Abstract
The root hair and nonhair cells in the Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) root epidermis are specified by a suite of transcriptional regulators. Two of these are WEREWOLF (WER) and CAPRICE (CPC), which encode MYB transcription factors that are required for promoting the nonhair cell fate and the hair cell fate, respectively. However, the precise function and relationship between these transcriptional regulators have not been fully defined experimentally. Here, we examine these issues by misexpressing the WER gene using the GAL4-upstream activation sequence transactivation system. We find that WER overexpression in the Arabidopsis root tip is sufficient to cause epidermal cells to adopt the nonhair cell fate through direct induction of GLABRA2 (GL2) gene expression. We also show that GLABRA3 (GL3) and ENHANCER OF GLABRA3 (EGL3), two closely related bHLH proteins, are required for the action of the overexpressed WER and that WER interacts with these bHLHs in plant cells. Furthermore, we find that CPC suppresses the WER overexpression phenotype quantitatively. These results show that WER acts together with GL3/EGL3 to induce GL2 expression and that WER and CPC compete with one another to define cell fates in the Arabidopsis root epidermis.
One of the fundamental questions in developmental biology is how a cell adopts its fate, and many studies have revealed that the relative position of a cell, rather than its lineage, plays an important role in cell fate decision (van den Berg et al., 1995; Kidner et al., 2000). Therefore, to adopt their appropriate fate, it is very important that cells communicate properly with neighboring cells and recognize their relative position.
The Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) root epidermis is a good model system for studying the process of cell fate specification. The root epidermis consists of two types of cells, root hair-bearing cells (hair cells) and nonhair cells. Their cell fates are determined in a position-dependent manner, so that the cells located over a single cortical cell (N-position) adopt the nonhair cell fate while the cells located over the anticlinal wall of the underlying cortical cells, and thereby in contact with two cortical cells (H-position), adopt the hair cell fate (Dolan et al., 1993; Galway et al., 1994).
Several regulators that are involved in this cell fate specification have been identified. MYB-type transcription factors including WEREWOLF (WER; Lee and Schiefelbein, 1999) and MYB23 (Kang et al., 2009), bHLH-type transcription factors including GLABRA3 (GL3) and ENHANCER OF GLABRA3 (EGL3; Bernhardt et al., 2003), a WD-repeat protein, TRANSPARENT TESTA GLABRA1 (Galway et al., 1994; Walker et al., 1999), and a homeodomain-Zip transcription factor, GLABRA2 (GL2) (Masucci et al., 1996), have been shown to induce the nonhair cell fate at the N position, while single repeat MYB-type transcription factors CAPRICE (CPC), TRIPTYCHON (TRY), and ENHANCER OF TRY AND CPC1 (ETC1) have been shown to positively regulate the hair cell fate at the H position (Wada et al., 1997; Schellmann et al., 2002; Simon et al., 2007). In addition, a Leu-rich repeat receptor-like kinase, SCRAMBLED (SCM), was also shown to be involved in this epidermal cell patterning (Kwak et al., 2005).
A complex action network of these regulators for root epidermal cell fate specification has been proposed (Kang et al., 2009). SCM is suggested to perceive a positional signal (not yet identified), and it suppresses WER expression in the H-position cells, which leads to a small difference in the WER expression level between the cells at the two positions (Kwak et al., 2005; Kwak and Schiefelbein, 2007). In the N-position cells, a relatively high level of WER, which can form a complex with GL3/EGL3, induces the nonhair cell fate by inducing the expression of GL2 and MYB23 (Lee and Schiefelbein, 1999, 2002; Kang et al., 2009). This complex also promotes the hair cell fate by inducing the expression of single-repeat MYB genes CPC, TRY, and ETC1 in the N-position cells (Lee and Schiefelbein, 2002; Koshino-Kimura et al., 2005; Ryu et al., 2005; Simon et al., 2007). These single-repeat MYBs move into the neighboring H-position cells (Kurata et al., 2005) and further down-regulate WER expression as well as the expression of CPC and GL2, which results in hair cell fate specification (Lee and Schiefelbein, 2002).
The above model is largely consistent with the available experimental evidence. However, aspects of this model have not been rigorously tested, and there are experimental results that do not appear to fit the model. For example, the overexpression of WER using the cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) 35S promoter (35Spro:WER) did not cause any discernible effect in the wild-type root epidermis (Lee and Schiefelbein, 1999, 2002), suggesting that WER may not be sufficient to induce GL2, CPC, or the nonhair cell fate in the H-position. On the other hand, 35Spro:WER caused a randomized cell fate specification in the wer mutant root epidermal cells independent of their position, leading to another explanation in which WER primarily functions in epidermal cell patterning rather than merely in the nonhair cell fate specification (Lee and Schiefelbein, 2002). Also, WER’s possible interactions with other cell fate regulators, including GL3/EGL3, CPC, and SCM, to regulate GL2 expression have not been critically examined.
In this report, we used several molecular genetic approaches to directly test and extend current models for root epidermal cell fate specification. In one line of experiments, we drove WER expression using the GAL4-upstream activation sequence (UAS) targeted expression system (Brand and Perrimon, 1993; Haseloff, 1999) and found that WER was able to promote the nonhair cell fate by directly inducing GL2 expression in every root epidermal cell and that GL3/EGL3 is required in this process. We also showed that the transcriptional repression of WER by CPC is not required for the hair cell fate specification in the root epidermis. We further discovered that WER and CPC compete with each other to specify one of the fates by regulating GL2 expression quantitatively.
RESULTS
WER Expression Is Sufficient to Induce the Nonhair Cell Fate in the Root Epidermis
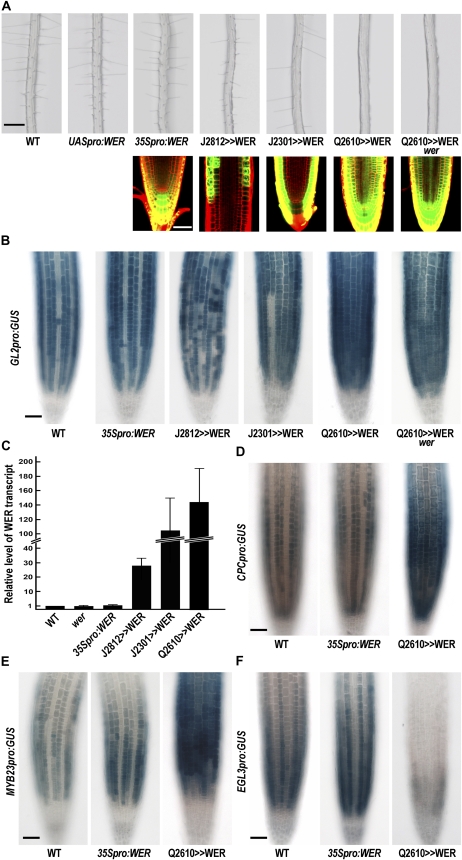
To determine whether WER is able to induce the nonhair cell fate in the H-position, we expressed WER using the GAL4-UAS targeted expression system (Brand and Perrimon, 1993; Haseloff, 1999). We generated an Arabidopsis line harboring a UASpro:WER construct and crossed it with three GAL4-GFP enhancer trap lines (J2812, J2301, and Q2610; Haseloff, 1999) to induce WER expression at the root tip with different tissue specificity (Fig. 1A). WER expression is induced in the cortex and the epidermis in J2812 roots, in the epidermis and the lateral root cap in J2301 roots, and in most of the tissues in Q2610 root tips. While WER expressed under the control of the 35S promoter (35Spro:WER) did not cause any noticeable defect in epidermal cell patterning, as reported earlier (Lee and Schiefelbein, 1999, 2002), WER expressed using the enhancer trap lines J2812, J2301, and Q2610 (designated as J2812>>WER, J2301>>WER, and Q2610>>WER) disrupted the epidermal cell patterning to cause some H-position cells to adopt the nonhair cell fate (Fig. 1A; Table I). In particular, the Q2610>>WER line showed the most severe effect on cell fate specification, so that most of the epidermal cells differentiated into a nonhair cell regardless of their position.
Figure 1.
WER induces the nonhair cell fate in the Arabidopsis root epidermis in a dose-dependent manner. A, Root hair phenotype for the wild type (WT) and the WER-overexpressing lines. The top panels show the wild-type and transgenic root phenotypes. WER was ectopically expressed under the regulation of the CaMV 35S promoter and enhancer trap lines of J2812, J2301, and Q2610 by using the GAL4-UAS transactivation system. A transgenic line harboring UASpro:WER was selected and crossed to the indicated enhancer trap lines, and F3 seedlings homozygous for both the enhancer trap line and the transgene were screened. The bottom panels show the expression patterns of 35Spro:GFP, J2812, J2301, and Q2610 in the root tip observed using confocal microscopy. Top bar = 200 μm; bottom bar = 50 μm. B, GL2pro:GUS reporter gene expression pattern in root tips of the wild type and WER-overexpressing lines. Wild-type and transgenic roots harboring the GL2pro:GUS transgene were stained for GUS activity using 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-β-GlcA as a substrate. C, Relative level of the WER transcript in root tips of the wild type and WER-overexpressing lines. The relative level of the WER transcript was determined by quantitative real-time PCR analysis. Error bars indicate sd from at least three replicates. D, Wild-type and transgenic roots harboring CPCpro:GUS. Four-day-old seedlings were stained for GUS activity. E, Wild-type and transgenic roots harboring MYB23pro:GUS. Four-day-old seedlings were stained for GUS activity. F, Wild-type and transgenic roots harboring EGL3pro:GUS. Four-day-old seedlings were stained for GUS activity. Bars in B and D to F = 50 μm.
Table I. Cell type pattern in the root epidermis in various mutants and transgenic plants.
At least 30 4-d-old seedlings were examined for each plant line. Values indicate means ± sd.
| Genotype | H-Position |
N-Position |
||
| Hair Cell | Nonhair Cell | Hair Cell | Nonhair Cell | |
| % | ||||
| Wild type (ecotype Columbia) | 95.0 ± 2.5 | 5.0 ± 2.5 | 2.5 ± 2.2 | 97.5 ± 2.2 |
| wer | 99.7 ± 0.6 | 0.3 ± 0.6 | 99.3 ± 0.6 | 0.7 ± 0.6 |
| gl2 | 100.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 99.2 ± 0.7 | 0.8 ± 0.7 |
| gl3 egl3 | 100.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 100.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| cpc | 34.6 ± 3.1 | 65.4 ± 3.1 | 0.4 ± 0.7 | 99.6 ± 0.7 |
| scm-2 | 73.3 ± 4.0 | 26.7 ± 4.0 | 19.6 ± 11.5 | 80.4 ± 11.5 |
| 35Spro:CPC | 100.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 97.0 ± 2.9 | 3.0 ± 2.9 |
| Q2610>>CPC | 99.6 ± 0.6 | 0.4 ± 0.6 | 100.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| 35Spro:WER | 97.7 ± 3.2 | 2.3 ± 3.2 | 1.3 ± 1.5 | 98.7 ± 1.5 |
| J2812>>WER | 54.0 ± 13.0 | 46.0 ± 13.0 | 7.0 ± 1.0 | 93.0 ± 1.0 |
| J2301>>WER | 47.6 ± 5.7 | 52.4 ± 5.7 | 2.9 ± 2.0 | 97.1 ± 2.0 |
| Q2610>>WER | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 100.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 100 ± 0.0 |
| Q2610>>WER wer | 6.4 ± 4.0 | 93.6 ± 4.0 | 0.9 ± 0.9 | 99.1 ± 0.9 |
| Q2610>>WER gl2 | 100.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 97.5 ± 1.2 | 2.5 ± 1.2 |
| Q2610>>WER gl3 egl3 | 100.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 99.6 ± 0.6 | 0.4 ± 0.6 |
| Q2610>>WER scm-2 | 0.9 ± 1.6 | 99.1 ± 1.6 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 100.0 ± 0.0 |
| Q2610>>WER cpc | 0.4 ± 0.6 | 99.6 ± 0.6 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 100.0 ± 0.0 |
| Q2610>>WER 35Spro:CPC | 15.2 ± 8.7 | 84.8 ± 8.7 | 0.6 ± 1.0 | 99.4 ± 1.0 |
| Q2610>>WER; CPC | 100.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 99.7 ± 0.5 | 0.3 ± 0.5 |
Although GL2 expression is known to require WER function (Lee and Schiefelbein, 1999), it is not clear whether WER induces GL2 expression quantitatively. To address this, we first examined GL2pro:GUS reporter gene expression in the root tip of the WER-overexpressing lines (Fig. 1B). It is well known that the GL2pro:GUS reporter gene is specifically expressed in the N-position cell files of the root epidermis (Masucci et al., 1996). However, in the J2812>>WER and J2301>>WER roots, some of the H-position epidermal cells also showed GUS activity, resulting in disruption of the file-specific expression pattern (Fig. 1B). Furthermore, Q2610>>WER caused almost every epidermal cell to express GL2pro:GUS at a similar level irrespective of their relative position. On the other hand, in the 35Spro:WER plant root, the GL2pro:GUS expression pattern was similar to the pattern in the wild-type roots (Fig. 1B).
We next examined the WER transcript level in the root tip of those lines using quantitative real-time PCR to determine whether these phenotypic differences were caused by a difference in WER expression level (Fig. 1C). We discovered that the WER transcript level in the 35Spro:WER line was 1.4-fold higher than in the wild type, which seems to be a very small addition to the endogenous WER transcript level in the root epidermis. However, the WER transcript levels in three different GAL4-UAS transgenic lines (J2812>>WER, J2301>>WER, and Q2610>>WER) were much higher than the levels in the wild type and the 35Spro:WER line (28.6-, 102.3-, and 145.4-fold higher, respectively, than in the wild type). Although it is difficult to compare the expression levels of WER in a particular cell type between the enhancer trap lines, the degree of hairless phenotype seemed to largely correlate with the WER transcript level, implying a quantitative effect of WER.
Altogether, these results show that WER expression is able to induce the nonhair cell fate in every epidermal cell, which implies that WER functions primarily in the nonhair cell fate specification.
WER Regulates GL2 Expression to Induce the Nonhair Cell Fate by Binding to Two Sites in the GL2 Promoter
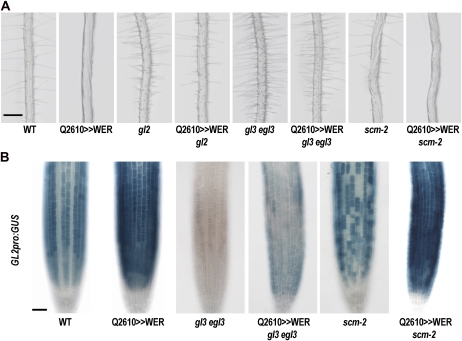
We questioned whether GL2 mediates the nonhair cell fate specification by WER, which is an issue that has not been examined directly. To test this, we introduced Q2610>>WER into the gl2 mutant background by a genetic cross. The resulting Q2610>>WER gl2 plant showed a hairy root phenotype similar to the phenotype of the gl2 single mutant (Fig. 2A; Table I).
Figure 2.
WER functions upstream of GL2 and GL3/EGL3 and downstream of SCM. A, Root hair phenotypes for the wild type (WT), mutants, Q2610>>WER, and mutants harboring Q2610>>WER. Bar = 200 μm. B, GL2pro:GUS reporter gene expression pattern in the root tip. Four-day-old seedling roots of the wild type, mutants, Q2610>>WER, and mutants bearing Q2610>>WER were stained for GUS activity after GL2pro:GUS was introduced into the backgrounds by genetic crosses. Bar = 50 μm. [See online article for color version of this figure.]
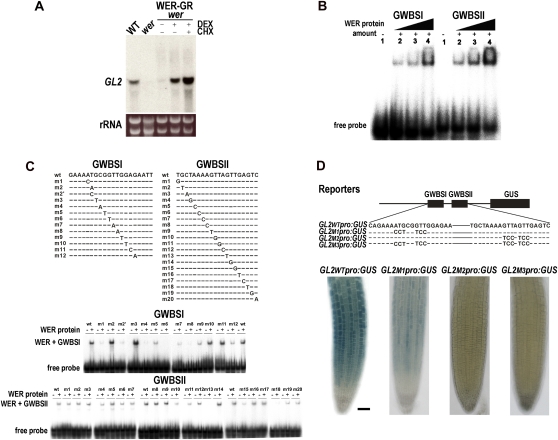
Next, we examined whether WER induces GL2 expression directly by using the glucocorticoid receptor (GR)-mediated inducible system (Picard et al., 1988; Lloyd et al., 1994; Ryu et al., 2005). We used the 35Spro:WER-GR wer-1 line, which was generated and verified previously (Ryu et al., 2005), and induced WER function with the same conditions (Fig. 3A). Whereas the seedling roots not exposed to dexamethasone (DEX) showed a very low level of GL2 transcript, the seedling roots treated with 10 μm DEX for 6 h accumulated a greater level of GL2 transcript. Furthermore, this increase was not diminished when cycloheximide was treated together with DEX, which suggests that de novo synthesis of proteins is not required and therefore that WER directly induces GL2 expression.
Figure 3.
WER directly regulates GL2 expression. A, Direct induction of GL2 expression by WER. The GL2 transcript was accumulated in the wer mutant seedlings harboring the 35Spro:WER-GR transgene when DEX and cycloheximide (CHX) were given. RNA gel-blot analysis was performed with total RNA extracted from the root tips using the GL2 fragment as a probe. WT, Wild type. B, Binding of WER to the GL2 promoter. EMSA was performed using the purified WER protein and 20-bp-long DNA fragments (GWBSI and GWBSII screened from the GL2 promoter). Lane 1, no WER; lanes 2 to 4, with increased amounts of WER (1×, 3×, and 6×, respectively). C, EMSA using the purified WER protein and the mutated probes. Sequences of mutated GWBSI and GWBSII used in this experiment are shown at the top. Each double-stranded probe contains a single base substitution as indicated. Dashes indicate no base change. A core sequence for GWBSI and GWBSII was deduced from these EMSA results. D, Importance of GWBSI and GWBSII in the proper expression of GL2 in the Arabidopsis root. The top panel shows schematic diagrams of the wild-type and mutated GL2pro:GUS reporter genes used for the stable transgenic lines. The bottom panel shows the GUS activity of the transgenic roots. Bar = 50 μm. [See online article for color version of this figure.]
To test whether WER binds to the GL2 promoter, electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSAs) were performed using several small DNA fragments in the GL2 promoter region including 2.1 kb upstream of the translation start codon as a probe (Fig. 3B), which is sufficient to induce proper GL2 expression (Lin and Schiefelbein, 2001). We identified two WER-binding DNA fragments, and the binding regions were further defined to two small segments located at 909 to 890 bp (GWBSI) and 932 to 915 bp (GWBSII) upstream from the translation start codon (Fig. 3B). Several point-mutated versions of these two DNA fragments were used in the EMSA to define the nucleotides important for WER binding (Fig. 3C). WER did not bind to some of the mutated versions of DNA fragments, which revealed that the nucleotides shown as uppercase letters in aaaTgcgGTTgg for GWBSI and in aaGTTaGTTga for GWBSII are important for WER binding. Next, these binding sites were validated in yeast using a yeast one-hybrid assay with these two binding sites and the WER protein (Supplemental Fig. S1). In addition, we examined the importance of these sites for GL2 expression in plants and found that these two sites are involved in the position-specific expression of GL2 (Fig. 3D). When the GL2 promoter had the mutated GWBSI (m1; aaCCTcgTCCgg), the promoter activity was greatly reduced in all of the individual transgenic plants compared with the activity of the wild-type GL2 promoter. The mutations at GWBSII (m2; aaTCCaTCCga) or at both of the sites completely abolished the promoter activity in the root epidermis of every individual transgenic plant examined.
These results show that WER causes epidermal cells to adopt the nonhair cell fate through direct induction of GL2 expression by binding to its promoter.
Expression of Other Cell Fate Regulators in the WER-Overexpressing Lines
It is well known that WER is necessary for CPC and MYB23 expression in the N-position epidermal cells (Lee and Schiefelbein, 2002; Kang et al., 2009) and that WER directly induces CPC and MYB23 expression by binding to their promoter (Koshino-Kimura et al., 2005; Ryu et al., 2005; Kang et al., 2009). However, it is not clear whether WER expression is sufficient to induce CPC and MYB23 in the root epidermis. To test this, we examined CPC and MYB23 expression in the WER-overexpressing plant roots using the reporter genes CPCpro:GUS and MYB23pro:GUS (Fig. 1, D and E). As expected, 35Spro:WER did not cause any noticeable change in CPCpro:GUS and MYB23pro:GUS expression in the root epidermis. However, Q2610>>WER was able to increase their expression levels and made almost every epidermal cell express these reporter genes regardless of its position relative to the underlying cortical cells. Furthermore, Q2610>>WER was able to reduce EGL3pro:GUS expression in the root epidermis, while 35Spro:WER was not (Fig. 1F). This is consistent with the report that EGL3pro:GUS expression was increased in the wer mutant root epidermis (Bernhardt et al., 2005).
Taken together, these results show that WER expression is sufficient to alter the expression of three cell fate regulators, CPC, MYB23, and EGL3, in the root epidermis.
WER Acts Together with GL3/EGL3 to Induce GL2 Expression
Although WER is required for GL3/EGL3 function in nonhair cell fate specification in the N position (Bernhardt et al., 2003), it is not known whether GL3/EGL3 is necessary for WER function in the root epidermis. To test this, we introduced the gl3 egl3 mutations into the Q2610>>WER line by a genetic cross. In the Q2610>>WER gl3 egl3 plant, the hairless phenotype caused by WER overexpression disappeared and most of the epidermal cells adopted the hair cell fate similar to the gl3 egl3 double mutant (Fig. 2A; Table I). Consistent with this, GL2pro:GUS expression in this line was very low, much lower than in the wild type and slightly higher than in the gl3 egl3 double mutant (Fig. 2B).
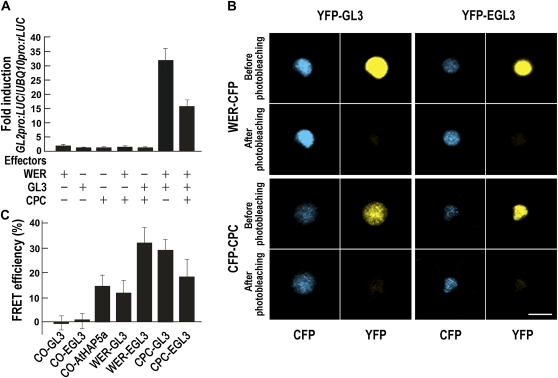
We also examined the interaction between WER and GL3 in regulating GL2 promoter activity. We expressed WER and GL3 transiently in Arabidopsis leaf protoplasts as effectors using the 35S promoters (35Spro:WER and 35Spro:GL3), and the reporter gene activity (GL2pro:LUC) was analyzed (Fig. 4A). WER alone was able to induce GL2 promoter activity slightly (1.6-fold), and GL3 alone did not induce. On the contrary, GL2 promoter activity was increased dramatically (32-fold) when WER and GL3 were coexpressed.
Figure 4.
WER interacts with GL3/EGL3 in the regulation of GL2 expression. A, Interactions among WER, GL3, and CPC in the regulation of GL2 expression in the Arabidopsis protoplast transient expression assay. Protoplasts were transfected with 35Spro:WER, 35Spro:GL3, 35Spro:CPC, and their combinations as indicated together with GL2pro:LUC as a reporter and UBQ10pro:rLUC as an internal control. B, In vivo FRET analysis for the interaction of WER and CPC with GL3 and EGL3 in plant cells. WER (top panels) and CPC (bottom panels) interaction with GL3 and EGL3 was visualized as an increase in the WER-CFP and CFP-CPC fluorescence after photobleaching of YFP-GL3 and YFP-EGL3. Images display the CFP and YFP channels in false colors before and after photobleaching. Blue color indicates CFP signal, and yellow color indicates YFP signal. Bar = 10 μm. C, Quantification of FRET efficiency after acceptor photobleaching. FRET efficiency was calculated from the formula FRET efficiency = {(CFP signal after photobleaching – CFP signal before photobleaching)/CFP signal after photobleaching} × 100. CO-CFP was used as a negative control. Error bars indicate sd from 10 to 14 independent FRET analyses through two independent experiments.
Next, we examined the physical interaction between WER and GL3/EGL3 in plant cells using fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) analysis. We expressed WER-CFP and the YFP-GL3 (or YFP-EGL3) chimeric proteins in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) leaf epidermal cells, and these colocalized in the nuclei (Fig. 4B). We analyzed the change in the cyan fluorescent protein (CFP) signal intensity after photobleaching of the yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) and discovered that, after photobleaching of YFP-GL3 and YFP-EGL3, WER-CFP signal intensity increased, with FRET efficiency of 11.6% and 33.5%, respectively, while FRET efficiencies of negative controls employing CONSTANS (CO)-CFP and YFP-GL3 or CO-CFP and YFP-EGL3 were negligible (0.8 and 0.9, respectively; Fig. 4, B and C). We also included a positive control of this FRET analysis with CO-YFP and AtHAP5a-CFP, which were shown to physically interact using FRET analysis (Wenkel et al., 2006).
SCM Does Not Affect the WER Function
To determine the genetic relationship between WER and SCM, we analyzed the effect of WER overexpression in the scm mutant background. In the Q2610>>WER scm root, every epidermal cell adopted the nonhair cell fate, which implies that SCM is not required for the WER overexpression effect (Fig. 2A; Table I). Furthermore, GL2pro:GUS expression in the Q2610>>WER scm plant root was indistinguishable from that in the Q2610>>WER plant root, while the scm mutant root showed a largely random expression pattern (Fig. 2B).
CPC Overexpression Does Not Inhibit WER Expression
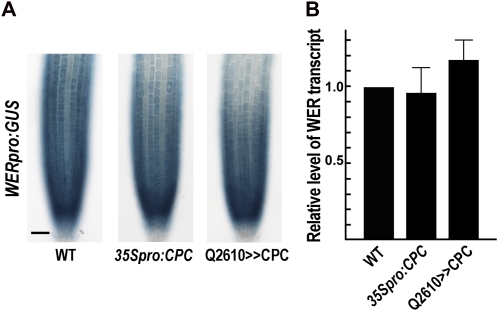
In the cpc mutant root epidermis, WER is expressed at a high level in some of the H-position cells, which suggested that CPC is able to suppress WER expression (Lee and Schiefelbein, 2002). To test this hypothesis, we examined WER expression in the root epidermis in CPC-overexpressing lines using the WERpro:GUS transgene as a reporter. This transgene has a shorter 5′ WER flanking DNA sequence (1.4 kb) than the reporter gene previously described (4 kb; Lee and Schiefelbein, 1999), but this shorter version was still able to drive WER expression sufficient to complement the wer mutant phenotype (Supplemental Fig. S2).
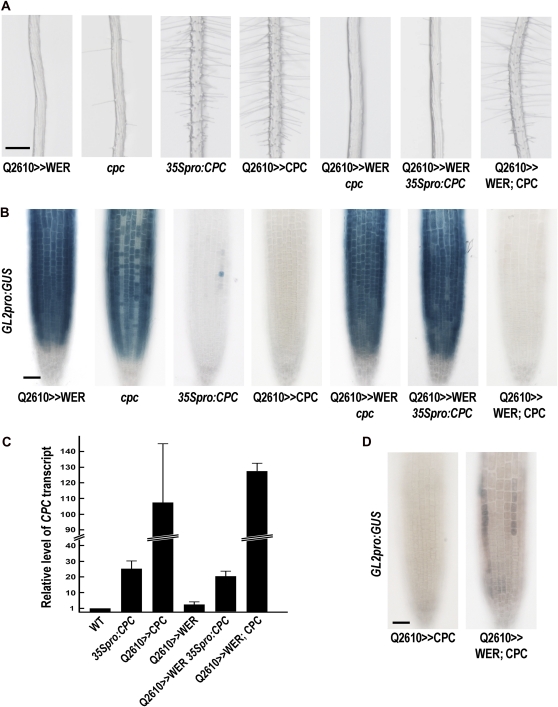
Overexpression of CPC using the 35S CaMV promoter (35Spro:CPC) was not able to change the WER expression pattern (Fig. 5A), even though it was sufficient to cause N-position cells to adopt the hair cell fate (Wada et al., 1997). Quantitative real-time PCR analysis revealed that the WER transcript level in the 35Spro:CPC plant root was not significantly different from its level in the wild-type root (Fig. 5B). In a separate experiment, we generated a Q2610>>CPC line and examined its effect on WER expression. Like the 35Spro:CPC line, we found that, in the root tip of the Q2610>>CPC line, the WER expression pattern was not altered and the WER transcript level was not reduced (indeed, perhaps slightly increased; Fig. 5), even though the hair cell fate was induced in every epidermal cell (Fig. 6A; Table I) and CPC expression was much higher than in the 35Spro:CPC root or the wild-type root (Fig. 6C). Because WER expression was not reduced in any of these CPC overexpression lines, these results suggest that CPC is not sufficient to inhibit WER gene expression.
Figure 5.
The ectopic expression of CPC does not affect WER expression. A, Wild-type (WT) and transgenic roots harboring WERpro:GUS were stained for GUS activity. Bar = 50 μm. B, Relative level of the WER transcript in wild-type, 35Spro:CPC, and Q2610>>CPC transgenic roots determined by quantitative real-time PCR analysis. Error bars indicate sd from at least three replicates. [See online article for color version of this figure.]
Figure 6.
CPC inhibits the WER function quantitatively. A, The phenotypes of root hair pattern in cpc and transgenic plants ectopically expressing CPC, WER, or both of them. Bar = 200 μm. B, GL2pro:GUS reporter gene expression pattern in the root tips of cpc and transgenic roots bearing GL2pro:GUS. Four-day-old seedlings were stained for GUS activity. Bar = 50 μm. C, Relative levels of the CPC transcript in wild-type (WT) and various transgenic roots determined by quantitative real-time PCR analysis. Error bars indicate sd from at least three replicates. D, GL2pro:GUS reporter gene expression pattern in the root tip of Q2610>>CPC and Q2610>>WER; CPC harboring GL2pro:GUS. Four-day-old seedlings were stained overnight for GUS activity to examine the effect of WER overexpression. Bar = 50 μm. [See online article for color version of this figure.]
CPC Can Inhibit WER Function Quantitatively
We conducted a series of experiments to investigate the proposed competition between WER and CPC in cell fate specification. First, we examined the effect of CPC on GL2 promoter activation by WER and GL3. When CPC was transiently expressed together with WER and GL3 in protoplasts, we observed a 50% decrease in GL2 promoter activation by WER and GL3 (Fig. 4A). Next, we analyzed the possible competition using stably transformed Arabidopsis plants. We introduced the cpc mutation, 35Spro:CPC, or UASpro:CPC into the Q2610>>WER plant by genetic crosses to express CPC at different levels (Fig. 6C). 35Spro:CPC has been known to inhibit GL2 expression so that most of the epidermal cells adopt the hair cell fate (Fig. 6, A and B; Table I; Wada et al., 1997, 2002; Lee and Schiefelbein, 2002). Q2610>>CPC strongly inhibited GL2pro:GUS expression to an undetectable level and caused almost every root epidermal cell to adopt the hair cell fate (Fig. 6, A and B; Table I). The 35Spro:CPC root tip showed about 25-fold higher accumulation of CPC transcript than the wild-type root tip, and the Q2610>>CPC root tip showed even higher accumulation of CPC transcript (108-fold higher than the wild type; Fig. 6C). Increased accumulation of CPC transcript was also observed in the Q2610>>WER background (Q2610>>WER 35Spro:CPC and Q2610>>WER; CPC; Fig. 6C). The cpc mutation did not alter the action of Q2610>>WER, based on the complete hairless phenotype of the Q2610>>WER cpc plant root (Fig. 6A). 35Spro:CPC in the Q2610>>WER plant made 15.2% of the epidermal cells differentiate into a hair cell, while none of the epidermal cells in the Q2610>>WER plant differentiated into a hair cell (Fig. 6A; Table I). Accordingly, some epidermal cells in the Q2610>>WER 35Spro:CPC roots were not expressing the GL2pro:GUS reporter gene (Fig. 6B). Furthermore, Q2610>>CPC in the Q2610>>WER background completely changed the hairless root phenotype into a hairy phenotype (Fig. 6A). A detailed analysis of the cell type pattern revealed that almost every epidermal cell differentiated into a hair cell (Table I). Although the epidermal cell type pattern in Q2610>>WER; CPC was almost the same as the cell type pattern found in Q2610>>CPC, GL2pro:GUS expression was detected in the Q2610>>WER; CPC plant after overnight staining (Fig. 6D). We have never been able to detect GL2pro:GUS expression in the Q2610>>CPC plant root, even after prolonged staining.
CPC Interacts with GL3/EGL3 in Plant Cells
To test for possible protein-protein interaction between CPC and GL3/EGL3 in plant cells, we used FRET analysis. CPC-CFP and the YFP-GL3 (or YFP-EGL3) chimeric proteins were expressed in tobacco leaf epidermal cells and were detected in nuclei (Fig. 4B). We analyzed the change in CFP signal intensity after photobleaching of the YFP. After photobleaching of YFP-GL3 and YFP-EGL3, the CPC-CFP signal intensity was increased with FRET efficiency of 29.1% and 18.2%, respectively (Fig. 4, B and C).
DISCUSSION
The Ratio of CPC to WER Specifies the Cell Fate in the Root Epidermis
Although 35Spro:WER did not affect the epidermal cell patterning in the wild-type root, it caused a novel pattern phenotype in the root epidermis in the wer mutant background (Lee and Schiefelbein, 2002). Specifically, the position-dependent cell fate specification was disrupted, so that both of the cell types were found in each position. It was suggested that this phenotype was due to increased and equivalent CPC and GL2 expression by 35Spro:WER in all epidermal cells. In the Q2610>>WER plant roots, however, every epidermal cell adopted the nonhair cell fate, even though CPC expression is high in every root epidermal cell (Fig. 1). This shows that CPC induced by the WER in this plant was not sufficient to induce the hair cell fate and generate a pattern of both cell types. This raised two possible explanations. One possibility is that the negative regulation of WER expression by CPC is critical for the hair cell fate specification, which was proposed previously (Lee and Schiefelbein, 2002). The second possibility is that the level of CPC protein in the Q2610>>WER plant might not be sufficient to inhibit the WER function in nonhair cell fate specification. CPC overexpressed using the 35S CaMV promoter or the Q2610 enhancer trap line did not suppress WER expression in the root, while it inhibited GL2 expression and made the root epidermal cells adopt the hair cell fate regardless of their relative positions (Figs. 5 and 6). Also, the more CPC was expressed in the Q2610>>WER plant, the fewer root epidermal cells expressed the GL2 gene and the more cells adopted the hair cell fate (Fig. 6; Table I). Furthermore, transiently expressed CPC suppressed the increase in GL2 promoter activity by WER and GL3 without affecting their expression (Fig. 4A). Together, these results strongly indicate that the most important factor in hair cell fate specification is not negative regulation of WER expression by CPC but the ratio of the level of CPC to the level of WER.
It has been shown that the CPC promoter is activated in the N-position cells by WER (Lee and Schiefelbein, 2002; Wada et al., 2002; Koshino-Kimura et al., 2005; Ryu et al., 2005) and that the CPC protein accumulates in the epidermal cells at both of the positions (Wada et al., 2002; Kurata et al., 2005). On the contrary, the WER protein was shown to preferentially accumulate in the N-position cell of the wild-type root epidermis (Ryu et al., 2005). Taken together, this suggests a possible mechanism based on a competition between WER and CPC quantitatively to specify the cell fate in the root epidermis. In this view, the N-position cells express WER and CPC, and CPC moves to the neighboring H-position cells while WER does not. This results in different ratios of the CPC level to the WER level between the cells at the two positions. In the H-position cell, the high ratio of CPC to WER inhibits GL2 expression, leading to the hair cell fate, while the low ratio of CPC to WER in the N-position cell induces GL2 expression, leading to the nonhair cell fate. This mechanism explains why CPC does not induce the hair cell fate in the N-position cell where it is expressed.
Possible Competition between WER and CPC in Interacting with GL3/EGL3
The maize (Zea mays) R gene encodes a bHLH protein, and it was shown to affect cell fate specification in the Arabidopsis root epidermis when it was overexpressed (Galway et al., 1994). WER was shown to interact with the maize R protein (Lee and Schiefelbein, 1999) and two Arabidopsis bHLH proteins, GL3 and EGL3 (Bernhardt et al., 2003), using yeast two-hybrid analysis. GL1, which is functionally equivalent to WER (Lee and Schiefelbein, 2001), was shown to interact with GL3 and EGL3 using yeast two-hybrid analysis (Payne et al., 2000; Zhang et al., 2003) and coimmunoprecipitation assay (Gao et al., 2008). Also, CPC and TRY, negative regulators of GL2 expression, were found to bind to GL3 and EGL3 in the yeast two-hybrid assay (Bernhardt et al., 2003; Esch et al., 2003) and in plant protoplasts using bimolecular fluorescence complementation (Wester et al., 2009). Furthermore, it was demonstrated that CPC and CPC-like proteins interfere with the interaction between GL1 and GL3 in yeast (Esch et al., 2003; Wester et al., 2009).
Here, we demonstrated that WER and GL3/EGL3 interact in plant cells using FRET analysis and that GL3/EGL3 is required for WER function using genetic analysis and a transient expression system in Arabidopsis protoplasts (Figs. 2 and 4; Table I). We also demonstrated the interaction between CPC and GL3/EGL3 in plant cells using FRET analysis (Fig. 4). Our results confirm that those protein-protein interactions previously suggested are able to occur in plant cells, and they further indicate that WER and CPC compete for binding to GL3/EGL3 to regulate GL2 expression quantitatively. A dose-dependent competition mechanism, especially for the interaction with a partner protein, has been also proposed in other biological processes. For example, it has been suggested that APETALA3 (AP3) and PISTILLATA (PI) antagonize AGAMOUS (AG) functions by competing for the MADS box protein complex formation in Arabidopsis and, therefore, that the balance between AP3/PI and AG is important in floral organ specification and floral meristem termination (Prunet et al., 2009). In the photoreceptor specification of the Drosophila melanogaster retina, SOC36E and Drk compete with each other for the physical interaction with Sevenless (Sev) to repress and activate the Sev pathway, respectively (Almudi et al., 2010).
TRY was demonstrated to bind to GL1 in a glutathione S-transferase pull-down experiment, and this direct interaction was proposed as another possible mechanism for the inhibition of GL1 function (Digiuni et al., 2008). However, in our experiment using the yeast two-hybrid assay and FRET analysis, we were not able to detect an interaction between WER and CPC (data not shown). This discrepancy might indicate the difference between WER and GL1 and/or between CPC and TRY.
In our FRET analyses, WER interacted with EGL3 more efficiently than with GL3, while CPC interacted more efficiently with GL3 than with EGL3 (Fig. 4C). Also, it was shown that overexpression of GL3 and EGL3 promotes the nonhair cell fate specification and that EGL3 overexpression caused a stronger hairless phenotype than overexpression of GL3 (Bernhardt et al., 2003). One possible explanation for these phenotypic differences could be the difference in the transgene expression level. Another possible explanation raised by our FRET results is a difference in the preference for an interacting partner.
WER Directly Induces the Expression of Three Different Genes in the N-Position Cell for Epidermal Cell Patterning in the Arabidopsis Root
It has been suggested that WER positively regulates the expression of three genes, GL2, CPC, and MYB23, in the N-position cells of the root epidermis based on the reduced level of their transcript in the wer mutant root epidermis (Lee and Schiefelbein, 1999, 2002; Kang et al., 2009). WER was shown to directly induce CPC expression using a DEX-inducible expression system and was further shown to bind to three sites in the CPC promoter (WBSI, WBSΙΙ/CPCMBS1, and CPCMBS2; Koshino-Kimura et al., 2005; Ryu et al., 2005). These sites were found to be necessary for the proper expression of CPC in the Arabidopsis root epidermis. WER also binds to multiple sites in the MYB23 promoter to directly induce its expression in the root epidermis (Kang et al., 2009). GL2 was reported to have two WER-binding sites in its promoter (GL2MBS1 and GL2MBS2) based on an EMSA result (Koshino-Kimura et al., 2005). Recently, it was reported that GL1 is associated with the GL2 promoter using chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis (Zhao et al., 2008; Morohashi and Grotewold, 2009). However, it is not known whether GL2 expression is directly regulated by WER or whether these two binding sites reported are important for GL2 expression. Here, we show that WER specifies the nonhair cell fate in the root epidermis through the induction of GL2 expression (Fig. 2) and that this induction is a direct effect ofWER by binding to two sites (GWBSI and GWBSII) in the GL2 promoter that are different from the previously reported sites (GL2MBS1 and GL2MBS2; Fig. 3, A and C). Importantly, these binding sites were tested in vivo as well as in vitro (Fig. 3C; Supplemental Fig. S1). Also, both of these two WER-binding sites are important for the position-specific expression of the GL2 gene (Fig. 3D). These binding sites are located within the region that was reported to be important for the appropriate expression of the GL2 gene (Hung et al., 1998) and to be a putative GL1-binding region based on a chromatin immunoprecipitation experiment (Zhao et al., 2008). These two binding sites are located approximately 350 to 550 bp downstream of the previously reported GL2MBS1 and GL2MBS2 (Koshino-Kimura et al., 2005), and we were unable to detect these GL2MBSs in our analysis. Furthermore, we were unable to find any significant disruption of the GL2 promoter activity in the root epidermis when we introduced a mutation in these binding sites, GL2MBS1 or GL2MBS2. Also, a GL2 reporter gene driven by a shorter promoter (1.2 kb) without these two sites had no significant change in promoter activity (Supplemental Fig. S3), whereas the GL2 reporter genes with a mutation in one of the GWBSs showed very low levels of expression in the root epidermis (Fig. 3D).
Analysis of the WER-binding sites confirmed in these three genes shows a shared core sequence, (C/T)DGTT(G/A), which is similar to the vertebrate MYB-binding site, CNGTTR (Howe and Watson, 1991). Plants possess a particularly large number of MYB genes in their genomes, and they appear to regulate many different cellular processes (Stracke et al., 2001). Therefore, their DNA-binding sites might be expected to differ considerably among themselves. Among the plant MYB-binding sites, the WER-binding site is similar to one of the binding sites of MYB.Ph3 from petunia (Petunia hybrida; Solano et al., 1995). In addition to this core sequence, the flanking sequence also seems to play an important role in vivo, because GL2MBS1 and GL2MBS2 are not involved in GL2 gene regulation by WER, in spite of their same core sequence, (C/T)DGTT(G/A) (Koshino-Kimura et al., 2005).
Each of these direct WER target genes (GL2, CPC, and MYB23) has multiple WER-binding sites in its promoter, and each binding site is important for proper expression except for some of the sites in the MYB23 promoter, which may function redundantly (Fig. 3D; Koshino-Kimura et al., 2005; Ryu et al., 2005; Kang et al., 2009). It has been reported that GL3 and EGL3 interact with each other as well as with themselves in yeast (Payne et al., 2000; Zhang et al., 2003). Taken together with the interaction between WER and GL3/EGL3, it seems that WER acts in a protein complex including at least two GL3/EGL3 proteins and two WER proteins. Therefore, multiple binding sites may be helpful for this protein complex to bind effectively to their promoter and induce appropriate transcription.
CONCLUSION
Through this work, we are able to define the primary function of WER in cell fate specification. WER primarily acts to specify the nonhair cell fate rather than as a master regulator in generating a pattern. Furthermore, this nonhair cell fate specification by WER is genetically mediated by GL2, which is a direct target gene of WER. GL3/EGL3 is also genetically shown to be necessary for the proper function of WER in GL2 expression, and interaction between WER and GL3/EGL3 is demonstrated in plant cells using FRET analysis. CPC also interacts with GL3/EGL3 in plant cells, suggesting a possible competition with WER in interacting with GL3/EGL3. We are able to show that negative regulation of WER expression by CPC is not required for hair cell fate specification and that the critical factor in epidermal cell fate specification is the ratio of the level of CPC to the level of WER.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
The following mutant lines have been described in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana): wer-1 (Lee and Schiefelbein, 1999), cpc (Wada et al., 1997), gl3-1 (Koornneef et al., 1982), egl3-1 (Zhang et al., 2003), gl2-1 (Koornneef, 1981), and scm-2 (Kwak et al., 2005). Plants harboring 35Spro:CPC, WERpro:GFP, MYB23pro:GUS, GL2pro:GUS, and CPCpro:GUS were also described previously (Masucci et al., 1996; Wada et al., 1997, 2002; Lee and Schiefelbein, 1999; Kirik et al., 2001). The enhancer trap lines were obtained from the Arabidopsis Biological Resource Center.
For plant growth, seeds were surface sterilized, germinated, and grown vertically on agarose-solidified medium containing mineral nutrients at 22°C under continuous light conditions (Schiefelbein and Somerville, 1990).
Histochemical GUS Staining
GUS activity was histochemically defined by staining 4-d-old seedlings as described (Lee and Schiefelbein, 2002).
Quantitative Real-Time Reverse Transcription -PCR
Quantitative real-time PCR was performed using SYBR Premix EX Taq (Takara) with an Mx3000P real-time PCR machine (Stratagene) as described previously (Kang et al., 2009). One microgram of total RNA extracted from the root tips of 4-d-old seedlings was used for the reverse transcription. Each experiment was repeated three to six times, and each time the experiment included triplicate samples.
EMSA
EMSA was carried out as described earlier (Ryu et al., 2005).
Yeast One-Hybrid Assay
To test GWBSI and GWBSII in vivo, we used the Matchmaker yeast one-hybrid system (Clontech) according to the manufacturer’s manual. Three tandem copies of GWBSI, GWBSII, or point-mutated GWBSs were synthesized and inserted into the reporter vectors pHISi and pLacZi. A reporter strain was made by integrating these reporter genes into the yeast strain YM4271 genome. WER was expressed in this reporter strain, and the reporter gene activity was assessed as described previously (Ryu et al., 2005).
Protein Expression and Purification
Expression of the WER protein in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) and purification of the protein using His∣Bind Quick 900 cartridges were described previously (Ryu et al., 2005).
Confocal Microscopy
Seedlings were counterstained with 5 μg mL−1 propidium iodide for 5 min, and GFP expression was examined using a LSM510 Meta confocal microscope (Carl Zeiss) as described (Lee and Schiefelbein, 1999).
FRET Analysis
The coding regions of GL3, EGL3, and CO were PCR amplified and fused to YFP, and then these recombinant genes were fused to 35S promoter (35Spro:YFP-GL3, 35Spro:YFP-EGL3, and 35Spro:CO-YFP). The coding regions of WER, CPC, CO, and AtHAP5a were also PCR amplified and fused to CFP and then fused to 35S promoter (35Spro:WER-CFP, 35Spro:CPC-CFP, 35Spro:CO-CFP, and 35Spro:AtHAP5a-CFP). The sequences of the PCR-amplified genes were confirmed. One of the YFP-fused genes and one of the CFP-fused genes were introduced together into 4-week-old Nicotiana benthamiana leaves as described previously (Ratcliff et al., 2001). After 48 h of incubation, leaf epidermal cells exhibiting coexpression of both fluorescent proteins were bleached five times in the acceptor YFP channel with a 514-nm argon laser. Before and after photobleaching, CFP fluorescence intensity was monitored by confocal microscopy (LSM510 Meta; Carl Zeiss), and FRET efficiency was calculated as follows: E = {(CFP signal after photobleaching – CFP signal before photobleaching)/CFP signal after photobleaching} × 100.
Arabidopsis Protoplast Transient Expression Assay
Single cell-based functional analyses were conducted using transient expression of the Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplast system as described previously (Yoo et al., 2007). For the reporter construct, the 2,032-bp genomic DNA region immediately upstream from the translation start site of the GL2 gene was PCR amplified. The promoter was fused to a luciferase reporter gene (GL2pro:LUC). We used three effectors: WER, GL3, and CPC. Genomic DNA fragments of their coding regions were PCR amplified and inserted into a plant expression vector containing 35S promoter. Twenty thousand protoplasts were transfected with 40 μg of plasmid DNA and different combinations of the reporter (GL2pro:Luc), effectors (35Spro:WER, 35Spro:GL3, and 35Spro:CPC), and the internal control (UBQ10pro:rLUC). An empty vector was used as a negative control. The luciferase reporter activity was determined by the Dual Luciferase Assay System (Promega).
The sequences of the PCR-amplified DNA fragments were confirmed.
Overexpression of WER and CPC
Genomic DNA fragments of the WER and CPC coding regions were PCR amplified and cloned into pJET1.2/blunt cloning vector (Fermentas). Their sequences were confirmed. Their genomic DNA fragments were inserted into pCB302 containing 5× UAS promoter and the nos terminator (Song et al., 2008). Plant transformation was achieved by electroporating constructs (UASpro:WER and UASpro:CPC) into the Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain GV3101 followed by introduction into Arabidopsis using the floral dip method as described previously (Clough and Bent, 1998). UASpro:WER and UASpro:CPC were introduced into the enhance trap lines by genetic crosses.
Other Constructs
For WERpro:GUS and WERpro:WER, the GUS gene or the genomic DNA fragment of the WER coding region was inserted between a 1.4-kb 5′ flanking region DNA fragment or a 1.1-kb 3′ flanking region DNA fragment, respectively, from the WER coding region. The resulting construct was introduced into Arabidopsis as described previously (Clough and Bent, 1998).
Primers
The sequences of the primers used in this experiment are listed in Supplemental Table S1.
Sequence data from this article can be found in the Arabidopsis Genome Initiative or GenBank/EMBL databases under the following accession numbers: CPC (At2g46410), EGL3 (At1g63650), GL2 (At1g79840), GL3 (At5g41315), MYB23 (At5g40330), and WER (At5g14750).
Supplemental Data
The following materials are available in the online version of this article.
Supplemental Figure S1. WER interacts with GWBSI and GWBSII for transcriptional activation in yeast.
Supplemental Figure S2. Complementation of the wer mutant phenotype using the WER gene including the 1.4-kb 5′ region DNA fragment and the 1.1-kb 3′ flanking region DNA fragment.
Supplemental Figure S3. The 1.2-kb GL2 promoter region containing GWBSI and GWBSII is sufficient for the proper expression of GL2.
Supplemental Table S1. Primer sequences used in these experiments.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Kyoung Hee Nam for critical reading of the manuscript.
References
- Almudi I, Corominas M, Serras F. (2010) Competition between SOCS36E and Drk modulates Sevenless receptor tyrosine kinase activity. J Cell Sci 123: 3857–3862 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhardt C, Lee MM, Gonzalez A, Zhang F, Lloyd A, Schiefelbein J. (2003) The bHLH genes GLABRA3 (GL3) and ENHANCER OF GLABRA3 (EGL3) specify epidermal cell fate in the Arabidopsis root. Development 130: 6431–6439 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhardt C, Zhao M, Gonzalez A, Lloyd A, Schiefelbein J. (2005) The bHLH genes GL3 and EGL3 participate in an intercellular regulatory circuit that controls cell patterning in the Arabidopsis root epidermis. Development 132: 291–298 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand AH, Perrimon N. (1993) Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development 118: 401–415 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clough SJ, Bent AF. (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16: 735–743 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Digiuni S, Schellmann S, Geier F, Greese B, Pesch M, Wester K, Dartan B, Mach V, Srinivas BP, Timmer J, et al. (2008) A competitive complex formation mechanism underlies trichome patterning on Arabidopsis leaves. Mol Syst Biol 4: 217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan L, Janmaat K, Willemsen V, Linstead P, Poethig S, Roberts K, Scheres B. (1993) Cellular organisation of the Arabidopsis thaliana root. Development 119: 71–84 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esch JJ, Chen M, Sanders M, Hillestad M, Ndkium S, Idelkope B, Neizer J, Marks MD. (2003) A contradictory GLABRA3 allele helps define gene interactions controlling trichome development in Arabidopsis. Development 130: 5885–5894 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galway ME, Masucci JD, Lloyd AM, Walbot V, Davis RW, Schiefelbein JW. (1994) The TTG gene is required to specify epidermal cell fate and cell patterning in the Arabidopsis root. Dev Biol 166: 740–754 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao Y, Gong X, Cao W, Zhao J, Fu L, Wang X, Schumaker KS, Guo Y. (2008) SAD2 in Arabidopsis functions in trichome initiation through mediating GL3 function and regulating GL1, TTG1 and GL2 expression. J Integr Plant Biol 50: 906–917 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseloff J. (1999) GFP variants for multispectral imaging of living cells. Methods Cell Biol 58: 139–151 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe KM, Watson RJ. (1991) Nucleotide preferences in sequence-specific recognition of DNA by c-myb protein. Nucleic Acids Res 19: 3913–3919 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung CY, Lin Y, Zhang M, Pollock S, Marks MD, Schiefelbein J. (1998) A common position-dependent mechanism controls cell-type patterning and GLABRA2 regulation in the root and hypocotyl epidermis of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 117: 73–84 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang YH, Kirik V, Hulskamp M, Nam KH, Hagely K, Lee MM, Schiefelbein J. (2009) The MYB23 gene provides a positive feedback loop for cell fate specification in the Arabidopsis root epidermis. Plant Cell 21: 1080–1094 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidner C, Sundaresan V, Roberts K, Dolan L. (2000) Clonal analysis of the Arabidopsis root confirms that position, not lineage, determines cell fate. Planta 211: 191–199 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirik V, Schnittger A, Radchuk V, Adler K, Hülskamp M, Bäumlein H. (2001) Ectopic expression of the Arabidopsis AtMYB23 gene induces differentiation of trichome cells. Dev Biol 235: 366–377 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koornneef M. (1981) The complex syndrome of ttg mutants. Arabidopsis Inf Serv 18: 45–51 [Google Scholar]
- Koornneef M, Dellaert LW, van der Veen JH. (1982) EMS- and radiation-induced mutation frequencies at individual loci in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. Mutat Res 93: 109–123 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshino-Kimura Y, Wada T, Tachibana T, Tsugeki R, Ishiguro S, Okada K. (2005) Regulation of CAPRICE transcription by MYB proteins for root epidermis differentiation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 46: 817–826 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurata T, Ishida T, Kawabata-Awai C, Noguchi M, Hattori S, Sano R, Nagasaka R, Tominaga R, Koshino-Kimura Y, Kato T, et al. (2005) Cell-to-cell movement of the CAPRICE protein in Arabidopsis root epidermal cell differentiation. Development 132: 5387–5398 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwak SH, Schiefelbein J. (2007) The role of the SCRAMBLED receptor-like kinase in patterning the Arabidopsis root epidermis. Dev Biol 302: 118–131 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwak SH, Shen R, Schiefelbein J. (2005) Positional signaling mediated by a receptor-like kinase in Arabidopsis. Science 307: 1111–1113 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee MM, Schiefelbein J. (1999) WEREWOLF, a MYB-related protein in Arabidopsis, is a position-dependent regulator of epidermal cell patterning. Cell 99: 473–483 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee MM, Schiefelbein J. (2001) Developmentally distinct MYB genes encode functionally equivalent proteins in Arabidopsis. Development 128: 1539–1546 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee MM, Schiefelbein J. (2002) Cell pattern in the Arabidopsis root epidermis determined by lateral inhibition with feedback. Plant Cell 14: 611–618 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y, Schiefelbein J. (2001) Embryonic control of epidermal cell patterning in the root and hypocotyl of Arabidopsis. Development 128: 3697–3705 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd AM, Schena M, Walbot V, Davis RW. (1994) Epidermal cell fate determination in Arabidopsis: patterns defined by a steroid-inducible regulator. Science 266: 436–439 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masucci JD, Rerie WG, Foreman DR, Zhang M, Galway ME, Marks MD, Schiefelbein JW. (1996) The homeobox gene GLABRA2 is required for position-dependent cell differentiation in the root epidermis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Development 122: 1253–1260 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morohashi K, Grotewold E. (2009) A systems approach reveals regulatory circuitry for Arabidopsis trichome initiation by the GL3 and GL1 selectors. PLoS Genet 5: e1000396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne CT, Zhang F, Lloyd AM. (2000) GL3 encodes a bHLH protein that regulates trichome development in Arabidopsis through interaction with GL1 and TTG1. Genetics 156: 1349–1362 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D, Salser SJ, Yamamoto KR. (1988) A movable and regulable inactivation function within the steroid binding domain of the glucocorticoid receptor. Cell 54: 1073–1080 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prunet N, Morel P, Negrutiu I, Trehin C. (2009) Time to stop: flower meristem termination. Plant Physiol 150: 1764–1772 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratcliff F, Martin-Hernandez AM, Baulcombe DC. (2001) Tobacco rattle virus as a vector for analysis of gene function by silencing. Plant J 25: 237–245 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu KH, Kang YH, Park YH, Hwang I, Schiefelbein J, Lee MM. (2005) The WEREWOLF MYB protein directly regulates CAPRICE transcription during cell fate specification in the Arabidopsis root epidermis. Development 132: 4765–4775 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellmann S, Schnittger A, Kirik V, Wada T, Okada K, Beermann A, Thumfahrt J, Jürgens G, Hülskamp M. (2002) TRIPTYCHON and CAPRICE mediate lateral inhibition during trichome and root hair patterning in Arabidopsis. EMBO J 21: 5036–5046 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiefelbein JW, Somerville C. (1990) Genetic control of root hair development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 2: 235–243 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M, Lee MM, Lin Y, Gish L, Schiefelbein J. (2007) Distinct and overlapping roles of single-repeat MYB genes in root epidermal patterning. Dev Biol 311: 566–578 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solano R, Nieto C, Paz-Ares J. (1995) MYB.Ph3 transcription factor from Petunia hybrida induces similar DNA-bending/distortions on its two types of binding site. Plant J 8: 673–682 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song SK, Hofhuis H, Lee MM, Clark SE. (2008) Key divisions in the early Arabidopsis embryo require POL and PLL1 phosphatases to establish the root stem cell organizer and vascular axis. Dev Cell 15: 98–109 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stracke R, Werber M, Weisshaar B. (2001) The R2R3-MYB gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4: 447–456 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg C, Willemsen V, Hage W, Weisbeek P, Scheres B. (1995) Cell fate in the Arabidopsis root meristem determined by directional signalling. Nature 378: 62–65 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada T, Kurata T, Tominaga R, Koshino-Kimura Y, Tachibana T, Goto K, Marks MD, Shimura Y, Okada K. (2002) Role of a positive regulator of root hair development, CAPRICE, in Arabidopsis root epidermal cell differentiation. Development 129: 5409–5419 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada T, Tachibana T, Shimura Y, Okada K. (1997) Epidermal cell differentiation in Arabidopsis determined by a Myb homolog, CPC. Science 277: 1113–1116 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker AR, Davison PA, Bolognesi-Winfield AC, James CM, Srinivasan N, Blundell TL, Esch JJ, Marks MD, Gray JC. (1999) The TRANSPARENT TESTA GLABRA1 locus, which regulates trichome differentiation and anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis, encodes a WD40 repeat protein. Plant Cell 11: 1337–1350 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenkel S, Turck F, Singer K, Gissot L, Le Gourrierec J, Samach A, Coupland G. (2006) CONSTANS and the CCAAT box binding complex share a functionally important domain and interact to regulate flowering of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 18: 2971–2984 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wester K, Digiuni S, Geier F, Timmer J, Fleck C, Hülskamp M. (2009) Functional diversity of R3 single-repeat genes in trichome development. Development 136: 1487–1496 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoo SD, Cho YH, Sheen J. (2007) Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts: a versatile cell system for transient gene expression analysis. Nat Protoc 2: 1565–1572 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang F, Gonzalez A, Zhao M, Payne CT, Lloyd A. (2003) A network of redundant bHLH proteins functions in all TTG1-dependent pathways of Arabidopsis. Development 130: 4859–4869 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao M, Morohashi K, Hatlestad G, Grotewold E, Lloyd A. (2008) The TTG1-bHLH-MYB complex controls trichome cell fate and patterning through direct targeting of regulatory loci. Development 135: 1991–1999 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]