Abstract
We describe here the isolation of 8 beta-lactamase-producing multidrug-resistant Enterococcus faecium isolates in 2010. All strains showed diverse pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) profiles, all belonging to the same clonal complex, CC17. By PCR and hybridization experiments, the entire blaZ-blaI-blaR1 operon was found. The beta-lactamase activity was demonstrated at a high inoculum and in the presence of methicillin after overnight incubation.
TEXT
Since the first beta-lactamase-producing (Bla+) Enterococcus faecalis strain was reported in 1981 by B. Murray (7), only a few reports have appeared in the literature: the second E. faecalis strain was isolated in 1983 (5), and since then, Bla+ E. faecalis strains have been isolated from 11 cities in 4 countries, including clusters and outbreak strains (8). In 1992, the first isolation of a Bla+ Enterococcus faecium strain was described (3): since then, no evidence of Bla+ enterococci has been reported (12).
In 2010, 8 strains of clinical isolates of E. faecium possessing 1- to 3-fold less susceptibility to ampicillin plus sulbactam with respect to ampicillin alone were studied for possible beta-lactamase production. After rigorous laboratory tests, they were found to be beta-lactamase producers. In this article, we report the preliminary characterization of these isolates, the presence of the genes encoding the enzyme, and its hydrolytic activity detected in cell debris and extracts of all strains.
(Part of this research was presented at the 51st Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, Chicago, IL, 17 to 20 September 2011.)
Eight strains of E. faecium were isolated from urine, blood, or peritoneal fluid of patients at the Clinical Microbiology Laboratory of S. Agostino-Estense Hospital (Modena, Italy) during 2010 (Table 1). All isolates were identified and tested for antibiotic susceptibility by standard procedures using the Vitek2 system with the GP and AST-GP586 cards (bioMérieux, Marcy l'Etoile, France) and reconfirmed by the API Strept system (bioMérieux, Marcy l'Etoile, France).
Table 1.
Isolates of E. faecium and their PFGE profiles and STs
| Strain | Date of isolation (mo/yr) | MIC (mg/liter) ofa: |
Clinical specimen | PFGE pattern | ST | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMP | SAM | |||||
| E030 | 2/2010 | 8 | <2 | Urine | B | 117 |
| C236 | 8/2010 | 16 | 4 | Urine | A | 18 |
| E032 | 2/2010 | 16 | 4 | Urine | C | 117 |
| E031 | 3/2010 | 8 | ≤2 | Urine | D | 202 |
| E029 | 3/2010 | 16 | 8 | Urine | E | 19 |
| F13 | 6/2010 | ≥32 | 16 | Peritoneal fluid | F | 192 |
| F14 | 6/2010 | ≥32 | 16 | Blood | G | 117 |
| G90 | 11/2010 | ≥32 | 32 | Blood | H | 78 |
AMP, ampicillin; SAM, ampicillin-sulbactam.
Strains were retested by a reference method (2) with broth microdilution for the antibiotics penicillin, ampicillin, ampicillin-sulbactam, erythromycin, clindamycin, tetracycline, levofloxacin, vancomycin, and teicoplanin and were tested for high-level resistance to aminoglycosides. All drugs, as standard reference powders, were purchased from Sigma Chemical Company, St. Louis, MO. E. faecalis ATCC 29212 was used as a standard control.
Beta-lactamase activity was evaluated with and without induction with methicillin and ampicillin by using two assays: (i) the nitrocefin disk test (Remel, Lenexa, KS) on whole cells and (ii) the detection of the hydrolysis activity on enzyme preparations and pellet (cellular debris), performed essentially following a protocol previously published (16). Both assays were performed in duplicate and reconfirmed. Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 was used as a Bla+ control strain.
Chromosomal extraction of whole genomic DNA was performed as previously described (11). The sequence of the bla operon blaZ-blaI-blaR1, carried on Tn552 by S. aureus (available in GenBank, under accession no. X52734), was used to design the primers by the VectorNTI program (Invitrogen). The bla operon blaZ-blaI-blaR1 oligonucleotides used in this study and the corresponding fragment sizes are provided in the supplemental material. All strains were also screened for the presence of the following resistance genes: erm(A), erm(B), and tet(M) (13); vanA, vanB, vanC-1, and vanC-2/3 (10); and aph3, aac(6′)-Ie-aph(2″)-Ia, aph(2″)-Ib, aph(2″)-Ic, aph(2″)-Id, aadA, and aadE (6). The 16S rRNA gene was used as an internal control. The PCR amplifications for the target were performed in a Biometra personal cycler (M-Medical srl, 2010; Comaredo, Milan, Italy).
Gene sequencing of the blaZ-blaI-blaR1 operon was carried out on strain E030, and the vanB genes were sequenced for confirmation of the resistance determinants in four strains.
Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) macrorestriction analysis was performed with SmaI (New England BioLabs, Ipswich, MA) following a modified protocol previously reported (1). Similarities among macrorestriction patterns were identified according to established criteria (15).
For the MLST scheme, PCR conditions and sequencing followed the instructions given at http://efaecium.mlst.net/. The presence of plasmids was investigated by using the Plasmid Midi kit (Qiagen srl, Milan, Italy) according to the manufacturer's instructions, preceded by one lysis step with 20 mg ml−1 lysozyme solution and incubation at 37°C for 30 min. The localization of blaZ was determined by hybridization of I-CeuI-digested genomic DNA with probes labeled with an enhanced chemiluminescence kit (Amersham Life Science, GE Healthcare, United Kingdom) for blaZ and 16S rRNA genes, as previously described (9).
The 8 strains of Bla+ E. faecium were from documented infections, and all patients received the appropriate antibiotic therapy. The strains were epidemiologically and genetically unrelated, belonging to 8 different PFGE profiles (Table 1). Sequence type (ST) analysis showed the isolates were distributed in 6 different lineages, all clustering in clonal complex 17 (CC17), the one in which most of the hospital-derived isolates belong. In particular, ST117, ST202, and ST78 are single-locus variants (slv) of ST17, while ST192 and ST19 are double-locus variants (dlv), and ST18 is a three-locus variant (tlv).
Table 2 shows the antibiotic susceptibilities of the 8 strains together with their resistance gene contents. In all strains, the MIC of ampicillin was also determined at a higher inoculum (107), showing 2-fold-less-susceptible values; also, the MIC of ampicillin/sulbactam was 1- to 3-fold less susceptible with respect to ampicillin alone. All strains were phenotypically confirmed by the nitrocefin test and genetically correlated with the presence—using PCR—of the entire bla operon constituted by the beta-lactamase blaZ gene, the repressor blaI, and the antirepressor blaR1. The internal sequences of the three genes showed the following nucleotide identities with Tn552 of S. aureus: blaZ, 97%; blaR1, 96%; and blaI, 95%.
Table 2.
Antibiotic resistance of strains and correlation with antibiotic resistance gene content
| Strain | MIC (mg/liter) ofa: |
HLARb |
Resistance gene content | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMP | SAM | ERY | CLI | TET | LVX | TEC | VAN | GEN | STR | ||
| E030 | 8 | ≤2 | 1 | ≤0.25 | ≥16 | 4 | ≤0.5 | 1 | No | No | blaZ-blaI-blaR1 tet(M) |
| C236 | 16 | 4 | ≥8 | ≥8 | ≥16 | ≥8 | ≤0.5 | ≤0.5 | Yes | Yes | blaZ-blaI-blaR1 erm(B) tet(M) aadE aphA3 aph(2″)-1b |
| E032 | 16 | 4 | 4 | ≤0.25 | 2 | ≥8 | 4 | 1 | No | No | blaZ-blaI-blaR1 |
| E031 | 8 | ≤2 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.25 | 2 | ≥8 | ≤0.5 | 1 | Yes | Yes | blaZ-blaI-blaR1 aadE aphA3 aph(2″)-1b vanB2 |
| E029 | 16 | 8 | ≥8 | ≥8 | ≤1 | ≥8 | ≤0.5 | 1 | Yes | Yes | blaZ-blaI-blaR1 erm(B) aadE aphA3 aph(2″)-1b |
| F13 | ≥32 | 16 | ≥8 | ≥8 | ≤1 | ≥8 | ≤0.5 | ≤0.5 | Yes | Yes | blaZ-blaI-blaR1 erm(B) aadE aphA3 aph(2″)-1b vanB2 |
| F14 | ≥32 | 16 | ≥8 | ≥8 | ≤1 | ≥8 | ≤0.5 | ≤0.5 | Yes | Yes | blaZ-blaI-blaR1 erm(B) aadE aphA3 aph(2″)-1b vanB2 |
| G90 | ≥32 | 32 | ≥8 | ≥8 | ≤1 | ≥8 | 2 | 8 | Yes | Yes | blaZ-blaI-blaR1 erm(B) aadE aphA3 aph(2″)-1b vanB2 |
AMP, ampicillin; SAM, ampicillin-sulbactam; ERY, erythromycin; CLI, clindamycin; TET, tetracycline; LVX, levofloxacin; TEC, teicoplanin; VAN, vancomycin.
HLAR, high-level aminoglycoside resistance.
As regards the other antibiotic families, 6/8 strains possessed high-level resistance (HLR) to both aminoglycosides due to the presence of modifying enzymes: i.e., the aadE enzyme and the bifunctional aac(6′)-Ie-aph(2″)-Ia enzyme. Two of eight strains were tetracycline resistant due to ribosomal protection [tet(M) gene], and 4/8 were resistant to erythromycin due to the presence of the erm(B) gene. One strain was resistant to vancomycin but teicoplanin susceptible, due to the presence of the vanB2 gene, and 3 strains were vanB2-containing E. faecium, showing vancomycin susceptibility, as already described (4, 14). The vanB2 genes were sequenced in all strains and were identical, showing 99% nucleotide identity to the vanB gene deposited in GenBank (accession no. AY9582201).
The beta-lactamase activity of our E. faecium strains was detected in supernatants, with or without methicillin, only when a high inoculum was used (108 CFU/ml); in all experiments, the reaction was very slow and developed only a pale color at 24 h, slightly recognizable with respect to the E. faecium ATCC 35667 negative control. In all strains tested, under these experimental conditions, it was difficult to recognize a difference in intensity between induced and uninduced cells.
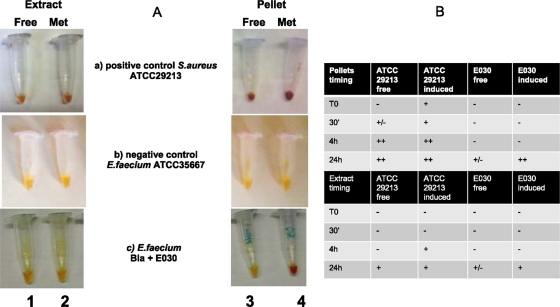
The hydrolytic activity was also detected in crude extracts in both the supernatants and the pellets containing cell debris and membranes, after their growth under induced and uninduced conditions with methicillin. Figure 1A shows the color difference in the beta-lactamase activity in strain E030 used as an example of the behavior of all of our strains. The nitrocefin reaction was detected only in the pellet of E. faecium cells grown in the presence of methicillin, rapidly developing a red color in 24 h (vial 4c), while all other vials remained negative, as did the negative control (vial 1b). On the contrary, both S. aureus vials (free extract and pellets with and without methicillin) rapidly developed a more intense red color demonstrating abundant enzyme release (vial 1a). Figure 1B shows the time of the color development in pellets and extracts. The enzymatic activity was better detected in pellets with respect to cell extracts, in the presence of methicillin, and at 24 h.
Fig 1.
Visual estimation of the beta-lactamase-activity in E. faecium strains. (A) Nitrocefin test in crude extract (vials 1 and 2) and cellular debris (pellets) (vials 3 and 4) obtained after incubation in antibiotic-free medium and with 8 mg/liter methicillin induction after 24 h of incubation. (a) positive control S. aureus strain ATCC 29213; (b) negative control E. faecium strain ATCC 35667; (c) E. faecium Bla+ strain E030. (B) Timing of positivity of the nitrocefin test in S. aureus ATCC 29213 and E. faecium E030. The negative control strain E. faecium ATCC 35667 remained negative.
Six out of the 8 Bla+ E.faecium strains harbored plasmids of small sizes ranging from 2 to 5 kb (Table 1). To define the localization of the blaZ gene cluster, hybridization experiments, using total DNA digested with I-CeuI, were performed in all strains. The bla operon was assigned to the chromosome after successive hybridizations with 16S rRNA and blaZ probes (see the supplemental material).
The Bla+ E. faecium isolates in our study remained generally ampicillin resistant even in the presence of a beta-lactamase inhibitor, demonstrating they are also intrinsically resistant to beta-lactams: in only two strains, possessing low-level resistance to ampicillin, was the addition of sulbactam able to restore a full susceptibility profile. Different characteristics seem to be important to explain the beta-lactamases activity demonstrated by the E. faecium isolates in this study. (i) Our strains possessed the entire blaZ-blaI-blaR1 operon located on the chromosome, and the three genes are highly homologous to those of S. aureus origin. (ii) Contrary to what has been published to date on E. faecium (3), our activity was better detected when strains were grown in the presence of methicillin. (iii) Nitrocefin hydrolysis was detected better in pellets with than in cell extracts (3, 8).
Further studies are in progress to address the many unanswered questions, regarding the functionality of this beta-lactamase in E. faecium, the sequence of the entire element, and its possible transferability. It is not clear if Bla+ enterococci are frequent in clinical settings, and the impact of this hydrolytic mechanism on the complex picture of ampicillin resistance in this species is less clear.
(While we were writing this article, other Bla+ isolates, both E. faecalis and E. faecium, were isolated.)
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by grant no. 20087SM5Hm from the MIUR (Italy) to S.S.
We are indebted to Gianfranco Amicosante (University of L'Aquila I) for helpful and critical discussion of the manuscript and Antony Bridgewood for language revision.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print 9 November 2011
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://jcm.asm.org/.
REFERENCES
- 1. Campanile F, et al. 2003. Molecular alterations of VanA element in vancomycin-resistant enterococci isolated during a survey of colonized patients in an Italian intensive care unit. Microb. Drug Resist. 9:191–199 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institutes 2011. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing: 21st informational supplement M100-S21. CLSI, Wayne, PA [Google Scholar]
- 3. Coudron PE, Markowitz SM, Wong ES. 1992. Isolation of a beta-lactamase-producing, aminoglycoside-resistant strain of Enterococcus faecium. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 36:1125–1126 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Grabsch EA, et al. 2008. Improved detection of vanB2-containing Enterococcus faecium with vancomycin susceptibility by Etest using oxgall supplementation. J. Clin. Microbiol. 46:1961–1964 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Ingerman M, et al. 1987. Beta-lactamase production in experimental endocarditis due to aminoglycoside-resistant Streptococcus faecalis. J. Infect. Dis. 155:1226–1232 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Leelaporn A, Yodkamol K, Waywa D, Pattanachaiwit S. 2008. A novel structure of Tn4001-truncated element, type V, in clinical enterococcal isolates and multiplex PCR for detecting aminoglycoside resistance genes. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 31:250–254 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Murray BE, Mederski-Samaroj B. 1983. Transferable beta-lactamase. A new mechanism for in vitro penicillin resistance in Streptococcus faecalis. J. Clin. Invest. 72:1168–1171 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Murray BE. 1992. Beta-lactamase-producing enterococci. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 36:2355–2359 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Novais C, et al. 2004. Local genetic patterns within a vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis clone isolated in three hospitals in Portugal. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 48:3613–3617 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Patel R, Uhl JR, Kohner P, Hopkins MK, Cockerill FR., III 1997. Multiplex PCR detection of vanA, vanB, vanC-1, and vanC-2/3 genes in enterococci. J. Clin. Microbiol. 35:703–707 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Pitcher DG, Saunders NA, Owen RJ. 1989. Rapid extraction of bacterial genomic DNA with guanidium thiocyanate. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 8:155–156 [Google Scholar]
- 12. Rhinehart E., et al. 1990. Rapid dissemination of beta-lactamase-producing, aminoglycoside-resistant Enterococcus faecalis among patients and staff on an infant-toddler surgical ward. N. Engl. J. Med. 323:1814–1818 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Santagati M, Lupo A, Scillato M, Di Martino A, Stefani S. 2009. Conjugal mobilization of the mega element carrying mef(E) from Streptococcus salivarius to Streptococcus pneumoniae. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 290:79–84 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Stampone L, et al. 2005. Clonal spread of a vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium strain among bloodstream-infecting isolates in Italy. J. Clin. Microbiol. 43:1575–1580 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Tenover FC., et al. 1995. Interpreting chromosomal DNA restriction patterns produced by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: criteria for bacterial strain typing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 33:2233–2239 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Tomayko JF, et al. 1996. Comparison of the beta-lactamase gene cluster in clonally distinct strains of Enterococcus faecalis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 40:1170–1174 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.