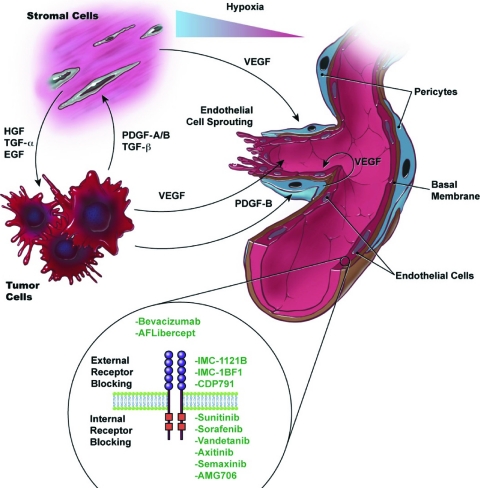
Figure 2.
Intercellular signaling among tumor cells, stroma cells, pericytes, and endothelial cells: cellular players in the tumor/microvascular microenvironment. VEGF is antiapoptotic for endothelial cells via several pathways, including induction of expression of the antiapoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and A1, activation of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway, stimulation of nitrous oxide and prostacyclin, and increasing focal adhesion kinase tyrosine phosphorylation [62]. The activity of VEGF receptors is primarily regulated by the availability of their respective ligands. Ligand expression levels depend on many factors, such as hypoxia, environmental stress, and glucose deficiency. VEGF-A is the most important factor whose expression is upregulated under hypoxic conditions. Hypoxia allows the stabilization of hypoxia-inducible factors that bind to specific promoter elements that are present in the promoter region of VEGF-A [63].
Abbreviations: EGF, endothelial growth factor; HGF, hepatocytic growth factor; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; TGF, transforming growth factor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.