Abstract
The ocular insert represents a significant advancement in the therapy of eye disease. Ocular inserts are defined as sterile, thin, multilayered, drug-impregnated, solid or semisolid consistency devices placed into the cul-de-sac or conjuctival sac, whose size and shape are especially designed for ophthalmic application. They are composed of a polymeric support that may or may not contain a drug. The drug can later be incorporated as dispersion or a solution in the polymeric support. They offer several advantages as increased ocular residence and sustained release of medication into the eye. The insert includes a body portion sized to position within a lachrymal canaliculus of the eyelid. The inserts are classified according to their solubility as insoluble, soluble, or bioerodible inserts. The release of drug from the insert depends upon the diffusion, osmosis, and bioerosion of the drug, and this article is an attempt to present a brief about this newer drug delivery system.
Keywords: Bioerosion, diffusion, membrane, ocular inserts
INTRODUCTION
Ocular drug delivery is one of the most challenging tasks faced by Pharmaceutical researchers. Major barriers in ocular medication are the ability to maintain a therapeutic level of the drug at the site of action for a prolonged duration. The anatomy, physiology, and biochemistry of the eye is such that it is impervious to foreign substances, therefore, it is a challenge for the formulator to pass through the protective barriers of the eye without causing any permanent tissue damage. The introduction of new sensitive diagnostic techniques and therapeutic agents necessitates the development of a successful and advanced ocular drug delivery system.[1]
The therapeutic efficacy of an ocular drug can be improved by increasing its contact time with the corneal surface. For increasing the contact time viscosity-enhancers are added in preparations or the drug is formulated in a water-insoluble ointment formulation, to sustain the duration of drug-eye contact. Unfortunately, these dosage forms give only a marginally sustained drug-eye contact than eye drop solutions and do not yield constant drug bioavailability. Repeated medications are still required throughout the therapy.[2] The conventional ocular dosage forms for the delivery of drugs are:
Eye drops (solution, suspension)
Ophthalmic Ointments
The eye drop dosage form is easy to administer, but has inherent drawback that most of the instilled volume is eliminated from the pre-corneal area resulting in poor bioavailability, ranging from 1 – 10% of the total administered dose.[3–5] This occurs mainly due to conjunctival absorption, rapid solution drainage by gravity, induced lachrymation, blinking reflex, low corneal permeability, and normal tear turnover. To overcome this, many ocular drugs are used in high concentrations. This causes both ocular and systemic side-effects.[6] The frequent instillations of eye drops are necessary to maintain a continuous sustained therapeutic drug level, which results in a massive and unpredictable dose of medication.[7] Ocular inserts, biodegradable polymeric systems, and collagen shields are being developed in order to attain better ocular bioavailability and sustained drug action.[8]
The following trends are in existence nowadays:[9]
Membrane-bound ocular inserts (biodegradable and non-biodegradable), for example, Ocuserts;, Alza Corp.
Mucoadhesives dosage forms (ocular films or sheath, ophthaCoil, polymer rods, HEMA hydrogel, Dispersion, polysulfone capillary fiber).
Collagen shields, cyclodextrine-based system, ophthalmic rods (artificial tear inserts, e.g., Lacrisert®).
Filter paper strips (drug-impregnated filter paper strips for staining agent — sodium fluorescent, lissamine green, and rose Bengal).
Soft contact lenses, implants, flexible coils, and cotton pledgets (Drug presoaked hydrogel type, polymeric gels).
Ocular inserts offer an attractive alternative approach to the difficult problem of limited pre-corneal drug residence time.[10] Disposition and elimination of a therapeutic agent depends on the physicochemical properties as well as the relevant ocular anatomy and physiology.[11] The successful design of a drug delivery system, therefore, requires a complete knowledge of the drug moiety and the constraints to delivery offered by the ocular route of administration.
Ocular Inserts as an Ocular Sustained Release Drug Delivery System
The main objective of the ophthalmic inserts is to increase the contact time between the preparation and the conjunctival tissue, to ensure a sustained release suited for topical or systemic treatment.[12,13] The advantages of ocular inserts over the traditional ophthalmic preparation can be summarized as follows:[7,13,14]
Increased ocular residence, hence, prolonged drug activity and higher bioavailability with respect to standard vehicles.
Release of drugs at a slow, constant rate.
Accurate dosing (insert contains a precise dose, which is fully retained at the administration site).
Reduction of systemic absorption.
Better patient compliance, due to reduced frequency of administration and less incidence of visual and systemic side-effects.
Possibility of targeting internal ocular tissues through non-corneal (conjunctival scleral) routes.
Increased shelf life with respect to aqueous solutions.
Exclusion of preservatives, thus reducing the risk of sensitivity reactions.
Incorporation of various novel chemical / technological approaches, such as pro-drugs, mucoadhesives, permeation enhancers, micro particulates, salts acting as a buffer.
All of the benefits listed above cannot be present in a single, ideal device. Each type of insert is a compromise between the desirable properties inherent to solid dosage forms and negative constraints possessed by the structure and components of the insert, fabrication costs, and physical / physiological constraints of the application site. It also bears some disadvantages, which are as follows:[7,13,14]
A major disadvantage of ocular inserts resides in their ‘solidity’, that is, they are felt by the (often oversensitive) patients as an extraneous body in the eye. This may constitute a difficult physical and psychological barrier to patient compliance.
Their movement around the eye, in rare instances, the simple removal is made more difficult by unwanted migration of the insert to the upper fornix.
The occasional unintentional loss during sleep or while rubbing the eyes.
Their interference with vision.
Difficulty in placement of the ocular inserts (and removal, for insoluble types).
Classification of Ocular Inserts (Based upon their solubility)
The foreign-body sensation leads to discomfort, which causes poor-patient compliance, excessive lachrymation that accompanies irritation, dilutes the drug, and reduces its concentration.[16] A properly designed ocular insert will minimize the sensation caused by its insertion and has [Figure 1]:[17]
Figure 1.
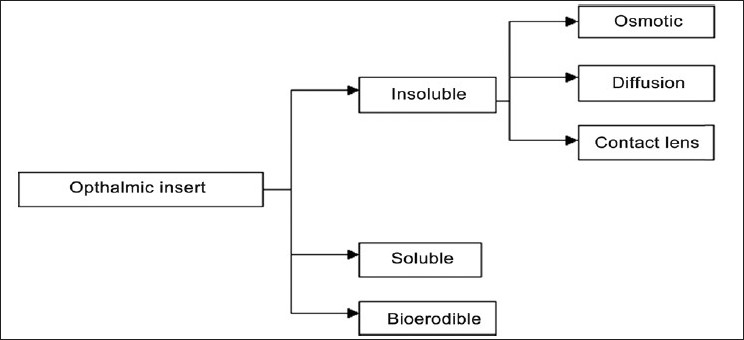
Classification of ocular inserts[15]
Ease of handling and insertion.
Lack of expulsion while wearing it.
Reproducibility of release kinetics (Zero-order drug delivery).
Applicable to variety of drugs.
No interference with vision and oxygen permeability.
Sterility.
Stability.
Ease of manufacturing.
Insoluble Ophthalmic Inserts
Diffusion inserts
The diffusion systems are composed of a drug reservoir enclosed in a specially designed semi-permeable or microporous membrane, which allows the drug to diffuse from the reservoir [Figure 2]. The drug release from such a system is controlled by the lachrymal fluid, which permeates through the membrane. A sufficient internal pressure is achieved to drive the drug out from the reservoir. The drug delivery rate is controlled by diffusion through the membrane.[18]
Figure 2.
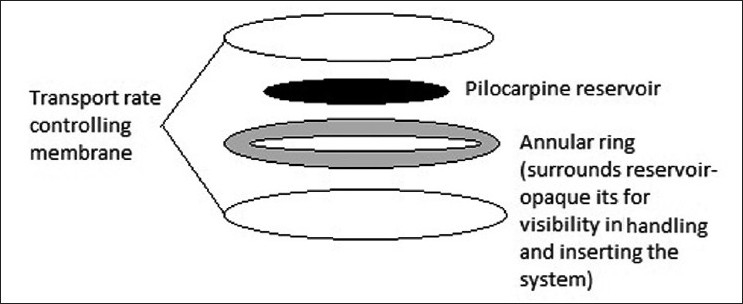
Diffusional inserts
Osmotic inserts
The osmotic inserts are generally divided into two types, in the first case the central part of the insert is surrounded by a peripheral part.[19] The central part can be composed of a single reservoir, which is composed of the drug with or without an osmotic solute dispersed through a polymeric matrix, so that the drug is surrounded by the polymer as discrete small deposits.[20] In the second case, the drug and the osmotic solutes are placed in two separate compartments, the drug reservoir is surrounded by an elastic impermeable membrane and the osmotic solute reservoir surrounded by a semi-permeable membrane. The peripheral part of these osmotic inserts are comprised of a film covering made of an insoluble semi-permeable polymer.[21] The tear fluid diffuses into the peripheral deposits through the semi-permeable polymeric membrane, wets them, and induces their dissolution. The solubilized deposits create a hydrostatic pressure against the polymer matrix, and cause its rupture in the form of apertures. Rge drug is then released through these apertures from the deposits near the surface of the device.[22] The release of drug through the osmotic insert follows the zero-order drug release profile.
Soft contact lenses
These structure are made up of a covalently cross-linked hydrophilic or hydrophobic polymer that forms a three-dimensional matrix capable of retaining water, aqueous solution or solid components [6].When a hydrophilic contact lens is soaked in a drug solution, it absorbs the drug, but does not deliver the drug as precisely as that provided by other non-soluble ophthalmic systems. The drug release from the system is generally very rapid at the beginning and then declines exponentially with time. The release rate can be decreased by adding the drug homogeneously during the manufacture or by adding a hydrophobic component.[23] Contact lenses have good prospects as ocular drug delivery systems.[24]
Soluble Ophthalmic Inserts
Soluble inserts correspond to the oldest class of ocular inserts, which offer the advantage of being wholly soluble, so they need not be removed from the site of application, thus, limiting the interventions to insertion only.[25] They are further categorized:
Based on natural polymers, for example, collagen.
Based on synthetic or semi-synthetic polymers.
The therapeutic agent is absorbed by soaking the insert in a solution containing the drug, and drying and rehydrating it before use in the eye. The amount of drug contained will depend upon the capacity of the binding agent, concentration of the drug solution into which the insert is soaked, and the duration of soaking.[26] The soluble ophthalmic inserts are easily processed by conventional methods – slow evaporating extrusion, compression or injection molding. The release of the drug takes place when tears penetrate into the insert. This induces drug release by diffusion and forms a layer of gel around the core of the insert. This gelification causes further release of the drug, but it is still controlled by diffusion. The release rate, J, is derived from Fick's law, which yields the following expression.[27]
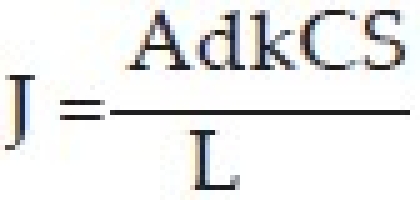
A – do not Surface area of the membrane
k – Diffusion coefficient of the drug
L – Membrane thickness
CS – Drug solubility in water
d – Diffusion coefficient of the Ocuserts membrane
As all the terms on the right hand side of the above equation are constant, the release rate of the device is also constant.
Bioerodible Ophthalmic Inserts
The bioerodible inserts are composed of homogeneous dispersion of a drug which can be included in or not included in the hydrophobic coat made of bioerodible polymers, which is impermeable to the drug. Successfully used bioerodible materials are the poly (orthoesters) and poly (orthocarbonates). Drug release from such a system is due to the contact of the device with the tear fluid, inducing a superficial bioerosion of the matrix.[28]
Mechanism of Drug Release from Ocular Inserts
Diffusion
In this mechanism, the drug is released continuously at a controlled rate through the membrane into the tear fluid. If the insert is formed of a solid non-erodible body having pores and drug is in a dispersed form, the drug release takes place via diffusion through the pores. Controlled release of the drug can be maintained by a gradual dissolution of the solid dispersed drug in the matrix, as a result of the inward diffusion of aqueous solutions. In a soluble device, true dissolution occurs mainly through polymer swelling. In swelling-controlled devices, the active agent is homogeneously dispersed in a glassy polymer. As glassy polymers are essentially drug-impermeable, no diffusion occurs through the dry matrix. When the insert is placed in the eye, water from the tear fluid begins to penetrate the matrix, swelling occurs, and consequently polymer chain relaxation occurs and drug diffusion takes place. The dissolution of the matrix, followed by the swelling process depends on the polymer structure. A linear amorphous polymer dissolves at a faster rate than a cross-linked or partially crystalline polymer.[29,30]
Osmosis
In the Osmosis mechanism, the insert is made of a transverse impermeable elastic membrane, which divides the interior of the insert into two compartments, first and second; the first compartment is surrounded by a semi-permeable membrane and the impermeable elastic membrane, and the second compartment is surrounded by an impermeable material and the elastic membrane. There is a drug release orifice in the impermeable membrane of the insert. The first compartment contains a solute that cannot pass through the semi-permeable membrane and the second compartment provides a reservoir for the drug, which is in liquid or gel form. When the insert is placed in the aqueous environment of the eye, water diffuses in the first compartment, which stretches the elastic membrane to expand the first compartment and contract the second compartment so that the drug is forced to come out through the drug release orifice.[30]
Bioerosion
In the bioerosion mechanism, the insert is comprised of a matrix of bioerodible material in which the drug is dispersed. Contact of the insert with the tear fluid results in controlled sustained release of the drug by bioerosion of the matrix. The drug is dispersed uniformly throughout the matrix, but it is believed that a more controlled release is obtained if the drug is superficially concentrated in the matrix. In truly erodible or E-type devices, the drug release is controlled by a chemical or enzymatic hydrolytic reaction that leads to polymer solubilization, or degrades to smaller, water-soluble molecules. These polymers may undergo bulk or surface hydrolysis, which displays zero-order release kinetics; provided the devices maintain a constant surface geometry and the drug is poorly water-soluble.[30]
Evaluation of Ocular Polymeric Films
Thickness of film
Film thickness is measured by using the Dial caliper at different points of the formulation and the mean value is calculated.[31]
Drug content uniformity
To check the uniformity of the drug in the film inserts, it is cut at different places, and each film is placed in vials containing 5 ml phosphate buffer of pH 7.4, and it is shaken to extract the drug from the piece of film. One milliliter from this solution is taken and diluted. Then this solution is analyzed with the help of a spectrophotometer, using pH 7.4 phosphate buffer as a blank.[32]
The drug content was calculated using the following formula:
![]()
As = Absorbance of sample solution.
Ar =Absorbance of standard solution.
Cr =Concentration of drug in Standard solution.
The same procedure is adopted for all batches of films in triplicate and the mean drug content and standard deviation of variance are calculated.
Uniformity of weight
The weight variation test is done by weighing three patches cut from different places of the same formulation and their individual weights are determined by using the digital balance. Next, their mean value is calculated. The standard deviation of weight variation is computed from the mean value.[33]
Percentage moisture absorption
The percentage moisture absorption is checked by the physical stability or integrity of the ocular inserts. The inserts are weighed and then placed in desiccators containing 100 ml of saturated solution of aluminum chloride and 79.5% humidity is maintained. After three days the ocular inserts are taken out and reweighed. The percentage moisture absorbed is calculated using the formula.[34]

Percentage moisture loss
The percentage moisture loss is done to check out the integrity of the film in dry conditions. The ocular inserts are weighed and kept in desiccators containing anhydrous calcium chloride. After three days, the ocular inserts are taken out and reweighed; the percentage of moisture loss is then calculated by using the formula.[34]

In-vitro drug release
In-vitro release studies are carried out using a bi-chamber donor-receiver compartment model design made by using a transparent and regenerated cellulose type of semi-permeable membrane. It is tied at one end of an open cylinder, which acts as the donor compartment. The ocular insert is placed inside the donor compartment. The semi permeable membrane is used to create ocular in vivo conditions, like a corneal epithelial barrier, which simulates the tear volume; 0.7 m1 of distilled water is placed in a donar compartment and maintained at the same level throughout the study. The surface of the membrane is in contact with the reservoir compartment containing 25 ml of phosphate buffer having a pH of 7.4. It is stirred continuously using a magnetic stirrer. Samples of 1 ml are withdrawn from the receptor compartment at periodic intervals and replaced with an equal volume of distilled water. The withdrawn sample is analyzed at 246 nm against the reference standard using a pH 7.4 phosphate buffer as a blank on a UV / visible spectrophotometer.[32]
In-vivo drug release rate study
The inserts are sterilized by using ultraviolet (UV) radiation before the in vivo study. Inserts are taken in a Petri dish with 100 mg of pure drug, which is spread as a thin layer. This Petri dish along with polyethylene bags and forceps is placed in a UV sterilization chamber (hood). The inserts and other materials are exposed to UV radiation for one hour. After sterilization, the inserts are transferred into a polyethylene bag with the help of the forceps, inside the sterilization chamber itself. The pure drugs, which are sterilized along with the inserts are analyzed for potency by the UV spectrophotometer, after suitable dilution with a pH 7.4 phosphate buffer. Male albino rabbits, weighing between 2.5 – 3.0 kg are required for the experiment. The animals are kept in individual cages in order to get them adapted to the laboratory conditions, for 1 day. The inserts are inserted into one of the eyes of seven albino rabbits at the same time, and the other eye of the seven rabbits serves as the control. The inserts are removed carefully at 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, and 24 hours and analyzed for drug content . The remaining drug is subtracted from the initial drug content of the insert. This will give the amount of drug released in the rabbits’ eyes. After one week of wash period the experiment is repeated twice, as before.[32]
Accelerated stability studies
The accelerated stability studies are carried out to predict the degradation that occurs over prolonged periods of storage, at normal conditions. The films of the insert are taken in a separate Petri dish and are kept at three different temperatures 400°C, 500°C, and 600°C, and the time taken for degradation of the ocular inserts is checked.[35,36]
Test for sterility
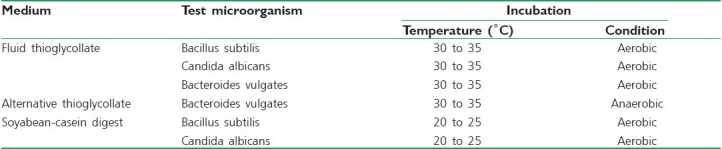
It is done for detecting the presence of viable forms of microorganisms in the preparation. The working conditions should be monitored regularly by taking the samples of air and surface of the working area, and there should not be any cross contamination. The test is based on the principle that if the nutrient media is provided to the microorganisms and they are kept in a favorable condition of temperature, the microorganisms will grow and their presence is indicated by the turbidity in medium. The batch size taken for sterility testing in case of ophthalmic and other non-injectable preparations is as follows:[37]
Incubate portions of the (a) Fluid Thioglycollate medium / Alternate Thioglycollate medium at 30°C to 35°C and (b) Soyabean casein digest medium at 20°C to 25°C for not less than seven days; no growth of microorganisms occurs [Table 1].
Table 1.
The number of containers required for sterility testing

Growth promotion test
Test the autoclaved load of each lot of the medium for its growth-promoting quality by separately inoculating duplicate test containers of each medium with about 100 viable microorganisms of each of the strains, as mentioned a little later in the text. The test media are satisfactory if clear evidence of the growth appears in all inoculated media containers within seven days, the test is invalid if there is inadequate growth response [Table 2].[38]
Table 2.
The test microorganisms, incubation condition, medium, and temperature required for the growth promotion test
CONCLUSION
The main efforts in ocular drug delivery during the past two decades has been on the design of systems, to prolong the residence time of topically applied drugs in the conjuctival sac. Various new approaches like ocular inserts, collagen shield, in-situ activated gel formation, non-corneal route of ocular drug penetration, and nanoparticle-based polymeric solutions and gels are being developed by the pharmaceutical scientists. The advantages gained by ocular inserts are many for the treatment of eye-related problems, but only few gain commercial acceptance. This is because of the high cost of these inserts and reluctance of the patient to use unfamiliar types of ophthalmic medication.
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: Nil.
REFERENCES
- 1.Katz IM. Shaped ophthalmic inserts for treating dry eyes syndrome. US Patent. 1982;4:343–787. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cohen EM, Grim WM, Harwood RJ, Mehta GN. Solid state ophthalmic medication. US Patent. 1979;4:179–597. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chrai SS, Robinson JR. Ocular evaluation of methylcellulose vehicle in albino rabbits. J Pharm Sci. 1974;63:1218–23. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600630810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chrai SS, Makoid MC, Erikson SP, Robinson JR. Drop size and initial dosing frequency problems of topically applied ophthalmic drugs. J Pharm Sci. 1974;64:333–8. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600630304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zaki I, Fitzgerald P, Hardy JG, Wilson CG. Comparison of effect of viscosity on the precorneal residence of solution in rabbit and man. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1986;38:463–6. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1986.tb04611.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lee VH, Robinson JF. Review: Topical ocular drug delivery; recent developments and future challenges. J Ocul Pharmacol. 1976;2:67. doi: 10.1089/jop.1986.2.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Saettone MF, Salminen L. Ocular inserts for topical delivery. Adv Drug Del Rev. 1995;16:95–106. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Schoenwald RD. Ocular Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics. In: Mitra AK, editor. Ophthalmic drug delivery systems. New York: Marcel Dekker; 1993. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Davis JL, Gilger BC, Robinson MR. Novel approaches to ocular drug delivery. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2004;6:195–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Neefe CW. Contact lens for ocular drug delivery. US Patent. 1974;3:786–812. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gibaldi M, Perrier D. 2nd ed. New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc; 1993. Pharmacokinetics. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Robinson JC. Ocular Anatomy and Physiology Relevant to Ocular Drug Delivery. In: Mitra AK, editor. Ophthalmic drug delivery systems. New York: Marcel Dekker; 1993. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chien YW. 2nd ed. New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc; 1992. Novel drug delivery systems. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Khar RK, Vyas SP. 1st ed. New Delhi: C.B.S. Publishers and Distributors, Inc; 2002. Targeted and controlled drug delivery novel carrier systems. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mainardes RM, Urban MC, Cinto PO, Chaud MV. Colloidal carriers for ophthalmic drug delivery. Curr Drug Targets. 2005;6:363–71. doi: 10.2174/1389450053765914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Friedrich SW, Saville BA, Cheng YL, Rootman DS. Pharmacokinetic differences betweenocular inserts and eyedrops. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 1996;12:5–18. doi: 10.1089/jop.1996.12.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Michaels AS, Guilloid MS. Osmotic bursting drug delivery device. US Patent. 1979;4:177–256. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gurtler F, Gurny R. Patent literature review of ophthalmic inserts. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 1995;21:1. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bloomfield SE, Miyata T, Dunn MW, Bueser N, Stenzel KH, Rubin AL. Soluble gentamacin ophthalmic inserts as a delivery system. Arch Opthalmol. 1978;96:885–7. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1978.03910050487020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ahmed I, Gokhale RD, Shah MV, Patton TF. Physicochemical determinants of drug diffusion across the conjunctiva, sclera and cornea. J Pharm Sci. 1987;76:583–6. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600760802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Eller MG, Schoenwald RD, Dixson JA, Segarra T, Barfknecht CF. Optimization models for corneal penetration of ethoxyzolamide analogues. J Pharm Sci. 1985;74:155–60. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600740210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Huang HS, Schoenwald RD, Lac JL. Corneal penetration behavior of b blocking agents II. J Pharm Sci. 1983;72:1272–9. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600721109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Grass GM, Robinson JR. Mechanisms of corneal drug penetration II: Ultra structural analysis of potential pathways for drug movements. J Pharm Sci. 1988;77:15–23. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600770104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Alvarez-Lorenzo C, Hiratani H. Soft contact lenses capable of sustained delivery of timolol. J Pharm Sci. 2002;91:2182–92. doi: 10.1002/jps.10209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Patton TF, Robinson JR. Quantitative precorneal disposition of topically applied pilocarpine nitrate in rabbit eye. J Pharm Sci. 1976;65:1295–301. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600650909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Himmelstein KJ, Guvenir I, Palton TP. Preliminary Pharmacokinetics model of pilocarpine uptake and distribution in the eye. J Pharm Sci. 1978;67:603–6. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600670507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Mitra AK. Opthalmic drug delivery. In: Tyle P, editor. Drug Delivery Devices. New York: Marcel Dekker; 1998. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Jain NK. New Delhi: C.B.S. Publisher and distributer, Inc; 2004. Controlled and novel drug delivery. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Korsmeyer RW, Peppas NA. Macromolecular and modeling aspects of swelling-controlled systems. In: Roseman TJ, Mansdorf SZ, editors. Controlled Release Delivery Systems. New York: Marcel Dekker; 1983. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Darougar S. Patent literature review of ocular inserts. US Patent. 1999;6:264–971. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sahane NK, Banarjee SK, Gaikwad DD, Jadhav SL, Throat RM. Ocular Inserts- A Review. Drug Inven Tod. 2010;2:57–64. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Rall TW. Drug used in the treatment of asthma. In: Goodman GA, editor. Goodman and Gilman's the Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York: Palmer Taylor Maxwell Macmillan pergamon Publishing Corporation; 1990. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Insel PA. Anlgesic-antiphyretic and anti-inflammatory agents and drugs employed in the treatment of Gout. In: Goodman GA, editor. Goodman and Gilman's the Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Health profession divisions; 1996. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Brogden RN, Heel RC, Pakes GE, Speight TM, Avery GS. Diclofenac sodium: A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutics use in rheumatic diseases and pain of varying origin. Drugs. 1980;20:48. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198020010-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lee VH, Li SY, Sasaki H, Saettone MF, Chetoni P. Influence of drug release rate on systemic timolol absorption from polymeric ocular inserts in the pigmented rabbit. J Ocul Pharmacol. 1994;10:421–9. doi: 10.1089/jop.1994.10.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Grass GM, Cobby J, Makoid MC. Ocular Delivery of pilocarpine from erodible matrices. J Pharm Sci. 1984;73:618–21. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600730509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Indian Pharmacopoeia. Delhi: Controller of Publication; 1996. Govenment of India Ministry of health and family welfare. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hughes PM, Mitra AK. Overview of ocular drug delivery and Iatrogenic ocular cytopathologies. In: Mitra AK, editor. Ophthalmic Drug Delivery Systems. New York: Marcel Dekker; 1993. [Google Scholar]


