Abstract
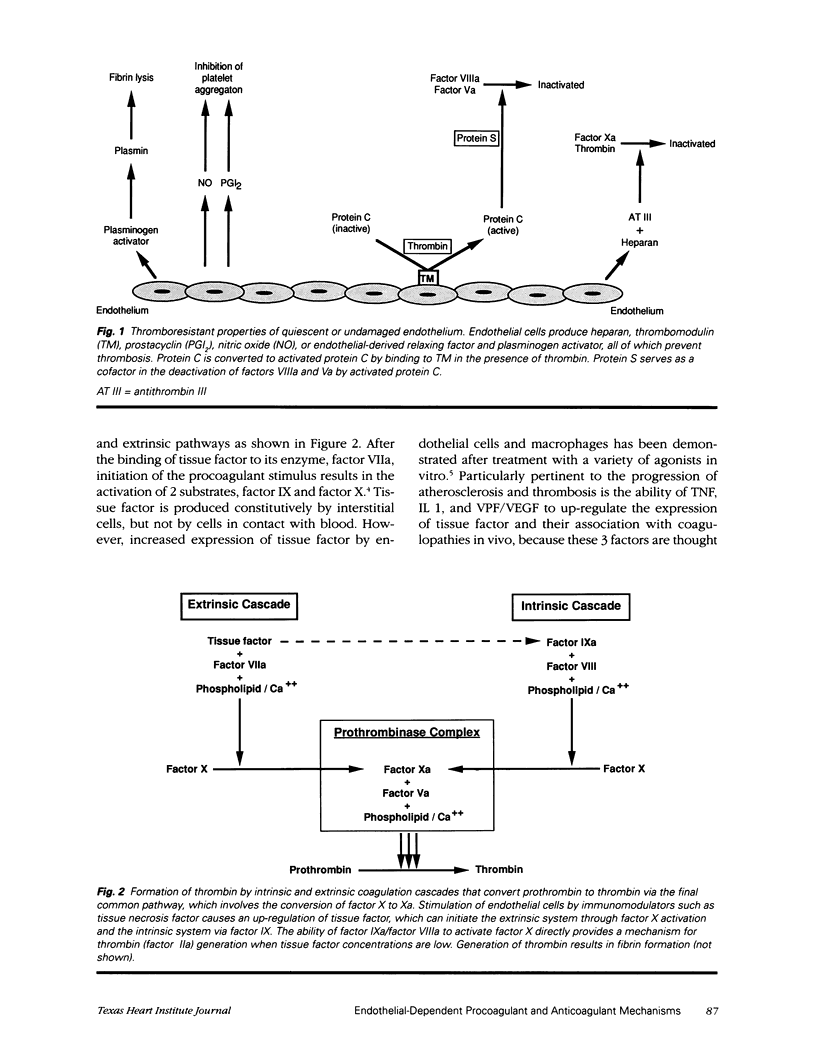
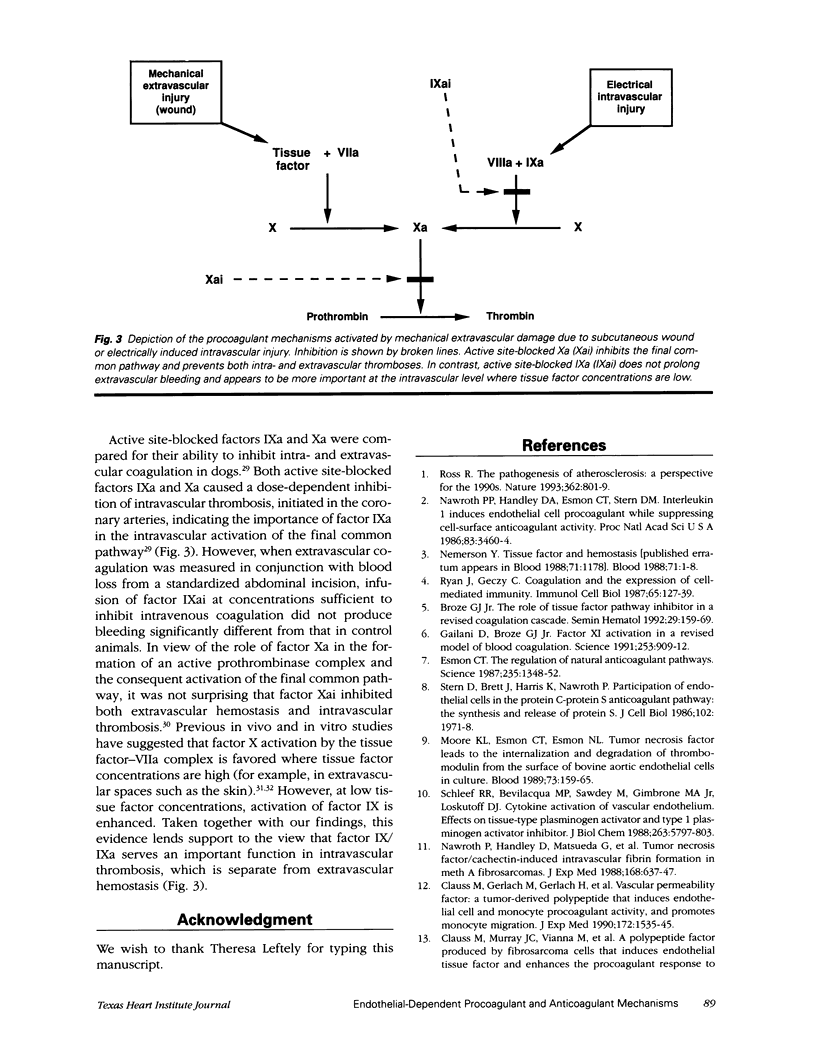
Modulation of endothelial cell coagulant function is one of a group of changes common to many cytokine-mediated events. Changes that 1) cause migration of leukocytes, 2) increase vascular permeability, and 3) increase the thrombotic potential occur at atherosclerotic arterial branch points, in tumor vasculature, and at sites of inflammation. Regulation of procoagulant activity on the luminal surface of the vessel is crucial and is achieved by presentation of a predominantly anticoagulant surface on the endothelium. Inflammatory mediators can cause a decrease in the expression of the anticoagulant mechanisms and up-regulation of the procoagulant tissue factor. However, under these conditions very little tissue factor is exposed to the blood; instead it is sequestered under the endothelium and presumably becomes exposed only when significant vascular damage is present. Inhibition of intravascular coagulation by factor IXai without impairment of extravascular hemostasis suggests that when tissue factor concentrations are low, the continued generation of factor Xa is dependent on the presence of factor IXa. The demonstration that the blockade of factor IXa is selective for prevention of intravascular thrombus formation suggests a new means for managing intravascular thrombosis without altering the normal hemostatic mechanisms.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad S. S., Rawala-Sheikh R., Ashby B., Walsh P. N. Platelet receptor-mediated factor X activation by factor IXa. High-affinity factor IXa receptors induced by factor VIII are deficient on platelets in Scott syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1989 Sep;84(3):824–828. doi: 10.1172/JCI114242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altieri D. C., Edgington T. S. Sequential receptor cascade for coagulation proteins on monocytes. Constitutive biosynthesis and functional prothrombinase activity of a membrane form of factor V/Va. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2969–2972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astermark J., Björk I., Ohlin A. K., Stenflo J. Structural requirements for Ca2+ binding to the gamma-carboxyglutamic acid and epidermal growth factor-like regions of factor IX. Studies using intact domains isolated from controlled proteolytic digests of bovine factor IX. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2430–2437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedict C. R., Ryan J., Todd J., Kuwabara K., Tijburg P., Cartwright J., Jr, Stern D. Active site-blocked factor Xa prevents thrombus formation in the coronary vasculature in parallel with inhibition of extravascular coagulation in a canine thrombosis model. Blood. 1993 Apr 15;81(8):2059–2066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedict C. R., Ryan J., Wolitzky B., Ramos R., Gerlach M., Tijburg P., Stern D. Active site-blocked factor IXa prevents intravascular thrombus formation in the coronary vasculature without inhibiting extravascular coagulation in a canine thrombosis model. J Clin Invest. 1991 Nov;88(5):1760–1765. doi: 10.1172/JCI115495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broze G. J., Jr The role of tissue factor pathway inhibitor in a revised coagulation cascade. Semin Hematol. 1992 Jul;29(3):159–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clauss M., Gerlach M., Gerlach H., Brett J., Wang F., Familletti P. C., Pan Y. C., Olander J. V., Connolly D. T., Stern D. Vascular permeability factor: a tumor-derived polypeptide that induces endothelial cell and monocyte procoagulant activity, and promotes monocyte migration. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1535–1545. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derian C. K., VanDusen W., Przysiecki C. T., Walsh P. N., Berkner K. L., Kaufman R. J., Friedman P. A. Inhibitors of 2-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases block aspartyl beta-hydroxylation of recombinant human factor IX in several mammalian expression systems. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6615–6618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake T. A., Morrissey J. H., Edgington T. S. Selective cellular expression of tissue factor in human tissues. Implications for disorders of hemostasis and thrombosis. Am J Pathol. 1989 May;134(5):1087–1097. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T. The regulation of natural anticoagulant pathways. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1348–1352. doi: 10.1126/science.3029867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gailani D., Broze G. J., Jr Factor XI activation in a revised model of blood coagulation. Science. 1991 Aug 23;253(5022):909–912. doi: 10.1126/science.1652157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski E. F., Zuckerman D. B., Nemerson Y. The functional expression of tissue factor by fibroblasts and endothelial cells under flow conditions. Blood. 1993 Jun 15;81(12):3265–3270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao J., Ryan J., Brett G., Chen J., Shen H., Fan Y. G., Godman G., Familletti P. C., Wang F., Pan Y. C. Endothelial monocyte-activating polypeptide II. A novel tumor-derived polypeptide that activates host-response mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20239–20247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindhout T., Blezer R., Schoen P., Nordfang O., Reutelingsperger C., Hemker H. C. Activation of factor X and its regulation by tissue factor pathway inhibitor in small-diameter capillaries lined with human endothelial cells. Blood. 1992 Jun 1;79(11):2909–2916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. L., Esmon C. T., Esmon N. L. Tumor necrosis factor leads to the internalization and degradation of thrombomodulin from the surface of bovine aortic endothelial cells in culture. Blood. 1989 Jan;73(1):159–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Handley D. A., Esmon C. T., Stern D. M. Interleukin 1 induces endothelial cell procoagulant while suppressing cell-surface anticoagulant activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3460–3464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P., Handley D., Matsueda G., De Waal R., Gerlach H., Blohm D., Stern D. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin-induced intravascular fibrin formation in meth A fibrosarcomas. J Exp Med. 1988 Aug 1;168(2):637–647. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.2.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y. Tissue factor and hemostasis. Blood. 1988 Jan;71(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawala-Sheikh R., Ahmad S. S., Monroe D. M., Roberts H. R., Walsh P. N. Role of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid residues in the binding of factor IXa to platelets and in factor-X activation. Blood. 1992 Jan 15;79(2):398–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimon S., Melamed R., Savion N., Scott T., Nawroth P. P., Stern D. M. Identification of a factor IX/IXa binding protein on the endothelial cell surface. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6023–6031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: a perspective for the 1990s. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):801–809. doi: 10.1038/362801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J., Brett J., Tijburg P., Bach R. R., Kisiel W., Stern D. Tumor necrosis factor-induced endothelial tissue factor is associated with subendothelial matrix vesicles but is not expressed on the apical surface. Blood. 1992 Aug 15;80(4):966–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J., Geczy C. Coagulation and the expression of cell-mediated immunity. Immunol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;65(Pt 2):127–139. doi: 10.1038/icb.1987.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J., Wolitzky B., Heimer E., Lambrose T., Felix A., Tam J. P., Huang L. H., Nawroth P., Wilner G., Kisiel W. Structural determinants of the factor IX molecule mediating interaction with the endothelial cell binding site are distinct from those involved in phospholipid binding. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20283–20287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleef R. R., Bevilacqua M. P., Sawdey M., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Loskutoff D. J. Cytokine activation of vascular endothelium. Effects on tissue-type plasminogen activator and type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5797–5803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. M., Knitter G., Kisiel W., Nawroth P. P. In vivo evidence of intravascular binding sites for coagulation factor IX. Br J Haematol. 1987 Jun;66(2):227–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1987.tb01303.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. M., Nawroth P. P., Kisiel W., Vehar G., Esmon C. T. The binding of factor IXa to cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. Induction of a specific site in the presence of factors VIII and X. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6717–6722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D., Brett J., Harris K., Nawroth P. Participation of endothelial cells in the protein C-protein S anticoagulant pathway: the synthesis and release of protein S. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1971–1978. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tijburg P. N., Ryan J., Stern D. M., Wollitzky B., Rimon S., Rimon A., Handley D., Nawroth P., Sixma J. J., de Groot P. G. Activation of the coagulation mechanism on tumor necrosis factor-stimulated cultured endothelial cells and their extracellular matrix. The role of flow and factor IX/IXa. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):12067–12074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toomey J. R., Smith K. J., Stafford D. W. Localization of the human tissue factor recognition determinant of human factor VIIa. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19198–19202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Lages B. Evidence for tissue factor-dependent activation of the classic extrinsic coagulation mechanism in blood obtained from bleeding time wounds. Blood. 1988 Mar;71(3):629–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


