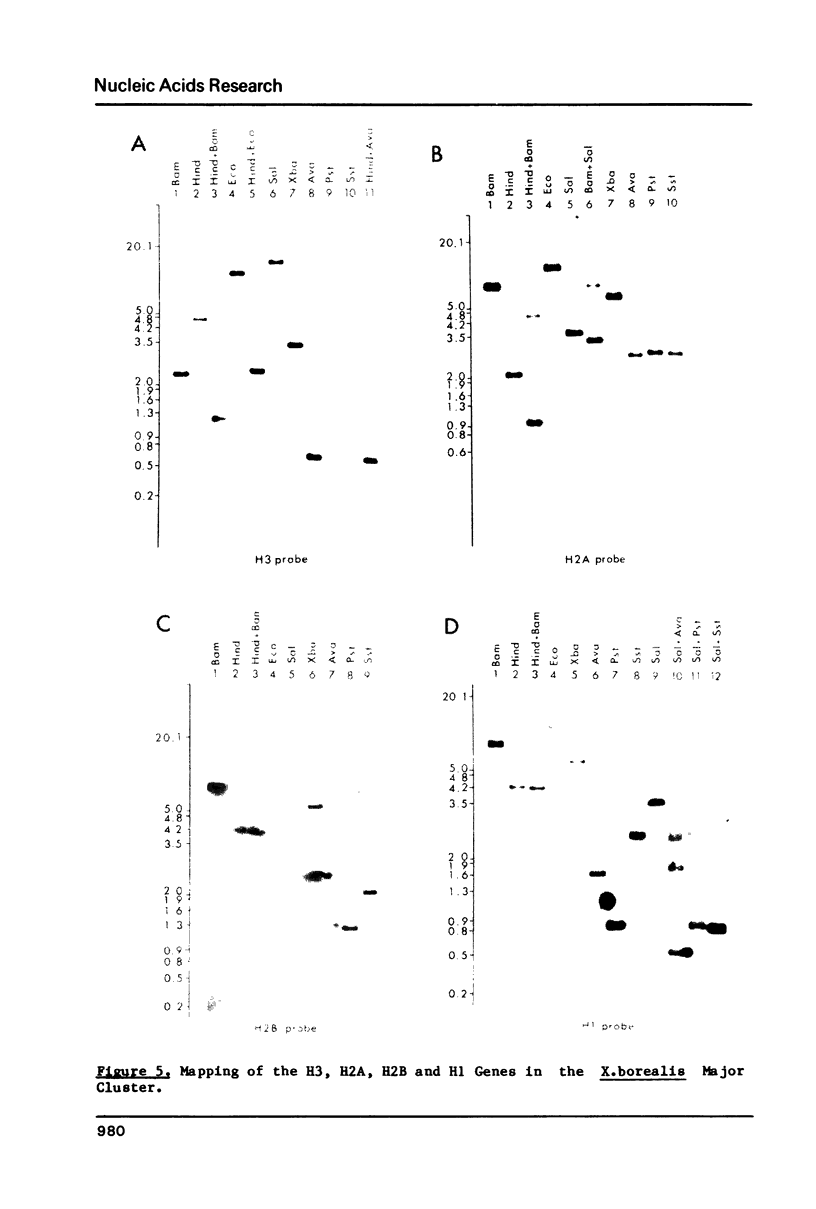
Abstract
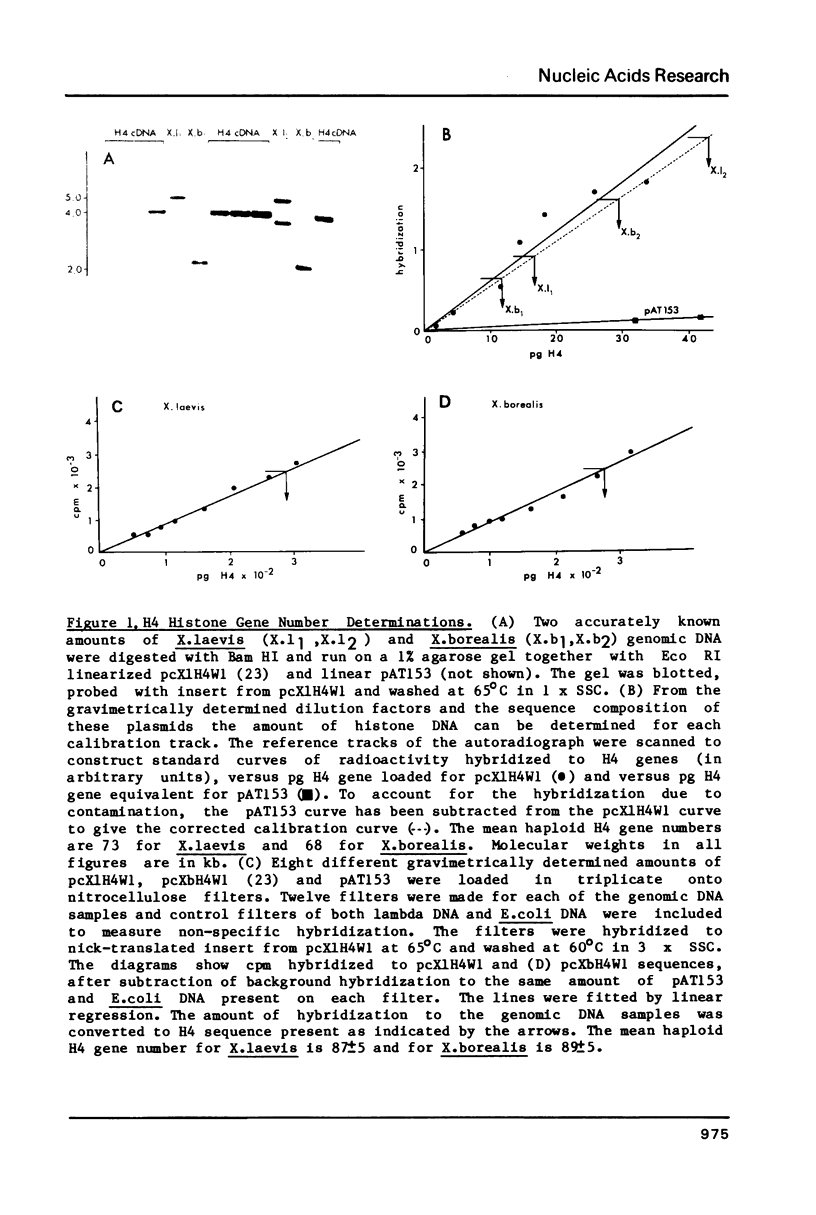
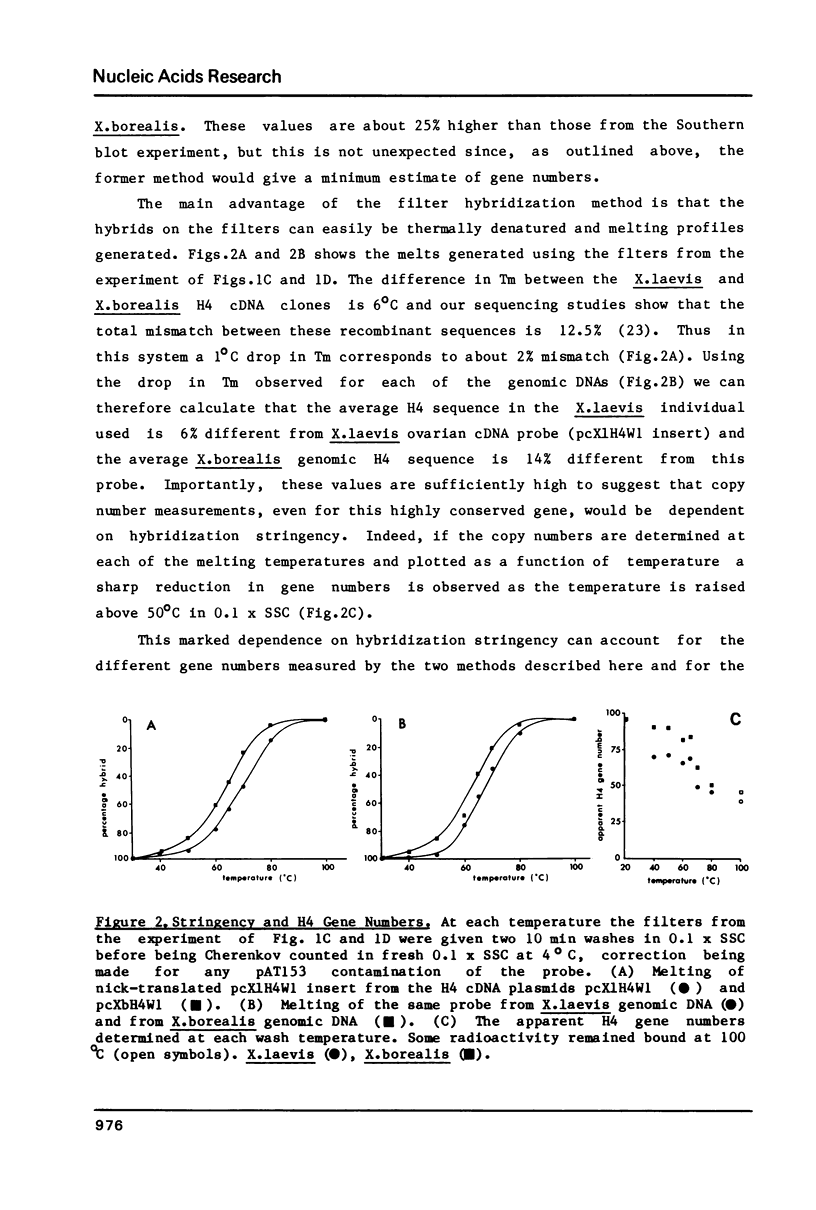
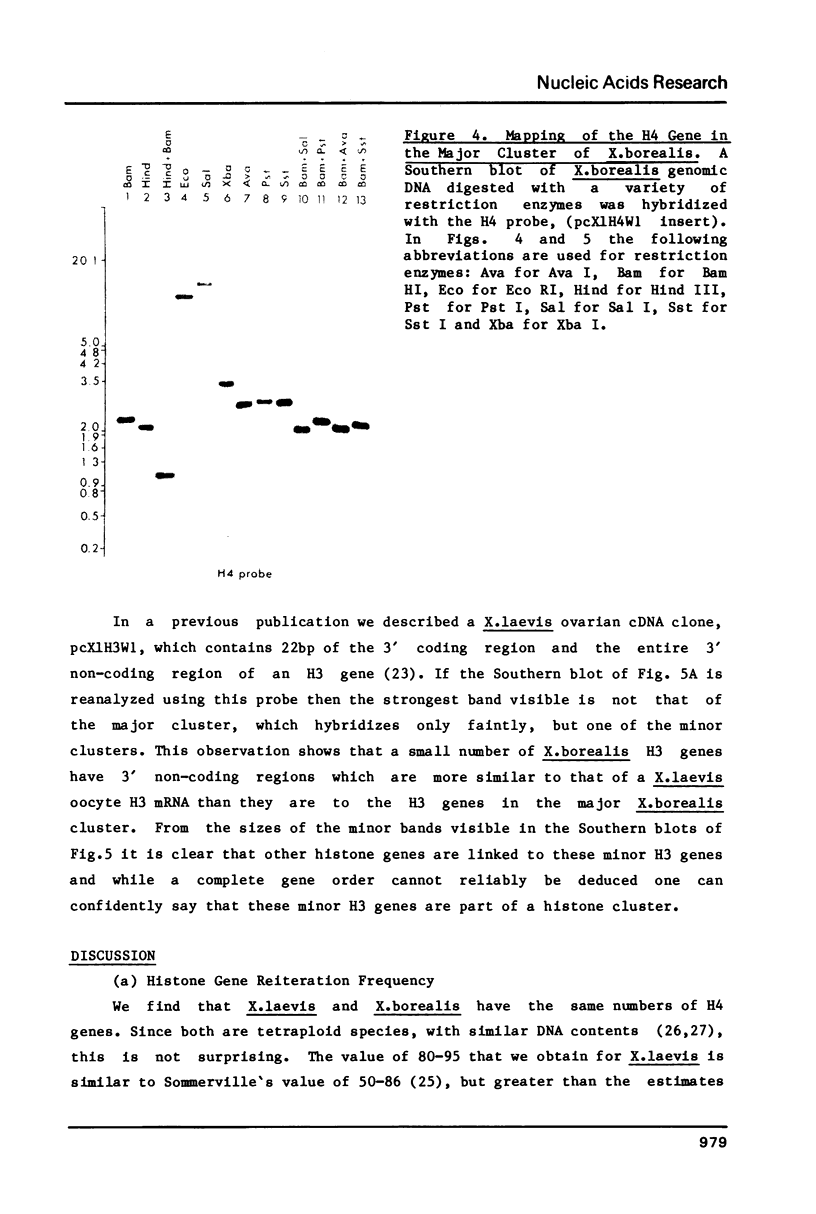
Using a Xenopus laevis H4 cDNA clone as a probe we have determined that the numbers of H4 histone genes in Xenopus laevis and Xenopus borealis are approximately the same. These numbers are dependent on the hybridization stringency and we measure about 90 H4 genes per haploid genome after a 60 degrees C wash in 3 X SSC. Using histone probes from both Xenopus and sea urchin we have studied the genomic organization of histone genes in these two species. In all of the X.borealis individuals analyzed about 70% of the histone genes were present in a very homogeneous major cluster. These genes are present in the order H1, H2B, H2A, H4 and H3, and the minimum length of the repeated unit is 16kb. In contrast, the histone gene clusters in X.laevis showed considerable sequence variation. However two major cluster types with different gene orders seem to be present in most individuals. The differences in histone gene organization seen in species of Xenopus suggest that even in closely related vertebrates the major histone gene clusters are quite fluid structures in evolutionary terms.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bisbee C. A., Baker M. A., Wilson A. C., Haji-Azimi I., Fischberg M. Albumin phylogeny for clawed frogs (Xenopus). Science. 1977 Feb 25;195(4280):785–787. doi: 10.1126/science.65013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busslinger M., Portmann R., Irminger J. C., Birnstiel M. L. Ubiquitous and gene-specific regulatory 5' sequences in a sea urchin histone DNA clone coding for histone protein variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 11;8(5):957–977. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.5.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman A., Byers M. J., Primrose S. B., Lyons A. Rapid purification of plasmid DNAs by hydroxyapatite chromatography. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Nov 2;91(1):303–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb20966.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J. D., Dodgson J. B. Histone genes are clustered but not tandemly repeated in the chicken genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2856–2860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goustin A. S. Two temporal phases for the control of histone gene activity in cleaving sea urchin embryos (S. purpuratus). Dev Biol. 1981 Oct 15;87(1):163–175. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90069-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Zernik M., Roeder R. G. The structure of the human histone genes: clustered but not tandemly repeated. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):661–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C., Birnstiel M. L. The organization and expression of histone gene families. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L., Fahrner K., Woolford J., Jr, Rosbash M., Kaback D. B. Isolation of yeast histone genes H2A and H2B. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1261–1271. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90237-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilder V. A., Livesey R. N., Turner P. C., Vlad M. T. Histone gene number in relation to C-value in amphibians. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5737–5746. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries P., Old R., Coggins L. W., McShane T., Watson C., Paul J. Recombinant plasmids containing Xenopus laevis globin structural genes derived from complementary DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Mar;5(3):905–924. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.3.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob E. Histone-gene reiteration in the genome of mouse. Eur J Biochem. 1976 May 17;65(1):275–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10415.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob E., Malacinski G., Birnstiel M. L. Reiteration frequency of the histone genes in the genome of the amphibian, Xenopus laevis. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Oct 1;69(1):45–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10856.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H. Histone genes and histone messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:837–870. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifton R. P., Goldberg M. L., Karp R. W., Hogness D. S. The organization of the histone genes in Drosophila melanogaster: functional and evolutionary implications. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):1047–1051. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxson R. E., Jr, Wilt F. H. The rate of synthesis of histone mRNA during the development of sea urchin embryos (Strongylocentrotus purpuratus). Dev Biol. 1981 Apr 30;83(2):380–386. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90485-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H., Kutter E., Nakanishi M. A restriction map of the bacteriophage T4 genome. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;179(2):421–435. doi: 10.1007/BF00425473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Kunz G., Daetwyler H., Telford J., Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. Genes and spacers of cloned sea urchin histone DNA analyzed by sequencing. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):655–671. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90249-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott A. C., Wells J. R. Reiteration frequency of the gene for tissue-specific histone H5 in the chicken genome. Nature. 1976 Feb 26;259(5545):635–638. doi: 10.1038/259635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler-Tuyns A., Birnstiel M. L. Structure and expression in L-cells of a cloned H4 histone gene of the mouse. J Mol Biol. 1981 Oct 5;151(4):607–625. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90426-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierra F., Lichtler A., Marashi F., Rickles R., Van Dyke T., Clark S., Wells J., Stein G., Stein J. Organization of human histone genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1795–1799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sittman D. B., Chiu I. M., Pan C. J., Cohn R. H., Kedes L. H., Marzluff W. F. Isolation of two clusters of mouse histone genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4078–4082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson E. C., Erba H. P., Gall J. G. Characterization of a cloned histone gene cluster of the newt Notophthalamus viridescens. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2281–2295. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson E. C., Erba H. P., Gall J. G. Histone gene clusters of the newt notophthalmus are separated by long tracts of satellite DNA. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):639–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90090-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sures I., Lowry J., Kedes L. H. The DNA sequence of sea urchin (S. purpuratus) H2A, H2B and H3 histone coding and spacer regions. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1033–1044. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiébaud C. H., Fischberg M. DNA content in the genus Xenopus. Chromosoma. 1977 Feb 3;59(3):253–257. doi: 10.1007/BF00292781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner P. C., Woodland H. R. H3 and H4 histone cDNA sequences from Xenopus: a sequence comparison of H4 genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 25;10(12):3769–3780. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.12.3769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodland H. R. Histone synthesis during the development of Xenopus. FEBS Lett. 1980 Nov 17;121(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81252-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodland H. R., Wilt F. H. The stability and translation of sea urchin histone messenger RNA molecules injected into Xenopus laevis eggs and developing embryos. Dev Biol. 1980 Mar;75(1):214–221. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90156-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zernik M., Heintz N., Boime I., Roeder R. G. Xenopus laevis histone genes: variant H1 genes are present in different clusters. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):807–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90557-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dongen W., de Laaf L., Zaal R., Moorman A., Destrée O. The organization of the histone genes in the genome of Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2297–2311. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]