Abstract
The title compound, C17H16N2O6, is a decomposition product of the hypertension drug nifedipine [systematic name: dimethyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate]. The dihedral angle between the nitrosophenyl ring and the pyridine ring is 67.1 (5)°.
Related literature
For the calcium antagonistic activity of compounds of the 1,4-dihydropyridine class, which inhibit the influx of Ca2+ ions through plasma membrane channels, see: Núnez-Vergara et al. (1994 ▶) and for their current use in the treatment of a variety of cardiovascular disorders such as angina and hypertension, see: Triggle et al. (1989 ▶); Hurwitz et al. (1991 ▶). For general background to derivatives of the dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers nifedipine [3,5-dimethyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate] and nisoldpine [isobutyl methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate], see: Chen et al. (2010 ▶); Rowan & Holt (1996 ▶, 1997a
▶,b
▶); Schultheiss et al. (2010 ▶). For standard bond lengths, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶). 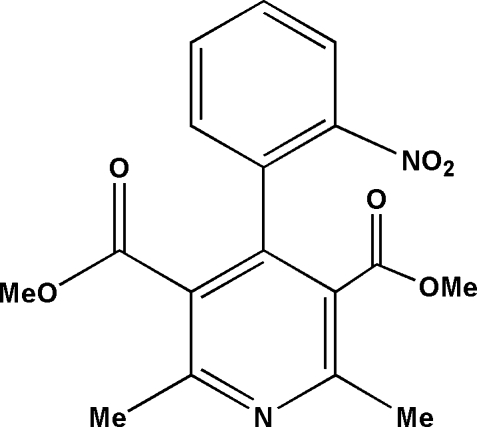
Experimental
Crystal data
C17H16N2O6
M r = 344.32
Triclinic,

a = 7.578 (4) Å
b = 8.141 (4) Å
c = 14.235 (9) Å
α = 103.32 (2)°
β = 93.75 (5)°
γ = 105.39 (3)°
V = 816.4 (8) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.11 mm−1
T = 298 K
0.20 × 0.18 × 0.12 mm
Data collection
Rigaku Saturn724 CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.979, T max = 0.987
8658 measured reflections
3843 independent reflections
2247 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.047
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.038
wR(F 2) = 0.097
S = 1.03
3843 reflections
230 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.21 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.29 e Å−3
Data collection: CrystalClear (Rigaku, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: CrystalClear; data reduction: CrystalClear; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: CrystalStructure (Rigaku, 2005 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811039626/qm2031sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811039626/qm2031Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811039626/qm2031Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Tianjin Natural Science Foundation (10JCZDJC23900).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Compounds of the 1,4-dihydropyridine class exhibit calcium antagonistic activity, as they inhibit the influx of Ca2+ ions through plasma membrane channels (Núnez-Vergara, Sunkel & Squella, 1994). Compounds of this class are currently being used in the treatment of a variety of cardiovascular disorders, such as angina and hypertension (Triggle et al., 1989; Hurwitz et al., 1991). Nifedipine [dimethyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate], is the best known member of this class. The molecular structure of (I) is shown in Fig. 1. The bond lengths and angles are within normal ranges (Allen et al., 1987). The dihedral angle between the nitrosophenyl ring and the pyridine ring is 67.1°.
Experimental
The title compound was prepared by adding following steps. 1: Add 1 g nifedipine and 10 g (NH4)2S2O8 to the 100 ml acetone solution(50%). 2: Stir for 12 h at 30 °C.3:Regulate the solution to pH=8 with Na2CO3. The resulting solution was extracted with methylene chloride. The organic layer was dried over MgSO4 and evaporated under reduced pressure. Following washing the extract with water, crystals of suitable size for single-crystal analysis were recrystallized from methanol.
Refinement
H atoms were positioned geometrically, with C—H = 0.93 and 0.96 A ° for aromatic and methyl H atoms, respectively, and constrained to ride on their parent atoms, with Uiso(H) = xUeq(C), where x = 1.2 for aromatic and x = 1.5 for methyl H atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
[3,5-dimethyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate]
Crystal data
| C17H16N2O6 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 344.32 | F(000) = 360 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.401 Mg m−3 |
| a = 7.578 (4) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 8.141 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 2919 reflections |
| c = 14.235 (9) Å | θ = 1.5–28.0° |
| α = 103.32 (2)° | µ = 0.11 mm−1 |
| β = 93.75 (5)° | T = 298 K |
| γ = 105.39 (3)° | Prism, yellow |
| V = 816.4 (8) Å3 | 0.20 × 0.18 × 0.12 mm |
Data collection
| Rigaku Saturn724 CCD diffractometer | 3843 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: rotating anode | 2247 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| multilayer | Rint = 0.047 |
| Detector resolution: 14.22 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.9°, θmin = 1.5° |
| ω and φ scans | h = −9→9 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku, 2005) | k = −10→10 |
| Tmin = 0.979, Tmax = 0.987 | l = −18→17 |
| 8658 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.038 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.097 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.03 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.028P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3843 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 230 parameters | Δρmax = 0.21 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.29 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.76803 (15) | 0.93198 (15) | 0.92024 (8) | 0.0333 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.84798 (13) | 0.68996 (14) | 0.85050 (7) | 0.0240 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.40716 (15) | 0.78829 (15) | 0.70787 (8) | 0.0344 (3) | |
| O4 | 0.63979 (19) | 0.91761 (16) | 0.64507 (10) | 0.0520 (4) | |
| O5 | 0.13443 (14) | 0.30250 (15) | 0.61801 (7) | 0.0279 (3) | |
| O6 | 0.18628 (14) | 0.11367 (14) | 0.70271 (7) | 0.0259 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.26875 (17) | 0.55143 (17) | 0.95102 (9) | 0.0218 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.54570 (19) | 0.78817 (18) | 0.66853 (9) | 0.0283 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.5124 (2) | 0.7905 (2) | 1.05399 (10) | 0.0256 (4) | |
| H1A | 0.4799 | 0.8996 | 1.0549 | 0.038* | |
| H1B | 0.6471 | 0.8165 | 1.0651 | 0.038* | |
| H1C | 0.4582 | 0.7401 | 1.1054 | 0.038* | |
| C2 | 0.4386 (2) | 0.6606 (2) | 0.95644 (10) | 0.0200 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.53855 (19) | 0.65051 (19) | 0.87679 (10) | 0.0184 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.45649 (19) | 0.52477 (19) | 0.78913 (10) | 0.0175 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.2806 (2) | 0.4125 (2) | 0.78490 (10) | 0.0188 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.1892 (2) | 0.4295 (2) | 0.86757 (11) | 0.0200 (3) | |
| C7 | −0.0011 (2) | 0.3140 (2) | 0.86810 (11) | 0.0278 (4) | |
| H7A | 0.0077 | 0.2160 | 0.8954 | 0.042* | |
| H7B | −0.0653 | 0.2675 | 0.8013 | 0.042* | |
| H7C | −0.0701 | 0.3832 | 0.9080 | 0.042* | |
| C8 | 0.7278 (2) | 0.7743 (2) | 0.88633 (11) | 0.0214 (3) | |
| C9 | 1.0316 (2) | 0.8018 (2) | 0.84997 (12) | 0.0297 (4) | |
| H9A | 1.0228 | 0.8948 | 0.8183 | 0.045* | |
| H9B | 1.1038 | 0.7310 | 0.8141 | 0.045* | |
| H9C | 1.0925 | 0.8554 | 0.9171 | 0.045* | |
| C10 | 0.55534 (18) | 0.50220 (19) | 0.70104 (10) | 0.0176 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.6085 (2) | 0.3487 (2) | 0.67264 (10) | 0.0226 (4) | |
| H11 | 0.5774 | 0.2612 | 0.7077 | 0.027* | |
| C12 | 0.7059 (2) | 0.3213 (2) | 0.59432 (11) | 0.0267 (4) | |
| H12 | 0.7401 | 0.2154 | 0.5759 | 0.032* | |
| C13 | 0.7538 (2) | 0.4482 (2) | 0.54255 (11) | 0.0263 (4) | |
| H13 | 0.8218 | 0.4296 | 0.4893 | 0.032* | |
| C14 | 0.7024 (2) | 0.6014 (2) | 0.56854 (11) | 0.0237 (4) | |
| H14 | 0.7342 | 0.6887 | 0.5334 | 0.028* | |
| C15 | 0.60384 (19) | 0.6254 (2) | 0.64663 (10) | 0.0202 (3) | |
| C16 | 0.19127 (19) | 0.2747 (2) | 0.69257 (11) | 0.0200 (3) | |
| C17 | 0.1122 (2) | −0.0294 (2) | 0.61593 (12) | 0.0364 (4) | |
| H17A | −0.0139 | −0.0318 | 0.5937 | 0.055* | |
| H17B | 0.1105 | −0.1415 | 0.6307 | 0.055* | |
| H17C | 0.1898 | −0.0116 | 0.5646 | 0.055* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0287 (7) | 0.0182 (6) | 0.0483 (8) | 0.0042 (5) | 0.0079 (5) | 0.0014 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0200 (6) | 0.0216 (6) | 0.0293 (6) | 0.0058 (5) | 0.0056 (5) | 0.0041 (5) |
| O3 | 0.0382 (7) | 0.0388 (8) | 0.0381 (7) | 0.0221 (6) | 0.0167 (6) | 0.0170 (6) |
| O4 | 0.0680 (10) | 0.0273 (8) | 0.0727 (10) | 0.0148 (7) | 0.0355 (8) | 0.0278 (8) |
| O5 | 0.0279 (6) | 0.0343 (7) | 0.0211 (6) | 0.0059 (5) | 0.0023 (5) | 0.0102 (5) |
| O6 | 0.0320 (6) | 0.0194 (6) | 0.0223 (6) | 0.0061 (5) | −0.0008 (5) | 0.0004 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0245 (7) | 0.0220 (7) | 0.0214 (7) | 0.0086 (6) | 0.0074 (5) | 0.0072 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0376 (9) | 0.0251 (8) | 0.0255 (8) | 0.0098 (7) | 0.0069 (6) | 0.0111 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0318 (9) | 0.0260 (9) | 0.0212 (8) | 0.0119 (8) | 0.0040 (7) | 0.0058 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0248 (8) | 0.0195 (8) | 0.0188 (8) | 0.0109 (7) | 0.0036 (6) | 0.0057 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0200 (8) | 0.0168 (8) | 0.0211 (8) | 0.0080 (7) | 0.0040 (6) | 0.0065 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0205 (8) | 0.0173 (8) | 0.0188 (8) | 0.0094 (7) | 0.0062 (6) | 0.0072 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0210 (8) | 0.0190 (8) | 0.0188 (8) | 0.0077 (7) | 0.0052 (6) | 0.0066 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0222 (8) | 0.0190 (8) | 0.0217 (8) | 0.0082 (7) | 0.0065 (6) | 0.0072 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0247 (9) | 0.0281 (10) | 0.0287 (9) | 0.0048 (8) | 0.0119 (7) | 0.0045 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0248 (8) | 0.0223 (9) | 0.0176 (8) | 0.0074 (7) | 0.0039 (6) | 0.0051 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0192 (8) | 0.0312 (10) | 0.0363 (10) | 0.0029 (7) | 0.0059 (7) | 0.0085 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0131 (7) | 0.0195 (8) | 0.0170 (8) | 0.0008 (6) | 0.0016 (6) | 0.0034 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0219 (8) | 0.0213 (9) | 0.0241 (9) | 0.0054 (7) | 0.0041 (7) | 0.0055 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0244 (9) | 0.0258 (9) | 0.0285 (9) | 0.0101 (8) | 0.0054 (7) | 0.0005 (8) |
| C13 | 0.0201 (8) | 0.0334 (10) | 0.0210 (9) | 0.0047 (8) | 0.0067 (6) | 0.0012 (8) |
| C14 | 0.0207 (8) | 0.0276 (9) | 0.0194 (8) | 0.0001 (7) | 0.0039 (6) | 0.0071 (7) |
| C15 | 0.0185 (8) | 0.0193 (8) | 0.0207 (8) | 0.0034 (7) | 0.0023 (6) | 0.0036 (7) |
| C16 | 0.0142 (7) | 0.0234 (9) | 0.0231 (9) | 0.0041 (7) | 0.0080 (6) | 0.0073 (7) |
| C17 | 0.0424 (11) | 0.0262 (10) | 0.0303 (10) | 0.0072 (9) | −0.0033 (8) | −0.0074 (8) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C8 | 1.2086 (18) | C5—C16 | 1.498 (2) |
| O2—C8 | 1.3392 (18) | C6—C7 | 1.500 (2) |
| O2—C9 | 1.4485 (18) | C7—H7A | 0.9800 |
| O3—N2 | 1.2218 (16) | C7—H7B | 0.9800 |
| O4—N2 | 1.2349 (16) | C7—H7C | 0.9800 |
| O5—C16 | 1.2107 (18) | C9—H9A | 0.9800 |
| O6—C16 | 1.3427 (19) | C9—H9B | 0.9800 |
| O6—C17 | 1.4481 (19) | C9—H9C | 0.9800 |
| N1—C2 | 1.342 (2) | C10—C15 | 1.393 (2) |
| N1—C6 | 1.344 (2) | C10—C11 | 1.394 (2) |
| N2—C15 | 1.478 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.385 (2) |
| C1—C2 | 1.506 (2) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| C1—H1A | 0.9800 | C12—C13 | 1.388 (2) |
| C1—H1B | 0.9800 | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C1—H1C | 0.9800 | C13—C14 | 1.381 (2) |
| C2—C3 | 1.403 (2) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C4 | 1.401 (2) | C14—C15 | 1.385 (2) |
| C3—C8 | 1.495 (2) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C4—C5 | 1.390 (2) | C17—H17A | 0.9800 |
| C4—C10 | 1.502 (2) | C17—H17B | 0.9800 |
| C5—C6 | 1.402 (2) | C17—H17C | 0.9800 |
| C8—O2—C9 | 115.40 (13) | O2—C8—C3 | 111.74 (14) |
| C16—O6—C17 | 115.28 (12) | O2—C9—H9A | 109.5 |
| C2—N1—C6 | 120.11 (13) | O2—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| O3—N2—O4 | 123.19 (15) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| O3—N2—C15 | 118.96 (13) | O2—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| O4—N2—C15 | 117.85 (14) | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—H1A | 109.5 | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C15—C10—C11 | 116.86 (13) |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C15—C10—C4 | 125.17 (14) |
| C2—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C11—C10—C4 | 117.94 (13) |
| H1A—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C12—C11—C10 | 121.28 (15) |
| H1B—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C12—C11—H11 | 119.4 |
| N1—C2—C3 | 121.69 (15) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.4 |
| N1—C2—C1 | 114.91 (13) | C11—C12—C13 | 120.22 (15) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 123.39 (14) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.9 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 118.72 (14) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.9 |
| C4—C3—C8 | 121.45 (13) | C14—C13—C12 | 119.93 (14) |
| C2—C3—C8 | 119.83 (14) | C14—C13—H13 | 120.0 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 118.81 (13) | C12—C13—H13 | 120.0 |
| C5—C4—C10 | 118.94 (14) | C13—C14—C15 | 118.90 (15) |
| C3—C4—C10 | 122.20 (13) | C13—C14—H14 | 120.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.36 (14) | C15—C14—H14 | 120.5 |
| C4—C5—C16 | 119.84 (13) | C14—C15—C10 | 122.80 (15) |
| C6—C5—C16 | 120.80 (14) | C14—C15—N2 | 116.56 (14) |
| N1—C6—C5 | 121.30 (14) | C10—C15—N2 | 120.61 (13) |
| N1—C6—C7 | 116.40 (13) | O5—C16—O6 | 123.94 (15) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 122.30 (14) | O5—C16—C5 | 125.59 (15) |
| C6—C7—H7A | 109.5 | O6—C16—C5 | 110.45 (13) |
| C6—C7—H7B | 109.5 | O6—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| H7A—C7—H7B | 109.5 | O6—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7C | 109.5 | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| H7A—C7—H7C | 109.5 | O6—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| H7B—C7—H7C | 109.5 | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| O1—C8—O2 | 123.61 (15) | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| O1—C8—C3 | 124.63 (14) | ||
| C6—N1—C2—C3 | −0.6 (2) | C5—C4—C10—C15 | 115.28 (17) |
| C6—N1—C2—C1 | −179.75 (12) | C3—C4—C10—C15 | −67.4 (2) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.1 (2) | C5—C4—C10—C11 | −66.86 (18) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −179.85 (13) | C3—C4—C10—C11 | 110.45 (17) |
| N1—C2—C3—C8 | −179.70 (13) | C15—C10—C11—C12 | 0.4 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C8 | −0.7 (2) | C4—C10—C11—C12 | −177.67 (14) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −1.2 (2) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.4 (2) |
| C8—C3—C4—C5 | 179.60 (13) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.7 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C10 | −178.56 (13) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 0.2 (2) |
| C8—C3—C4—C10 | 2.3 (2) | C13—C14—C15—C10 | 0.6 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.9 (2) | C13—C14—C15—N2 | −177.47 (13) |
| C10—C4—C5—C6 | 178.33 (13) | C11—C10—C15—C14 | −0.9 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C16 | −178.88 (13) | C4—C10—C15—C14 | 176.99 (14) |
| C10—C4—C5—C16 | −1.5 (2) | C11—C10—C15—N2 | 177.12 (13) |
| C2—N1—C6—C5 | 0.3 (2) | C4—C10—C15—N2 | −5.0 (2) |
| C2—N1—C6—C7 | −179.65 (13) | O3—N2—C15—C14 | 152.38 (14) |
| C4—C5—C6—N1 | −0.5 (2) | O4—N2—C15—C14 | −27.0 (2) |
| C16—C5—C6—N1 | 179.35 (13) | O3—N2—C15—C10 | −25.7 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 179.50 (13) | O4—N2—C15—C10 | 154.89 (15) |
| C16—C5—C6—C7 | −0.7 (2) | C17—O6—C16—O5 | 1.9 (2) |
| C9—O2—C8—O1 | −3.1 (2) | C17—O6—C16—C5 | −176.59 (11) |
| C9—O2—C8—C3 | 175.45 (12) | C4—C5—C16—O5 | −70.6 (2) |
| C4—C3—C8—O1 | 131.12 (17) | C6—C5—C16—O5 | 109.63 (18) |
| C2—C3—C8—O1 | −48.0 (2) | C4—C5—C16—O6 | 107.95 (15) |
| C4—C3—C8—O2 | −47.44 (18) | C6—C5—C16—O6 | −71.86 (17) |
| C2—C3—C8—O2 | 133.40 (14) |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: QM2031).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Chen, H., Qu, D., Wang, Q.-F. & Jiang, R. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hurwitz, L., Partridge, L. D. & Leach, J. K. (1991). In Calcium Channels: Their Properties, Functions, Regulation and Clinical Relevance Boca Raton, Florida, USA: CRC Press.
- Núnez-Vergara, L. J., Sunkel, C. & Squella, J. A. (1994). J. Pharm. Sci. 83, 502–507. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rigaku (2005). CrystalClear and CrystalStructure Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Rowan, K. R. & Holt, E. M. (1996). Acta Cryst. C52, 1565–1570.
- Rowan, K. R. & Holt, E. M. (1997a). Acta Cryst. C53, 106–108.
- Rowan, K. R. & Holt, E. M. (1997b). Acta Cryst. C53, 257–261.
- Schultheiss, N., Roe, M. & Smit, J. P. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o2297–o2298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Triggle, D. J., Langs, D. A. & Janis, R. A. (1989). Med. Res. Rev. 9, 123–180. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811039626/qm2031sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811039626/qm2031Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811039626/qm2031Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



