Abstract
In the title compound, C20H16N2OS, the aniline substituent essentially coplanar with the benzothiazole moiety (with an r.m.s. deviation of all fitted non-H atoms of 0.0612 Å). The phenol group is almost perpendicular to the benzothiazolylaniline group, with an interplanar angle of 88.36 (2)°. In the crystal, molecules aggregate as centrosymmetric dimers by pairs of O—H⋯N hydrogen bonds. C—H⋯O contacts and N—H⋯π(arene) interactions also occur.
Related literature
For general information about rhenium-supported radio-pharmaceuticals, see: Gerber et al. (2011 ▶). For the crystal structure of 4-(1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)-N-(2-pyridylmethyl)aniline monohydrate, see: Su et al. (2009 ▶). For graph-set analysis of hydrogen bonds, see: Etter et al. (1990 ▶); Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C20H16N2OS
M r = 332.41
Monoclinic,
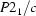
a = 13.3260 (4) Å
b = 5.7940 (1) Å
c = 24.2246 (6) Å
β = 121.546 (1)°
V = 1593.99 (7) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.21 mm−1
T = 200 K
0.44 × 0.17 × 0.11 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008 ▶) T min = 0.929, T max = 1.000
15126 measured reflections
3953 independent reflections
3272 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.018
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.033
wR(F 2) = 0.092
S = 1.03
3953 reflections
221 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.30 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2010 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2010 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SIR97 (Altomare et al., 1999 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and Mercury (Macrae et al., 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97 and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811051580/gg2063sup1.cif
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811051580/gg2063Isup2.cdx
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811051580/gg2063Isup3.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811051580/gg2063Isup4.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg is the centroid of the C31–C36 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1⋯N1i | 0.82 | 1.95 | 2.7459 (14) | 164 |
| C26—H26⋯O1i | 0.95 | 2.48 | 3.3645 (16) | 156 |
| N2—H72⋯Cgii | 0.82 (2) | 2.61 (2) | 3.4024 (14) | 163.0 (19) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 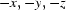 ; (ii)
; (ii) 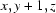 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mr Jason Kopp for helpful discussions.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
In our continuous efforts to create new radio-pharmaceuticals (Gerber et al., 2011), we attempted the coordination reaction of a potentially multidentate ligand towards a rhenium precursor upon which a crystalline reaction product was obtained. The crystal structure analysis showed the presence of the free ligand only whose molecular and crystal structure has not been reported to date. The structure of 4-(1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)-N-(2-pyridylmethyl) aniline monohydrate is noted in the literature (Su et al., 2009).
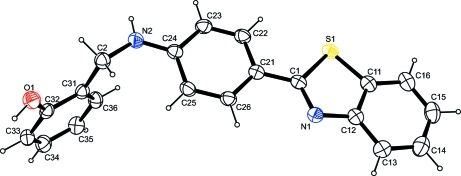
The benzothiazolyl system and the attached aniline system are nearly co-planar (r.m.s. of all fitted non-hydrogen atoms including the nitrogen bound methylene group = 0.0612 Å). The phenolic substituent, however, adopts a nearly perpendicular orientation with respect to the rest of the molecule, with an interplanar angle of 88.36 (2)° between the two least-squares planes defined by both moieties (Fig. 1).
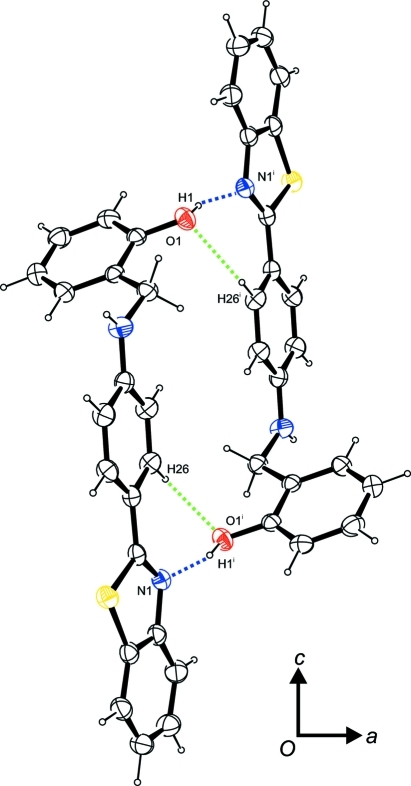
In the crystal, classical hydrogen bonds of the O–H···N type as well as C–H···O contacts (whose range lies by more than 0.1 Å below the sum of van-der-Waals radii of the atoms participating) are observed. The latter are supported by one of the hydrogen atoms of the central phenyl ring. In total, the molecules are connected to centrosymmetric dimers by these two interactions. In terms of graph-set analysis (Etter et al., 1990; Bernstein et al., 1995), the descriptor for these contacts is R22(18)R22(24) on the unitary level. The nitrogen-bonded hydrogen atom forms a hydrogen bond to the aromatic system of the phenolic moiety, connecting the molecules to chains along the crystallographic b axis. Metrical parameters about these contacts as well as information about their symmetry is listed in Table 1. The shortest intercentroid distance between two aromatic systems was measured at 4.6019 (10) Å and is apparent between the phenyl unit of the benzothiazole moiety and the central C6 aromatic ring (Fig 2.)
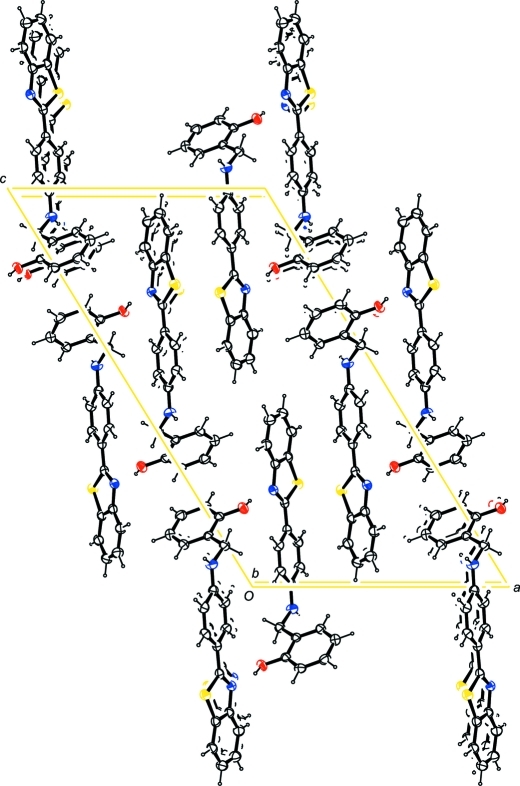
The packing of the title compound in the crystal structure is shown in Figure 3.
Experimental
A mixture of 2.00 g of 4-aminobenzoic acid and 1.33 g of 2-aminothiophenol was added to hot polyphosphoric acid. The stirring solution was heated to 220 °C for four hours. The reaction solution was cooled to room temperature and poured into a 10% K2CO3 solution. The yellow precipitate which formed was filtered and dried under vacuum, yielding 4-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)benzenamine. A solution of 1.0 g of this product dissolved in 25 cm3 of methanol was added to a 25 cm3 methanol solution of 2-hydroxybenzaldehyde (0.4 g). The solution was refluxed for three hours after which it was cooled to room temperature and stirred overnight. An excess of NaBH4 (2.0 g) was added in portions with stirring and the mixture was left to stir at room temperature overnight. The solvent was removed by evaporation and 50 cm3 of water was added. HCl was added to adjust the pH to 6, resulting in the formation of a light yellow precipitate which was filtered and dried under vacuum. Crystals suitable for the X-ray diffraction study were obtained upon the attempted synthesis of a rhenium coordination compound in ethanol.
Refinement
Carbon-bound H atoms were placed in calculated positions (C—H 0.95 Å for aromatic carbon atoms, C—H 0.99 Å for the methylene group) and were included in the refinement in the riding model approximation, with U(H) set to 1.2Ueq(C). The H atom of the hydroxyl group was allowed to rotate with a fixed angle around the C—O bond to best fit the experimental electron density (HFIX 147 in the SHELX program suite (Sheldrick, 2008)), with U(H) set to 1.5Ueq(O). The nitrogen-bound H atom was located on a difference Fourier map and refined freely with isotropic parameters.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, with atom labels and anisotropic displacement ellipsoids (drawn at 50% probability level).
Fig. 2.
Intermolecular contacts, viewed along [0 1 0]. Blue dashed lines indicate classical hydrogen bonds of the O–H···N type, green dashed lines indicate C–H···O contacts. Symmetry operator: i -x, -y, -z.
Fig. 3.
Molecular packing of the title compound, viewed along [0 1 0] (anisotropic displacement ellipsoids drawn at 50% probability level).
Crystal data
| C20H16N2OS | F(000) = 696 |
| Mr = 332.41 | Dx = 1.385 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71069 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 7469 reflections |
| a = 13.3260 (4) Å | θ = 3.1–28.3° |
| b = 5.7940 (1) Å | µ = 0.21 mm−1 |
| c = 24.2246 (6) Å | T = 200 K |
| β = 121.546 (1)° | Platelet, brown |
| V = 1593.99 (7) Å3 | 0.44 × 0.17 × 0.11 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 3953 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3272 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.018 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 28.3°, θmin = 1.9° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008) | h = −17→17 |
| Tmin = 0.929, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −4→7 |
| 15126 measured reflections | l = −31→32 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.033 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.092 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.03 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0417P)2 + 0.6757P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3953 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 221 parameters | Δρmax = 0.30 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.42147 (3) | 0.68632 (6) | 0.257240 (17) | 0.03011 (10) | |
| O1 | −0.15303 (8) | 0.05617 (17) | −0.19880 (5) | 0.0317 (2) | |
| H1 | −0.1951 | −0.0563 | −0.2167 | 0.048* | |
| N1 | 0.31149 (9) | 0.30173 (19) | 0.24291 (5) | 0.0264 (2) | |
| N2 | 0.09494 (11) | 0.5026 (2) | −0.06249 (6) | 0.0317 (3) | |
| H72 | 0.1055 (16) | 0.621 (4) | −0.0774 (9) | 0.049 (5)* | |
| C1 | 0.32433 (11) | 0.4656 (2) | 0.20995 (6) | 0.0246 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.00373 (12) | 0.3473 (2) | −0.10753 (6) | 0.0291 (3) | |
| H2A | −0.0541 | 0.4367 | −0.1460 | 0.035* | |
| H2B | −0.0380 | 0.2851 | −0.0869 | 0.035* | |
| C11 | 0.44852 (11) | 0.5440 (2) | 0.32639 (7) | 0.0284 (3) | |
| C12 | 0.38217 (11) | 0.3396 (2) | 0.30904 (6) | 0.0273 (3) | |
| C13 | 0.39226 (13) | 0.1916 (3) | 0.35715 (7) | 0.0343 (3) | |
| H13 | 0.3484 | 0.0521 | 0.3461 | 0.041* | |
| C14 | 0.46741 (14) | 0.2528 (3) | 0.42110 (7) | 0.0398 (3) | |
| H14 | 0.4755 | 0.1534 | 0.4544 | 0.048* | |
| C15 | 0.53187 (13) | 0.4580 (3) | 0.43785 (7) | 0.0390 (3) | |
| H15 | 0.5821 | 0.4962 | 0.4823 | 0.047* | |
| C16 | 0.52407 (12) | 0.6063 (3) | 0.39127 (7) | 0.0344 (3) | |
| H16 | 0.5683 | 0.7454 | 0.4028 | 0.041* | |
| C21 | 0.26744 (11) | 0.4708 (2) | 0.13979 (6) | 0.0254 (3) | |
| C22 | 0.27965 (12) | 0.6609 (2) | 0.10797 (7) | 0.0295 (3) | |
| H22 | 0.3280 | 0.7866 | 0.1328 | 0.035* | |
| C23 | 0.22327 (12) | 0.6691 (2) | 0.04174 (7) | 0.0305 (3) | |
| H23 | 0.2331 | 0.8004 | 0.0215 | 0.037* | |
| C24 | 0.15098 (11) | 0.4861 (2) | 0.00317 (6) | 0.0266 (3) | |
| C25 | 0.14071 (12) | 0.2928 (2) | 0.03483 (7) | 0.0296 (3) | |
| H25 | 0.0941 | 0.1652 | 0.0101 | 0.035* | |
| C26 | 0.19777 (12) | 0.2865 (2) | 0.10154 (6) | 0.0286 (3) | |
| H26 | 0.1896 | 0.1541 | 0.1220 | 0.034* | |
| C31 | 0.04626 (11) | 0.1472 (2) | −0.12987 (6) | 0.0250 (3) | |
| C32 | −0.03897 (11) | 0.0004 (2) | −0.17724 (6) | 0.0258 (3) | |
| C33 | −0.00650 (12) | −0.1827 (2) | −0.20165 (6) | 0.0306 (3) | |
| H33 | −0.0649 | −0.2806 | −0.2340 | 0.037* | |
| C34 | 0.11211 (13) | −0.2216 (3) | −0.17839 (7) | 0.0351 (3) | |
| H34 | 0.1348 | −0.3467 | −0.1949 | 0.042* | |
| C35 | 0.19715 (12) | −0.0793 (3) | −0.13149 (7) | 0.0343 (3) | |
| H35 | 0.2781 | −0.1073 | −0.1155 | 0.041* | |
| C36 | 0.16400 (11) | 0.1046 (3) | −0.10779 (6) | 0.0302 (3) | |
| H36 | 0.2228 | 0.2031 | −0.0759 | 0.036* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.02935 (17) | 0.02586 (17) | 0.03296 (18) | −0.00579 (12) | 0.01480 (14) | −0.00429 (13) |
| O1 | 0.0241 (5) | 0.0321 (5) | 0.0340 (5) | −0.0054 (4) | 0.0118 (4) | −0.0005 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0234 (5) | 0.0264 (5) | 0.0283 (5) | −0.0015 (4) | 0.0129 (4) | −0.0011 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0387 (7) | 0.0273 (6) | 0.0282 (6) | −0.0073 (5) | 0.0170 (5) | −0.0016 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0209 (6) | 0.0219 (6) | 0.0310 (6) | −0.0003 (4) | 0.0137 (5) | −0.0028 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0284 (6) | 0.0303 (7) | 0.0277 (6) | −0.0025 (5) | 0.0139 (5) | −0.0015 (5) |
| C11 | 0.0235 (6) | 0.0298 (7) | 0.0322 (7) | 0.0015 (5) | 0.0147 (5) | −0.0033 (5) |
| C12 | 0.0227 (6) | 0.0293 (6) | 0.0297 (6) | 0.0017 (5) | 0.0137 (5) | −0.0015 (5) |
| C13 | 0.0342 (7) | 0.0341 (7) | 0.0349 (7) | 0.0010 (6) | 0.0182 (6) | 0.0023 (6) |
| C14 | 0.0390 (8) | 0.0489 (9) | 0.0314 (7) | 0.0077 (7) | 0.0184 (6) | 0.0055 (7) |
| C15 | 0.0305 (7) | 0.0531 (9) | 0.0281 (7) | 0.0051 (6) | 0.0117 (6) | −0.0059 (6) |
| C16 | 0.0264 (6) | 0.0396 (8) | 0.0342 (7) | 0.0003 (6) | 0.0138 (6) | −0.0093 (6) |
| C21 | 0.0231 (6) | 0.0245 (6) | 0.0300 (6) | 0.0003 (5) | 0.0149 (5) | −0.0010 (5) |
| C22 | 0.0281 (6) | 0.0244 (6) | 0.0332 (7) | −0.0057 (5) | 0.0142 (6) | −0.0027 (5) |
| C23 | 0.0328 (7) | 0.0252 (6) | 0.0339 (7) | −0.0044 (5) | 0.0177 (6) | 0.0018 (5) |
| C24 | 0.0275 (6) | 0.0246 (6) | 0.0299 (6) | 0.0004 (5) | 0.0166 (5) | −0.0007 (5) |
| C25 | 0.0352 (7) | 0.0237 (6) | 0.0314 (7) | −0.0058 (5) | 0.0186 (6) | −0.0043 (5) |
| C26 | 0.0346 (7) | 0.0228 (6) | 0.0321 (7) | −0.0030 (5) | 0.0201 (6) | −0.0009 (5) |
| C31 | 0.0266 (6) | 0.0275 (6) | 0.0216 (6) | −0.0027 (5) | 0.0131 (5) | 0.0017 (5) |
| C32 | 0.0253 (6) | 0.0294 (6) | 0.0211 (6) | −0.0027 (5) | 0.0111 (5) | 0.0038 (5) |
| C33 | 0.0344 (7) | 0.0301 (7) | 0.0236 (6) | −0.0045 (5) | 0.0128 (5) | −0.0019 (5) |
| C34 | 0.0400 (8) | 0.0370 (8) | 0.0309 (7) | 0.0022 (6) | 0.0204 (6) | −0.0031 (6) |
| C35 | 0.0279 (7) | 0.0420 (8) | 0.0337 (7) | 0.0009 (6) | 0.0165 (6) | −0.0007 (6) |
| C36 | 0.0260 (6) | 0.0350 (7) | 0.0274 (6) | −0.0046 (5) | 0.0124 (5) | −0.0023 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| S1—C11 | 1.7275 (14) | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| S1—C1 | 1.7526 (13) | C21—C26 | 1.3999 (18) |
| O1—C32 | 1.3627 (15) | C21—C22 | 1.4018 (18) |
| O1—H1 | 0.8200 | C22—C23 | 1.3709 (19) |
| N1—C1 | 1.3082 (17) | C22—H22 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C12 | 1.3866 (16) | C23—C24 | 1.4083 (18) |
| N2—C24 | 1.3616 (17) | C23—H23 | 0.9500 |
| N2—C2 | 1.4459 (17) | C24—C25 | 1.4038 (18) |
| N2—H72 | 0.82 (2) | C25—C26 | 1.3804 (19) |
| C1—C21 | 1.4547 (18) | C25—H25 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C31 | 1.5098 (19) | C26—H26 | 0.9500 |
| C2—H2A | 0.9900 | C31—C36 | 1.3893 (18) |
| C2—H2B | 0.9900 | C31—C32 | 1.4022 (17) |
| C11—C16 | 1.3995 (19) | C32—C33 | 1.3890 (19) |
| C11—C12 | 1.4042 (19) | C33—C34 | 1.391 (2) |
| C12—C13 | 1.3954 (19) | C33—H33 | 0.9500 |
| C13—C14 | 1.380 (2) | C34—C35 | 1.381 (2) |
| C13—H13 | 0.9500 | C34—H34 | 0.9500 |
| C14—C15 | 1.397 (2) | C35—C36 | 1.388 (2) |
| C14—H14 | 0.9500 | C35—H35 | 0.9500 |
| C15—C16 | 1.378 (2) | C36—H36 | 0.9500 |
| C15—H15 | 0.9500 | ||
| C11—S1—C1 | 89.62 (6) | C22—C21—C1 | 121.28 (11) |
| C32—O1—H1 | 109.4 | C23—C22—C21 | 121.38 (12) |
| C1—N1—C12 | 111.32 (11) | C23—C22—H22 | 119.3 |
| C24—N2—C2 | 124.65 (12) | C21—C22—H22 | 119.3 |
| C24—N2—H72 | 117.2 (13) | C22—C23—C24 | 121.07 (12) |
| C2—N2—H72 | 117.3 (13) | C22—C23—H23 | 119.5 |
| N1—C1—C21 | 124.99 (11) | C24—C23—H23 | 119.5 |
| N1—C1—S1 | 114.74 (10) | N2—C24—C25 | 122.93 (12) |
| C21—C1—S1 | 120.26 (9) | N2—C24—C23 | 119.26 (12) |
| N2—C2—C31 | 115.06 (11) | C25—C24—C23 | 117.81 (12) |
| N2—C2—H2A | 108.5 | C26—C25—C24 | 120.60 (12) |
| C31—C2—H2A | 108.5 | C26—C25—H25 | 119.7 |
| N2—C2—H2B | 108.5 | C24—C25—H25 | 119.7 |
| C31—C2—H2B | 108.5 | C25—C26—C21 | 121.54 (12) |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 107.5 | C25—C26—H26 | 119.2 |
| C16—C11—C12 | 121.61 (13) | C21—C26—H26 | 119.2 |
| C16—C11—S1 | 128.92 (11) | C36—C31—C32 | 118.40 (12) |
| C12—C11—S1 | 109.46 (10) | C36—C31—C2 | 123.94 (12) |
| N1—C12—C13 | 125.32 (12) | C32—C31—C2 | 117.63 (11) |
| N1—C12—C11 | 114.83 (12) | O1—C32—C33 | 123.46 (12) |
| C13—C12—C11 | 119.84 (13) | O1—C32—C31 | 115.67 (12) |
| C14—C13—C12 | 118.43 (14) | C33—C32—C31 | 120.80 (12) |
| C14—C13—H13 | 120.8 | C32—C33—C34 | 119.49 (12) |
| C12—C13—H13 | 120.8 | C32—C33—H33 | 120.3 |
| C13—C14—C15 | 121.28 (15) | C34—C33—H33 | 120.3 |
| C13—C14—H14 | 119.4 | C35—C34—C33 | 120.40 (13) |
| C15—C14—H14 | 119.4 | C35—C34—H34 | 119.8 |
| C16—C15—C14 | 121.42 (14) | C33—C34—H34 | 119.8 |
| C16—C15—H15 | 119.3 | C34—C35—C36 | 119.79 (13) |
| C14—C15—H15 | 119.3 | C34—C35—H35 | 120.1 |
| C15—C16—C11 | 117.41 (14) | C36—C35—H35 | 120.1 |
| C15—C16—H16 | 121.3 | C35—C36—C31 | 121.11 (12) |
| C11—C16—H16 | 121.3 | C35—C36—H36 | 119.4 |
| C26—C21—C22 | 117.56 (12) | C31—C36—H36 | 119.4 |
| C26—C21—C1 | 121.16 (11) | ||
| C12—N1—C1—C21 | 176.61 (11) | C1—C21—C22—C23 | −178.02 (12) |
| C12—N1—C1—S1 | −1.79 (14) | C21—C22—C23—C24 | −0.1 (2) |
| C11—S1—C1—N1 | 1.11 (10) | C2—N2—C24—C25 | 11.3 (2) |
| C11—S1—C1—C21 | −177.37 (11) | C2—N2—C24—C23 | −169.07 (13) |
| C24—N2—C2—C31 | −93.43 (16) | C22—C23—C24—N2 | 178.90 (13) |
| C1—S1—C11—C16 | 178.94 (13) | C22—C23—C24—C25 | −1.4 (2) |
| C1—S1—C11—C12 | −0.09 (10) | N2—C24—C25—C26 | −178.83 (13) |
| C1—N1—C12—C13 | −177.24 (13) | C23—C24—C25—C26 | 1.5 (2) |
| C1—N1—C12—C11 | 1.72 (15) | C24—C25—C26—C21 | −0.1 (2) |
| C16—C11—C12—N1 | 180.00 (12) | C22—C21—C26—C25 | −1.5 (2) |
| S1—C11—C12—N1 | −0.88 (14) | C1—C21—C26—C25 | 178.10 (12) |
| C16—C11—C12—C13 | −1.0 (2) | N2—C2—C31—C36 | 2.59 (19) |
| S1—C11—C12—C13 | 178.14 (10) | N2—C2—C31—C32 | −175.35 (11) |
| N1—C12—C13—C14 | 179.44 (13) | C36—C31—C32—O1 | −177.51 (11) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.5 (2) | C2—C31—C32—O1 | 0.55 (16) |
| C12—C13—C14—C15 | 0.3 (2) | C36—C31—C32—C33 | −0.21 (18) |
| C13—C14—C15—C16 | −0.8 (2) | C2—C31—C32—C33 | 177.85 (12) |
| C14—C15—C16—C11 | 0.3 (2) | O1—C32—C33—C34 | 177.58 (12) |
| C12—C11—C16—C15 | 0.5 (2) | C31—C32—C33—C34 | 0.49 (19) |
| S1—C11—C16—C15 | −178.40 (11) | C32—C33—C34—C35 | −0.1 (2) |
| N1—C1—C21—C26 | −3.99 (19) | C33—C34—C35—C36 | −0.5 (2) |
| S1—C1—C21—C26 | 174.33 (10) | C34—C35—C36—C31 | 0.8 (2) |
| N1—C1—C21—C22 | 175.56 (12) | C32—C31—C36—C35 | −0.44 (19) |
| S1—C1—C21—C22 | −6.12 (17) | C2—C31—C36—C35 | −178.37 (13) |
| C26—C21—C22—C23 | 1.5 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| Cg is the centroid of the C31–C36 ring. |
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1···N1i | 0.82 | 1.95 | 2.7459 (14) | 164. |
| C26—H26···O1i | 0.95 | 2.48 | 3.3645 (16) | 156. |
| N2—H72···Cgii | 0.82 (2) | 2.61 (2) | 3.4024 (14) | 163.0 (19) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y, −z; (ii) x, y+1, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: GG2063).
References
- Altomare, A., Burla, M. C., Camalli, M., Cascarano, G. L., Giacovazzo, C., Guagliardi, A., Moliterni, A. G. G., Polidori, G. & Spagna, R. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 115–119.
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Bruker (2008). SADABS Bruker Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2010). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Etter, M. C., MacDonald, J. C. & Bernstein, J. (1990). Acta Cryst. B46, 256–262. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Gerber, T. I. A., Betz, R., Booysen, I. N., Potgieter, K. C. & Mayer, P. (2011). Polyhedron, 30, 1739–1745.
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Su, Z.-H., Wang, Q.-Z., Teng, L. & Zhang, Y. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811051580/gg2063sup1.cif
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811051580/gg2063Isup2.cdx
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811051580/gg2063Isup3.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811051580/gg2063Isup4.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report