O4i | 0.93 | 2.69 | 3.543 (6) | 153. |
| C3—H3···O3ii | 0.93 | 2.60 | 3.335 (5) | 136. |
| C13—H13···O3iii | 0.93 | 2.67 | 3.460 (5) | 143. |
| C12—H12···O1iv | 0.93 | 2.50 | 3.237 (5) | 137. |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (ii) −x+1, −y, −z+1; (iii) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (iv) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HG5114).
References
- Allen, F. H. (2002). Acta Cryst. B58, 380–388. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Etter, M. (1990). Acc. Chem. Res. 23, 120–126.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 837–838.
- Jefford, C. W., Kubota, T. & Zaslona, A. (1986). Helv. Chim. Acta, 69, 2048–2061.
- Jefford, C. W. & Zaslona, A. (1985). Tetrahedron Lett. 26, 6035–6038.
- Macrae, C. F., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Shields, G. P., Taylor, R., Towler, M. & van de Streek, J. (2006). J. Appl. Cryst. 39, 453–457.
- Nardelli, M. (1995). J. Appl. Cryst. 28, 659.
- Nonius (1998). COLLECT Nonius BV, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. (1997). Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 276, Macromolecular Crystallography, Part A, edited by C. W. Carter Jr & R. M. Sweet, pp. 307–326. New York: Academic Press.
- Politzer, P., Murray, J. S. & Clark, T. (2010). Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 12, 7748–7757. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ritter, S. K. (2009). Sci. Technol. 87, 39–42.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Wardell, J. L., Skakle, J. M. S., Low, J. N. & Glidewell, C. (2005). Acta Cryst. E61, o3334–o3336.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811043923/hg5114sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811043923/hg5114Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811043923/hg5114Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




