Abstract
In mice infected sublethally with Listeria monocytogenes, fibrin is deposited at low levels within hepatic tissue, where it functions protectively by limiting bacterial growth and suppressing hemorrhagic pathology. Here we demonstrate that mice infected with lethal doses of L. monocytogenes produce higher levels of fibrin and display evidence of systemic coagulopathy (i.e., thrombocytopenia, fibrinogen depletion, and elevated levels of thrombin-antithrombin complexes). When the hepatic bacterial burden exceeds 1 × 106 CFU, levels of hepatic fibrin correlate with the bacterial burden, which also correlates with levels of hepatic mRNA encoding the hemostatic enzyme factor XI (FXI). Gene-targeted FXI-deficient mice show significantly improved survival upon challenge with high doses of L. monocytogenes and also display reduced levels of hepatic fibrin, decreased evidence of coagulopathy, and diminished cytokine production (interleukin-6 [IL-6] and IL-10). While fibrin limits the bacterial burden during sublethal listeriosis in wild-type mice, FXI-deficient mice display a significantly improved capacity to restrain the bacterial burden during lethal listeriosis despite their reduced fibrin levels. They also show less evidence of hepatic necrosis. In conjunction with suboptimal antibiotic therapy, FXI-specific monoclonal antibody 14E11 improves survival when administered therapeutically to wild-type mice challenged with high doses of L. monocytogenes. Together, these findings demonstrate the utility of murine listeriosis as a model for dissecting qualitative differences between protective and pathological host responses and reveal novel roles for FXI in exacerbating inflammation and pathogen burden during a lethal bacterial infection.
INTRODUCTION
Sepsis, defined as a systemic inflammatory response to generalized infection, is a major cause of morbidity worldwide. In its more severe forms, sepsis progresses to multiple-organ failure, shock, and/or death (5). The incidence of severe sepsis has increased steadily in the United States over recent decades, and mortality rates exceeding 30% are common despite tremendous research expenditures and significant advances in antimicrobial therapy and critical care (1, 5, 33). Experimental therapeutics have failed to demonstrate efficacy in a large number of phase II and phase III clinical trials despite promising preclinical data from animal models (8, 33). The clinical trial failures highlight the exceptionally complex pathogenesis of sepsis, which appears to be dominated by the multifaceted and poorly understood cross talk between the inflammatory and coagulation systems that accompanies the host response to infection (21, 36).
The classical “extrinsic” coagulation cascade is driven by the exposure of plasma to tissue factor, which facilitates the activation of factor VII (FVII), FIX, FX, and prothrombin, in turn leading to the generation of thrombin, the activation of platelets, and the feedback activation of factors XI, V, and VIII, further accelerating thrombin generation and, ultimately, prompting the deposition of insoluble fibrin, a structural component of the blood clot (10). Tissue factor is constitutively expressed by extravascular cells (30, 39) and can be upregulated on leukocytes during infection (21, 30, 39). During severe sepsis, the activation of coagulation pathways is insufficiently balanced by endogenous anticoagulation and fibrinolysis, thus prompting disseminated intravascular coagulation, multifocal thrombosis, consumptive coagulopathy, and hemorrhage (17, 19–21). Therapeutic anticoagulation would seem to be a rational approach to mitigating sepsis-associated coagulopathy. Indeed, the only therapeutic approved for the treatment of sepsis in the United States is recombinant human activated protein C (APC), a well-characterized natural anticoagulant (4, 18). However, APC therapy is associated with a high risk of serious bleeding, and a recent meta-analysis concluded that patients with severe sepsis should not be treated with APC (22). The efficacy of other anticoagulants, including highly selective antagonists of tissue factor, FX, or thrombin, may be limited by similar bleeding complications (2, 43); like APC, all these treatments target factors known to be critical for controlling bleeding and maintaining normal hemostasis.
APC possesses both anticoagulant and anti-inflammatory activities. The therapeutic efficacy of APC in animal models of sepsis may be derived primarily from its anti-inflammatory activity (16, 18, 34). As such, mutant versions of APC with reduced anticoagulant activity are under development (16). However, optimal therapy for sepsis may require treatments that target dysregulations of both the inflammatory and coagulation systems. While the targeting of the extrinsic coagulation pathway is likely to increase the risk of bleeding in septic patients, relatively few studies have assessed roles for the “intrinsic” or “contact-activated” coagulation pathway during sepsis. The initiating elements of the intrinsic pathway are not thought to play a major role during hemostasis in response to vascular trauma, but infectious agents are known to trigger both the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways (27, 38).
One key component of the intrinsic pathway is activated FXI (FXIa), a protease produced by the liver that circulates in plasma as an inactive homodimer (32). The FXI zymogen can be activated by FXIIa, thrombin, or FXIa (11, 13, 26, 42). Once formed, FXIa activates FIX, which facilitates the activation of FX, in turn leading to thrombin production. FXIa thus amplifies and sustains thrombin production (11, 13, 26, 42). Humans with a severe FXI deficiency rarely bleed spontaneously but often exhibit moderate injury-related bleeding tendencies, particularly in tissues with high levels of fibrinolytic activity (35). Gene-targeted mice lacking the capacity to produce FXI are healthy and fertile and do not display increased bleeding tendencies in response to tail tip amputation or large surgical procedures (12, 32). However, both FXI-deficient mice and primates treated with FXI-blocking antibodies are significantly protected against experimentally induced thrombosis (12, 32). Together, these observations suggest that FXI is not critical for normal hemostasis but may contribute to thrombosis. Interestingly, it was recently shown that FXI-deficient mice display a survival advantage during peritoneal sepsis induced by cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) (40). The improved survival was associated with a reduced evidence of systemic coagulopathy (40). Bacterial burdens did not appear to differ significantly between FXI-deficient and wild-type mice, but that analysis was hampered by the nature of the CLP model, which causes infection by a complex mixture of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial species.
To further investigate the utility of FXI antagonism as a potential treatment for septic peritonitis and to further define the underlying mechanisms of protection, here we evaluate the response of FXI-deficient mice to a single bacterial pathogen. Specifically, we evaluate intraperitoneal infection with Listeria monocytogenes, a Gram-positive bacterium that causes severe sepsis in humans, most commonly in pregnant women, newborns, and the immunocompromised (29, 44). In addition to extending findings to a distinct sepsis model performed by a second laboratory, a potential advantage of listeriosis over CLP is that the microbiology and host response to infection have been exceptionally well characterized in the mouse model of human listeriosis (29, 44). The facultative intracellular bacteria disseminate to spleen and liver tissues, where most organisms are killed by phagocytes activated by infection-induced inflammatory responses. However, some of the bacteria evade these innate immune defenses and multiply intracellularly. When sublethal doses of L. monocytogenes are employed, CD8 T cells ultimately confer protection against the intracellular bacteria.
In a previous study, we determined that fibrin, a product of the common coagulation pathway, performs critical protective roles during sublethal listeriosis in mice (25). Specifically, fibrin functions to limit bacterial growth in the liver while also restraining hepatic bleeding (25). Here we demonstrate that FXI deficiency does not prevent the production of protective fibrin during sublethal listeriosis in mice. Moreover, we establish that FXI deficiency improves survival and reduces coagulopathy when mice are inoculated with higher, lethal doses of L. monocytogenes. Additionally, we report that FXI deficiency reduces bacterial burden, systemic inflammation, and hepatic pathology during lethal listeriosis. In combination with the previous report employing the CLP model (40), our data support the notion that FXI can contribute substantively to septic pathology in mice and thus constitutes a rational target for sepsis therapeutics.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Mice.
All experimental mice were bred in a specific-pathogen-free facility at the Trudeau Institute. They were matched for age and sex and were typically infected at between 6 and 8 weeks of age. C57BL/6 wild-type mice were purchased from the Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME) and bred after embryo rederivation. FXI-deficient mice had been backcrossed 9 generations to C57BL/6 (12). After intercrossing with C57BL/6 wild-type mice, heterozygote matings were used to generate experimental littermate FXI+/+, FXI+/−, and FXI−/− mice. Fibrinogen-deficient mice were generously supplied by Jay Degen (Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center) (37). All animal studies were conducted in accordance with Trudeau Institute Animal Care and Use Committee guidelines.
Bacterial infections and treatments.
Stocks of L. monocytogenes (strain EGD; supplied by Robert North, Trudeau Institute) were prepared after passage through C57BL/6 mice (25). The 50% lethal dose (LD50) of this stock was 2 × 106 CFU when administered via the intraperitoneal route to wild-type C57BL/6 mice (25). For experimental infections, frozen bacteria were diluted with saline to the desired dose and administered in a 200-μl volume. The number of bacteria in the inoculating dose was confirmed by plating onto tryptic soy broth agar. The actual number of bacteria delivered to mice inoculated with low doses of L. monocytogenes ranged from 0.6 × 105 to 1 × 105 CFU, whereas the number delivered to mice inoculated with high doses of L. monocytogenes ranged from 2.5 × 106 to 2.7 × 106 CFU.
Where indicated, wild-type C57BL/6 mice received a single dose of 5 mg ampicillin (Sandoz) subcutaneously on day 2 after intraperitoneal inoculation with L. monocytogenes (3). Some animals simultaneously received 100 μg of FXI-specific monoclonal antibody (MAb) (clone 14E11), which interferes with the activation of FXI by FXIIa (6).
Measurements of survival and bacterial burden.
Mice were monitored and weighed daily. Unresponsive or recumbent animals were considered moribund and euthanized. For measurements of the bacterial burden, tissues were collected after mice were euthanized by carbon dioxide narcosis. The number of CFU was measured by homogenizing tissues in saline, plating serial dilutions onto tryptic soy broth agar, incubating dilutions overnight at 37°C, and counting colonies.
Measurements of inflammation and coagulation.
Hepatic fibrin levels were quantified by Western blotting using fibrin-specific MAb 350 as described previously (15); the limit of detection was 15 ng/mg of tissue, and samples that fell below this limit were assigned values of 10 ng/mg of tissue. Levels of hepatic mRNA encoding interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-10, IL-1-beta, tumor necrosis factor alpha, gamma interferon, and FXI were measured by real-time PCR as described previously (15). The primers and probe used for quantifying FXI mRNA were FXI forward primer GCCCTGTTAAAACTGGAATCAGC, FXI reverse primer CGTTTCTATCTCCTTTGGAAGGC, and FXI probe CACAGATTTTCAGCGGCCAATATGCC. After normalization to levels of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), mRNA levels were expressed as log10-fold changes relative to levels measured in uninfected wild-type C57BL/6 mice (15). To enumerate platelet numbers, blood was collected by cardiac puncture from mice that received 500 units of heparin intravenously just prior to euthanasia. After the dilution of blood in saline containing 5 mM EDTA, platelets were measured by using a Coulter Counter (Beckman). Levels of thrombin-antithrombin (TAT) complexes in plasma were measured by an Enzygnost TAT microimmunoassay (Dade Behring). IL-6 levels in plasma were determined by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using OptEIA kits (BD Biosciences). Levels of fibrinogen in plasma were measured by Western blotting using rabbit anti-human fibrinogen (diluted 1:2,250 in phosphate-buffered saline [PBS]–Tween; Dako) and goat anti-rabbit IgG-horseradish peroxidase (HRP) (diluted 1:10,000 in PBS-Tween; Dako). Standard curves for fibrinogen assays were constructed by using plasma from naïve C57BL/6 mice, which was assigned a value of 2 mg/ml fibrinogen.
Histology.
Tissues were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin, embedded in paraffin, sectioned, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. The pathological foci in each section were counted and characterized according to the extent of hepatocellular damage. Results depict the number of foci in each of the following four categories: type 1, small to medium midzone collections of mixed inflammatory cells with no observable tissue damage; type 2, medium-sized areas of inflammation with evidence of mild hepatocellular damage, limited to sporadic acidophilic bodies and occasional necrotic hepatocytes; type 3, medium to large inflammatory foci interspersed with significant (20 to 50% coverage) hepatocellular damage and coagulation necrosis; type 4, large foci dominated by contiguous coagulation necrosis (50 to 100% coverage). The representative photomicrographs depict a ×200 magnification.
Statistics.
Statistical analyses were performed by using the computer program Prism 4.0 (GraphPad Software, Inc.). Survival data were analyzed by log rank tests. Levels of CFU, fibrinogen, TAT, cytokines, and platelets were compared by Student's t tests. Fibrin levels and histological scoring were analyzed by nonparametric Mann-Whitney tests. Box and whisker plots depict the maximum, minimum, median, 25th percentile, and 75th percentile.
RESULTS
Hepatic levels of fibrin and FXI mRNA correlate after inoculation of lethal doses of L. monocytogenes.
Our previous studies demonstrated that fibrin functions protectively when wild-type mice are inoculated intraperitoneally with a sublethal dose of L. monocytogenes; wild-type mice survived inoculation with 1 × 105 CFU L. monocytogenes, whereas gene-targeted fibrinogen-deficient mice and wild-type mice anticoagulated pharmacologically with coumadin each succumbed after inoculation with this dose of bacteria (25). The liver appeared to be a particularly important site of fibrin-mediated host defense, as hepatic hemorrhage was evident in the infected fibrin(ogen)-deficient and anticoagulated mice but not in the infected wild-type control mice (25). Given the critical protective role of fibrin during sublethal listeriosis, and given the pathological potential of excessive fibrin deposition during severe sepsis, we investigated the regulation of fibrin deposition during sublethal and lethal listeriosis.
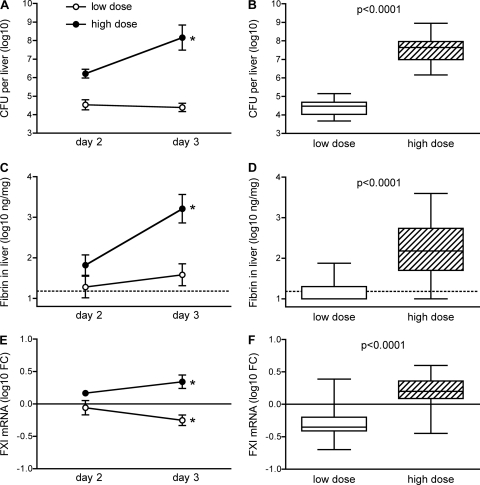
As shown in Fig. 1A, wild-type C57BL/6 mice inoculated intraperitoneally with a sublethal dose (1 × 105 CFU) of L. monocytogenes exhibited a hepatic bacterial burden of approximately 4.5 logs on both days 2 and 3 after the initiation of infection. In contrast, mice inoculated intraperitoneally with a lethal, 25-fold-higher, dose of L. monocytogenes (2.5 × 106 CFU) exhibited approximately 6 logs of hepatic bacterial CFU on day 2, and their average burden increased by another 90-fold by day 3. The kinetic analysis was terminated on day 3 because many of the mice that received high-dose inoculations succumbed to listeriosis by day 4. When data from three separate studies were combined, there was a highly significant difference in the hepatic burden 3 days after mice received low- or high-dose inoculations (P < 0.0001) (Fig. 1B).
Fig 1.
Increased levels of fibrin and FXI mRNA during lethal listeriosis. Wild-type C57BL/6 mice were inoculated intraperitoneally with 1 × 105 CFU (low dose) or 2.5 × 106 CFU (high dose) L. monocytogenes. (A, C, and E) On days 2 and 3 after the inoculations, mice were euthanized, and hepatic bacterial burden, fibrin protein, and FXI mRNA levels were measured (an asterisk indicates a P value of <0.05 when comparing day 3 to day 2 for the indicated dose; n = 5 mice per group). (B, D, and F) The day 3 study was repeated 3 additional times, and the combined data (n = 19 to 20 per group) are shown, with open boxes depicting low-dose data and hatched boxes depicting high-dose data. Thin dashed lines in panels C and D depict the limit of detection. Thin solid lines in panels E and F depict the average FXI mRNA values for naïve mice. FC, fold change in comparison with average values for naïve mice.
As reported previously (25), fibrin was detectable in the livers of mice inoculated with the low dose of L. monocytogenes; however, the levels of fibrin measured were only marginally above the detection limit of our assay on both days 2 and 3 (Fig. 1C). In contrast, fibrin levels increased markedly between days 2 and 3 in mice inoculated with high doses of L. monocytogenes (Fig. 1C). By day 3, fibrin levels differed significantly between the mice that received low-dose and those that received high-dose inoculations (Fig. 1D).
While investigating possible explanations for the increased fibrin deposition in mice inoculated with lethal doses of bacteria, we observed that hepatic levels of FXI mRNA decreased significantly between days 2 and 3 after the initiation of infection in the mice inoculated with low doses of L. monocytogenes, whereas they increased significantly over that period in mice inoculated with high doses (Fig. 1E). By day 3, the FXI mRNA levels in the low-dose group had fallen below those measured for uninfected control mice and differed significantly from those measured for the high-dose group (Fig. 1F).
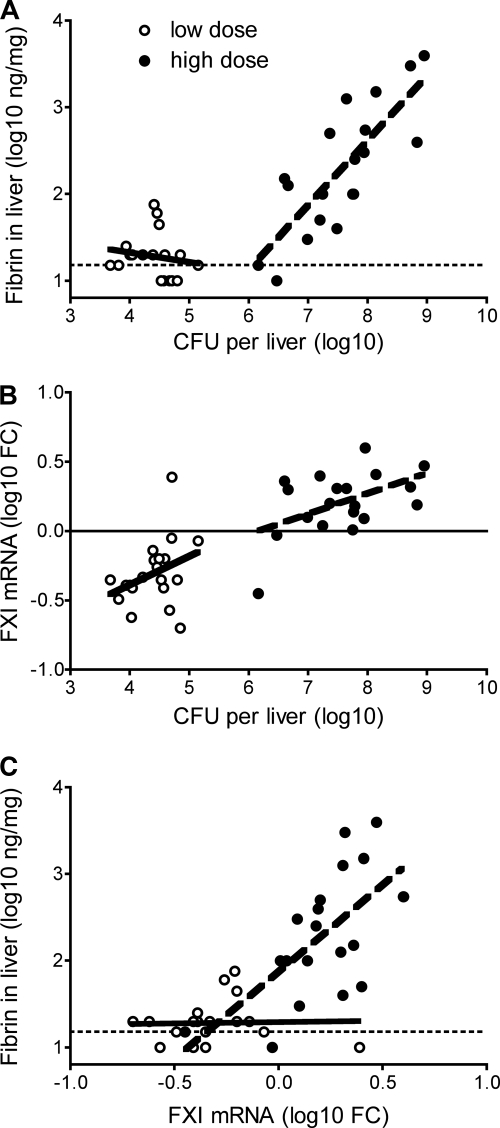
Fibrin levels correlated significantly with hepatic CFU for the high-dose inoculations but not for the low-dose inoculations (Fig. 2A), suggesting that fibrin deposition is differentially regulated during survivable and lethal L. monocytogenes infections. FXI mRNA levels also correlated with levels of hepatic CFU in mice inoculated with high doses of L. monocytogenes (Fig. 2B). Notably, mice harboring burdens of over 6 log CFU typically showed an upregulation of FXI mRNA relative to naïve animals whereas, mice with burdens below 6 log CFU tended to show a downregulation of FXI. Interestingly, hepatic levels of FXI mRNA and fibrin were strongly correlated for mice that received high-dose inoculations with L. monocytogenes but not for mice that received low-dose inoculations (Fig. 2C).
Fig 2.
Levels of fibrin correlate with FXI mRNA levels during lethal listeriosis. Wild-type C57BL/6 mice were inoculated intraperitoneally with ∼1 × 105 CFU (low dose) or ∼2.5 × 106 CFU (high dose) L. monocytogenes. On day 3 after the inoculations, mice were euthanized, and hepatic bacterial burden, fibrin protein, and FXI mRNA levels were measured (n = 19 to 20 per group). (A) Fibrin levels correlated with CFU after high-dose inoculation (P < 0.0001) but not after low-dose inoculation (P = 0.5). (B) FXI levels correlated with CFU after high-dose inoculation (P = 0.03) but not after low-dose inoculation (P = 0.1). (C) Fibrin levels correlated with FXI levels after high-dose inoculation (P = 0.004) but not after low-dose inoculation (P = 0.9). Thick solid lines and thick dotted represent least-squares fits for low- and high-dose inoculations, respectively. Thin dashed lines in panels A and C depict the limit of detection. The thin solid line in panel B depicts the average FXI value for naïve mice.
FXI deficiency improves survival after inoculation of lethal doses of L. monocytogenes.
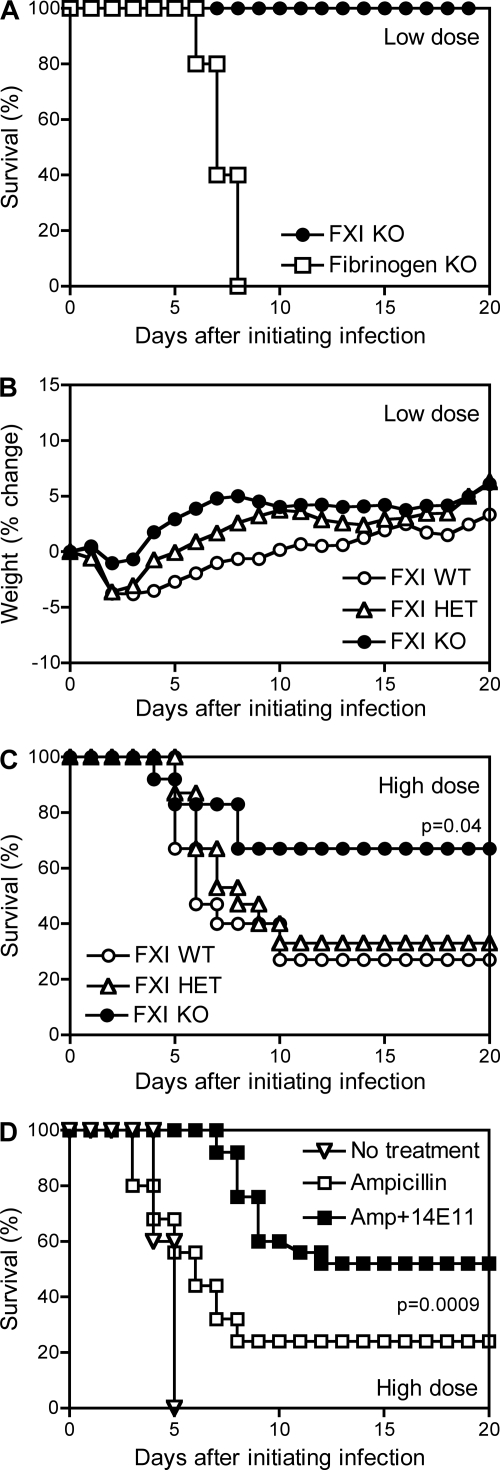
To investigate the functional importance of FXI during listeriosis, we evaluated gene-targeted mice lacking the capacity to produce FXI. Specifically, we compared wild-type mice with littermate controls that were heterozygous or homozygous for an FXI allele that had been disrupted by gene targeting (12). Upon intraperitoneal inoculation with the low dose (1 × 105 CFU) of L. monocytogenes, the wild-type, heterozygous, and homozygous mice all survived infection (Fig. 3A and data not shown). As observed previously (25), fibrinogen-deficient mice lacking the capacity to produce fibrin readily succumbed to low-dose infection with L. monocytogenes (Fig. 3A). Parallel evaluations of body weight changes over the course of infection suggested that the FXI-deficient mice experienced less severe disease than did their wild-type littermates, but these body weight differences did not achieve statistical significance (Fig. 3B). We conclude that FXI, unlike fibrin(ogen), does not perform a critical protective function during sublethal listeriosis.
Fig 3.
FXI is dispensable for survival after inoculation with low doses of L. monocytogenes and exacerbates mortality after inoculation with high doses of L. monocytogenes. (A and B) FXI wild-type (WT), FXI heterozygous (HET), and FXI-deficient (knockout [KO]) mice as well as fibrinogen-deficient mice were inoculated with a low dose (∼1 × 105 CFU) of L. monocytogenes. (A and B) Survival (A) and percent body weight change (B). All the FXI wild-type, heterozygous, and KO mice survived (n = 9 to 10 per group), whereas all fibrinogen KO mice succumbed (n = 5 per group). The FXI KO mice showed less weight loss, but this trend did not achieve statistical significance at any time point. (C) FXI wild-type, heterozygous, and KO mice were inoculated with a high dose (∼2.5 × 106 CFU) of L. monocytogenes. The wild-type mice demonstrated significantly improved survival (P = 0.04; n = 12 to 15 mice per group). (D) Wild-type C57BL/6 mice were inoculated with a high dose(∼2.5 × 106 CFU) of L. monocytogenes. On day 2 after inoculation, some mice received ampicillin, and others received ampicillin along with FXI-specific MAb 14E11 (Amp + 14E11). The mice that received 14E11 demonstrated significantly improved survival in comparison with those that received only ampicillin (P = 0.0009; n = 25 mice per group). Notably, the wild-type littermate mice from the FXI colony were less susceptible to L. monocytogenes than the Trudeau Institute's colony of wild-type C57BL/6 mice, as evidenced by a 1-day lag in time to morbidity (not shown) and reduced mortality (compare panels C and D).
When the wild-type mice from this colony were inoculated with the high dose of L. monocytogenes, they began to succumb on day 4, and only 30% survived until day 10 (Fig. 3C). The heterozygous mice behaved similarly to the wild-type mice. In contrast, the FXI-deficient mice showed significantly improved survival (P = 0.04), with 67% surviving until day 20 (Fig. 3C).
Monoclonal antibody 14E11 blocks the activation of FXI by FXIIa (6). The administration of 14E11 on day −1 and days 1 and 3 after the initiation of infection did not suffice to improve the survival of wild-type C57BL/6 mice inoculated with the high dose of L. monocytogenes (not shown). However, further studies revealed that the therapeutic administration of 14E11 did improve survival in wild-type mice that also received suboptimal antibiotic therapy. As shown in Fig. 3D, treatment with 5 mg ampicillin on day 2 after the initiation of the high-dose infection modestly improved the survival of wild-type mice inoculated with the high dose of L. monocytogenes. When this suboptimal antibiotic therapy was combined with the therapeutic administration of 14E11 on day 2, the mice that received both 14E11 and ampicillin demonstrated significantly improved survival compared with mice that received only antibiotic therapy (P = 0.0009) (Fig. 3D).
FXI deficiency reduces coagulopathy, inflammation, and bacterial burden after inoculation of lethal doses of L. monocytogenes.
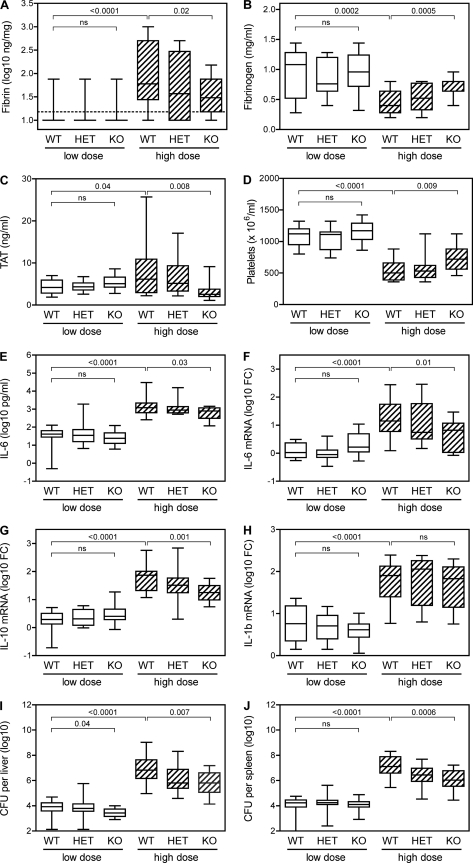
To investigate the mechanisms of protection conferred by FXI deficiency, we measured markers of coagulation and inflammation in FXI-deficient and littermate control mice at day 3 after inoculation of low or high doses of L. monocytogenes. The data presented in Fig. 4 are pooled from 3 separate experiments in which mice received either low- or high-dose inoculations of L. monocytogenes. Consistent with our previous studies of C57BL/6 mice (Fig. 1A), levels of hepatic fibrin increased significantly in FXI wild-type mice inoculated with high doses of L. monocytogenes compared to those inoculated with low doses (P < 0.0001) (Fig. 4A). Additional measures of coagulation revealed significantly decreased levels of circulating fibrinogen (P = 0.0002) (Fig. 4B), increased levels of TAT complexes (P = 0.04) (Fig. 4C), and decreased platelet numbers (P < 0.0001) (Fig. 4D) after high-dose inoculations compared with low-dose inoculations. Together, these observations suggest that the inoculation of wild-type mice with high doses of L. monocytogenes induces coagulopathy.
Fig 4.
Factor XI-deficient mice display reduced coagulopathy, inflammation, and bacterial burden during listeriosis. FXI wild-type, heterozygous, and KO mice were inoculated with a low dose (∼1 × 105 CFU) or high dose (∼2.5 × 106 CFU) of L. monocytogenes. On day 3 after the inoculations, mice were euthanized, and hepatic fibrin protein (A), plasma fibrinogen (B), plasma TAT (C), blood platelets (D), plasma IL-6 (E), hepatic IL-6 mRNA (F), hepatic IL-10 mRNA (G), hepatic IL-1-beta mRNA (H), hepatic bacterial burden (I), and splenic bacterial burden (J) were measured (n = 13 to 16 per group). ns, not significant.
The low levels of fibrin measured after low-dose inoculations did not appear to differ between the FXI wild-type and FXI-deficient mice. In contrast, FXI-deficient mice exhibited significantly lower fibrin levels than wild-type mice after high-dose inoculation (P = 0.02) (Fig. 4A). Moreover, the FXI-deficient mice showed reduced levels of coagulopathy after high-dose inoculation with L. monocytogenes, as evidenced by significantly increased fibrinogen levels (P = 0.0005), decreased TAT levels (P = 0.008), and increased platelet numbers (P = 0.009). Similar trends were observed for markers of inflammation, including plasma levels of IL-6 and hepatic levels of mRNA encoding IL-6 and IL-10 (Fig. 4E to G). The differences between wild-type and FXI-deficient mice were highly significant for levels of plasma IL-6 (P = 0.03), IL-6 mRNA (P = 0.01), and IL-10 mRNA (P = 0.001). Levels of hepatic mRNA encoding IL-1-beta, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and gamma interferon were also impacted by infection but did not differ significantly between wild-type and FXI-deficient mice (Fig. 4H and data not shown).
The bacterial burden was also impacted by FXI deficiency. Wild-type and FXI-deficient mice displayed significant differences in both hepatic and splenic bacterial burdens on day 3 after inoculation of high doses of L. monocytogenes (P = 0.007 and 0.0006, respectively) (Fig. 4I and J).
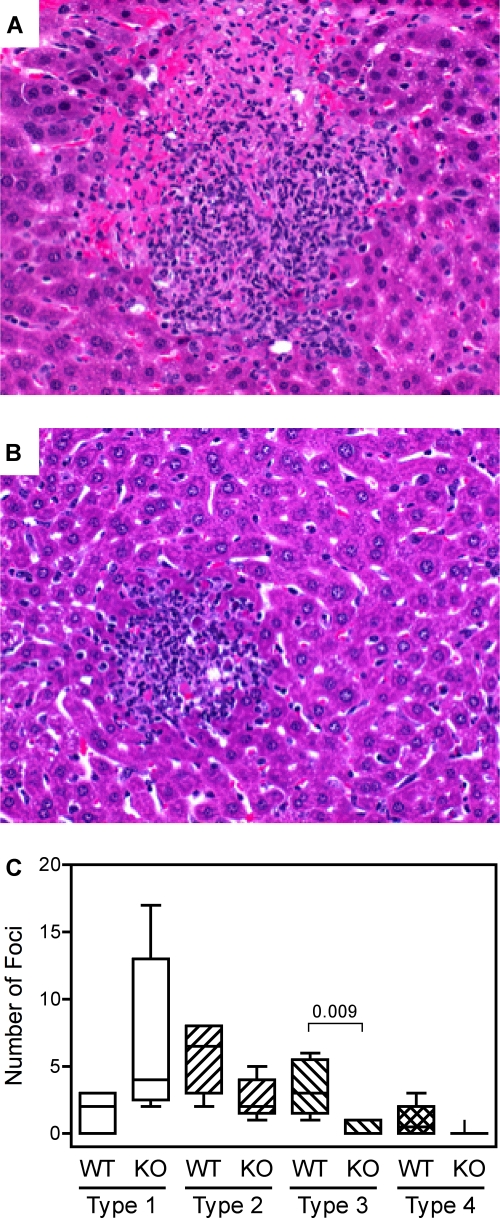
Histological evaluations revealed liver pathology typical of listeriosis, with the mice that received high-dose inoculations showing many inflammatory foci with various degrees of hepatocellular damage. In the FXI wild-type mice, the cellular infiltrates tended to be medium to large and were frequently associated with large areas of coagulation necrosis (Fig. 5A), whereas the foci in the FXI-deficient mice tended to be small to medium, with little evidence of necrosis (Fig. 5B). Pathological scoring revealed significant differences in the number and quality of hepatic foci showing high degrees of necrosis (Fig. 5C).
Fig 5.
Factor XI-deficient mice display reduced hepatic pathology during listeriosis. (A and B) Lesions observed in hematoxylin-and-eosin-stained liver sections from FXI wild-type (A) and FXI KO (B) mice that had been inoculated with a high dose (∼2.5 × 106 CFU) of L. monocytogenes 3 days prior to tissue collection. (C) Histological scoring of inflammatory foci revealed significant differences in the numbers of type 3 foci per section (P = 0.009; n = 5 mice per group). The micrographs in panels A and B depict representative type 3 and 2 foci, respectively. See Materials and Methods for definitions of focus types.
DISCUSSION
Infection of mice with L. monocytogenes has been a useful model for defining protective elements of innate and adaptive immunity and establishing how they contribute to bacterial clearance and the development of immunological memory (29, 44). Previously, we demonstrated that hemostasis prevents hemorrhage and limits bacterial growth in mice infected with sublethal doses of L. monocytogenes. Our subsequent studies revealed that mice inoculated with lethal doses of Listeria exhibit significantly elevated levels of fibrin, TAT, and thrombocytopenia and decreased levels of plasma fibrinogen (Fig. 1, 2, and 4). Together, these observations suggested that the protective hemostatic response that accompanies sublethal Listeria infections becomes dysregulated and coagulopathic during lethal infections. Accordingly, we sought to use the mouse model of listeriosis to identify therapeutically targetable mechanisms that regulate hemostasis during infection and sepsis. We anticipate that treatments that antagonize factors specifically upregulated during sepsis will be easier to manage clinically than treatments, like APC, that aim to replace actively depleted factors. Thus, we sought to identify proteins specifically upregulated during lethal infections whose therapeutic targeting might allow the selective alleviation of septic coagulopathy without a disruption of the protective hemostatic responses that can be critical for surviving infection.
The studies reported here suggest that FXI antagonists may alleviate septic pathology without disrupting protective hemostasis. Previously, FXI-deficient mice were shown to display improved survival and reduced evidence of coagulopathy in a CLP model of septic peritonitis (40). Here, we have demonstrated that FXI expression is upregulated when mice are infected via the peritoneal route with lethal, but not sublethal, doses of L. monocytogenes (Fig. 1 and 2). We also demonstrated that the FXI deficiency does not compromise the protective hemostasis that is critical for surviving L. monocytogenes infection but improves survival and reduces coagulopathy, inflammation, bacterial burden, and hepatic damage during lethal septic listeriosis (Fig. 3 to 5). Moreover, we demonstrated that an antibody that blocks the activation of FXI by FXIIa can be used therapeutically to improve survival during septic listeriosis (Fig. 3). This antibody has also been shown to reduce experimentally induced thrombus formation in mice and baboons (6).
Classically, FXI is considered a key component of the intrinsic coagulation pathway (13, 32). In that setting, FXIIa activates FXI. However, FXI can be activated without evidence of FXII activation during sepsis (23, 41), and both thrombin and FXIa can activate FXI directly (11, 13, 26, 42). These observations led to a revised model of coagulation in which initial thrombin generation results primarily from the extrinsic coagulation pathway but is then sustained within the vicinity of the fibrin clot via a feedback mechanism involving the thrombin-mediated activation of FXI (13). MAb 14E11 suppresses FXI activation by FXIIa but does not suppress FXI activation by thrombin or FXIa (6). Our data indicate that treatment with MAb 14E11 significantly improves survival when administered therapeutically in conjunction with ampicillin during lethal listeriosis, suggesting that FXII and the intrinsic pathway may contribute to septic pathology during listeriosis.
Continuous treatment with MAb 14E11 in the absence of antibiotics did not mimic the FXI deficiency. Specifically, we administered 14E11 on day −1 and days 1 and 3 after the initiation of infection at doses of either 100 μg/day or 500 μg/day. Neither protocol significantly improved survival (data not shown). Thus, in the presence of suboptimal antibiotics, but not in their absence, the targeting of the FXIIa-dependent activation of FXI with MAb 14E11 sufficed to provide a significant therapeutic benefit. These studies suggest that an FXI deficiency improves survival during listeriosis by FXIIa-dependent and -independent mechanisms.
The CLP model exposes the peritoneal cavity to endogenous gut flora, thereby initiating a polymicrobial infection with a variable mixture of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria (7, 40). Our studies establish that FXI-deficient mice display a survival advantage and reduced hepatic and splenic bacterial burdens after peritoneal infection with a single species of Gram-positive bacterium, L. monocytogenes. Interestingly, we did not observe a survival advantage or reduced bacterial burden after intravenous infection with L. monocytogenes (data not shown). These observations suggest that FXI may function to limit bacterial growth within the peritoneal cavity or bacterial dissemination to visceral organs.
Pilot studies have failed thus far to reveal a survival benefit in FXI-deficient mice infected with defined Gram-negative bacteria. Specifically, we have not observed a survival benefit upon peritoneal infection with Yersinia enterocolitica (not shown). Consistent with previous studies in another laboratory (40), we also did not observe a survival advantage in FXI-deficient mice after the peritoneal injection of lipopolysaccharide (not shown). Since the procoagulant response to Gram-negative bacteria is likely driven by lipopolysaccharide-induced tissue factor expression on monocytes (9, 30), which may bypass the intrinsic coagulation pathway, the benefits of an intrinsic pathway blockade during Gram-negative infections may be limited. Notably, an antibody targeting FXII reduces hypotension and IL-6 production but does not suppress coagulopathy in baboons infused with Escherichia coli, a Gram-negative bacterium (14, 31), whereas the inhibition of high-molecular-weight kininogen, another key element of the intrinsic pathway, improves survival in mice infected with the Gram-positive bacterium Streptococcus pyogenes (28). Further studies are required to determine whether the antagonism of FXI and other elements of the intrinsic pathway confers a survival advantage for all Gram-positive infections or only for certain bacteria.
Presently, it is unclear whether the reduced coagulopathy observed during listeriosis in FXI-deficient mice results directly from reduced FXI-facilitated thrombin production or, alternatively, from impacts of FXI on inflammation, bacterial burden, or tissue pathology that secondarily affect thrombin production and coagulopathy. Notably, many elements downstream of FXI activation reportedly possess both hemostatic functions and inflammation-related activities (21, 36). These elements include components of the coagulation pathway, such as FIX, FX, thrombin, fibrin, and platelets, and also components of anticoagulant and fibrinolytic pathways activated in response to coagulation, such as APC and thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor. For example, FX and APC can activate protease-activated receptors that initiate signaling cascades in various cell types, thereby contributing to the production of cytokines, including IL-6 (21), and thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor can inactivate proinflammatory mediators such as bradykinin and complement factor C5a (24). Additional studies will be required to decipher precisely how FXI activation and activity contribute to septic pathology during listeriosis. Regardless, our findings add to the growing appreciation of the extensive cross talk between inflammatory and coagulation pathways and support the development of FXI antagonism as a strategy for the treatment of sepsis.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by PHS grants R01-HL81326 to D.G., R43-AI088937 to E.I.T. and A.G., and R01-AI071295 to S.T.S.
We thank Deborah K. Duso for technical assistance, and we are indebted to employees of Trudeau Institute Animal Breeding and Maintenance Facilities for dedicated care of the mice used in these studies.
A.G., E.I.T., and Oregon Health and Science University have a significant financial interest in Aronora, LLC, a company that may have a commercial interest in the result of this research. This potential conflict of interest has been reviewed and managed by the Oregon Health and Science University Conflict of Interest in Research Committee.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print 17 October 2011
REFERENCES
- 1. Angus DC, et al. 2001. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit. Care Med. 29: 1303–1310 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Ansell J. 2007. Factor Xa or thrombin: is factor Xa a better target? J. Thromb. Haemost. 5(Suppl. 1): 60–64 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Bakker-Woudenberg IA, de Bos P, van Leeuwen WB, Michel MF. 1981. Efficacy of ampicillin therapy in experimental listeriosis in mice with impaired T-cell-mediated immune response. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 19: 76–81 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Bernard GR, et al. 2001. Efficacy and safety of recombinant human activated protein C for severe sepsis. N. Engl. J. Med. 344: 699–709 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Bone RC, et al. 1992. Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. The ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference Committee. American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine. Chest 101: 1644–1655 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Cheng Q, et al. 2010. A role for factor XIIa-mediated factor XI activation in thrombus formation in vivo. Blood 116: 3981–3989 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Dejager L, Pinheiro I, Dejonckheere E, Libert C. 2011. Cecal ligation and puncture: the gold standard model for polymicrobial sepsis? Trends Microbiol. 19: 198–208 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Dyson A, Singer M. 2009. Animal models of sepsis: why does preclinical efficacy fail to translate to the clinical setting? Crit. Care Med. 37: S30–S37 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Franco RF, et al. 2000. The in vivo kinetics of tissue factor messenger RNA expression during human endotoxemia: relationship with activation of coagulation. Blood 96: 554–559 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Furie B, Furie BC. 1988. The molecular basis of blood coagulation. Cell 53: 505–518 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Gailani D, Broze GJ., Jr 1991. Factor XI activation in a revised model of blood coagulation. Science 253: 909–912 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Gailani D, Lasky NM, Broze GJ., Jr 1997. A murine model of factor XI deficiency. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 8: 134–144 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Gailani D, Renne T. 2007. The intrinsic pathway of coagulation: a target for treating thromboembolic disease? J. Thromb. Haemost. 5: 1106–1112 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Jansen PM, et al. 1996. Inhibition of factor XII in septic baboons attenuates the activation of complement and fibrinolytic systems and reduces the release of interleukin-6 and neutrophil elastase. Blood 87: 2337–2344 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Johnson LL, Berggren KN, Szaba FM, Chen W, Smiley ST. 2003. Fibrin-mediated protection against infection-stimulated immunopathology. J. Exp. Med. 197: 801–806 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Kerschen EJ, et al. 2007. Endotoxemia and sepsis mortality reduction by non-anticoagulant activated protein C. J. Exp. Med. 204: 2439–2448 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Kinasewitz GT, et al. 2004. Universal changes in biomarkers of coagulation and inflammation occur in patients with severe sepsis, regardless of causative micro-organism. Crit. Care 8: R82–R90 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Levi M. 2008. Activated protein C in sepsis: a critical review. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 15: 481–486 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Levi M. 2007. Disseminated intravascular coagulation. Crit. Care Med. 35: 2191–2195 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Levi M, Van Der Poll T. 2004. Coagulation in sepsis: all bugs bite equally. Crit. Care 8: 99–100 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Levi M, van der Poll T. 2010. Inflammation and coagulation. Crit. Care Med. 38: S26–S34 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Marti-Carvajal AJ, Sola I, Lathyris D, Cardona AF. 2011. Human recombinant activated protein C for severe sepsis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 4: CD004388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Minnema MC, et al. 1998. Activation of clotting factor XI without detectable contact activation in experimental human endotoxemia. Blood 92: 3294–3301 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Morser J, Gabazza EC, Myles T, Leung LL. 2010. What has been learnt from the thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor-deficient mouse? J. Thromb. Haemost. 8: 868–876 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Mullarky IK, et al. 2005. Infection-stimulated fibrin deposition controls hemorrhage and limits hepatic bacterial growth during listeriosis. Infect. Immun. 73: 3888–3895 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Naito K, Fujikawa K. 1991. Activation of human blood coagulation factor XI independent of factor XII. Factor XI is activated by thrombin and factor XIa in the presence of negatively charged surfaces. J. Biol. Chem. 266: 7353–7358 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Oehmcke S, Herwald H. 2010. Contact system activation in severe infectious diseases. J. Mol. Med. 88: 121–126 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Oehmcke S, et al. 2009. Treatment of invasive streptococcal infection with a peptide derived from human high-molecular weight kininogen. Blood 114: 444–451 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Pamer EG. 2004. Immune responses to Listeria monocytogenes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4: 812–823 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Pawlinski R, Mackman N. 2010. Cellular sources of tissue factor in endotoxemia and sepsis. Thromb. Res. 125(Suppl. 1): S70–S73 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Pixley RA, et al. 1993. The contact system contributes to hypotension but not disseminated intravascular coagulation in lethal bacteremia. In vivo use of a monoclonal anti-factor XII antibody to block contact activation in baboons. J. Clin. Invest. 91: 61–68 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Renne T, et al. 2009. Factor XI deficiency in animal models. J. Thromb. Haemost. 7(Suppl. 1): 79–83 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Riedemann NC, Guo RF, Ward PA. 2003. The enigma of sepsis. J. Clin. Invest. 112: 460–467 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Riewald M, Petrovan RJ, Donner A, Mueller BM, Ruf W. 2002. Activation of endothelial cell protease activated receptor 1 by the protein C pathway. Science 296: 1880–1882 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Seligsohn U. 2009. Factor XI deficiency in humans. J. Thromb. Haemost. 7(Suppl. 1): 84–87 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Stearns-Kurosawa DJ, Osuchowski MF, Valentine C, Kurosawa S, Remick DG. 2011. The pathogenesis of sepsis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 6: 19–48 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Suh TT, et al. 1995. Resolution of spontaneous bleeding events but failure of pregnancy in fibrinogen-deficient mice. Genes Dev. 9: 2020–2033 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Tapper H, Herwald H. 2000. Modulation of hemostatic mechanisms in bacterial infectious diseases. Blood 96: 2329–2337 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Tilley R, Mackman N. 2006. Tissue factor in hemostasis and thrombosis. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 32: 5–10 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Tucker EI, et al. 2008. Survival advantage of coagulation factor XI-deficient mice during peritoneal sepsis. J. Infect. Dis. 198: 271–274 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. van Gorp EC, et al. 2001. Activation of coagulation factor XI, without detectable contact activation in dengue haemorrhagic fever. Br. J. Haematol. 113: 94–99 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. von dem Borne PA, Meijers JC, Bouma BN. 1995. Feedback activation of factor XI by thrombin in plasma results in additional formation of thrombin that protects fibrin clots from fibrinolysis. Blood 86: 3035–3042 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Weitz JI, Linkins LA. 2007. Beyond heparin and warfarin: the new generation of anticoagulants. Expert Opin. Invest. Drugs 16: 271–282 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Wing EJ, Gregory SH. 2002. Listeria monocytogenes: clinical and experimental update. J. Infect. Dis. 185(Suppl. 1): S18–S24 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]