Abstract
Using the Hey3Met2 human ovarian cancer cell line, we previously found the RNASET2 gene to possess a remarkable in vivo tumor suppressor activity, although no in vitro features such as inhibition of cell proliferation, clonogenic potential, impaired growth in soft agar and increase in apoptotic rate could be detected. This is reminiscent of the behavior of genes belonging to the class of tumor antagonizing genes (TAG) which act mainly within the context of the microenvironment. Here we present transcriptional profiles analysis which indicates that investigations of the mechanisms of TAG biological functions require a comparison between the in vitro and in vivo expression patterns. Indeed several genes displaying a biological function potentially related to tumor suppression could not be validated by subsequent in vivo expression analysis. On the other hand the fact that we could find congruency for three genes both in vivo and in vitro adds a warning to a too much stringent categorization of this class of genes which relies on the sensitivity of the methodological approaches.
Keywords: RNases, cancer microenvironment, transcriptional profile
RNASET2, A NEW MEMBER OF THE GROWING CLASS OF TUMOR ANTAGONIZING GENES
Among the gynaecological malignancies, ovarian cancer is considered to be the most lethal tumor, with an incidence of 42,000 new cases per year in Europe [1] and 22,000 cases in the USA [2]. In more than 60% of the patients, the diagnosis is made in advanced stage, owing both to the lack of symptoms and the to fact that a panel of highly predictive biomarkers for screening and early stage detection is still missing. It is estimated that 80% of the patients with advanced disease will develop recurrence and succumb to the illness, despite their good initial responsiveness to primary therapy.
We reckon that one of the main reasons for such regrettable scenario is a poor understanding of the biological bases of ovarian cancer pathogenesis. Indeed, one of the salient feature of these tumors is their high heterogeneity, both at the morphological and biological levels, which make the contribution of genetic lesions difficult to interpret in a causative way. Among human cancers located in the ovary, those derived from the ovarian surface epithelium are the most frequent [3] and all epithelial ovarian cancer subtypes have been postulated to originate from the single layer of cells representing the ovary’s surface epithelium (OSE cells) [4]. These cells are known to undergo repeated cycles of proliferation due to the recurrent growth and rupture of ovarian follicles during the ovulatory cycle and one feature of this phenomenon is a well characterized interaction between the ovarian mesenchymal and surface epithelial cells [5]. Any imbalance in the microenviromental homeostasis has therefore the potential to contribute to ovarian cancerogenesis, and a growing interest has indeed been placed toward the active role for stromal misregulation in the progression of neoplasias [6]. Within this frame, a special class of genes has been recently described that seems to play a crucial role in tumor suppression by means of regulating the cross-talk between stromal and epithelial cells. These genes belong to the growing but still poorly characterized class of tumor antagonizing/ malignancy suppressor genes (TAG/MSG) [7], whose principal feature is their ability to suppress malignant growth in vivo but not in vitro.
We have recently reported a preliminary biological characterization of one of these genes, called RNASET2, which codes for an extracellular RNase highly conserved among the phila from viruses to humans, suggesting an evolutionary important function [8].
In a xenograph model for ovarian cancer, we found RNASET2 to carry out a strong oncosuppressive activity by recruiting cells of the monocyte/macrophage lineage into the tumour mass. This subset of cells represents the main component of the host immunological response [9]. Although the main function of RNASET2 was found to take place in the context of the microenvironment, namely in the extracellular compartment, we could not completely rule out that this conserved RNase might also carry out a cell-autonomous role, as suggested by a recent work on S.Cerevisiae [10].
This was basically the rationale that prompted us to further investigate the cell-autonomous expression profile induced by RNASET2 in ovarian cancer cells.
IN VITRO WHOLE GENOME TRANSCRIPTIONAL PROFILING OF CONTROL AND RNASET2-OVEXPRESSING HUMAN OVARIAN CANCER CELLS
As previously reported, using the Hey3Met2 human ovarian cancer cell line, we found the RNASET2 gene to possess a remarkable in vivo tumor suppressor activity, irrespective of the protein’s catalytic activity [9]. Noteworthy, when tested in vitro, the same cell clones did not show inhibition of cell proliferation, changes in the clonogenic potential, impaired growth in soft agar and increase in apoptotic rate.
As stated in the previous section, although these data strongly suggest that RNASET2 might represent a new member of the family of TAG/MSG (acting mostly in a non-cell autonomous fashion), we could not formally rule out a cell-autonomous effect elicited by this gene on the cancer cells, which might have escaped detection by our panel of in vitro standard assays. We therefore decided to carry out a more thorough analysis to shed light on this issue.
Accordingly, we defined the expression profile of the RNASET2-overexpressing Hey3Met2 cells and compared it with that of control cells. An Agilent Whole Human Genome Oligo Microarray was employed with total RNA extracted from Hey3Met2 clones transfected with wild-type or a catalytically mutant form of RNASET2 (whose cDNA was mutagenized in the two CAS catalytic sites). Total RNA from Hey3Met2 cells, transfected with the empty vector, was used as a control.
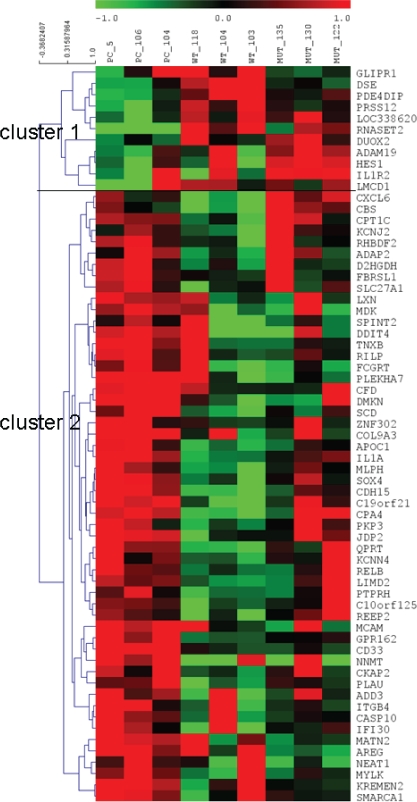
Sixty-five genes were found to be modulated by at least one of the two RNASET2 protein forms tested (i.e. either wild-type or catalytically dead RNASET2), with a fold-induction or repression greater than 2 and a p-value smaller than 0.01. These genes were further organized by hierarchical clustering using squared Pearson correlation into 2 clusters, as shown in figure 1. Overall, for several of these genes we noticed a trend for a higher degree of change in their expression levels in Hey3met2 cells transfected with wild-type rather than catalytically-mutant RNASET2 expression vectors. This might, hypothetically, suggest some influence of RNASET2 ribonucleolytic activity on the steady state level of these gene’s transcripts.
Figure 1. Heatmap of genes differentially expressed.
Modulated genes were organized in 2 clusters by hierarchical clustering. Each column corresponds to a single biological replicate. Each row represents a gene, with red and green for high and low expression levels, respectively.
In order to define the cellular processes/pathways affected by RNASET2, all differentially expressed genes were cross-referenced to the Gene Ontology (GO) database to identify functional categories over-represented in the panel of genes associated with the two clusters.
The GO analysis was done at GO FAT level of biological process and molecular function, whereas Expression Analysis Systematic Explorer (EASE) biological theme analysis was carried out online (at http://david.niaid.nih.gov) using DAVID [11]. The GO survey did not show any significant enrichment, probably due to the small number of genes analyzed (54 genes in cluster 1 and 11 genes in cluster 2). Nevertheless, within the above mentioned gene set a few associated categories were shown to represent biologically relevant process that were worth investigating.
Since TAG/MSG genes are postulated to encode for products involved in the cross-talk between the cancer cell and the tumor microenvironment [12,13], we selected five RNASET2-responsive genes, mainly because of of their involvement in cell adhesion and migration. The five selected genes are MDKN, encoding an angiogenic growth factor over-expressed in various human malignant tumors and recently suggested as a new biomarker for ovarian cancer [14-16]; AREG (cell invasion breast cancer), a regulator of cancer cells invasiveness which was reported to be frequently overexpressed in colon, breast, prostate, pancreas, lung and ovarian cancer [17-19]; MCAM, a well known marker of poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer, whose gene product promotes the growth, invasion and metastasic potential of malignant cells [20-22]; PLAU (PLasminogen Activator Urokinase-type), which promotes fibrinolysis and degradation of extracellular matrix [23]; and NNMT (nicotinamide N-methyltransferase), a serum tumor marker for colorectal cancer recently identified as novel regulator of cell migration [24,25].
Moreover, on the basis of their biological function we decided to validate a few genes that were also shown to be down-regulated after RNASET2 overexpression. The first is DMKN, a gene differentially regulated in inflammatory conditions, and whose role in activating Rab5 function was recently defined [26]. The genes encoding for the transcription factors RELB and JPD2 were also selected, due to their involvement in the NF-kB pathway and cell proliferation/differentiation, respectively [27-30].
The DDIT4 gene was chosen due to its role in RAS-mediated transformation of ovarian epithelial cells [31]. Significantly, transfection of DDIT4 expression vectors in immortalized human ovarian surface epithelial cells has been shown to render the cells tumorigenic in substitution for oncogenic Ras mutations.
Recent studies have suggested a relation between CPA4 gene expression and prostate cancer aggressiveness, possibly due to its role in extracellular peptide processing [32]. We thus included CPA4 in the panel of genes to be further investigated.
The PTPRH gene, encoding a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family [33], was also selected, since PTP proteins are known to regulate a variety of cellular processes including cell growth, differentiation, mitotic cycle, and oncogenic transformation.
Finally, two genes that were up-regulated by RNASET2 were also selected for validation: LMCD1, belonging to the category of the LIMD1 tumor suppressor gene, and DSE (dermatan sulfate epimerase), whose protein product elicits specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes responses in cancer patients [34,35]. Table 1 provides a list of the thirteen genes selected for validation.
Table 1. List of RNASET2-modulated genes selected on the basis of fold change, GO analysis and biological relevance.
| GENE SYMBOL | GENE DESCRIPTION | FOLD-CHANGE WT | FOLD-CHANGE MUT | GENE ONTOLOGY |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDK | midkine (neurite growth promoting factor 2) | −2.5 | −2.9 | heparin binding; glycosaminoglycan binding |
| MCAM | melanoma cell adhesion molecule | −3 | −2.8 | cell adhesion;motility |
| AREG | amphiregulin | −2.1 | −3.8 | growth factor activity-cell invasion |
| NNMT | nicotinamide N-methyltransferase | −4.1 | −5.1 | cell migration |
| PLAU | plasminogen activator,urokinase | −2.0 | −1.2 | wound healing; fibrinolysis and degradation of extracellular matrix. |
| DDIT4 | DNA-damage-inducible transcript 4 | −4.3 | −2.2 | |
| CPA4 | Carboxypeptidase A4 | −3.8 | −1.3 | peptidase activity;zinc ion binding. |
| RELB | v-rel reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog B | −2.1 | −1.8 | DNA binding; transcription factor activity; transcription regulator activity |
| JDP2 | Jun dimerization protein 2 | −3.4 | −2.4 | DNA binding;transcription factor activity;transcription regulator activity |
| DMKN | dermokine | −6.7 | −6.2 | Rab GTPase binding |
| PTPRH | protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type H | −2 | −1.5 | phosphoprotein phosphatase activity;transmembrane receptor protein phosphatase activity |
| DSE | dermatan sulfate epimerase | +2.1 | +1.2 | racemase and epimerase activity;chondroitin-glucuronate 5-epimerase activity |
| LIMCD1 | LIM and cysteine-rich domains 1 | +2.6 | +2.3 | zinc ion binding;transcription factor binding;transcription regulator activity |
VALIDATION AND COMPARISON OF THE TRANSCRIPTIONAL PROFILES IN VITRO AND IN VIVO
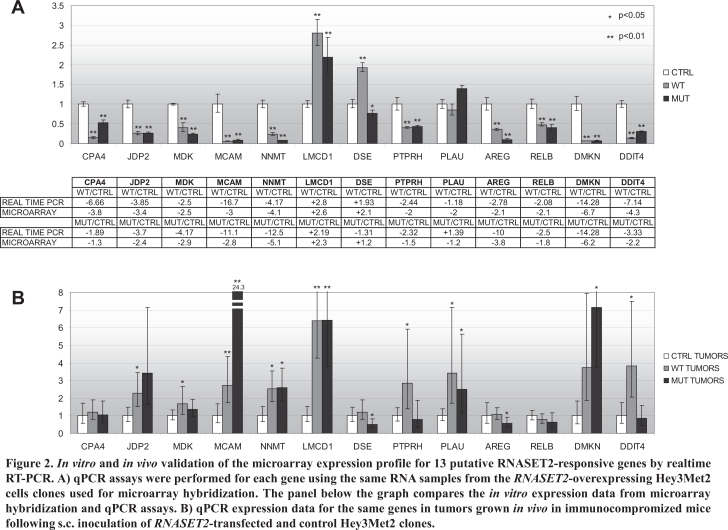
To validate these genes, realtime RT-PCR (qPCR) assays were performed on the same RNA samples used for microarray hybridization. In order to allow for cross-references of the expression data, the sequence of all primer pairs was designed to span the region of the cDNA corresponding to the hybridization probes placed on the microarray chip. As shown in figure 2A, the pattern of gene expression changes observed following microarray hybridization was confirmed by qPCR for most tested genes. The only exception was represented by the DSE and PLAU genes, whose expression pattern in Hey3Met2 cells expressing the catalytically-mutant RNASET2 protein turned out to be down-regulated by microarray hybridization but upregulated by qPCR. However, for both genes the observed change in expression pattern with respect to control clones was below the chosen 2-fold threshold for significance (+1.2-fold by microarray hybridization vs. −1.43-fold by qPCR for DSE and −1.2-fold by microarray hybridization vs. + 1.05-fold by qPCR for PLAU, respectively). Moreover, for both genes the expression pattern observed by qPCR in Hey3Met2 cells expressing wild-type RNASET2 was in agreement with that observed by microarray hybridization.
Figure 2. In vitro and in vivo validation of the microarray expression profile for 13 putative RNASET2-responsive genes by realtime RT-PCR.
A) qPCR assays were performed for each gene using the same RNA samples from the RNASET2-overexpressing Hey3Met2 cells clones used for microarray hybridization. The panel below the graph compares the in vitro expression data from microarray hybridization and qPCR assays. B) qPCR expression data for the same genes in tumors grown in vivo in immunocompromized mice following s.c. inoculation of RNASET2-transfected and control Hey3Met2 clones.
As expected for using a more sensitive test, the observed fold-changes in the expression levels appeared to be slightly higher for several genes when tested by qPCR. For example, the RNASET2-mediated downregulation of the CPA4, DMKN and MCAM genes that was observed by microarray hybridization turned out to be much more evident when assayed by qPCR. Of note, the fold-change expression for the RNASET2 gene turned out to be much higher by qPCR, in keeping with previous expression data obtained by western blot analysis carried out on the same clones (data not shown). We next asked whether some of these genes could have any relevance in RNASET2-mediated tumor suppression in vivo. To this end, total RNA extracted from xenograph tumors [9] was used to assess whether the expression pattern was congruent with the qPCR data. Clearly at variance with the in vitro setting, the in vivo tumor population is rather heterogeneous, comprising both human Hey3Met2 cancer cells and host-derived murine stromal cells. The results of this survey are shown in figure 2B. As shown, the RNASET2-mediated changes in the expression levels that we previously observed in vitro were not confirmed for most tested genes in the in vivo setting. Indeed, significant changes in the expression pattern that were found to be in agreement with those previously observed in vitro could be reported for just three genes, namely LMCD1, DSE and RELB.
As for the remaining genes, whereas some of them (i.e. CPA4, MDK and AREG) are almost unresponsive to RNASET2 expression in vivo, others showed obvious changes in expression pattern mediated by RNASET2, but these changes were in the opposite direction with respect to those observed in vitro.
FUTURE DIRECTIONS
Undoubtly, the observed RNASET2-mediated modulation of LMCD1, DSE and RELB gene expression deserves further investigation, since it has been detected in vitro and subsequently confirmed in vivo. These three genes thus represent bona fide candidate effector genes for RNASET2-mediated tumor suppression. A panel of ovarian cancer cell lines, characterized for RNASET2 expression levels, is available in our laboratory and will be used to investigate the relationship between RNASET2 levels, expression of these three genes and putative phenotypic outcomes. Furthermore a RNASET2-knock-down model recently established in our laboratory in the OVCAR3 ovarian cancer cell line will further contribute to investigate this issue.
As for the putative mechanisms by which these three genes might contribute to RNASET2-mediated tumor suppression, it is worth noting that two of them show a plausible link with cellular functions related to tumor rejection by the immune system. Indeed, it is well established that one of the several biological functions of this pleiomorphic RNase is the modulation of host immune system [8].
Accordingly, the RELB gene has long been associated with adaptive immune responses mediated by dendritic cells [28,29]. Moreover, since RELB is directly involved in the NK-κB pathway, it is tempting to postulate a role for RNASET2 in RELB-mediated control of tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) polarization. In fact, tumor progression is thought to involve a gradual switch of macrophage polarization from M1 to M2 class, which is paralleled by a gradual inhibition of NK-κB activity [36]. This role for the NK-κB pathway in macrophage polarization might therefore be relevant, considering that RNASET2 is apparently able to recruit specific subclass of stromal macrophages in the Hey3Met2 ovarian cancer model studied by our group [9]. It will be of interest in future studies to define whether RNASET2 derived from cancer cell, could influence, the NK-κB pathway by changing the RELB expression levels in cells of the monocyte/macrophage lineage. Moreover, due to the observed downregulation of RELB in Hey3Mey2 cells expressing RNASET2, a cell-autonomous role for RNASET2 cannot be completely ruled out, since the RELB protein is known to promote cancer cell survival by inducing the expression of proteins with anti-apoptotic roles, such as Survivin and Bcl-2 [37]. A close inspection of the RELB yeast ortologue’ s behaviour in yeast cells could be very instructive in this regard.
The second RNASET2-responsive gene that might be related to immune cell function is DSE. It encodes for dermatan sulfate epimerase, an enzyme involved in D-glucuronic acid to L-iduronic acid conversion in the dermatan sulphate biosynthetic pathway [38]. The DSE gene was originally identified on the basis of the ability of its gene product to be recognized with high efficiency by a subset of cytotoxic T lymphocytes in certain tumors [35]. Moreover, expression of DSE was found to be altered in laryngeal cancer specimens when compared to normal tissue samples [39]. Significantly, abnormal dermatane sulphate composition has also been reported in both ovarian carcinomas and ovarian cancer cell lines [40], providing further support for a putative role of DSE in our ovarian model.
As for the third gene whose change in expression level was confirmed in vivo (LMCD1), its direct involvement in RNASET2-mediated tumor suppression is rather speculative. LMCD1 encodes for a poorly characterized cysteine-rich and LIM domain-containing protein, which has been so far implicated in cardiac hypertrophy [41]. However, LIM-domain proteins belonging to the related CRP family have been described as potent tumor suppressor genes [42] and, most importantly, the related LIMD1 gene has been recently reported to display functional properties reminiscent of tumor antagonizing genes [7].
Taken together, the results of our studies provides a clear indication that investigations of the molecular mechanisms through which TAG/MSG carry out their biological functions necessitate a thorough comparison between the in vitro and in vivo expression patterns. Indeed, several genes displaying a biological function potentially related to tumor suppression, and thus defined as candidate based on their in vitro expression pattern, were not validated by subsequent in vivo expression profiling.
On the other hand, the fact that the same changes in the expression levels of a few genes (i.e. RELB, LIMD1 and DSE) were observed both in vitro and in vivo deserves some comments. t We rekon that the results gathered in the present report highlight some of the limitations inherent in the conceptual process of categorizing relevant biological processes. In our case, the strict categorization of tumor antagonizing genes as genes endorsed with an asymmetric behavior (i.e. suppressing tumorigenicity without affecting in vitro growth) was clearly dependent on the sensitivity of the methodological approach employed. In fact, using the highly sensitive microarray analysis some genes’ features were detected in a congruent fashion in both the in vivo and in vitro.
The three above mentioned genes are therefore worth to be investigated in depth, as they could represent not only relevant candidates for the carcinogenetic process taking place in our ovarian cancer model, but they could also be instrumental and paradigmatic of a more molecularly-oriented classification of the growing family of tumor antagonizing genes.
We reckon that the latter issue is not irrelevant in contributing some conceptual and experimental support for a more systematic search and characterization of tumor antagonizing genes. To this end, it is worth reminding that the genome of a cancer cell is mainly characterized by DNA losses and given the limited number of tumor suppressor genes identified and characterized so far, we are probably seeing just the “tip of the iceberg”, with a large fraction of genes (including TAGs) protecting against malignant growth yet undiscovered.
REFERENCES
- 1.Ferlay J, Autier P, Boniol M, Heanue M, Colombet M, Boyle P. Estimates of the cancer incidence and mortality in Europe in 2006. Ann Oncol. 2007;18:581–92. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdl498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Murray T, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58:71–96. doi: 10.3322/CA.2007.0010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Feeley KM, Wells M. Precursor lesions of ovarian epithelial malignancy. Histopathology. 2001;38:87–95. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2559.2001.01042.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Auersperg N, Maines-Bandiera SL, Dyck HG, Kruk PA. Characterization of cultured human ovarian surface epithelial cells: phenotypic plasticity and premalignant changes. Laboratory Investigation. 1994;71:510–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Mueller M, Fusenig N. Friends or foes-bipolar effects of the tumor stroma in cancer. Nature Rev Cancer. 2004;4:839–42. doi: 10.1038/nrc1477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Liotta L, Kohn E. The microenvironment of the tumor-host interface. Nature. 2001;411:375–9. doi: 10.1038/35077241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Klein G, Imreh S, Zabarovsky ER. Why do we not all die of cancer at an early age? Adv Cancer Res. 2007;98:1–16. doi: 10.1016/S0065-230X(06)98001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Luthala N, Parker R. T2 Family ribonucleases: ancient enzymes with diverse roles. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2010;35:253–9. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2010.02.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Acquati F, Bertilaccio S, Grimaldi A, Monti L, Cinquetti R, Bonetti P, Lualdi M, Vidalino L, Fabbri M, Sacco MG, Rooijen N, Campomenosi P, Vigetti D, Passi A, Riva C, Capella C, et al. Microenvironmental control of malignancy exerted by RNASET2, a widely conserved extracellular RNase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:1104–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1013746108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Thompson DM, Parker R. The RNase Rny1p cleaves tRNAs and promotes cell death during oxidative stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 2009;185:43–50. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200811119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Huang DW, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nature Protocols. 2009;4:44–57. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2008.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Imreh S, Klein G, Zabarovsky ER. Search for unknown tumor-antagonizing genes. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2003;38:307–21. doi: 10.1002/gcc.10271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Klein G. Toward a genetics of cancer resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:859–63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0811616106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kerzerho J, Adotevi O, Castelli FA, Dosset M, Bernardeau K, Szely N, Lang F, Tartour E, Maillere B. The angiogenic growth factor and biomarker midkine is a tumor-shared antigen. J Immunol. 2010;185:418–23. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0901014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ota K, Fujimori H, Ueda M, Jono H, Shinriki S, Ota T, Sueyoshi T, Taura M, Taguma A, Kai H, Shinohara M, Ando Y. Midkine expression is correlated with an adverse prognosis and is down-regulated by p53 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 2010;37:797–804. doi: 10.3892/ijo_00000729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Rice GE, Edgell TA, Autelitano DJ. Evaluation of midkine and anterior gradient 2 in a multimarker panel for the detection of ovarian cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2010;29:62. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-29-62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Baillo A., Giroux C., Ethier S.P. Knock-down of Amphiregulin Inhibits Cellular Invasion in Inflammatory Breast Cancer. Journal of Cellular Physiology. 2011;(Feb 1) doi: 10.1002/jcp.22620. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22620. [Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bles N, Di Pietrantonio L, Boeynaems JM, Communi D. ATP confers tumorigenic properties to dendritic cells by inducing amphiregulin secretion. Blood. 2010;116:3219–26. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-01-265611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lamber EP, Horwitz AA, Parvin JD. BRCA1 represses amphiregulin gene expression. Cancer Res. 2010;70:996–1005. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Aldovini D, Demichelis F, Doglioni C, Di Vizio D, Galligioni E, Brugnara S, Zeni B, Griso C, Pegoraro C, Zannoni M, Gariboldi M, Balladore E, Mezzanzanica D, Canevari S, Barbareschi M. M-cam expression as marker of poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer, Int. J. Cancer. 2006;119:1920–6. doi: 10.1002/ijc.22082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chen W, Zhang HL, Jiang YG, Li JH, Liu BL, Sun MY. Inhibition of CD146 gene expression via RNA interference reduces in vitro perineural invasion on ACC-M cell. J Oral Pathol Med. 2009;38:198–205. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.2008.00706.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zabouo G, Imbert AM, Jacquemier J, Finetti P, Moreau T, Esterni B, Birnbaum D, Bertucci F, Chabannon C. CD146 expression is associated with a poor prognosis in human breast tumors and with enhanced motility in breast cancer cell lines. Breast Cancer Research. 2009;11:1–14. doi: 10.1186/bcr2215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sudol M. From Rous sarcoma virus to plasminogen activator, src oncogene and cancer management. Oncogene. 2011;(Mar 7) doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.38. [Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Roessler M, Rollinger W, Palme S, Hagmann ML, Berndt P, Engel AM, Schneidinger B, Pfeffer M, Andres H, Karl J, Bodenmüller H, Rüschoff J, Henkel T, Rohr G, Rossol S, Rösch W, et al. Identification of nicotinamide N methyltransferase as a novel serum tumor marker for colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:6550–7. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wu Y, Siadaty MS, Berens ME, Hampton GM, Theodorescu D. Overlapping gene expression profiles of cell migration and tumor invasion in human bladder cancer identify metallothionein 1E and nicotinamide N-methyltransferase as novel regulators of cell migration. Oncogene. 2008;27:6679–89. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Leclerc EA, Gazeilles L, Serre G, Guerrin M, Jonca N. The ubiquitous dermokine delta activates rab5 function in the early endocytic pathway. PLoS One. 2011;6:e17816. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Xu Y, Josson S, Fang F, Oberley TD, St Clair DK, Wan XS, Sun Y, Bakthavatchalu V, Muthuswamy A, St Clair WH. RelB enhances prostate cancer growth: implications for the role of the nuclear factor-kappaB alternative pathway in tumorigenicity. Cancer Res. 2009;69:3267–71. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Burkly L, Hession C, Ogata L, Reilly C, Marconi LA, Olson D, Tizard R, Cate R, Lo D. Expression of relB is required for the development of thymic medulla and dendritic cells. Nature. 1995;373:531–6. doi: 10.1038/373531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Clark GJ, Gunningham S, Troy A, Vuckovic S, Hart DN. Expression of the RelB transcription factor correlates with the activation of human dendritic cells. Immunology. 1999;98:189–96. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1999.00829.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bitton-Worms K, Pikarsky E, Aronheim A. The AP-1 repressor protein, JDP2, potentiates hepatocellular carcinoma in mice. Mol Cancer. 2010;9:54–8. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Chang B, Liu G, Yang G, Mercado-Uribe I, Huang M, Liu J. REDD1 is required for RAS-mediated transformation of human ovarian epithelial cells. Cell cycle. 2009;8:780–6. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.5.7887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Tanco S, Zhang X, Morano C, Avilés FX, Lorenzo J, Fricker LD. Characterization of the substrate specificity of human carboxypeptidase A4 and implications for a role in extracellular peptide processing. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:18385–96. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.060350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Pasquali C, Curchod ML, Wälchli S, Espanel X, Guerrier M, Arigoni F, Strous G, Hooft van Huijsduijnen R. Identification of protein tyrosine phosphatases with specificity for the ligand-activated growth hormone receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 2003;17:2228–39. doi: 10.1210/me.2003-0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sharp TV, Munoz F, Bourboulia D, Presneau N, Darai E, Wang HW, Cannon M, Butcher DN, Nicholson AG, Klein G, Imreh S, Boshoff C. LIM domains-containing protein 1 (LIMD1), a tumor suppressor encoded at chromosome 3p21.3, binds pRB and represses E2F-driven transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:16531–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0407123101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Nakao M, Shichijo S, Imaizumi T, Inoue Y, Matsunaga K, Yamada A, Kikuchi M, Tsuda N, Ohta K, Takamori S, Yamana H, Fujita H, Itoh K. Identification of a gene coding for a new squamous cell carcinoma antigen recognized by the CTL. J Immunol. 2000;164:2565–74. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.5.2565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sica A, Larghi P, Mancino A, Rubino L, Porta C, Totaro MG, Rimoldi M, Biswas SK, Allavena P, Mantovani A. Macrophage polarization in tumour progression. Semin Cancer Biol. 2008;18:349–55. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2008.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Mineva ND, Rothstein TL, Meyers JA, Lerner A, Sonenshein GE. CD40 ligand-mediated activation of the de novo RelB NF-kappaB synthesis pathway in transformed B cells promotes rescue from apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:17475–85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M607313200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Maccarana M, Olander B, Malmström J, Tiedemann K, Aebersold R, Lindahl U, Li JP, Malmström A. Biosynthesis of dermatan sulfate: chondroitin-glucuronate C5-epimerase is identical to SART2. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:11560–8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M513373200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kalathas D, Triantaphyllidou IE, Mastronikolis NS, Goumas PD, Papadas TA, Tsiropoulos G, Vynios DH. The chondroitin/dermatan sulfate synthesizing and modifying enzymes in laryngeal cancer: expressional and epigenetic studies. Head Neck Oncol. 2010;2:27. doi: 10.1186/1758-3284-2-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Ten Dam GB, Yamada S, Kobayashi F, Purushothaman A, van de Westerlo EM, Bulten J, Malmström A, Sugahara K, Massuger LF, van Kuppevelt TH. Dermatan sulfate domains defined by the novel antibody GD3A12, in normal tissues and ovarian adenocarcinomas. Histochem Cell Biol. 2009;132:117–27. doi: 10.1007/s00418-009-0592-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Frank D, Frauen R, Hanselmann C, Kuhn C, Will R, Gantenberg J, Füzesi L, Katus HA, Frey N. Lmcd1/Dyxin, a novel Z-disc associated LIM protein, mediates cardiac hypertrophy in vitro and in vivo. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010;49:673–82. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2010.06.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Latonen L, Järvinen PM, Laiho M. Cytoskeleton-interacting LIM-domain protein CRP1 suppresses cell proliferation and protects from stress-induced cell death. Exp Cell Res. 2008;314:738–47. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.11.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]