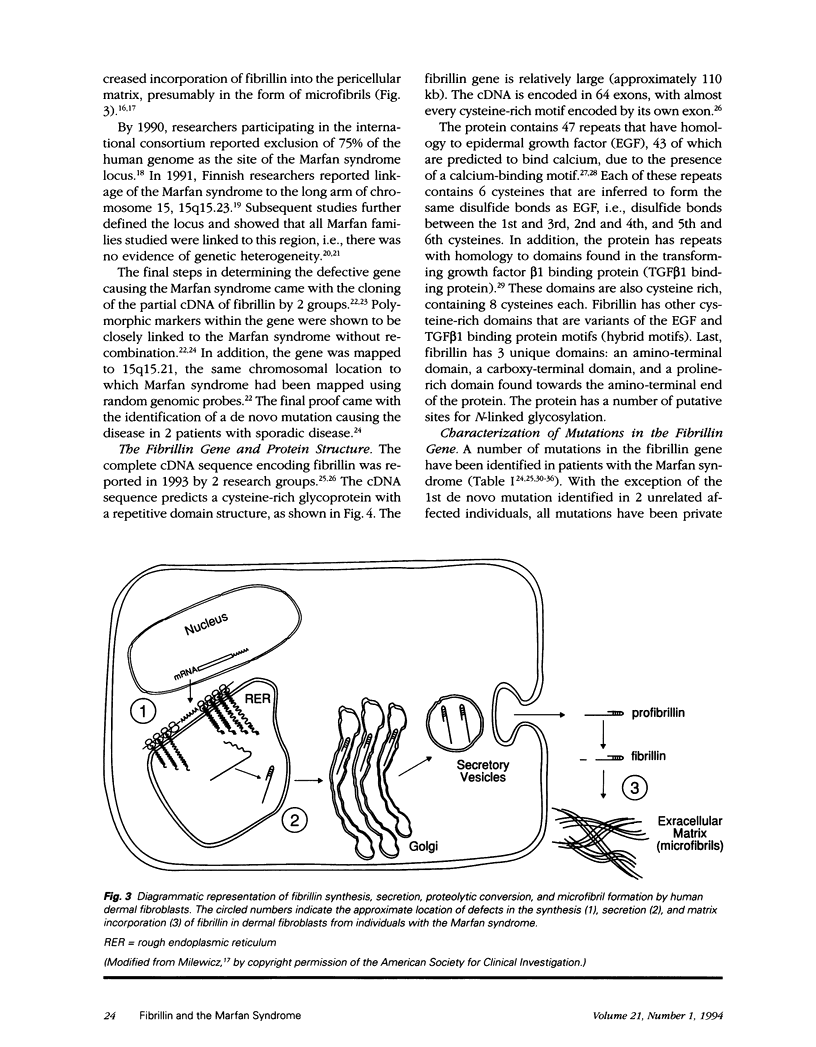
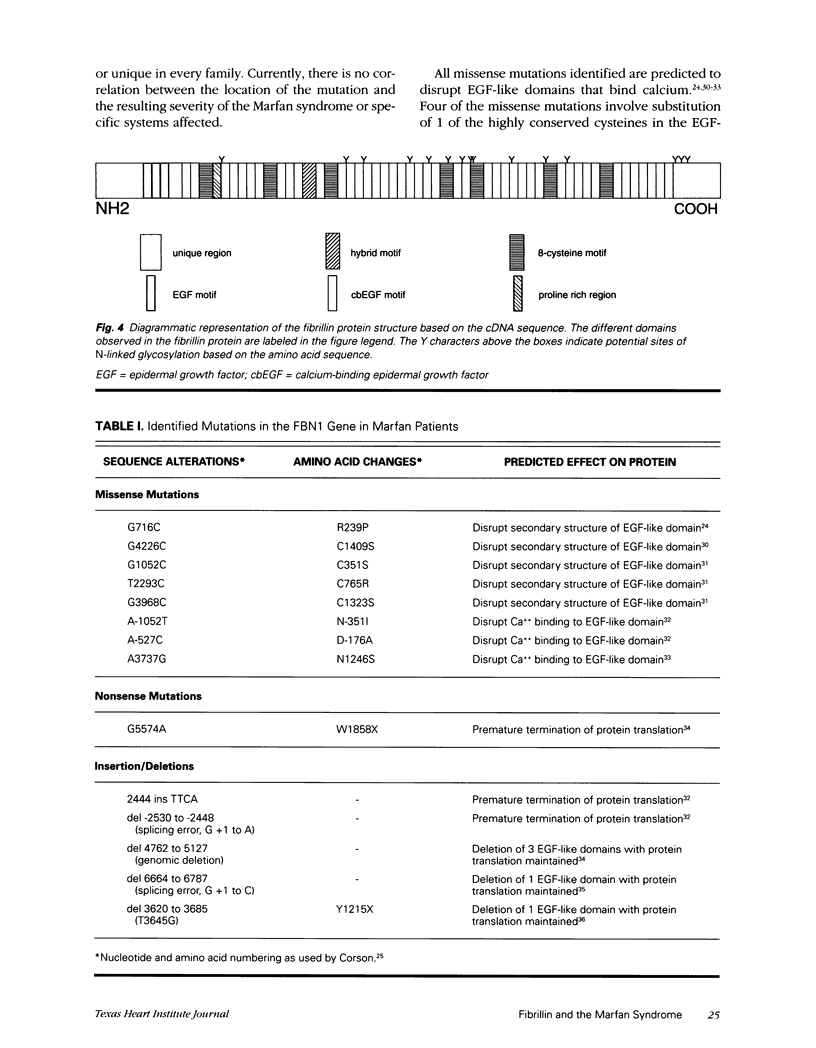
Abstract
The Marfan syndrome is an autosomal dominant disorder with pleiotropic manifestations that involve the cardiovascular, ocular, and skeletal systems. Through a number of investigational approaches, the gene encoding for fibrillin, the FBN1 gene on chromosome 15, has been identified as the defective gene causing the Marfan syndrome. Fibrillin is the large glycoprotein with a repetitive domain structure and is a major protein component of microfibrils, a fibrillar system closely associated with elastin in connective tissue. Mutational analysis of defects in the FBN1 gene in patients with the Marfan syndrome has revealed that most mutations are private or unique in an affected individual or family. Analysis of fibrillin protein or gene defects in individuals with related phenotypes has revealed that a perinatal lethal syndrome, termed neonatal Marfan syndrome, is due to FBN1 gene mutations. In addition, fibroblast cell strains from a subset of patients with idiopathic scoliosis have fibrillin protein defects. Last, fibroblasts from calves affected with bovine Marfan syndrome display defects in the fibrillin protein. These studies have wide-ranging implications in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of Marfan syndrome and related disorders.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Besser T. E., Potter K. A., Bryan G. M., Knowlen G. G. An animal model of the Marfan syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Sep;37(1):159–165. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320370137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanton S. H., Sarfarazi M., Eiberg H., de Groote J., Farndon P. A., Kilpatrick M. W., Child A. H., Pope F. M., Peltonen L., Francomano C. A. An exclusion map of Marfan syndrome. J Med Genet. 1990 Feb;27(2):73–77. doi: 10.1136/jmg.27.2.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corson G. M., Chalberg S. C., Dietz H. C., Charbonneau N. L., Sakai L. Y. Fibrillin binds calcium and is coded by cDNAs that reveal a multidomain structure and alternatively spliced exons at the 5' end. Genomics. 1993 Aug;17(2):476–484. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day D. L., Burke B. A. Pulmonary emphysema in a neonate with Marfan syndrome. Pediatr Radiol. 1986;16(6):518–521. doi: 10.1007/BF02387973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz H. C., McIntosh I., Sakai L. Y., Corson G. M., Chalberg S. C., Pyeritz R. E., Francomano C. A. Four novel FBN1 mutations: significance for mutant transcript level and EGF-like domain calcium binding in the pathogenesis of Marfan syndrome. Genomics. 1993 Aug;17(2):468–475. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz H. C., Pyeritz R. E., Hall B. D., Cadle R. G., Hamosh A., Schwartz J., Meyers D. A., Francomano C. A. The Marfan syndrome locus: confirmation of assignment to chromosome 15 and identification of tightly linked markers at 15q15-q21.3. Genomics. 1991 Feb;9(2):355–361. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90264-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz H. C., Pyeritz R. E., Puffenberger E. G., Kendzior R. J., Jr, Corson G. M., Maslen C. L., Sakai L. Y., Francomano C. A., Cutting G. R. Marfan phenotype variability in a family segregating a missense mutation in the epidermal growth factor-like motif of the fibrillin gene. J Clin Invest. 1992 May;89(5):1674–1680. doi: 10.1172/JCI115766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz H. C., Saraiva J. M., Pyeritz R. E., Cutting G. R., Francomano C. A. Clustering of fibrillin (FBN1) missense mutations in Marfan syndrome patients at cysteine residues in EGF-like domains. Hum Mutat. 1992;1(5):366–374. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380010504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz H. C., Valle D., Francomano C. A., Kendzior R. J., Jr, Pyeritz R. E., Cutting G. R. The skipping of constitutive exons in vivo induced by nonsense mutations. Science. 1993 Jan 29;259(5095):680–683. doi: 10.1126/science.8430317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey M., Menashe V., Weleber R. G., Koler R. D., Bigley R. H., Lovrien E., Zonana J., Hollister D. W. Cosegregation of elastin-associated microfibrillar abnormalities with the Marfan phenotype in families. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;46(4):652–660. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey M., Olson S., Burgio R. G., Martini A., Valli M., Cetta G., Hori H., Hollister D. W. Unilateral microfibrillar abnormalities in a case of asymmetric Marfan syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;46(4):661–671. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey M., Vandemark N., Wang M., Velinov M., Wargowski D., Tsipouras P., Han J., Becker J., Robertson W., Droste S. Prenatal diagnosis and a donor splice site mutation in fibrillin in a family with Marfan syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Aug;53(2):472–480. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfischer S., Coltoff-Schiller B., Goldfischer M. Microfibrils, elastic anchoring components of the extracellular matrix, are associated with fibronectin in the zonule of Zinn and aorta. Tissue Cell. 1985;17(4):441–450. doi: 10.1016/0040-8166(85)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. M., Robinson L. K., Smith L. T., Glass N., Rosenberg H., Duvic M. Severe perinatal Marfan syndrome. Pediatrics. 1989 Jul;84(1):83–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handford P. A., Baron M., Mayhew M., Willis A., Beesley T., Brownlee G. G., Campbell I. D. The first EGF-like domain from human factor IX contains a high-affinity calcium binding site. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):475–480. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08133.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handford P. A., Mayhew M., Baron M., Winship P. R., Campbell I. D., Brownlee G. G. Key residues involved in calcium-binding motifs in EGF-like domains. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):164–167. doi: 10.1038/351164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewett D. R., Lynch J. R., Smith R., Sykes B. C. A novel fibrillin mutation in the Marfan syndrome which could disrupt calcium binding of the epidermal growth factor-like module. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Apr;2(4):475–477. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.4.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook K. A., Byers P. H. Structural abnormalities in the dermal collagen and elastic matrix from the skin of patients with inherited connective tissue disorders. J Invest Dermatol. 1982 Jul;79 (Suppl 1):7s–16s. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12544609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollister D. W., Godfrey M., Sakai L. Y., Pyeritz R. E. Immunohistologic abnormalities of the microfibrillar-fiber system in the Marfan syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 19;323(3):152–159. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007193230303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huggon I. C., Burke J. P., Talbot J. F. Contractural arachnodactyly with mitral regurgitation and iridodonesis. Arch Dis Child. 1990 Mar;65(3):317–319. doi: 10.1136/adc.65.3.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kainulainen K., Pulkkinen L., Savolainen A., Kaitila I., Peltonen L. Location on chromosome 15 of the gene defect causing Marfan syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1990 Oct 4;323(14):935–939. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199010043231402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kainulainen K., Sakai L. Y., Child A., Pope F. M., Puhakka L., Ryhänen L., Palotie A., Kaitila I., Peltonen L. Two mutations in Marfan syndrome resulting in truncated fibrillin polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5917–5921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kainulainen K., Steinmann B., Collins F., Dietz H. C., Francomano C. A., Child A., Kilpatrick M. W., Brock D. J., Keston M., Pyeritz R. E. Marfan syndrome: no evidence for heterogeneity in different populations, and more precise mapping of the gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Sep;49(3):662–667. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanzaki T., Olofsson A., Morén A., Wernstedt C., Hellman U., Miyazono K., Claesson-Welsh L., Heldin C. H. TGF-beta 1 binding protein: a component of the large latent complex of TGF-beta 1 with multiple repeat sequences. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1051–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90069-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lababidi Z., Monzon C. Early cardiac manifestations of Marfan's syndrome in the newborn. Am Heart J. 1981 Nov;102(5):943–945. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(81)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B., Godfrey M., Vitale E., Hori H., Mattei M. G., Sarfarazi M., Tsipouras P., Ramirez F., Hollister D. W. Linkage of Marfan syndrome and a phenotypically related disorder to two different fibrillin genes. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):330–334. doi: 10.1038/352330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsalese D. L., Moodie D. S., Vacante M., Lytle B. W., Gill C. C., Sterba R., Cosgrove D. M., Passalacqua M., Goormastic M., Kovacs A. Marfan's syndrome: natural history and long-term follow-up of cardiovascular involvement. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1989 Aug;14(2):422–431. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(89)90197-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maslen C. L., Corson G. M., Maddox B. K., Glanville R. W., Sakai L. Y. Partial sequence of a candidate gene for the Marfan syndrome. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):334–337. doi: 10.1038/352334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayhew M., Handford P., Baron M., Tse A. G., Campbell I. D., Brownlee G. G. Ligand requirements for Ca2+ binding to EGF-like domains. Protein Eng. 1992 Sep;5(6):489–494. doi: 10.1093/protein/5.6.489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milewicz D. M., Pyeritz R. E., Crawford E. S., Byers P. H. Marfan syndrome: defective synthesis, secretion, and extracellular matrix formation of fibrillin by cultured dermal fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jan;89(1):79–86. doi: 10.1172/JCI115589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murdoch J. L., Walker B. A., Halpern B. L., Kuzma J. W., McKusick V. A. Life expectancy and causes of death in the Marfan syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1972 Apr 13;286(15):804–808. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197204132861502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., D'Alessio M., Ramirez F., Lynch J. R., Sykes B., Pangilinan T., Bonadio J. Genomic organization of the sequence coding for fibrillin, the defective gene product in Marfan syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jul;2(7):961–968. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.7.961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perejda A. J., Abraham P. A., Carnes W. H., Coulson W. F., Uitto J. Marfan's syndrome: structural, biochemical, and mechanical studies of the aortic media. J Lab Clin Med. 1985 Oct;106(4):376–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pini R., Roman M. J., Kramer-Fox R., Devereux R. B. Mitral valve dimensions and motion in Marfan patients with and without mitral valve prolapse. Comparison to primary mitral valve prolapse and normal subjects. Circulation. 1989 Oct;80(4):915–924. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.80.4.915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter K. A., Hoffman Y., Sakai L. Y., Byers P. H., Besser T. E., Milewicz D. M. Abnormal fibrillin metabolism in bovine Marfan syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1993 Mar;142(3):803–810. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyeritz R. E., Wappel M. A. Mitral valve dysfunction in the Marfan syndrome. Clinical and echocardiographic study of prevalence and natural history. Am J Med. 1983 May;74(5):797–807. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)91070-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. C., Honig H. S. The spectrum of cardiovascular disease in the Marfan syndrome: a clinico-morphologic study of 18 necropsy patients and comparison to 151 previously reported necropsy patients. Am Heart J. 1982 Jul;104(1):115–135. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(82)90650-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai L. Y., Keene D. R., Engvall E. Fibrillin, a new 350-kD glycoprotein, is a component of extracellular microfibrils. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2499–2509. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayers C. P., Goltz R. W., Mottiaz J. Pulmonary elastic tissue in generalized elastolysis (cutis laxa) and Marfan's syndrome: a light and electron microscopic study. J Invest Dermatol. 1975 Nov;65(5):451–457. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12608193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander-Sunnerhagen M., Ullner M., Persson E., Teleman O., Stenflo J., Drakenberg T. How an epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domain binds calcium. High resolution NMR structure of the calcium form of the NH2-terminal EGF-like domain in coagulation factor X. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19642–19649. doi: 10.2210/pdb1ccf/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shankar K. R., Hultgren M. K., Lauer R. M., Diehl A. M. Lethal tricuspid and mitral regurgitation in Marfan's syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 1967 Jul;20(1):122–127. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(67)90117-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsipouras P., Del Mastro R., Sarfarazi M., Lee B., Vitale E., Child A. H., Godfrey M., Devereux R. B., Hewett D., Steinmann B. Genetic linkage of the Marfan syndrome, ectopia lentis, and congenital contractural arachnodactyly to the fibrillin genes on chromosomes 15 and 5. The International Marfan Syndrome Collaborative Study. N Engl J Med. 1992 Apr 2;326(14):905–909. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199204023261401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]