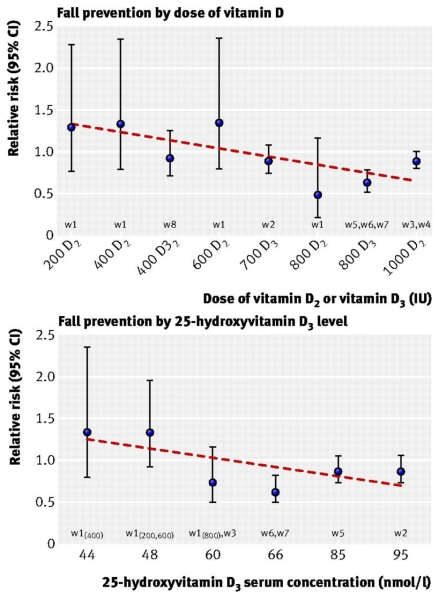
Figure 1.
Fall prevention by dose and achieved 25(OH)D concentrations. Circles represent relative risks and error bars represent 95% confidence intervals. Trendline is based on series of effect sizes (circles). There were three trials with 800 IU D3w5 w6 w7, so the effect size for 800 IU D3 is the pooled result from these three trials. Likewise, the effect size for 1,000 IU D2 is the pooled result from the two trials with 1,000 IU D2w3 w4. We have listed the same dose D2 and D3 separately in the graph to account for their potential different impact on fall reduction. As there were two data points from the Broe et al. [37] trial that reached 48 nmol/L w1, two trials that reached 60 nmol/L w1 w3 and two trials that reached 66 nmol/L w6 w7, we pooled each of the sets. On the basis of visual inspection of Figure 1, the benefits of vitamin D for fall risk started at a dose of 700 IU a day. Reproduced from Bischoff-Ferrari et al. [35], with permission from BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.