Abstract
In the title molecule, C24H18N2O3S, the 13-atom ring system comprising the quinoxaline and fused five-membered ring exhibits an r.m.s. deviation from coplanarity of 0.039 Å, with a maximum deviation of 0.0710 (10) Å for the PhCO-bearing C atom of the five-membered ring. The 10-membered C8N2 quinoxaline ring system has an r.m.s. deviation from coplanarity of 0.022 Å, with a maximum deviation of 0.0403 (9) Å for the C atom involved in the C=C bond in the five-membered ring. The three atoms of the five-membered ring fused to the quinoxaline ring system show deviations of up to 0.118 (2) Å for the PhCO-bearing C atom. C—N bond distances in the quinoxaline ring system of the title molecule deviate from those in unsubstituted quinoxaline. In particular, the two C—N distances to the N atom involved in the five-membered ring are essentially equal, with values of 1.3786 (17) and 1.3773 (16) Å, unlike the difference of nearly 0.06 Å in quinoxaline.
Related literature
For the transformation of benzimidazoles into pyrroloquinoxalines, see: Ager et al. (1988 ▶); Methcohn (1975 ▶). For the synthesis of condensed pyrazines, see: Cheeseman & Cookson (1979 ▶). For the biological activity of quinoxalines, see: Porter (1984 ▶); He et al. (2003 ▶); Kim et al. (2004 ▶). For cyclization reactions of quinoxaline derivatives, see: Taylor & Hand (1962 ▶, 1963 ▶); Yadav et al. (2008 ▶). For the structure of an analogous compound with COOMe at C9 and C10, see: Hirano et al. (2002 ▶). For polymorphs of quinoxaline, see: Ranganathan et al. (2010 ▶); Anthony et al. (1998 ▶). For a description of the Cambridge Structural Database, see: Allen (2002 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C24H18N2O3S
M r = 414.46
Monoclinic,
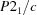
a = 19.0915 (9) Å
b = 9.9636 (5) Å
c = 10.4203 (5) Å
β = 104.6190 (13)°
V = 1917.98 (16) Å3
Z = 4
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 1.75 mm−1
T = 90 K
0.30 × 0.27 × 0.13 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2004 ▶) T min = 0.622, T max = 0.804
31213 measured reflections
3621 independent reflections
3543 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.032
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.029
wR(F 2) = 0.076
S = 1.04
3621 reflections
272 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.41 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.39 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811040335/nk2116sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811040335/nk2116Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811040335/nk2116Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
TŪBİTAK (the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey, grant 109 T875) is gratefully acknowledged for financial support.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Despite the fact that pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoxalines have valuable characteristics, in particular, marked biological activity, very limited publications regarding their synthesis have appeared in comparison with similar heterocyles (Cheeseman & Cookson, 1979). One of the most widespread and most widely used methods for the synthesis of pyrrolo-[1,2-a]quinoxalines involves the intramolecular cyclization of derivatives of quinoxaline with substituents at position 2, containing at least three carbon atoms with reaction centers capable of nucleophilic attack (Taylor & Hand, 1962; 1963). The benzimidazoles are also transformed into pyrroloquinoxalines by the action of acetylenecarboxylic acid derivatives (Methcohn, 1975; Ager et al., 1988). It is also well known that nitrogen-containing heterocycles are abundant in nature and exhibit diverse and important biological properties (Porter, 1984). While rarely found in nature, quinoxalines find important applications in the pharmaceutical industry and have been shown to possess a broad spectrum of biological activity, including antiviral and antibacterial properties and also act as kinase inhibitors (He et al., 2003; Kim et al., 2004). These heterocyclic ring systems are most commonly assembled by the annulation of a heterocyclic ring onto a pre-existing benzene ring (Yadav et al., 2008). In continuation of our chemistry related to the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition of heterocyclic N-ylides to electron-deficient alkenes, we have prepared phenylsulfonyl substituted-1,2-dihydropyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoxalin-1-ylmethanone by the reaction of in situ-generated quinoxalinium ylide and phenyl vinyl sulfone and determined its crystal structure.
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (version 5.32, Nov. 2010 with May 2011 update, Allen, 2002) yielded only one previous report of a crystal structure (Hirano et al., 2002) containing the 13-atom C11N2 ring system. It has COOMe groups at C9 and C10 and is unsubstituted at C11, but its coordinates were not deposited. The structures of two polymorphs of unsubstituted quinoxaline have been reported (Anthony et al., 1998; Ranganathan et al., 2010). It is of interest to note the changes to the geometry of the C4N2 heterocyclic ring of quinoxaline brought about by its fusion to the five-membered ring of the present compound. In quinoxaline, there is considerable double-bond localization into the C═N bonds analogous to C7═N1 and C8═N2. Those bonds have a mean distance of 1.314 Å, averaged over 12 values with a range of values 1.299 - 1.329 Å in the two polymorphs. This is shorter than the mean (of 12) value of 1.371 Å for the bonds corresponding to C1–N1 (range 1.353 - 1.392 Å). The mean distance for the bond analogous to C7–C8 in quinoxaline is 1.406 Å, range 1.373 - 1.421 Å. In the title compound, N1–C1, 1.4007 (17) Å is longer than N1–C7, 1.2904 (18) by an amount greater than in quinoxaline. Also unlike quinoxaline, the two endocyclic bonds to N2 in the title compound are equal, 1.3786 (17) and 1.3773 (16) Å., and C7–C8 is elongated to 1.4536 (17) Å. This is accompanied by a C8═C9 double-bond distance of 1.3555 (18) Å.
The 13-atom ring system C1 through C11, N1 and N2 exhibits an r.m.s. deviation of 0.039 Å, the largest deviations being in the 5-membered ring, 0.0614 (10) Å for C9 and 0.0710 (10) Å for C11. The r.m.s. deviation from coplanarity of the 10-atom quinoxaline fragment C1 through C8, N1 and N2 is only 0.022 Å, with C10 also lying in that plane; +0.002 (2) Å deviation, and C9 and C11 lying farther out of plane, -0.104 (2) and -0.118 (2) Å, respectively.
Experimental
The quinoxalinium salt (1 mmol, 329 mg), obtained from phenacyl bromide and quinoxaline in acetone, was suspended in dichloromethane (10 ml) and then phenylvinylsulfone (1 mmol, 168 mg) was added. Under vigorous stirring, triethylamine (1.4 ml, 1 mmol) was added dropwise. The progress of the reaction was monitored by TLC. After 20 min the reaction mixture was washed with water (2 X 10 ml) and solvent was evaporated. The residual crude product was purified with column chromatography using hexane-ethyl acetate as eluent. The cycloaddition product was recrystallized from CDCl3 to give orange crystals. M.p.148–150°C. Rf: 0.65 (ethyl acetate-n-hexane; 1:1). IR (KBr): ν= 1696 (C═O),1594,1566 1479, 1300, 1223, 1149, 1078, 719, 611 cm-1. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 9.11 (s, 1H), 7.92 (d, J =7.2 Hz, 2H), 7.86 (d, J =7.6 Hz, 2H), 7.69–7.65 (q, 2H), 7.56–7.47 (m, 5H), 7.36 (s, 1H), 7.21 (t, 1H), 7.06 (t, 1H), 6.30 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 5.84–5.79 (dd, J = 14.0, 6.4 Hz, 1H), 3.56 (t, J = 16.0 Hz, 1H), 3.00–2.95 (dd, J = 14.6, 6.0 Hz, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 193.3 (C═O), 145.1, 142.7, 142.5, 135.2, 135.0, 133.4, 132.7, 132.4, 132.3, 130.2, 129.8, 129.8, 126.4, 123.1, 113.6, 99.1, 63.7, 33.9. LC—MS (70 eV): (m/z, %)= 415.80 (100) [M+H]+.
Refinement
H atoms on C were placed in idealized positions with C—H distances 0.95 - 1.00 Å and thereafter treated as riding. Uiso for H were assigned as 1.2 times Ueq of the attached atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Ellipsoids at the 50% level, with H atoms having arbitrary radius.
Crystal data
| C24H18N2O3S | F(000) = 864 |
| Mr = 414.46 | Dx = 1.435 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 9862 reflections |
| a = 19.0915 (9) Å | θ = 4.4–70.1° |
| b = 9.9636 (5) Å | µ = 1.75 mm−1 |
| c = 10.4203 (5) Å | T = 90 K |
| β = 104.6190 (13)° | Rectangular prism, orange |
| V = 1917.98 (16) Å3 | 0.30 × 0.27 × 0.13 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 3621 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3543 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.032 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 70.2°, θmin = 2.4° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2004) | h = −23→23 |
| Tmin = 0.622, Tmax = 0.804 | k = −10→12 |
| 31213 measured reflections | l = −12→12 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.029 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.076 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0349P)2 + 1.1954P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.04 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 3621 reflections | Δρmax = 0.41 e Å−3 |
| 272 parameters | Δρmin = −0.39 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.00108 (12) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.347686 (15) | 0.61731 (3) | 0.66691 (3) | 0.01450 (10) | |
| O1 | 0.36497 (5) | 0.53406 (10) | 0.56612 (9) | 0.0205 (2) | |
| O2 | 0.31216 (5) | 0.74476 (9) | 0.63034 (9) | 0.0200 (2) | |
| O3 | 0.11000 (5) | 0.43117 (9) | 0.71433 (9) | 0.0190 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.29905 (6) | 0.15898 (11) | 0.69500 (10) | 0.0166 (2) | |
| N2 | 0.24574 (6) | 0.35506 (11) | 0.83452 (10) | 0.0146 (2) | |
| C1 | 0.25306 (7) | 0.12578 (13) | 0.77577 (12) | 0.0155 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.23431 (7) | −0.00846 (13) | 0.78555 (13) | 0.0182 (3) | |
| H2 | 0.2537 | −0.0755 | 0.7395 | 0.022* | |
| C3 | 0.18766 (7) | −0.04454 (13) | 0.86193 (13) | 0.0198 (3) | |
| H3 | 0.1741 | −0.1358 | 0.8665 | 0.024* | |
| C4 | 0.16049 (7) | 0.05308 (13) | 0.93218 (13) | 0.0181 (3) | |
| H4 | 0.1290 | 0.0275 | 0.9854 | 0.022* | |
| C5 | 0.17878 (7) | 0.18683 (13) | 0.92537 (12) | 0.0162 (3) | |
| H5 | 0.1602 | 0.2527 | 0.9739 | 0.019* | |
| C6 | 0.22492 (6) | 0.22410 (13) | 0.84637 (12) | 0.0142 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.31442 (7) | 0.28371 (13) | 0.68290 (12) | 0.0159 (3) | |
| H7 | 0.3450 | 0.3057 | 0.6268 | 0.019* | |
| C8 | 0.28749 (6) | 0.39240 (13) | 0.75032 (12) | 0.0142 (3) | |
| C9 | 0.29573 (6) | 0.52749 (13) | 0.74933 (12) | 0.0150 (3) | |
| C10 | 0.25941 (7) | 0.59237 (13) | 0.84700 (13) | 0.0170 (3) | |
| H10A | 0.2265 | 0.6655 | 0.8048 | 0.020* | |
| H10B | 0.2955 | 0.6285 | 0.9247 | 0.020* | |
| C11 | 0.21643 (7) | 0.47295 (12) | 0.88718 (12) | 0.0145 (3) | |
| H11 | 0.2249 | 0.4671 | 0.9857 | 0.017* | |
| C12 | 0.13534 (7) | 0.48735 (12) | 0.81931 (12) | 0.0139 (3) | |
| C13 | 0.09098 (7) | 0.57500 (12) | 0.88358 (12) | 0.0144 (3) | |
| C14 | 0.12184 (7) | 0.65545 (13) | 0.99308 (12) | 0.0163 (3) | |
| H14 | 0.1727 | 0.6549 | 1.0296 | 0.020* | |
| C15 | 0.07783 (7) | 0.73617 (14) | 1.04836 (13) | 0.0210 (3) | |
| H15 | 0.0987 | 0.7912 | 1.1226 | 0.025* | |
| C16 | 0.00346 (8) | 0.73669 (14) | 0.99538 (15) | 0.0231 (3) | |
| H16 | −0.0264 | 0.7924 | 1.0333 | 0.028* | |
| C17 | −0.02763 (7) | 0.65613 (15) | 0.88708 (14) | 0.0223 (3) | |
| H17 | −0.0786 | 0.6563 | 0.8515 | 0.027* | |
| C18 | 0.01584 (7) | 0.57577 (14) | 0.83122 (13) | 0.0181 (3) | |
| H18 | −0.0054 | 0.5209 | 0.7570 | 0.022* | |
| C19 | 0.42916 (7) | 0.64997 (14) | 0.78853 (12) | 0.0168 (3) | |
| C20 | 0.48648 (7) | 0.56023 (15) | 0.80223 (14) | 0.0223 (3) | |
| H20 | 0.4825 | 0.4844 | 0.7456 | 0.027* | |
| C21 | 0.54965 (8) | 0.58369 (18) | 0.90036 (15) | 0.0304 (4) | |
| H21 | 0.5896 | 0.5242 | 0.9109 | 0.037* | |
| C22 | 0.55422 (8) | 0.69423 (19) | 0.98282 (14) | 0.0326 (4) | |
| H22 | 0.5975 | 0.7099 | 1.0497 | 0.039* | |
| C23 | 0.49673 (8) | 0.78208 (17) | 0.96936 (14) | 0.0292 (3) | |
| H23 | 0.5006 | 0.8570 | 1.0272 | 0.035* | |
| C24 | 0.43328 (7) | 0.76078 (15) | 0.87121 (13) | 0.0218 (3) | |
| H24 | 0.3936 | 0.8207 | 0.8608 | 0.026* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.01365 (16) | 0.01546 (17) | 0.01436 (16) | −0.00031 (11) | 0.00346 (11) | 0.00024 (11) |
| O1 | 0.0224 (5) | 0.0226 (5) | 0.0183 (5) | −0.0015 (4) | 0.0087 (4) | −0.0023 (4) |
| O2 | 0.0200 (5) | 0.0191 (5) | 0.0203 (5) | 0.0021 (4) | 0.0039 (4) | 0.0038 (4) |
| O3 | 0.0197 (5) | 0.0201 (5) | 0.0166 (4) | 0.0001 (4) | 0.0035 (4) | −0.0032 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0158 (5) | 0.0174 (6) | 0.0162 (5) | 0.0023 (4) | 0.0034 (4) | −0.0019 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0142 (5) | 0.0138 (5) | 0.0169 (5) | 0.0011 (4) | 0.0060 (4) | −0.0022 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0137 (6) | 0.0174 (7) | 0.0142 (6) | 0.0026 (5) | 0.0014 (5) | −0.0007 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0204 (6) | 0.0151 (6) | 0.0179 (6) | 0.0039 (5) | 0.0025 (5) | −0.0022 (5) |
| C3 | 0.0235 (7) | 0.0136 (6) | 0.0210 (7) | 0.0000 (5) | 0.0034 (5) | 0.0012 (5) |
| C4 | 0.0172 (6) | 0.0191 (7) | 0.0175 (6) | −0.0001 (5) | 0.0033 (5) | 0.0024 (5) |
| C5 | 0.0151 (6) | 0.0167 (6) | 0.0166 (6) | 0.0022 (5) | 0.0037 (5) | −0.0008 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0125 (6) | 0.0143 (6) | 0.0141 (6) | 0.0012 (5) | −0.0002 (5) | −0.0005 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0139 (6) | 0.0185 (7) | 0.0156 (6) | 0.0018 (5) | 0.0043 (5) | −0.0024 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0103 (5) | 0.0180 (6) | 0.0134 (6) | 0.0004 (5) | 0.0015 (4) | −0.0010 (5) |
| C9 | 0.0124 (6) | 0.0166 (6) | 0.0158 (6) | −0.0003 (5) | 0.0033 (5) | −0.0016 (5) |
| C10 | 0.0164 (6) | 0.0144 (6) | 0.0218 (6) | −0.0009 (5) | 0.0077 (5) | −0.0034 (5) |
| C11 | 0.0158 (6) | 0.0125 (6) | 0.0159 (6) | 0.0016 (5) | 0.0051 (5) | −0.0024 (5) |
| C12 | 0.0165 (6) | 0.0113 (6) | 0.0146 (6) | −0.0010 (5) | 0.0052 (5) | 0.0024 (5) |
| C13 | 0.0162 (6) | 0.0126 (6) | 0.0155 (6) | 0.0013 (5) | 0.0060 (5) | 0.0033 (5) |
| C14 | 0.0155 (6) | 0.0153 (6) | 0.0185 (6) | 0.0003 (5) | 0.0047 (5) | 0.0008 (5) |
| C15 | 0.0233 (7) | 0.0187 (7) | 0.0212 (6) | 0.0012 (5) | 0.0062 (5) | −0.0047 (5) |
| C16 | 0.0223 (7) | 0.0220 (7) | 0.0274 (7) | 0.0077 (5) | 0.0110 (6) | −0.0004 (6) |
| C17 | 0.0148 (6) | 0.0264 (7) | 0.0254 (7) | 0.0045 (5) | 0.0044 (5) | 0.0023 (6) |
| C18 | 0.0176 (6) | 0.0188 (7) | 0.0170 (6) | 0.0004 (5) | 0.0028 (5) | 0.0012 (5) |
| C19 | 0.0138 (6) | 0.0215 (7) | 0.0158 (6) | −0.0034 (5) | 0.0049 (5) | 0.0039 (5) |
| C20 | 0.0181 (6) | 0.0270 (7) | 0.0240 (7) | 0.0009 (5) | 0.0094 (5) | 0.0079 (6) |
| C21 | 0.0140 (6) | 0.0467 (10) | 0.0311 (8) | 0.0020 (6) | 0.0065 (6) | 0.0193 (7) |
| C22 | 0.0188 (7) | 0.0560 (11) | 0.0203 (7) | −0.0147 (7) | −0.0002 (5) | 0.0121 (7) |
| C23 | 0.0287 (8) | 0.0396 (9) | 0.0196 (7) | −0.0167 (7) | 0.0063 (6) | −0.0021 (6) |
| C24 | 0.0205 (7) | 0.0253 (7) | 0.0206 (6) | −0.0059 (5) | 0.0070 (5) | −0.0001 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| S1—O1 | 1.4404 (9) | C10—H10B | 0.9900 |
| S1—O2 | 1.4448 (10) | C11—C12 | 1.5377 (17) |
| S1—C9 | 1.7183 (13) | C11—H11 | 1.0000 |
| S1—C19 | 1.7710 (13) | C12—C13 | 1.4882 (17) |
| O3—C12 | 1.2152 (16) | C13—C14 | 1.3972 (18) |
| N1—C7 | 1.2904 (18) | C13—C18 | 1.4003 (18) |
| N1—C1 | 1.4007 (17) | C14—C15 | 1.3889 (18) |
| N2—C8 | 1.3773 (16) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| N2—C6 | 1.3786 (17) | C15—C16 | 1.387 (2) |
| N2—C11 | 1.4660 (15) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C2 | 1.3950 (19) | C16—C17 | 1.390 (2) |
| C1—C6 | 1.4103 (17) | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C3 | 1.3833 (19) | C17—C18 | 1.3829 (19) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C17—H17 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C4 | 1.3937 (19) | C18—H18 | 0.9500 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C19—C20 | 1.3924 (19) |
| C4—C5 | 1.3840 (19) | C19—C24 | 1.390 (2) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C20—C21 | 1.390 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.3991 (18) | C20—H20 | 0.9500 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C21—C22 | 1.386 (3) |
| C7—C8 | 1.4536 (17) | C21—H21 | 0.9500 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9500 | C22—C23 | 1.383 (2) |
| C8—C9 | 1.3555 (18) | C22—H22 | 0.9500 |
| C9—C10 | 1.5135 (17) | C23—C24 | 1.390 (2) |
| C10—C11 | 1.5613 (17) | C23—H23 | 0.9500 |
| C10—H10A | 0.9900 | C24—H24 | 0.9500 |
| O1—S1—O2 | 119.51 (6) | N2—C11—C10 | 103.55 (9) |
| O1—S1—C9 | 109.38 (6) | C12—C11—C10 | 109.99 (10) |
| O2—S1—C9 | 107.32 (6) | N2—C11—H11 | 111.1 |
| O1—S1—C19 | 107.83 (6) | C12—C11—H11 | 111.1 |
| O2—S1—C19 | 107.24 (6) | C10—C11—H11 | 111.1 |
| C9—S1—C19 | 104.57 (6) | O3—C12—C13 | 122.20 (11) |
| C7—N1—C1 | 118.60 (11) | O3—C12—C11 | 119.79 (11) |
| C8—N2—C6 | 122.62 (11) | C13—C12—C11 | 117.97 (10) |
| C8—N2—C11 | 111.04 (10) | C14—C13—C18 | 119.63 (12) |
| C6—N2—C11 | 125.38 (10) | C14—C13—C12 | 122.25 (11) |
| C2—C1—N1 | 118.80 (11) | C18—C13—C12 | 118.12 (11) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 119.30 (12) | C15—C14—C13 | 119.77 (12) |
| N1—C1—C6 | 121.90 (12) | C15—C14—H14 | 120.1 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.36 (12) | C13—C14—H14 | 120.1 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.8 | C14—C15—C16 | 120.17 (13) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.8 | C14—C15—H15 | 119.9 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.99 (12) | C16—C15—H15 | 119.9 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.0 | C17—C16—C15 | 120.35 (12) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.0 | C17—C16—H16 | 119.8 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.85 (12) | C15—C16—H16 | 119.8 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.6 | C18—C17—C16 | 119.83 (12) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.6 | C18—C17—H17 | 120.1 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.35 (12) | C16—C17—H17 | 120.1 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.3 | C17—C18—C13 | 120.25 (12) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.3 | C17—C18—H18 | 119.9 |
| N2—C6—C5 | 122.85 (11) | C13—C18—H18 | 119.9 |
| N2—C6—C1 | 117.02 (11) | C20—C19—C24 | 121.75 (13) |
| C5—C6—C1 | 120.12 (12) | C20—C19—S1 | 118.75 (11) |
| N1—C7—C8 | 123.60 (12) | C24—C19—S1 | 119.44 (10) |
| N1—C7—H7 | 118.2 | C21—C20—C19 | 118.75 (14) |
| C8—C7—H7 | 118.2 | C21—C20—H20 | 120.6 |
| C9—C8—N2 | 111.10 (11) | C19—C20—H20 | 120.6 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 132.87 (12) | C22—C21—C20 | 119.79 (14) |
| N2—C8—C7 | 116.03 (11) | C22—C21—H21 | 120.1 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 110.20 (11) | C20—C21—H21 | 120.1 |
| C8—C9—S1 | 127.13 (10) | C23—C22—C21 | 121.06 (13) |
| C10—C9—S1 | 122.27 (9) | C23—C22—H22 | 119.5 |
| C9—C10—C11 | 102.46 (10) | C21—C22—H22 | 119.5 |
| C9—C10—H10A | 111.3 | C22—C23—C24 | 119.98 (15) |
| C11—C10—H10A | 111.3 | C22—C23—H23 | 120.0 |
| C9—C10—H10B | 111.3 | C24—C23—H23 | 120.0 |
| C11—C10—H10B | 111.3 | C23—C24—C19 | 118.67 (14) |
| H10A—C10—H10B | 109.2 | C23—C24—H24 | 120.7 |
| N2—C11—C12 | 109.74 (10) | C19—C24—H24 | 120.7 |
| C7—N1—C1—C2 | 177.83 (12) | C8—N2—C11—C12 | 105.72 (11) |
| C7—N1—C1—C6 | −1.70 (18) | C6—N2—C11—C12 | −63.24 (15) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −178.48 (11) | C8—N2—C11—C10 | −11.67 (13) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 1.06 (19) | C6—N2—C11—C10 | 179.38 (11) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −1.5 (2) | C9—C10—C11—N2 | 12.32 (12) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.9 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −104.89 (11) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.27 (19) | N2—C11—C12—O3 | −19.31 (16) |
| C8—N2—C6—C5 | −175.85 (11) | C10—C11—C12—O3 | 93.98 (13) |
| C11—N2—C6—C5 | −8.11 (19) | N2—C11—C12—C13 | 162.91 (10) |
| C8—N2—C6—C1 | 4.95 (17) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −83.80 (13) |
| C11—N2—C6—C1 | 172.69 (11) | O3—C12—C13—C14 | −170.10 (12) |
| C4—C5—C6—N2 | −179.91 (11) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 7.62 (17) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.74 (18) | O3—C12—C13—C18 | 9.85 (18) |
| C2—C1—C6—N2 | 179.30 (11) | C11—C12—C13—C18 | −172.43 (11) |
| N1—C1—C6—N2 | −1.17 (17) | C18—C13—C14—C15 | −0.50 (19) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.08 (18) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 179.45 (12) |
| N1—C1—C6—C5 | 179.61 (11) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.2 (2) |
| C1—N1—C7—C8 | 1.00 (18) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | 0.3 (2) |
| C6—N2—C8—C9 | 175.24 (11) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | −0.5 (2) |
| C11—N2—C8—C9 | 5.93 (14) | C16—C17—C18—C13 | 0.2 (2) |
| C6—N2—C8—C7 | −5.56 (17) | C14—C13—C18—C17 | 0.30 (19) |
| C11—N2—C8—C7 | −174.87 (10) | C12—C13—C18—C17 | −179.65 (12) |
| N1—C7—C8—C9 | −178.52 (13) | O1—S1—C19—C20 | −24.23 (12) |
| N1—C7—C8—N2 | 2.50 (18) | O2—S1—C19—C20 | −154.13 (10) |
| N2—C8—C9—C10 | 2.97 (15) | C9—S1—C19—C20 | 92.12 (11) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | −176.05 (13) | O1—S1—C19—C24 | 158.43 (10) |
| N2—C8—C9—S1 | 175.80 (9) | O2—S1—C19—C24 | 28.53 (12) |
| C7—C8—C9—S1 | −3.2 (2) | C9—S1—C19—C24 | −85.22 (11) |
| O1—S1—C9—C8 | 17.24 (14) | C24—C19—C20—C21 | −0.8 (2) |
| O2—S1—C9—C8 | 148.29 (12) | S1—C19—C20—C21 | −178.08 (10) |
| C19—S1—C9—C8 | −98.03 (12) | C19—C20—C21—C22 | 0.6 (2) |
| O1—S1—C9—C10 | −170.72 (10) | C20—C21—C22—C23 | 0.1 (2) |
| O2—S1—C9—C10 | −39.67 (11) | C21—C22—C23—C24 | −0.5 (2) |
| C19—S1—C9—C10 | 74.02 (11) | C22—C23—C24—C19 | 0.3 (2) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | −9.76 (13) | C20—C19—C24—C23 | 0.4 (2) |
| S1—C9—C10—C11 | 176.99 (9) | S1—C19—C24—C23 | 177.63 (10) |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: NK2116).
References
- Ager, I. A., Barnes, A. C., Danswan, G. W. P., Hairsine, W., Kay, D. P., Kennewell, P. D., Matharu, S. S., Miller, P., Robson, P., Rowlands, D. A., Tully, W. R. & Westwood, R. (1988). J. Med. Chem. 31, 1098–1115. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Allen, F. H. (2002). Acta Cryst. B58, 380–388. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Anthony, A., Desiraju, G. R., Jetti, R. K. R., Kuduva, S. S., Madhavi, N. N. L., Nangia, A., Thaimattam, R. & Thalladi, V. R. (1998). Cryst. Eng. 1, 1–18.
- Bruker (2007). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cheeseman, G. W. H. & Cookson, R. F. (1979). In Condensed Pyrazines New York: John Wiley and Sons.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- He, W., Meyers, M. R., Hanney, B., Spada, A. P., Bilder, G., Galzcinski, H., Amin, D., Needle, S., Page, K., Jayyosi, Z. & Perrone, M. H. (2003). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 13, 3097–3100. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Hirano, K., Yamaoka, S., Minikata, S. & Komatsu, M. (2002). Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn, 75, 2075–2078.
- Kim, Y. B., Kim, Y. H., Park, J. Y. & Kim, S. K. (2004). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 14, 541–544. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Methcohn, O. (1975). Tetrahedron Lett. 16, 413–416.
- Porter, A. E. A. (1984). Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry: the Structure, Reactions, Synthesis, and Uses of Heterocyclic Compounds, edited by A. R. Katritzky & C. W. Rees, pp. 157–197. Oxford: Pergamon Press.
- Ranganathan, S., Mahapatra, S., Thakur, T. S. & Desiraju, G. R. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o2789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2004). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Taylor, E. C. & Hand, E. S. (1962). Tetrahedron Lett. 3, 1225–1230.
- Taylor, E. C. & Hand, E. S. (1963). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 85, 770–776.
- Yadav, J. S., Reddy, B. V. S., Rao, Y. G. & Narsaiah, A. V. (2008). Chem. Lett. 37, 348–349.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811040335/nk2116sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811040335/nk2116Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811040335/nk2116Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



